Bio Final
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
What is natural selection? What is the typical 'selecting force' for natural selection?
A process which random changes are selected by nature in a consistant non-random way. Biological fitness
What is the definition of 'fitness' and how is it determined?
the ability to survive, reproduce and produce viable off spring
Distinguish natural versus artificial selection.
Natural selection: nature
Artificial selection: human interference
Compare homologous versus analogous structures. WHICH ONES INDICATE COMMON ANCESTRY?
Homologous structures are similar in morphology, anatomy, and genetics but have different functions (common ancestry)
Analogous structures anatomically different but perform the same function
What are the different types of evidence can be seen today that supports the theory of evolution? (hint: ABEFG)
Anatomy
Biochemistry
Embryology
Fossils
Geography
What does it mean if a population IS or IS NOT in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
If the population isn’t evolving then it is in HWE, if it is then it isn’t in HWE
What are the different types of microevolution/genetic drift? How does each influence population frequencies?
Genetic drift are changes in allele frequencies due to chance, causing changes in genetic makeup; while microevolution is change in gene frequency in a population from environmental changes.
There are 4 different concepts of "species" that we discussed:
morphological (physical traits)
phylogenetic (DNA similarities)
evolutionary (fossil record)
biological (can reproduce and have offspring that reproduce)
Distinguish allopatric from sympatric speciation.
Allopatric speciation occurs when a population is divided by geographic barriers. Sympatric speciation is present when a population is divided into different groups
Compare/contrast convergent versus divergent evolution. What do they say about common ancestry?
Convergent evolution occurs when 2 unrelates species share a biological trait due to the environment. Divergent evolution when a single ancestor starts a variety of new species.
What is early Earth’s atmosphere hypothesized to have contained?
water vapor, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, and ammonia
The major eras of the Earth’s history. What major events happened in each?
Precambrian: very first cell (photosynthetic prokaryotes)
Paleozoic: mass extinction
Mesozoic: seeded plants, dinosaurs, mass extinction
Cenozoic: mammals and primates evolved
Distinguish a prokaryotic cell from a eukaryotic cell. cellularity (multi vs unicellular), relative cell size, DNA packaging (single circular chromosome in nuclei region in prok vs. ??? in euk) , cell division / reproduction, internal compartmentalization (organelles).
eukaryotic cells
have a nucleus (stores DNA)
multicellular
larger
sexual
mitosis
prokaryotic cell
singular double stranded DNA
small
asexual
unicellular
binary fission
no membrane bounded orgenelles
How do bacteria and archaea differ?
plasma membrane
cell walls
dna replication
gene expression
Identify the 3 main shapes of bacteria.
coccus - round
bacillus - rod
spiral - curve
What does it mean for a bacterium to be gram positive or gram negative?
referring to the thickness
Positive - very thick
negative - thin
Bacteria can recombine DNA by transformation, transduction, and conjugation
Bacteria can recombine DNA by transformation, transduction, and conjugation
Describe protists
eukaryotic organisms that are not plant, animal, or fungi
Be able to distinguish green algae, red algae, brown algae, diatoms, zooflagellates, amoebas, ciliates,dinoflagellates, and slime molds AS PROTISTS! You will NOT be asked specifics about each - just that they all go in the protist bucket.
green algae - protists that carry out photosynthesis (phylum = chlorophyta and charophyta)
red algae - rhodophyta
brown algae - phaeophyceae ( excess food stored as carbs called laminarin)
diatoms - most numerous unicellular algae in the ocean ( phytoplankton)
zooflagellates - most parasitic, causes various diseases in humans
amoeba - move and ingest food with pseudopods, phagolysosomes to digest food
ciliates - among the most complex protozoans, hundreds beat in coordinated rhythm
dinoflagellates - two perpendicular flagella causes a spinning motion, bioluminescence
slime molds - feel like algae, no cell wall
What is common among all algae? (i.e. what defines them)
cellularity
What general role do most protists play in their ecosystem?
feed most of the worlds aquatic species
Describe general fungi structure and feeding characteristics.
multicellular eukaryotes that share a common mode of nutrition
they release digestive enzymes and absorb nutrients
What other organisms are fungi closely related to? (remember - fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants - but an animal is ALWAYS more closely related to another animal than it is to a fungi.
fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants - but an animal is ALWAYS more closely related to another animal than it is to a fungi.
Describe the mycorrhizal relationship between fungi and plants.
80-90%of plant species gave mycorrhizal partners
the fungal mycelia channels water and mineral from the soil into the plant, the plant uses supplies from photosynthesis to fuel the metabolism of the fungus
The following are all fungi
zygomycota
chytridiomycota
ac fungi (including molds and yeast),
club fungi.
(They all go in the fungi bucket.)
Bryophytes go in the 'nonvascular plants' bucket.
Vascular plants can be seedless (ferns) or seeded(gymnosperms and angiosperms)
What adaptations needed to occur for plants to move to land and grow tall?
lignin
Describe the concept of alternation of generations and how it functions in plants. (briefly)
Haplontic: life cycle in which there is a dominant haploid stage ( gametophyte)
Diplontic: life cycle in which diploid is a dominant stage (sporophyte, humans)
To transition to tall plants, vasculature was important. Describe how xylem and phloem help a plant grow tall
xylem tissue is lignified for support, strength, and to make it impermeable to water.
phloem transports sugars, proteins, and other material throughout the plant
Why is a damp environment important for seedless vascular plant?
reproduction still depend on water during fertilization
List the 4 seedless vascular plants discussed. Know they go in the seedless vascular plants bucket.
club moss
whisk ferns
horsetails
ferns
Distinguish gymnosperms from angiosperms. Which evolved most recently?
how their seeds develop, angiosperms
How do/did animals contribute to the evolution of seed plants?
animals aid seed dispersal
What 8 characteristics define the animal kingdom? (lesson 10 - first few slides)
Multicellularity
Complex tissue structure
Heterotrophy
Active movement
Diversity of form and size
Sexual reproduction
Developmental stages
Body plan
Animals have complex tissue structure. What 4 types of tissues are found in animals?
Connective tissue
Epithelial tissue
Nervous tissue
Muscle tissue
Describe the 4 features used to classify animals.
Symmetry
Number of tissue layers
Origin of mouth and anus
Body plan and cavities
How was animal phylogeny originally determined? How is it determined now?
Originally morphological characteristics, now: biochemical, molecular, genetic evidence
The Cambrian explosion created great animal diversity. Be able to identify WHEN the Cambrian periodoccurred. (see # 12 above
during the paleozoic era 540 mya
How many mass extinction events are there in history? What were their causes? How does that differ from current day extinction rates?
5 mass extinctions, caused by climate change , the current mass extinctions are human related.
Look at slide 4 of Lesson 11 - be able to put the invertebrates in the Invertebrate bucket and the vertebrates in the vertebrate bucket. YOU DO NOT NEED TO GIVE SPECIFIC EXAMPLES FOR EACH OR DISTINGUISH BETWEEN EACH PHYLUM. You're welcome. :-)
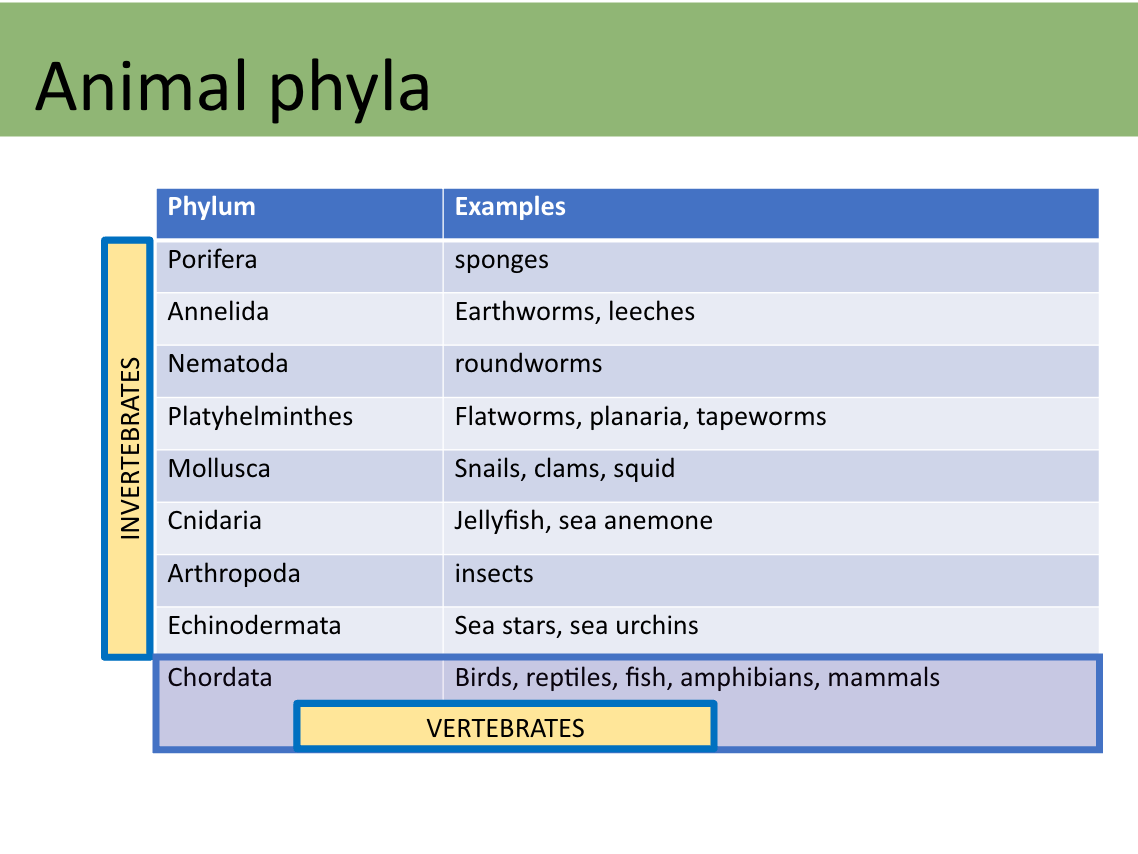
All chordates have 4 common features. List/describe the 4.
Notochord: flexible, rod-shaped structure, develops into vertebrae
Dorsal hollow nerve cord: develops into spinal cord
Pharyngeal gill slits: gills, ears, tonsils
Post-anal tail
What makes an organism an amniote?
lay eggs on land or retain them within mother
reptiles
birds
mammals
Distinguish endothermic from ectothermic. What are we?
Ectothermic require fewer calories but cannot maintain body temp, Endothermic produce their own body heat. We are endothermic
What are the two organ systems in plants?
Shoot system
Root system
What are the three types of tissues that plants have?
Dermal: leaves, stem, roots
Ground tissues: metabolism, storage, support
Vascular tissues: xylem
What is the function of stomata?
take up carbon dioxide and release oxygen and water vapor
How is vascular tissue arranged in monocots vs. dicots - in stems? in roots?
monocots, vascular tissue is scattered throughout the stem and arranged in a complex network in roots. dicots, vascular tissue forms distinct rings in stems and a central vascular cylinder in roots.
Distinguish tap roots from fibrous roots. Which type of plants have which type of roots?
Tap root systems have a main root that grows down, fibrous root systems consists of many small roots.
What is the purpose of root hairs?
increase surface area of roots
Primary growth in plants occurs at the apical meristem
in both roots and shoots
What four (4) things do plants need from their environment?
Water
Sunlight
Carbon dioxide
Essential inorganic nutrients/minerals
What makes a nutrient 'essential'?
its necessary for normal growth
How are minerals absorbed by plants?
through the roots
What does xylem carry - and in which direction(s)? Alive or dead?
carries water and nutrients from roots to leaves, non living.
Define water potential. Which direction does water always flow? (high to low or low to high?)
Water potential: the mechanical energy of water. water flows from higher to lower.
Why does water move INTO the roots? Be able to explain how this relates to water potential.
plants accumulate high concentrations of minerals just inside the root epidermis, which uses water potential.
In addition to root pressure, what two phenomena contribute to the ability of water to reach the top of tall plants and trees?
Stoma: openings on the bottom of the leaves that help gas exchange.
Guard cells: open and close stoma to prevent evaporation of water.
What does the phloem carry - and in which direction(s)? Alive or dead?
Transports products of photosynthesis - from leaves to other parts of the plant
In what ways do plants respond to light? (focus on what they do - not the vocab)
photomorphogenesis, growth and development of plants in response to light. Photoperiodism, ability to use light to track time. Phototropism, directional response that allows plants to grow toward, or away from light.
What are some mechanisms by which plants protect themselves from herbivores?
Bark
waxy cuticle
Thorns
Spines
Flowers are the gametophyte generation in plants. (know this)
Flowers are the gametophyte generation in plants
Be able to identify the female and male reproductive structures in plants. (which parts are male, which parts are female)
Stamen = male
Pistil = female
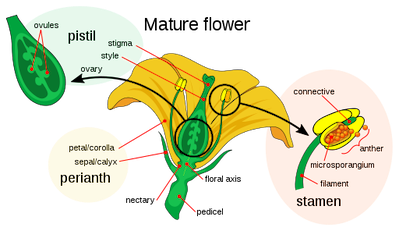
Where does pollen form?
Stamen
How does self-pollination differ from cross-pollination?
Self-pollination is when pollen is deposited on the stigma from the same flower, while Cross-pollination is when a pollinator is involved transferring pollen from the anther of one flower to the sigma of a different flower of the same species
What are the major ways in which pollination can occur?
biotic agents, like, insects, birds, etc.
How are seeds an important adaptation for plants?
they maintain dormancy under trying conditions
protect young plant
provide food
facilitate dispersal of the embryo
What are fruits?
mature ovaries
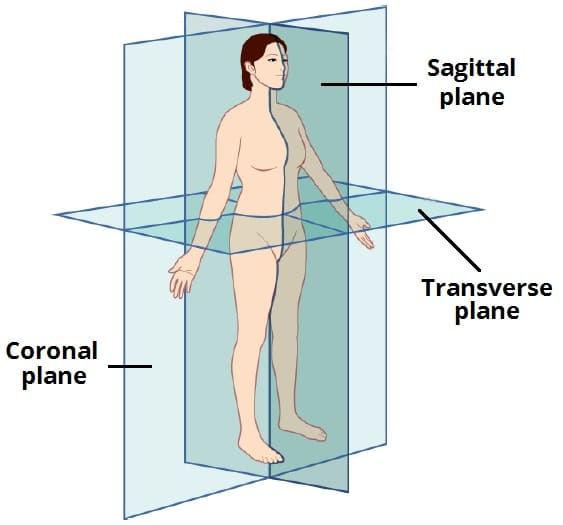
Be able to recognize (simple) body sectioning as being frontal/coronal, transverse, or sagittal.
How is positive feedback different from a negative feedback loop? What are examples of each?
Positive feedback maintains the response to a stimulus, negative feedback counteracts internal changes
What are the four (4) different types of tissues found in animals?
epithelia - line surfaces
connective - connect tissue
muscles - movement
neurons - send and receive messages
How are epithelial cells distinguished
shapes and layers
What common features do all connective tissues have?
fibers, gel like substance (matrix), fibroblast
What are some examples of connective tissues?
blood
loose
adipose (fat)
cartilage
bone
dense
What are the three (3) types of muscle tissues?
Smooth
Skeletal
cardiac
What two (2) types of cells are found in nervous tissue? What is the purpose of each?
Neurons and neuroglia, generate and transmit electrical impulses
Distinguish asexual and sexual reproduction in animals. (What are several ways in which animals can reproduce asexually?)
asexual reproduction result in the offspring being genetically identical, sexual reproduction results in unique offspring
ways animals can reproduce asexually:
bud
splitting
regenerate from fragments
Define the process of fertilization.
process by which a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell
External fertilization involves broadcast spawning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of this mode of reproduction?
Advantages:
high diversity
colonization of new environments
Disadvantages:
opportunities for predation
offspring must mature quickly
survival rate of eggs is low
What are some advantages to internal fertilization?
protects the fertilized egg from dehydration
limits predation
enhances the fertilization
higher survival rate
Be able to trace the fate of sperm from their beginnings in the testes to exit from the body.
testes: produce sperm
epididymis: site of maturation, storage
Vasa deferentia: conduct and store
seminal vesicles: contribute fluid to sperm
prostate gland: contribute fluid to sperm
Urethra: conducts sperm (and urine)
bulbourethral gland: contribute fluid to seman
penis: organ of copulation
On a very basic level - what is semen composed of? Where does the fluid enter the process and how does it help the sperm?
fluid and sperm. enters through the seminal vesicles and prostate gland, helps the sperm travel
What part of the brain helps to control hormonal secretions? What other gland is involved?
hypothalamus, pituitary gland
Be able to trace the fate of an egg - from ovary to the birth of a baby. Where does fertilization typically occur?
ovary - produce egg
fallopian tubes - location of fertilization
uterus- (womb) houses developing embryo and fetus
vagina - receives penis during copulation and birth canal
Over the course of the month, what happens to the endometrium?
Days 1-5
endometrium disintegrates causing menses
Days 6-13
endometrium thickens, ovulation occurs on 14th day
Days 15-28
Endometrium doubles in thickness
What happens on Day 1 of the uterine cycle?
endometrium breaks down
How long does an egg live after ovulation? How long do sperm survive once released?
copulation and fertilization don't always happen on the same day.
oocytes survive 24 hours after ovulation. Sperm can survive for a couple minutes outside the body, but remain viable within.
Why do females experience menopause?
eggs are old since they were formed before birth
What are the three phases of digestion?
Cephalic phase - natural response, triggers salivation
Gastric phase - begins once the food arrives in the stomach
Intestinal phase - begins when chyme enters the small intestine triggering digestive secretions
How does food get from the mouth to the stomach? Include the words bolus and peristalsis.
after the bolus is swallowed it goes through the esophagus which uses peristalsis to move food to the stomach
What are some accessory organs for digestion?
Accessory organs add secretions (enzymes) that catabolize food nto nutrients
salivary glands
liver: produces bile, processed vitamins and fats, synthesized many plasma proteins
pancreas: neutralize the acidic chyme, digest protein and carbs
gallbladder: store bile
Where in the digestive system does absorption take place?
small intestine
What is chyme? Which opening controls its release? Chyme is released through this opening from the___ to the ____
chyme is food mixed with gastric juices.
Chyme is released through this opening from the pyloric sphincter to the stomach
What is the purpose of having villi in the small intestine?
greatly increase absorptive area
Where are each of the major macromolecules (carbs, lipids, proteins) digested?
small intestine
What is the main function of the nervous system?
receiving sensory input
performing integration
generating motor output
What is the purpose of the spinal cord?
reflex actions
communication between the brain and spinal nerves
The two main divisions of the nervous system are the CNS and PNS. What makes up the CNS? The PNS?What subdivisions are there in the PNS?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain
spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
somatic and autonomic nervous systems
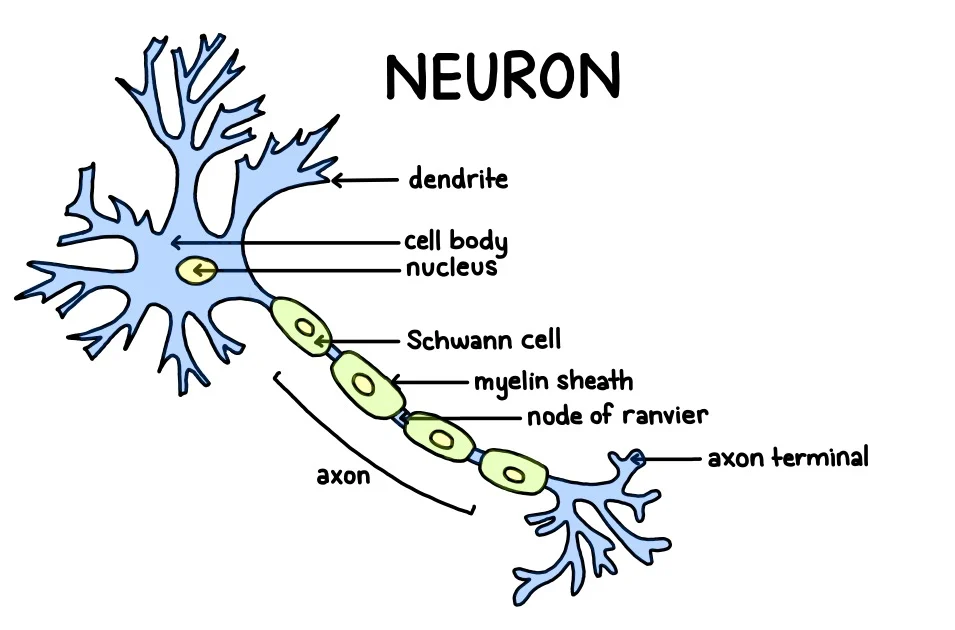
Describe the structure of a neuron. Be able to label the parts.
Neurons- cell body contains nucleus
Dendrites - receive signals from other neurons
axon - conduct nerve impulses
myelin sheath - covering
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are secreted from one neuron by the axon terminal into the synaptic cleft and picked up by the dendrites of the next neuron in order pass the signal along.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are secreted from one neuron by the axon terminal into the synaptic cleft and picked up by the dendrites of the next neuron in order pass the signal along.
What is resting membrane potential in a neuron? How is this achieved?
created and maintained by increasing the concentration of cations