Graph Titrations
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
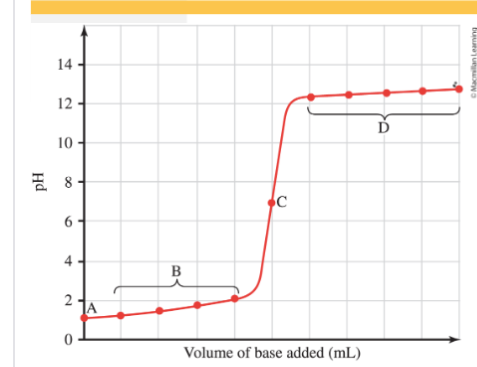
Strong Acid-Strong Base Titration (neutral solution)
A=initial pH of acid, pH=-log [H3O+]
B= Base is added until acid is neutralized. Account for moles of base added moles of unnaturalized H3O+ determine the pH.
C= equivalence point moles of acid = moles of base, pH=7
D= pH will be based on OH- left in solution.
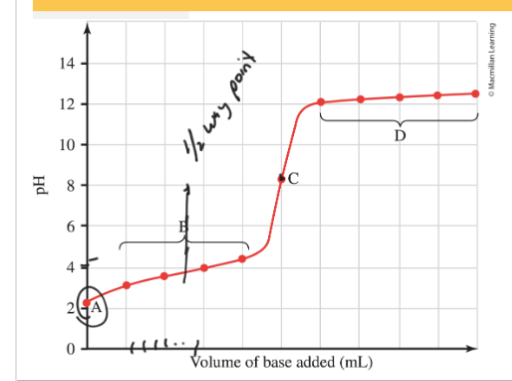
Weak Acid-Strong Base Titration (Acidic Solution)
A= pH depends on concentration of weak acid, using ICE table
B= HA+OH- ←→A-+H2O. Buffer region, use H-H equation to calculate pH at ½ way point (1/2 way point pH=pKa)
C= Equivalence point, pH will depend on [A-] use ICE table Kb
D= pH determined by [OH-]
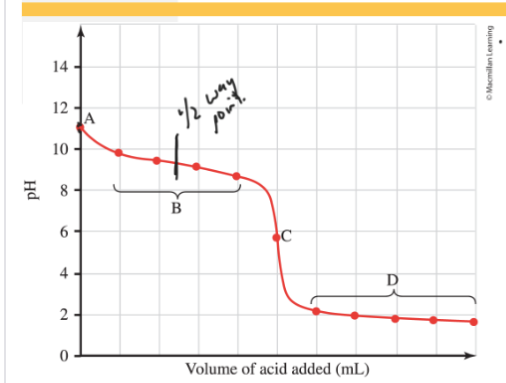
Weak Base-Strong Acid Titration (Basic Solution)
A= pH depends on [weak base] use ICE table Kb
B= A-+H3O+<-> HA+ H2O. Buffer region. use H-H equation to calculate pH at 1/2 way point [HA]=[A-]. pH=pKa
C= equivalence point pH will depend on [HA] use ICE table and Ka
D= All Base is neutralized. HA will remain and so will H3O+. [H3O+] will determine the pH of the solution.
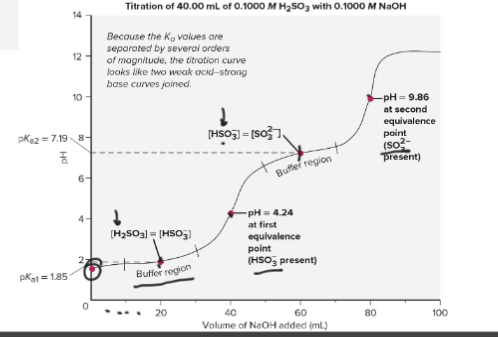
Titration of a Weak Polyprotic Acid
Polyprotic acids have 2 buffer regions
The top pH is determined by [OH-]
All three can exist at the same time