adaptations of the arteries, veins and capillaries Jan 8
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
label the heart
Blood enters the heart through the Superior and Inferior Vena. Cava-
Right Atrium-through the Tricuspid Valve-
Right Ventricle- through the Pulmonary valve-
Pulmonary Artery- Lungs-
Comes back to the heart through Pulmonary Veins
- Left Atrium- atria ventricular Valve-Left Ventricle- semilunar Valve- Aorta- out of the body
What is the direction of blood flow?
Oxygenated blood flows from the lungs into the left atrium via the pulmonary vein and then through the left ventricle and aorta to the whole of the body.
Deoxygenated blood flows from the body to the heart goes through the vena cava into the right atrium and up the pulmonary artery to the lungs
what is left ventricle
The ventricle on the left side that pumps blood to the body and is more muscular than the right ventricle this allows it contact more powerfully to pump blood all around the body
What do the AV valves do?
they open and allow flowing of blood into the ventricles and prevent regurgitation of black flow into the atria the papillary muscles constrict at this time do the valves leaflets
What do the semi-lunar valves do?
between the ventricle and arteries.
-each valve has three cusps that look like half of moons
-pulmonic valve on the right side
-aortic valve on the left side of the heart
-they open during pumping or systole to allow blood to be ejected from the heart
What are tendons chords?
They are attached to valves and the ventricles and prevent valves from inverting under high pressure
How is oxygenated blood pumped around the body?
Blood enters the left atrium through the pulmonary vein. Once the atria has filled it contracts causing the volume to decrease and the pressure to increase pushing blood toward the left ventricle. The pressure of the blood causes the AV valves to open allowing blood to flow in. Whilst this happens the left ventricle is relaxing which means the volume is increasing and the pressure is decreasing. Once the left ventricle has filled it then contracts and the pressure increases and the volume decreases blood then flows upwards toward the atria but as the atria is relaxed the AV valves prevent the back flow of blood and so the blood flows up to through the aorta pushing the semi-lunar valves open. After this both the left ventricle and atria relax and the semi-lunar valves close and the blood is pumped through the body
What is the structure of arteries?
Arteries have thick walls containing a large amount of smooth muscle and elastic fibres. The endothelium is folded and the lining is smooth. Arteries have a narrow lumen and contain collagen fibres to provide strength.
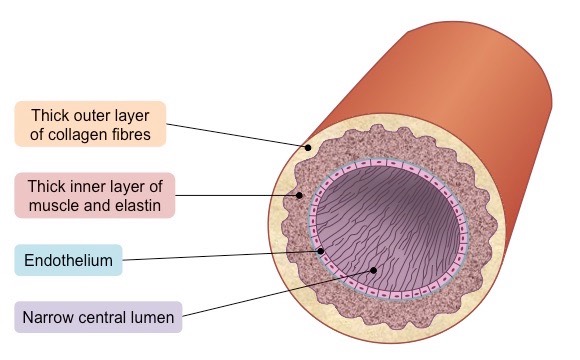
How are arteries adapted to their function?
Arteries are adapted to carry blood away from the heart at high pressure. They contain many elastic fibres, which allow the artery wall to stretch when blood is forced through at high pressure and recoil to help maintain blood flow.
. A thick layer of smooth muscle allows the artery to constrict or dilate, helping to control blood flow and pressure.
The artery has a smooth lining, which reduces friction and resistance to blood flow.
Arteries have a narrow lumen, which helps to maintain high blood pressure. They also contain collagen fibres, which provide strength and prevent the artery from rupturing under high pressure.
What is the structure of veins?
-Large radius offers little resistance to blood flow
-low pressure system
-valves (semi-lunar)
-thin elastic tissue
How are veins adapted?
Veins are adapted to carry blood back to the heart at low pressure.
They have a large lumen, which reduces resistance to blood flow.
Veins have thin walls with less smooth muscle and fewer elastic fibres because the blood pressure is low.
They contain valves, which prevent backflow of blood and ensure blood flows towards the heart.
The lining of veins is smooth, reducing friction and aiding blood flow.
What is the structure of capillaries?
narrow vessels with thin walls due to having only one endothelium layer and have pores for gas exchange
How are capillaries adapted?
- high surface area as they are in large number and are branched
- short diffusion pathway due to single endothelial layer
- small lumen that means red blood cells have to squeeze through decreeing the rate of blood flow allowing longer time for gas exchange
- higher total cross sectional are increasing frictional resistance
What is the process of vasoconstriction in arterioles?
They have more smooth muscle and so when this muscle contracts the size of the lumen decreases and the amount of blood flow also decreases
What is the process of vasodilation in arterioles?
They have more smooth muscle and so when this muscle relaxes the size of the lumen increases and the amount of blood flow also increases and this is occurs during exercise and high temperatures
What causes changes in the speed of blood flow?
Arteries have a lower total cross sectional area which causes the frictional resistance to decrease and so blood flow is faster
Explain the difference in thickness of the wall of the right atrium and the wall of the right ventricle
right atrium has less muscle
thickness is related to blood pressure required
right atrium pumps blood to right ventricle
right ventricle pumps blood to lungs
Explain why the heart is divided into a right side and a left side
. keeps oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood separate
this results in as much oxygen as possible being carried to tissues
different pressures at each side of the heart