Psychology: Lifespan Development: Heredity, Prenatal Development, and Birth | Chapter 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Genes
are specific sequence of nucleotides and are recipes for making proteins.
NOTE:
- Proteins are responsible for the structure and function of cells
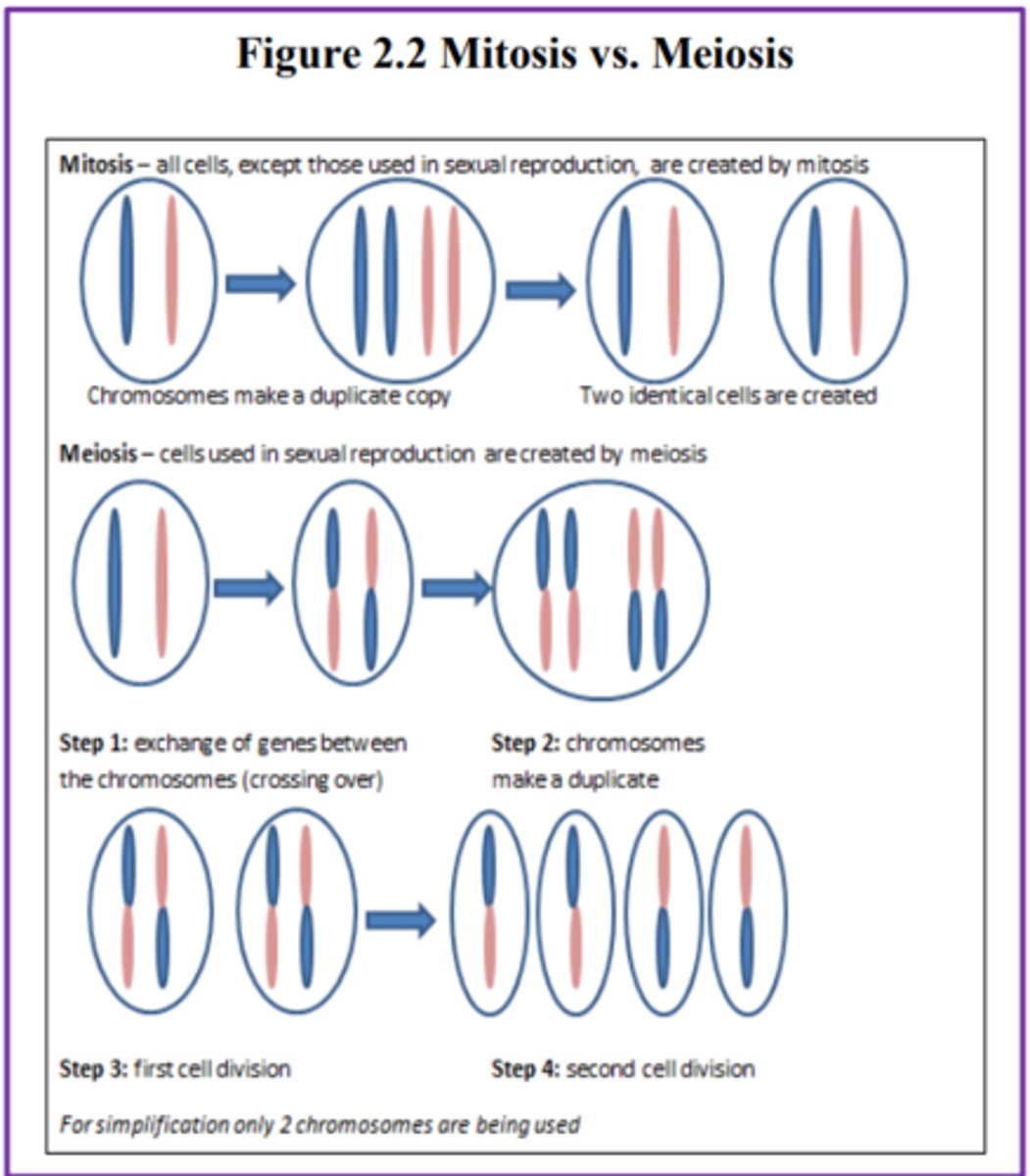
Mitosis
is defined as the cell's nucleus making an exact copy of all the chromosomes and splitting into two new cells.
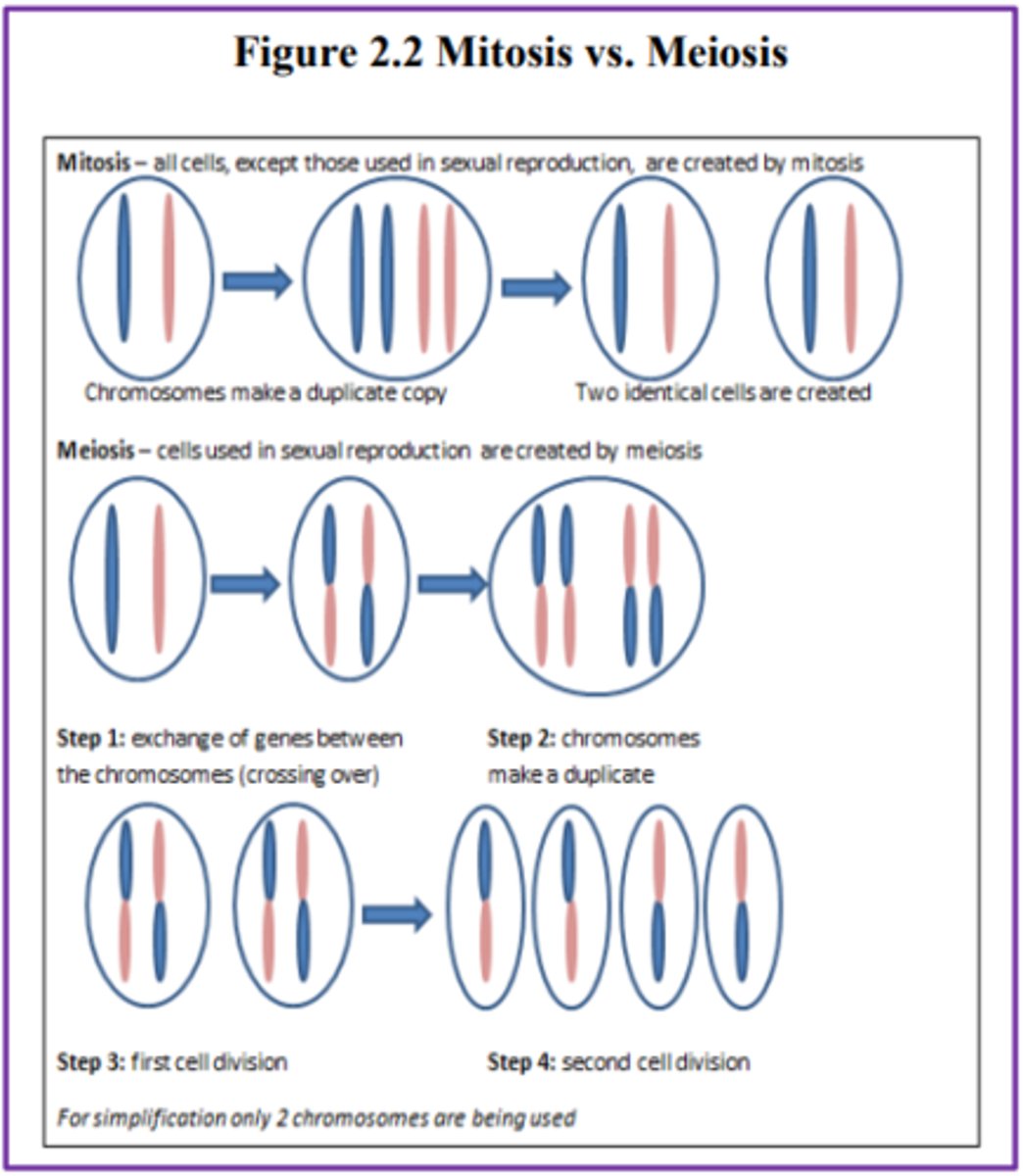
Meiosis
the gamete's chromosomes duplicate, and then divide twice resulting in four cells containing only half the genetic material of the original gamete.
NOTE:
- Used in sexual reproduction
- Each sperm and egg possesses only 23 chromosomes and combine to produce the normal 46.
Genotype
refers to the sum total of all the genes a person inherits.
Phenotype
refers to the features that are actually expressed.
Homozygous
we may receive either the same version of a gene from our mother and father
NOTE:
- We will display that characteristic given by the parent

Heterozygous
we receive a different version of the gene from each parent
NOTE:
- It becomes clear that not all genes are created equal

Dominant
express themselves in the phenotype even when paired with a different version of the gene
NOTE:
- Example: Facial dimples, curly hair, normal vision, and dark hair.
Recessive
express themselves only when paired with a similar version gene.
NOTE:
- Example: Red hair, being nearsighted, and straight hair.

Alleles
different versions of a gene
Polygenic
they are the result of several genes.
Incomplete Dominance
Sometimes the dominant gene does not completely suppress the recessive gene
Carriers
Those who have inherited only one recessive-gene
NOTE:
- Under circumstances they might express the recessive-gene
Monozygotic (Identical Twins)
identical twins occur when a fertilized egg splits apart in the first two weeks of development
NOTE:
- The result is the creation of two separate, but genetically identical offspring.
- They posses the same genotype and phenotype
Dizygotic (Fraternal Twins)
two eggs or ova are released and fertilized by two separate sperm.
NOTE:
- These individuals share the same amount of genetic material as would any two children would from the same mother and father
Sex-linked
the defective gene is found on the X-chromosome.
NOTE:
- Males have only one X chromosome so are at greater risk for sex-linked disorders due to a recessive gene
- Females need to inherit the recessive gene on both X-chromosomes to be affected by the genetic defects.

Recessive Disorders (Homozygous):
- The individual inherits a gene change from both parents.
- If the gene is inherited from just one parent, the person is a carrier and does not have the condition.

Autosomal Dominant Disorders (Heterozygous):
In order to have the disorder, the individual only needs to inherit the gene change from one parent.

Sex-Linked Disorders:
- When the X chromosome carries the mutated gene, the disorder is referred to as an X-linked disorder.
- Males are more affected than females because they possess only one X chromosome without an additional X chromosome to counter the harmful gene.

Chromosomal Abnormality
occurs when a child inherits too many or two few chromosomes.
NOTE:
- The common cause of chromosomal abnormalities is the age of the mother.
- As the mother ages, the ovum is more likely to suffer abnormalities due to longer-term exposure to environmental factors.
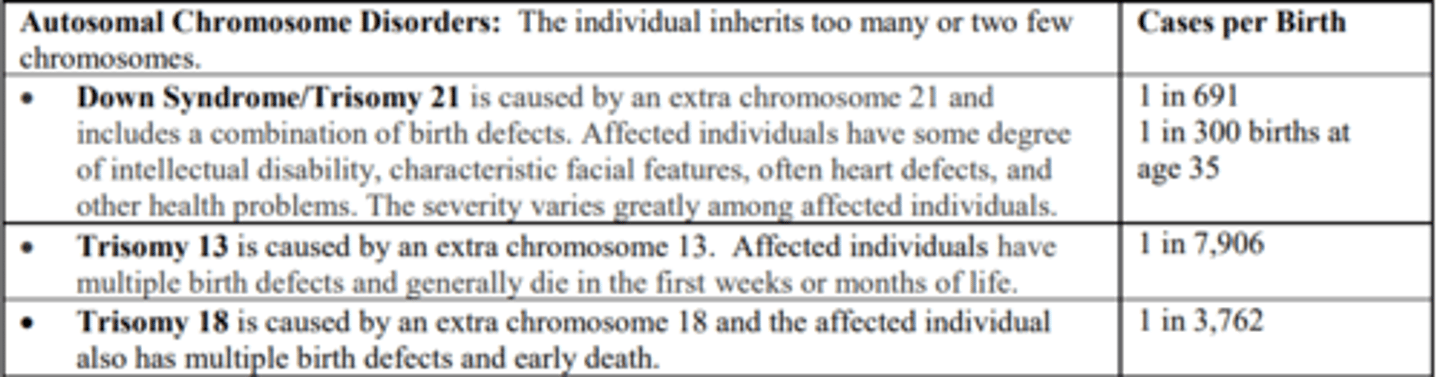
Trisomy 21 or Down syndrome
occurs when there are three rather than two 21st chromosomes.
NOTE:
- Exhibits an intellectual disability and possesses certain physical features.
- There is as much variation in people with Down syndrome as in most populations.
Sex-linked Chromosomal Abnormality
When the abnormality is on 23rd pair
NOTE:
- XXY, XYY, XXX, XO.
- Common Sex-linked Chromosomal Disorder: Turner Syndrome & Klinefelter Syndrome
Turner syndrome
occurs when part or all of one of the X chromosomes is lost and the resulting zygote has an XO composition.
NOTE:
- Affects the individual's cognitive functioning and sexual maturation.
- The external genitalia appear normal, but breasts and ovaries do not develop fully and the woman does not menstruate.
- Results in short stature and other physical characteristics.
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
results when an extra X chromosome is present in the cells of a male.
NOTE:
- The additional X chromosome inhibits the development (not the growth) of the male genitalia.
- Results in small testes, some breast development, infertility, and low levels of testosterone
Autosomal Chromosome Disorders:
The individual inherits too many or two few chromosomes.
Sex-Linked Chromosomal Disorders:
The disorder occurs on chromosome pair #23 or the sex chromosomes.

Genetic Counseling
A service that assists individuals identify, test for, and explain potential genetic conditions that could adversely affect themselves or their offspring.
NOTE:
- Reasons for genetic counseling include:
• Family history of a genetic condition
• Membership in a certain ethnic group with a higher risk of a genetic condition
• Information regarding the results of genetic testing, including blood tests, amniocentesis, or ultra sounds
• Learning about the chances of having a baby with a genetic condition if the parents are older, have had several miscarriages, have offspring with birth defects, experience infertility, or have a medical condition
Behavioral Genetics (nature/nurture debate)
is the scientific study of the interplay between the genetic and environmental contributions to behavior
NOTE:
- The environment can affect the expression of genes just as genetic predispositions can impact a person's potentials.
- Environmental circumstances can trigger symptoms of a genetic disorder.
Genotype-Environment Correlations
refer to the processes by which genetic factors contribute to variations in the environment
NOTE:
- Three types of genotype-environment correlation: Passive genotype-environment correlation; Evocative genotype-environment correlation; Active genotype-environment correlation.
Passive genotype-environment correlation
occurs when children passively inherit the genes and the environments their family provides.
NOTE:
- "Runs in the family"
- The children have inherited both the genes that would enable success at these activities, and given the environmental encouragement to engage in these actions.

Evocative genotype-environment correlation
refers to how the social environment reacts to individuals based on their inherited characteristics.
NOTE:
- For example, whether one has a more outgoing or shy temperament will affect how he or she is treated by others
Active genotype-environment correlation (niche picking)
occurs when individuals seek out environments that support their genetic tendencies.
NOTE:
- For example, children who are musically inclined seek out music instruction and opportunities that facilitate their natural musical ability.
Genotype-Environment Interactions
involve genetic susceptibility to the environment.
NOTE:
- Children whose biological parents exhibited psychopathology, exhibited significantly fewer behavior problems when their adoptive parents used more structured parenting than unstructured.
- Adoptive parents increased the risk for the children's development of behavior problems, but only when the biological parents' psychopathology was high.
- The environmental effects on behavior differ based on the genotype, especially in stressful environments on genetically at-risk children.
Epigenetics
Studies modifications in DNA that affect gene expression and are passed on when the cells divide
NOTE:
- Environmental factors, such as nutrition, stress, and teratogens are thought to change gene expression by switching genes on and off.
- These gene changes can then be inherited by daughter cells.
The Germinal Period
lasts from conception to implantation of the fertilized egg in the lining of the uterus.
NOTE:
- At ejaculation millions of sperm are released into the vagina, but only a few reach the egg and typically only one fertilizes the egg.
- Once a single sperm has entered the wall of the egg, the wall becomes hard and prevents other sperm from entering.
- After the sperm has entered the egg, the tail of the sperm breaks off and the head of the sperm, containing the genetic information from the father, unites with the nucleus of the egg.
- It is typically fertilized in the top section of the fallopian tube and continues its journey to the uterus.
- As a result, a new cell is formed. This cell, containing the combined genetic information from both parents, is referred to as a zygote.
- During this time, the organism begins cell division through mitosis.
- After five days of mitosis there are 100 cells, which is now called a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst consists of both an inner and outer group of cells.
- The inner group of cells, or embryonic disk will become the embryo, while the outer group of cells, or trophoblast, becomes the support system which nourishes the developing organism.
- This stage ends when the blastocyst fully implants into the uterine wall
Zygote
This cell, containing the combined genetic information from both parents.
Blastocyst
The blastocyst consists of both an inner and outer group of cells
NOTE:
- There are 100 cells
Embryonic Disk
The inner group of cells of the blastocyst, which becomes the embryo.
Trophoblast
The outer group of cells of the blastocyst, which becomes the support system which nourishes the developing organism.
The Embryonic Period
Starting the third week the blastocyst has implanted in the uterine wall.
NOTE:
- Upon implantation, this multi-cellular organism is called an embryo.
- Now blood vessels grow forming the placenta.
- During this period, cells continue to differentiate.
- Growth during prenatal development occurs in two major directions: from head to tail called cephalocaudal development and from the midline outward referred to as proximodistal development.
- Those structures nearest the head develop before those nearest the feet and those structures nearest the torso develop before those away from the center of the body (such as hands and fingers).
- The head develops in the fourth week and the precursor to the heart begins to pulse.
- By the end of this stage they disappear and the organism takes on a more human appearance.
- The embryo is approximately 1 inch in length and weighs about 8 grams at the end of eight weeks.
- The embryo can move and respond to touch at this time.
Embryo
Upon implantation (into the uterine wall) this multi-cellular organism is called an
Placenta
The placenta is a structure connected to the uterus that provides nourishment and oxygen from the mother to the developing embryo via the umbilical cord.
NOTE:
- Formulated by blood vessels
Cephalocaudal Development
Growth during prenatal development occurring from head to tail
NOTE:
- Structures nearest the head develop before those nearest the feet.
Proximodistal Development.
Growth during prenatal development occurring from the midline outward
NOTE:
- Structures nearest the torso develop before those away from the center of the body.
The Fetal Period
From the ninth week until birth, the organism is referred to as a fetus. During this stage, the major structures are continuing to develop.
NOTE:
- By the third month, the fetus has all its body parts including external genitalia.
- In the following weeks, the fetus will develop hair, nails, teeth and the excretory and digestive systems will continue to develop.
- During the 4th - 6th months, the eyes become more sensitive to light and hearing develops.
- The respiratory system continues to develop, and reflexes develop during the 5th month.
- Cycles of sleep and wakefulness are present at this time as well.
- The first chance of survival outside the womb, known as the age of viability is reached at about 24 weeks
- The majority of the neurons in the brain have developed by 24 weeks and the glial or nurse cells that support neurons continue to grow.
- At 24 weeks the fetus can feel pain.
- Between the 7th - 9th months, the fetus is primarily preparing for birth.
- It is exercising its muscles and its lungs begin to expand and contract.
- The fetus during the 8th month a layer of fat develops under the skin.
- This layer of fat serves as insulation and helps the baby regulate body temperature after birth.
- At around 36 weeks the fetus is almost ready for birth.
- By week 37 all of the fetus’s organ systems are developed enough that it could survive outside the mother’s uterus without many of the risks associated with premature birth.
- The fetus continues to gain weight and grow in length until approximately 40 weeks.
- By then the fetus has very little room to move around and birth becomes imminent
Fetus
From the ninth week until birth, the organism is referred to as a
NOTE:
- During this stage, the major structures are continuing to develop.
- By the third month, the fetus has all its body parts including external genitalia.
Age of Viability
The first chance of survival outside the womb around 24 weeks
NOTE:
- The majority of the neurons in the brain have developed by 24 weeks, although they are still rudimentary, and the glial or nurse cells that support neurons continue to grow.
- At 24 weeks the fetus can feel pain
Prenatal Brain Development
Prenatal brain development begins in the third gestational week with the differentiation of stem cells, which are capable of producing all the different cells that make up the brain.
NOTE:
- By the end of the third week, two ridges appear along the neural plate first forming the neural groove and then the neural tube.
- The open region in the center of the neural tube forms the brain’s ventricles and spinal canal.
- By the end of the embryonic period, or week eight, the neural tube has further differentiated into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
- Brain development during the fetal period involves neuron production, migration, and differentiation.
- From the early fetal period until midgestation, most of the 85 billion neurons have been generated and many have already migrated to their brain positions.
- Neurogenesis, or the formation of neurons, is largely completed after five months of gestation.
- Neurons that form the neocortex, or the layer of cells that lie on the surface of the brain, migrate to their location in an orderly way.
- Neural migration is mostly completed in the cerebral cortex by 24 weeks.
- Once in position, neurons begin to produce dendrites and axons that begin to form the neural networks responsible for information processing.
- Regions of the brain that contain the cell bodies are referred to as the gray matter
- The axons that form the neural pathways are white matter.
- Myelin aids in both the insulation and efficiency of neural transmission.
- Although cell differentiation is complete at birth, the growth of dendrites, axons, and synapses continue for years.
Neural Plate
The location of stem cells in the embryo is referred to as the
NOTE:
- During the third gestational week
- It is capable of producing all the different cells that make up the brain
Neurogenesis
the formation of neurons
NOTE:
- Completed after give months of gestation
Gray Matter
Regions of the brain that contain the cell bodies are referred to as the
White Matter
The axons that form the neural pathways make up the
Teratology
The study of factors that contribute to birth defects is called
Teratogens
are environmental factors that can contribute to birth defects, and include some maternal diseases, pollutants, drugs and alcohol.
Teratogens:
• Alcohol
• Tobacco
• Prescription/Over-the-counter Drugs
• Pollutants (Lead, pesticides, bisphenol, radiation, Mercury)
• Toxoplasmosis
• Sexually Transmitted Diseases
• Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
• German Measles (or rubella)
Factors influencing prenatal risks:
• The timing of the exposure: Structures in the body are vulnerable to the most severe damage when they are forming. If a substance is introduced during a particular structure's critical period (time of development), the damage to that structure may be greater. For example, the ears and arms reach their critical periods at about 6 weeks after conception. If a mother exposes the embryo to certain substances during this period, the arms and ears may be malformed.
• The amount of exposure: Some substances are not harmful unless the amounts reach a certain level. The critical level depends in part on the size and metabolism of the mother. 48
• The number of teratogens: Fetuses exposed to multiple teratogens typically have more problems than those exposed to only one.
• Genetics: Genetic make-up also plays a role on the impact a particular teratogen might have on the child. This is suggested by fraternal twins exposed to the same prenatal environment, but they do not experience the same teratogenic effects. The genetic makeup of the mother can also have an effect; some mothers may be more resistant to teratogenic effects than others.
• Being male or female: Males are more likely to experience damage due to teratogens than are females. It is believed that the Y chromosome, which contains fewer genes than the X, may have an impact.
Alcohol:
One of the most commonly used teratogens
NOTE:
- It is recommended that women of child-bearing age take great caution against drinking alcohol when not using birth control or when pregnant.
- Alcohol use during pregnancy is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities in children in the United States.
- Alcohol consumption, particularly during the second month of prenatal development, may lead to neurocognitive and behavioral difficulties.
- In extreme cases, alcohol consumption during pregnancy can lead to fetal death, but also can result in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD).
- Binge drinking during pregnancy increases the chance of having a baby with FASD.
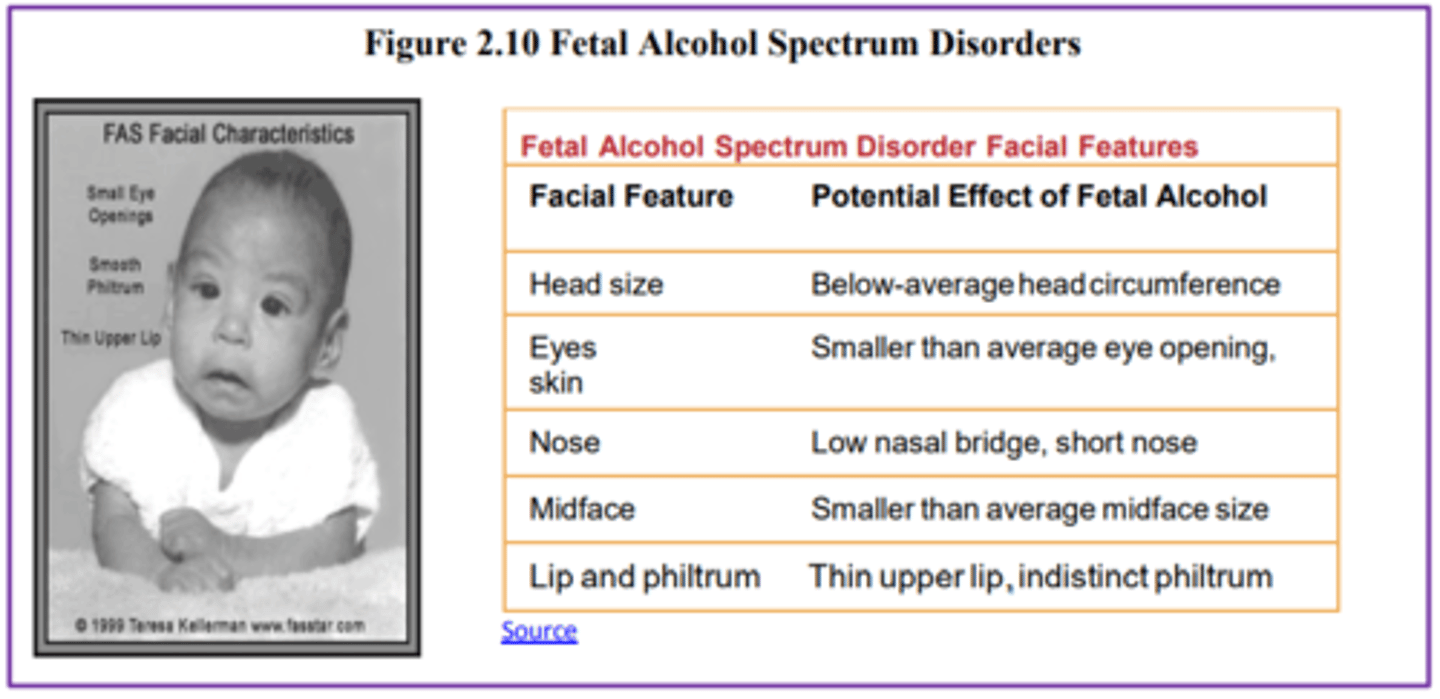
Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
an umbrella term for the range of effects that can occur due to alcohol consumption during pregnancy
NOTE:
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
- Flattened noses, small eye holes, and small heads.
- Cognitively, these children have poor judgment, poor impulse control, higher rates of ADHD, learning issues, and lower IQ scores.
Binge Drinking
4 or more drinks in 2 to 3 hours
NOTE:
- Increases the chance of having a baby with FASD
Tobacco:
Another widely used teratogen
NOTE:
- When a pregnant woman smokes the fetus is exposed to dangerous chemicals including nicotine, carbon monoxide and tar, which lessen the amount of oxygen available to the fetus.
- Tobacco use during pregnancy has been associated with low birth weight, ecotopic pregnancy, placenta previa, placenta abruption, preterm delivery, stillbirth, fetal growth restriction, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), birth defects, learning disabilities, and early puberty in girls.
- A woman being exposed to secondhand smoke during pregnancy has also been linked to lowbirth weight infants.
- Exposure to thirdhand smoke results in a negative impact on infants’ lung development, altering the function of the lungs in children.
Ecotopic Pregnancy
Fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus
placenta previa
Placenta lies low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix
Placenta Abruption
Placenta separates prematurely from the uterine wall
Thirdhand Smoke
Toxins from tobacco smoke that linger on clothing, furniture, and in locations where smoking has occurred
NOTE:
- Results in a negative impact on infants' lung development.
- It plays a greater role in altered lung functioning in children.
Prescription/Over-the-counter Drugs:
A woman should not be taking any prescription drug during pregnancy unless it was prescribed by a health care provider who knows she is pregnant.
Over-the-counter drugs are also a concern during the prenatal period because they may cause certain health problems.
NOTE:
- Some prescription drugs can cause birth defects, problems in overall health, and the development of the fetus.
Illicit Drugs:
- Common illicit drugs include cocaine, ecstasy and other club drugs, heroin, marijuana, and prescription drugs that are abused.
- The use of cocaine is connected with low birth weight, stillbirths and spontaneous abortion.
- Heavy marijuana use is associated with problems in brain development
- If a baby's mother used an addictive drug during pregnancy that baby can get addicted to the drug before birth and go through drug withdrawal after birth.
- Other complications of illicit drug use include premature birth, smaller than normal head size, birth defects, heart defects, and infections.
- Additionally, babies born to mothers who use drugs may have problems later in life, including learning and behavior difficulties, slower than normal growth, and die from sudden infant death syndrome.
- Children of substance abusing parents are also considered at high risk for a range of biological, developmental, academic, and behavioral problems, including developing substance abuse problems of their own
Neonatal abstinence syndrome
If a baby's mother used an addictive drug during pregnancy that baby can get addicted to the drug before birth and go through drug withdrawal after birth.
Pollutants:
• Lead: An environmental pollutant of significant concern is lead poisoning, which has been linked to fertility problems, high blood pressure, low birth weight, prematurity, miscarriage, and slowed neurological development.
• Pesticides: The chemicals in certain pesticides are also potentially damaging and may lead to birth defects, learning problems, low birth weight, miscarriage, and premature birth (
• Bisphenol A: Prenatal exposure to bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical commonly used in plastics and food and beverage containers, may disrupt the action of certain genes contributing to certain birth defects.
• Radiation: If a mother is exposed to radiation, it can get into the bloodstream and pass through the umbilical cord to the baby. Radiation can also build up in body areas close to the uterus, such as the bladder. Exposure to radiation can slow the baby’s growth, cause birth defects, affect brain development, cause cancer, and result in a miscarriage.
• Mercury: Mecury, a heavy metal, can cause brain damage and affect the baby’s hearing and vision. This is why women are cautioned about the amount and type of fish they consume during pregnancy.
Toxoplasmosis:
The tiny parasite, toxoplasma gondii, causes an infection
NOTE:
- A healthy immune system can keep the parasite at bay producing no symptoms.
- Toxoplasmosis can cause premature birth, stillbirth, and can result in birth defects to the eyes and brain.
- Some may experience eye infections, enlarged liver and spleen, jaundice, and pneumonia.
- To avoid being infected, women should avoid eating undercooked or raw meat and unwashed fruits and vegetables, touching cooking utensils that touched raw meat or unwashed fruits and vegetables, and touching cat feces, soil or sand.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases:
- Gonorrhea, syphilis, and chlamydia are sexually transmitted infections that can be passed to the fetus by an infected mother.
- Mothers should be tested as early as possible to minimize the risk of spreading these infections to their unborn child.
- Additionally, the earlier the treatment begins, the better the health outcomes for mother and baby.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can cause premature birth, premature rupture of the amniotic sac, an ectopic pregnancy, birth defects, miscarriage, and still births.
- Most babies become infected with STDS while passing through the birth canal during delivery.
- Some STDs can cross the placenta and infect the developing fetus.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV):
- Most potentially devastating teratogens.
- HIV and Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) are leading causes of illness and death in the United States.
- One of the main ways children under age 13 become infected with HIV is via mother-to-child transmission of the virus prenatally, during labor, or by breastfeeding.
- HIV positive mothers who take antiviral medications during their pregnancy greatly reduce the chance of passing the virus to the fetus.
- It is recommended that women with HIV deliver the child by c-section, and that after birth they avoid breast feeding.
German measles (or rubella):
An infection that causes mild flu-like symptoms and a rash on the skin.
NOTE:
- Only about half of children infected have these symptoms, while others have no symptoms.
- Rubella has been associated with a number of birth defects.
- If the mother contracts the disease during the first three months of pregnancy, damage can occur in the eyes, ears, heart or brain of the unborn child.
- Deafness is almost certain if the mother has German measles before the 11th week of prenatal development and can also cause brain damage.
Maternal Factors:
• Mothers over 35
• Teenage Pregnancy
• Gestational Diabetes
• High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
• Rh Disease
• Weight Gain during Pregnancy
• Stress
• Depression
• Paternal Impact
Mothers over 35:
Women over age 35 are more likely to have an increased risk of:
• Fertility problems
• High blood pressure
• Diabetes
• Miscarriages
• Placenta Previa
• Cesarean section
• Premature birth
• Stillbirth
• A baby with a genetic disorder or other birth defects
NOTE:
- Because a woman is born with all her eggs, environmental teratogens can affect the quality of the eggs as women get older.
- A woman's reproductive system ages which can adversely affect the pregnancy.
Teenage Pregnancy:
A teenage mother is at a greater risk for having pregnancy complications including anemia, and high blood pressure.
NOTE:
- These risks are even greater for those under age 15.
- Infants born to teenage mothers have a higher risk for being premature and having low birthweight or other serious health problems.
- Premature and low birthweight babies may have organs that are not fully developed which can result in breathing problems, bleeding in the brain, vision loss, and serious intestinal problems.
- Teenagers are the least likely of all age groups to get early and regular prenatal care.
- They may engage in negative behaviors including eating unhealthy food, smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking drugs.
- Teenagers are repeat births.
Gestational Diabetes:
Diabetes is a condition where the body has too much glucose in the bloodstream.
NOTE:
- Usually goes away after the mother gives birth, but it might indicate a risk for developing diabetes later in life.
- If untreated, gestational diabetes can cause premature birth, stillbirth, the baby having breathing problems at birth, jaundice, or low blood sugar.
- Babies born to mothers with gestational diabetes can also be considerably heavier making the labor and birth process more difficult.
- For expectant mothers, untreated gestational diabetes can cause preeclampsia (high blood pressure and signs that the liver and kidneys may not be working properly) discussed later in the chapter.
- Risk factors for gestational diabetes include age (being over age 25), being overweight or gaining too much weight during pregnancy, family history of diabetes, having had gestational diabetes with a prior pregnancy, and race and ethnicity.
- Eating healthy and maintaining a healthy weight during pregnancy can reduce the chance of gestational diabetes.
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension):
is a condition in which the pressure against the wall of the arteries becomes too high.
NOTE:
- Gestational hypertension only occurs during pregnancy and goes away after birth.
- Chronic hypertension refers to women who already had hypertension before the pregnancy or to those who developed it during pregnancy and it continued after birth.
- High blood pressure during pregnancy can cause premature birth and low birth weight, placental abruption, and mothers can develop preeclampsia.
Rh Disease:
a form of anemia
NOTE:
- Rh is a protein found in the blood.
- Most people are Rh positive, meaning they have this protein.
- Some people are Rh negative, meaning this protein is absent.
- Mothers who are Rh negative are at risk of having a baby with a form of anemia called Rh disease.
- A father who is Rh-positive and mother who is Rh-negative can conceive a baby who is Rh-positive.
- Some of the fetus’s blood cells may get into the mother’s bloodstream and her immune system is unable to recognize the Rh factor.
- The immune system starts to produce antibodies to fight off what it thinks is a foreign invader.
- Once her body produces immunity, the antibodies can cross the placenta and start to destroy the red blood cells of the developing fetus.
- In the newborn, Rh disease can lead to jaundice, anemia, heart failure, brain damage and death.
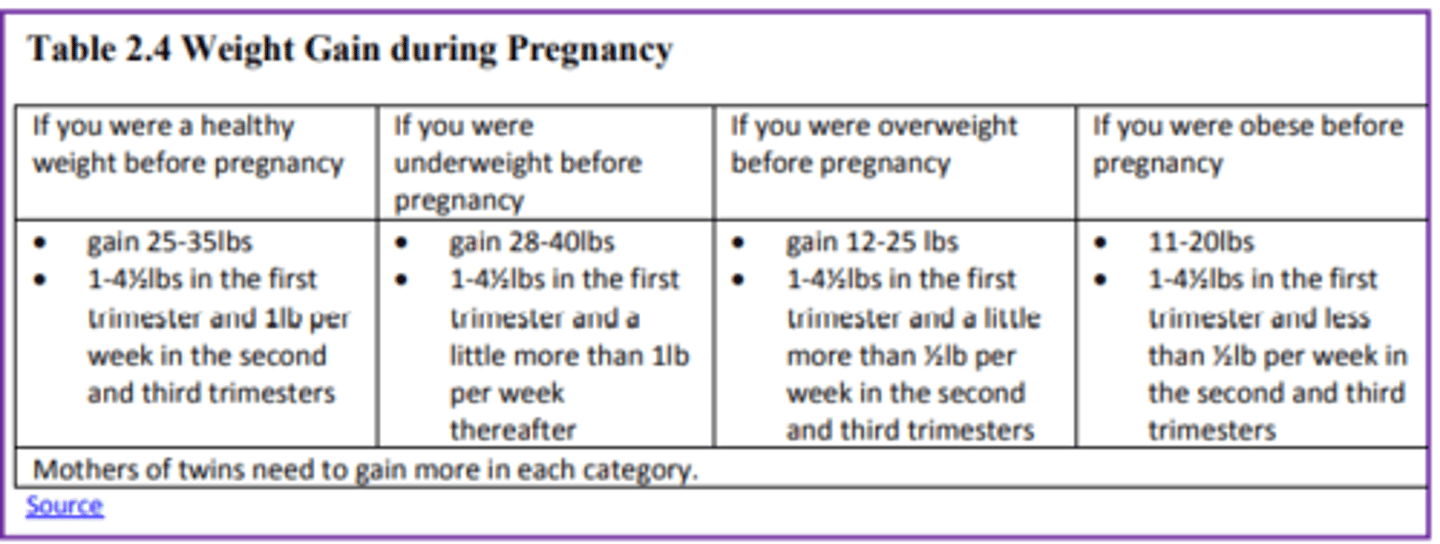
Weight Gain during Pregnancy:
During pregnancy most women need only an additional 300 calories per day to aid in the growth of the fetus. Gaining too little or too much weight during pregnancy can be harmful.
NOTE:
- Women who gain too little may have a baby who is low-birth weight, while those who gain too much are likely to have a premature or large baby.
- There is also a greater risk for the mother developing preeclampsia and diabetes, which can cause further problems during the pregnancy.
- Putting on the weight slowly is best. Mothers.
Stress:
- Feeling stressed is common during pregnancy, but high levels of stress can cause complications including having a premature baby or a low-birthweight baby.
- Babies born early or too small are at an increased risk for health problems.
- Stress-related hormones may cause these complications by affecting a woman's immune systems resulting in an infection and premature birth.
- Additionally, some women deal with stress by smoking, drinking alcohol, or taking drugs, which can lead to problems in the pregnancy.
- High levels of stress in pregnancy have also been correlated with problems in the baby's brain development and immune system functioning, as well as childhood problems such as trouble paying attention and being afraid
Depression:
A significant medical condition in which feelings of sadness, worthlessness, guilt, and fatigue interfere with one's daily functioning.
NOTE:
- Depression can occur before, during, or after pregnancy.
- Women who have experienced depression previously are more likely to have depression during pregnancy.
- Consequences of depression include the baby being born premature, having a low birthweight, being more irritable, less active, less attentive, and having fewer facial expressions.
- It is important that women taking antidepressants during pregnancy discuss the medication with a health care provider as some medications can cause harm to the developing organism..
Paternal Impact:
The age of fathers at the time of conception is also an important factor in health risks for children.
NOTE:
- Offspring of men over 40 face an increased risk of miscarriages, autism, birth defects, achondroplasia (bone growth disorder) and schizophrenia.
- These increased health risks are thought to be due to accumulated chromosomal aberrations and mutations during the maturation of sperm cells in older men.
- However, like older women, the overall risks are small.
- Men are more likely than women to work in occupations where hazardous chemicals, many of which have teratogenic effects or may cause genetic mutations.
- Men are also more likely to be a source of secondhand smoke for their developing offspring.
Ultrasound
is a test in which sound waves are used to examine the fetus.
NOTE:
- Transvaginal ultrasounds are used in early pregnancy.
- Transabdominal ultrasounds are more common and used after 10 weeks of pregnancy (typically, 16 to 20 weeks).
Amniocentesis
is a procedure in which a needle is used to withdraw a small amount of amniotic fluid and cells from the sac surrounding the fetus and later tested
NOTE:
- Has a risk of miscarriage, and consequently they are not done routinely.
Chorionic Villus Sampling
is a procedure in which a small sample of cells is taken from the placenta and tested.
NOTE:
- Has a risk of miscarriage, and consequently they are not done routinely.
Infertility:
- For men, the most common cause is a lack of, or low sperm production
- For women, it is the failure to ovulate.
- Another common cause for women is pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- It is often a complication caused by and STD, such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, although other infections that are not sexually transmitted can also cause PID.
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
an infection of a woman's reproductive organs
Fertility treatment:
The majority of infertility cases are treated using fertility drugs to increase ovulation, or with surgical procedures to repair the reproductive organs or remove scar tissue from the reproductive tract.
NOTE:
- Vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Intra-fallopian tube transfer (GIFT)
- Zygote intra-fallopian tube transfer (ZIFT)
Vitro fertilization (IVF)
eggs are removed from the female and are fertilized outside the woman's body.
NOTE:
- The fertilized egg is then reinserted in the woman's uterus. The success rate varies depending on the type of egg implanted, such as whether the egg was recently removed from the woman, used after being frozen, or donated from another woman.
- Success is also highly dependent on the age of the mother.
Intra-fallopian tube transfer (GIFT)
which involves implanting both sperm and ova into the fallopian tube and fertilization is allowed to occur naturally
Zygote intra-fallopian tube transfer (ZIFT)
is another procedure in which sperm and ova are fertilized outside of the woman's body and the fertilized egg is then implanted in the fallopian tube.
NOTE:
- This allows the zygote to travel down the fallopian tube and embed in the lining of the uterus naturally.
Complications of Pregnancy:
• Minor complications
• Major Complications
• Maternal Mortality
Minor complications:
- There are a number of common side effects of pregnancy.
- Not everyone experiences all of these, nor to the same degree.
- And although they are considered "minor" this is not to say that these problems are not potentially very uncomfortable.
- These side effects include nausea, heartburn, gas, hemorrhoids, backache, leg cramps, insomnia, constipation, shortness of breath or varicose veins.
Major Complications:
The following are some serious complications of pregnancy which can pose health risks to mother and child and that often require hospitalization.
NOTE:
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Preeclampsia (Toxemia)
- Eclampsia
Ectopic Pregnancy
occurs when the zygote becomes attached to the fallopian tube before reaching the uterus.
NOTE:
- Abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, nausea and fainting are symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
Preeclampsia (Toxemia)
is characterized by a sharp rise in blood pressure, a leakage of protein into the urine as a result of kidney problems, and swelling of the hands, feet, and face during the third trimester of pregnancy.
NOTE:
- Accounts for 40% to 60% of maternal deaths
- Preeclampsia occurs most frequently in first pregnancies, and it is more common in women who are obese, have diabetes, or are carrying twins.
-Leading cause of fetal complications, which include low birth weight, premature birth, and stillbirth.
- Treatment is typically bed rest and sometimes medication. If this treatment is ineffective, labor may be induced.
Eclampsia
When preeclampsia causes seizures, the condition is known as
Maternal Mortality:
- About 700 American women die from complications related to pregnancy each year, and this number is rising.
- Bleeding, infections, and heart-related problems are the main causes.
- Possible contributing factors include the high caesarean section rate and obesity.
Spontaneous abortion
- Usually the body aborts due to chromosomal abnormalities, and this typically happens before the 12th week of pregnancy.
- Cramping and bleeding result and normal periods return after several months.
- Some women are more likely to have repeated miscarriages due to chromosomal, amniotic, or hormonal problems, but miscarriage can also be a result of defective sperm.
Choosing Where to Have the Baby and Who Will Deliver:
- The vast majority of births occur in a hospital setting.
- However, one percent of women choose to deliver at home.
- Women who are at low risk for birth complications can successfully deliver at home.
- Midwives are trained and licensed to assist in delivery and are far less expensive than the cost of a hospital delivery.
- In addition to home births, one-third of out-of- 61 hospital births occur in freestanding clinics, birthing centers, in physician's offices, or other locations.