PERSONALITY PSYC 002
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Hippocrates
Physiology of the body underlies temperament and personality
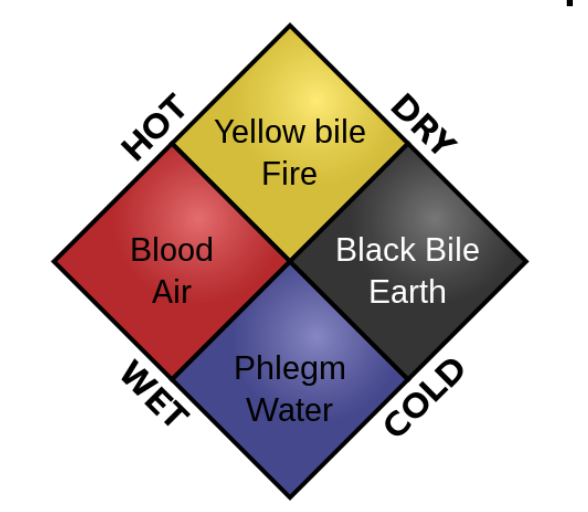
Four humors:
Yellow = bile from liver
Black = bile from kidneys
Red = blood from heart
White = phlegm from lungs
Galen
believe both diseases and personality differences were explained by imbalances in the humors
Choleric (yellow bile)= passionate, ambitious, bold
Melancholic (black bile)= reserved, anxious, unhappy
Sanguine (blood) = joyful, eager, optimistic
Phlegmatic (phlegm)= calm, reliable, thoughtful
Kant
divided the four temperaments into two categories
Feeling:
Sanguine (optimistic) = strong but short lasting feelings
Melancholic = weak but enduring feelings
Activity:
Choleric (grumpy) = intense but not persistent activity
Phlegmatic (calm ) = inactive but enduring
Wundt
Emotional/non-emotional
separated strong emotions (melancholic/choleric) from the weak emotions (phlegmatic, sanguine)
Changeable/unchangelable
divided the changeable temperaments (choleric, sanguine) from the unchangeable ones (melancholic, phlegmatic)
Phrenology
Franz Joseph Gall
bumps on surface of skull reflect brain surface and related personality traits and abilities
Reforms in the Treatment of Mental Illness
Psychiatrists were divided into two
camps: the somatic and the psychic
• Emmanuel movement: talk therapy
session for the mentally ill
• Hypnosis used as a therapeutic
technique
• Physicians began to think in terms
of curing emotional disturbances by
treating the mind instead of the body
Was it Only a Dream?
Little Freuds dream:
mother is carried into a room
people carrying her are not human, extremely tall, dressed in strange clothing, bird like faces
30 years later : dream is still highly emotional for Freud
superficial meaning: little boy afraid of losing his mother
True meaning : symbolizes sexual longing of a 7 yr old boy for his mother????
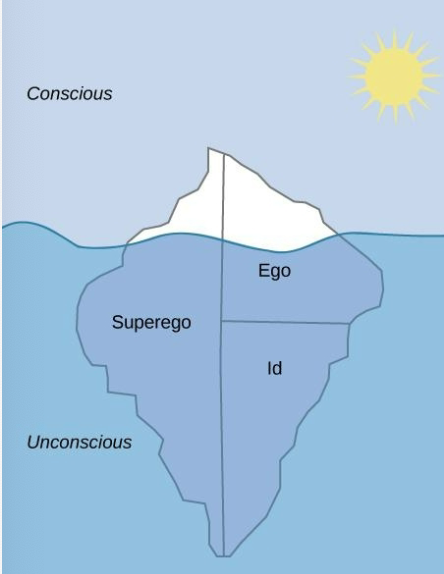
Levels of Consciousness
Unconscious
mental activity that we are unaware of and are unable to access
According to FREUD
we are only aware of small amount (1/10) of our minds activities and most of it remains hidden from us in our unconscious
unacceptable urges & desires are kept in our unconscious through repression.
information in our unconscious affects our behavior
FREUDIAN SLIP
saying a word you did not intend to say are sexual/aggressive urges accidentally slipping out of our unconscious
Psychoanalysis as a System of Personality
Instincts
mental representation of internal stimuli that motivate personality and behaviors
Life instinct (libido)
death instinct
Levels of Personality
conscious vs. unconscious
Id
Ego
Superego
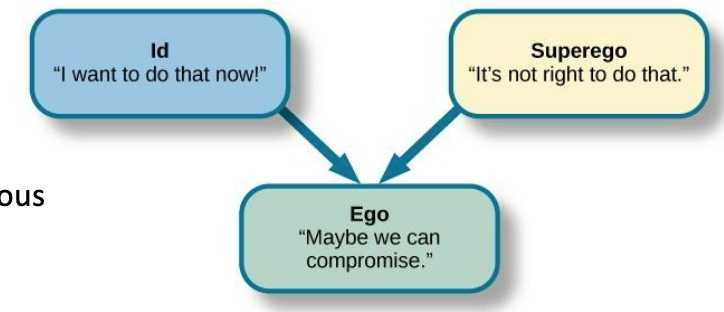
Anxiety
warning that the ego is being threatened
Defense mechanisms: behaviors that represent unconscious denials or distortions of reality adopted to protect the ego
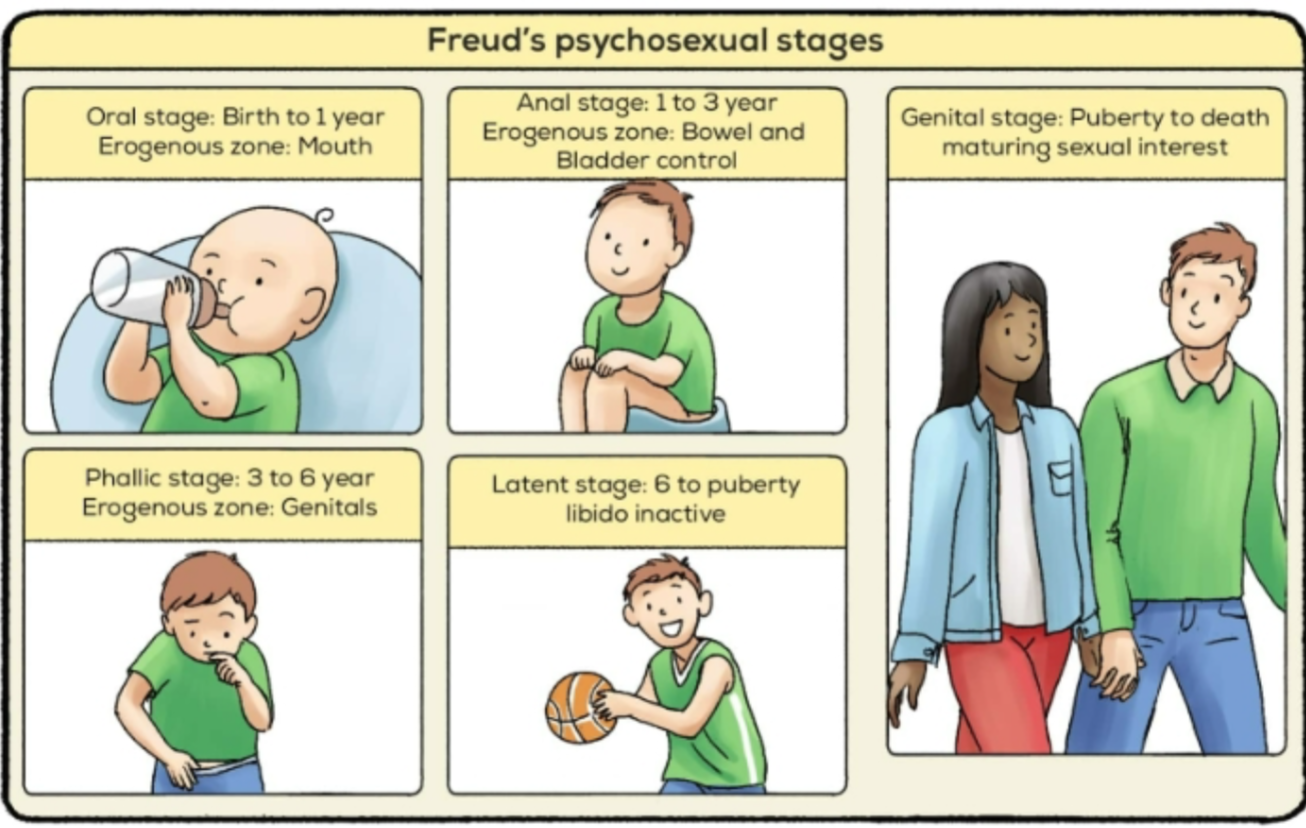
PSYCHOSEXUAL STAGES OF PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT (SIGMUND FREUD)
stages of childhood centering on erogenous zones
Competing Factors
Psychoanalysis later split into factions that disagreed on basic points
Alfred Adler
Erik Erikson
Carl Jung
Karen Horney
Abraham Maslow
Carl Rogers
The Neo-Freudians and Ego Psychology
loyalists who called for an expansion of the concept of the ego
ego seen as having a more extensive role
ego was more independent of the id, possessed its own energy not derived from the id, had functions separate from the id
suggested that the ego was free of conflict produced when id impulses pressed for satisfaction
less emphasis on biological forces as influences on personality
Alfred Adler’s Individual Psychology
Adler’s theory of personality that incorporates social as well as biological factors
Social interest
innate potential to cooperate with other people to achieve personal and societal goals
believed we are more strongly affected by our plans for the future
striving for goals or anticipant coming events can influence peresent behavior
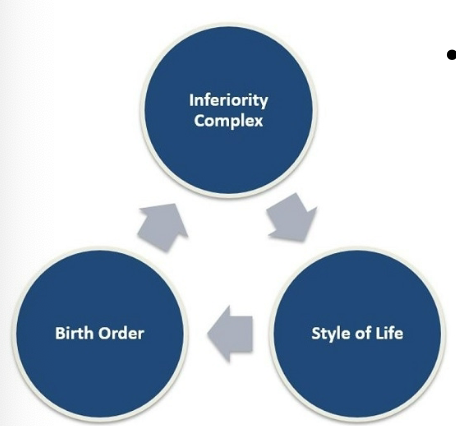
Adler’s Individual Psychology #2
drive for superiority or perfection = universal
ppl have capacity to determine our own personality as as unique style of life
Birth Order
relationship between both order and personality because of how one is treated in relation to others in family
First Borns = perfectionist, achiever, leader, bossy, responsible. motivated, conscientious, controlling, reliable
Middle Borns = adaptable, independent, go-between, people pleaser, rebellious, left out, peacemaker, social
Last Borns = social , charming, outgoing, uncomplicated, manipulative, seeks attention, self centered, fun
Only Child = confident , conscientious, responsible, perfectionist, center of attention, mature for age, seeks approval, sensitive, leader
Inferiority Complex
condition that develops when a person is unable to compensate for normal inferiority feelings
proposed that a feelings of inferiority is a motivating force in behavior
helplessness & dependence on other people awaken this sense of inferiority in infancy
Fundamental Life Tasks
Occupational Tasks
careers
Societal Tasks
friendship
Love Tasks
finding intimate partner
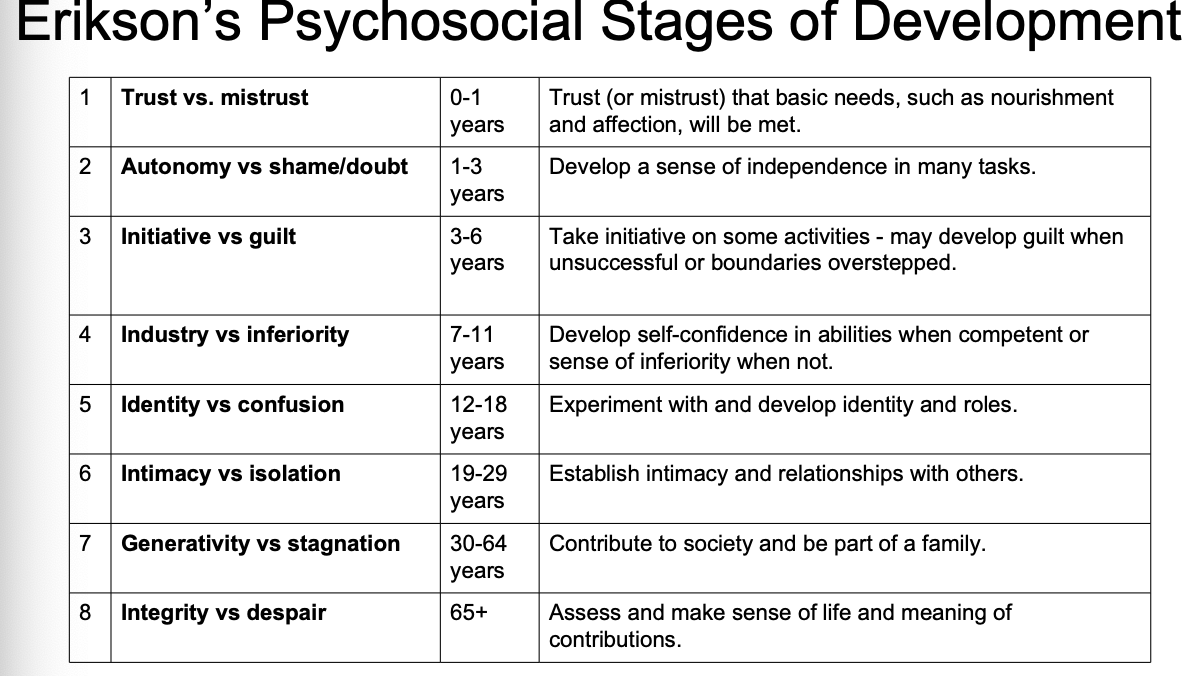
Erickson’s Psychosocial Theory
the social nature of development
personality development takes place across lifespan
based on belief that social interactions affect our sense of self (ego identity)
psychosocial task we must master in order to feel a sense of competence
Carl Jung
surrogate son & heir to psychoanalytic movement
Analytic Psychology : Jung’s theory of personality (opposition to Freud’s work)
Jung’s Analytic Psychology
no place for Oedipus complex
sex played small roll in human motivation
The Libido: generalized life energy of which sex was only a part
believed we are shaped by past, goals, hopes, aspirations
Personality is not fully determined by experiences during the first five years of childhood & could be changes
Two Levels of The Unconscious Mind
Personal Unconscious
reservoir of material that once was conscious but has been forgotten or suppressed
Collective Unconscious
deepest level of psyche containing inherited experiences of human & prehuman species
Extroversion & Introversion (Jung)
Jung’s greatest contribution to personality psychology was the idea of different attitudes towards life = Introverts & Extroverts
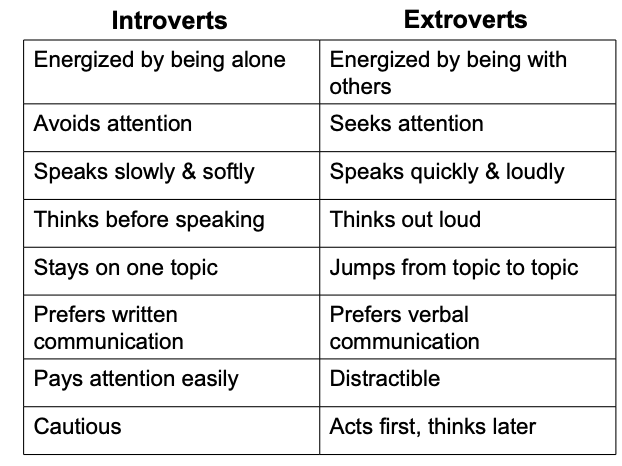
Psychological Types: functions & attitudes
thinking
feeling
sensing
intuiting
Myers Briggs Personality Types
test discovering personality type

Karen Horney
early feminist
culturally based personality differences between men and women
Basic Anxiety
pervasive loneliness and helplessness are feelings that give rise to neuroses
result from parental actions such as dominance, lack of protection and love and erratic behavior
believed personality develops in early childhood years (Freud)
Neurotic Needs
Gives rise to three personality types:
Compliant Personality
Detached Personality
Aggressive Personality
Idealized self image : provides person with false picture of personality or self
Skinner’s Behavioral Perspectives
learning approaches to personality focused on observable, measurable phenomena
we LEARN to behave in particular ways
behavior is environmentally determined
Personality
shaped by reinforcements and consequences in environment (operant conditioning)
develops over our entire life and can vary as we experience new situations
Keller and Marians Breland “The IG Zoo”
apply psychological conditioning techniques to animal behaviors
used basic conditioning techniques learned from B.F. Skinner
ran 140-trained-animal shows at major tourist attractions
Sociobehaviorism: The Cognitive Challenge
third stage of behaviorism
Leaders = Bandura and Rotter
return to study of mental or cognitive processes: reflection of the broader cognitive movement in psychology as a whole
Social Cognitive Theory
both learning and cognition as sources of individual difference in personality
though processes such as beliefs, expectations, and instructions influence external reinforcement schedules
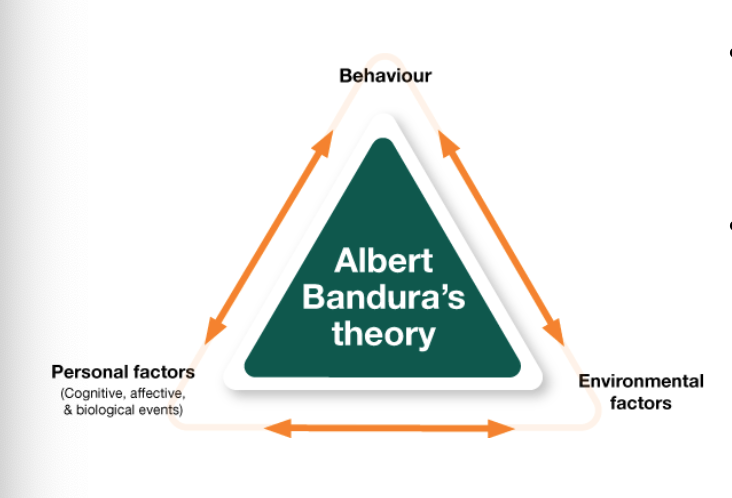
Factors in Personality Development
Reciprocal Determinism - behavior, cognitive processes, situational context all influence each other
Observational Learning
Self Efficacy - confidence in own abilities & how we approach challenges
Julian Rotter
First Psychologist to use the term “Social Learning Theory”
argued that we learn primarily through social experiences
Cognitive Processes
we perceive ourselves as conscious being capable of influencing the experiences that affect our lives
internal cognitive states determine the effects of different external experiences
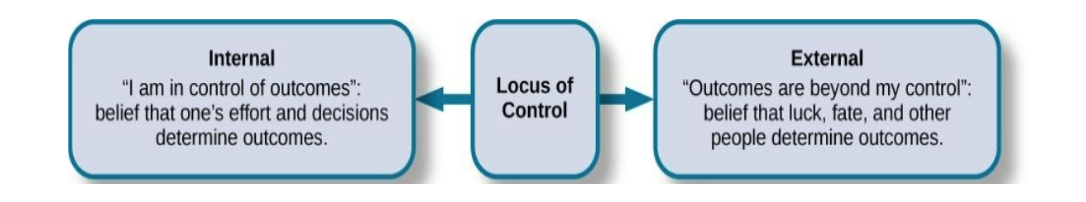
Locus of Control
Rotter’s idea about the perceived source of reinforcement
Internal locus of control = reinforcement depends of ones OWN BEHAVIOR
External locus of control = reinforcement depends on OUTSIDE FORCES
ppl with internal locus of control tend to be physically & mentally healthier than those with an external locus of control
Self- Regulation (Will Power)
ability to delay gratification
“Marshmallow Test”
Children with more self control (waited for two marshmallows) in preschool were more successful in high school
Children with less self control (took one marshmallow) in preschool were more likely to have academic & behavioral problems
The Person-Situation Debate
Behavior
Inconsistent across different situations
more consistent within situations
consisten in equivalent situations
Theory that personality traits are consistent across situations not supported
People use cognitive processes to assess situations and behave in accordance with that interpretation
Humanistic Approach
how healthy people develop
emphasized human strengths, positive aspirations, conscious experience, free will, fulfillment of human potential, and belief in the wholeness of human nature
Abraham Maslow
Studied ppl he considered health, creative, productive
albert Einstein, Eleanor roosevelt, thomas jefferson, abraham lincoln
found they all shared similar characteristics : open, creative, loving, spontaneous, compassionate, concerned for others, accepting of themselves
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Self- Actualization
desire to become the most that one can be
Hierarchy of needs
full development of ones abilities and the realization of ones potential

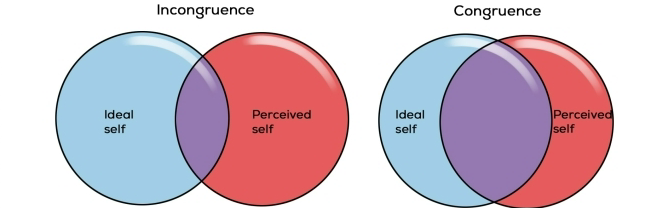
Carl Rogers
Personality is shaped by the PRESENT and how we CONSCIOUSLY PERCEIVE it
self concept (thoughts/feelings ab ourselves)
Ideal Self
person we would like yo be
Real Self
person we actually are
High congruence → greater sense of self-worth, healthy, productive life
• Incongruence → maladjustment
Qualities of Psychologically Health Persons
openness to and a freshness of appreciation of all experiences
lives fully in every moment
ability to be guided by their instincts rather than by reason or opinions of others
sense of freedom in thought and action
high degree of creativity
continual need to maximize potential
The Jim Twins
The Jim Twins
• Jim Lewis and Jim Springer were identical twins raised apart
from the age of 4 weeks.
• Reunited at the age of 39 in 1979
• Both suffered from tension headaches, were prone to nail biting,
smoked Salem cigarettes, drove the same type of car, and even
vacationed at the same beach in Florida.
Minnesota Study of Twins Raised Apart
identical twins, whether raised together or apart, have very similar personalities
suggests heritability of some personality traits
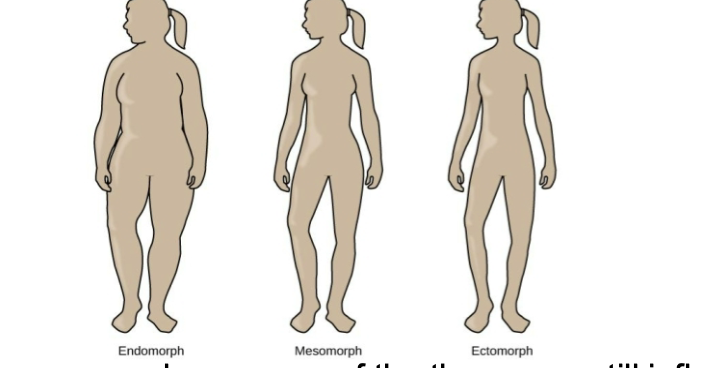
Somatotypes (Sheldon’s theory)
believed body types could be linked to personality
Endomorphs – relaxed, comfortable, good-humored, even-tempered, sociable, tolerant
Mesomorphs – adventurous, assertive, competitive, fearless
Ectomorphs – Anxious, self-conscious, artistic, thoughtful, quiet, private
Discredited but even people unaware of the theory are still influenced in their assessments of personality by body type
Trait Theories of Personality
People have certain basic traits and it is the strength and intensity of those traits that account for personality differences
Allport’s trait theory
Cattell’s 16 factor personality model
Eysenck’s three-dimensional model
The five factory model
Allports Trait Theory
Cardinal Traits
single trait which dominates (rare)
Central Traits
general characteristics
Secondary Traits
less obvious or consistent, only present under certain circumstances
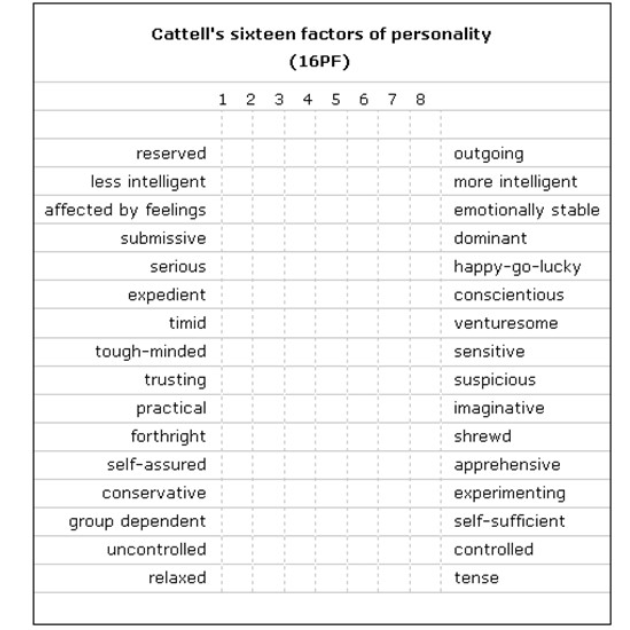
Cattell’s 16-factor Personality Model
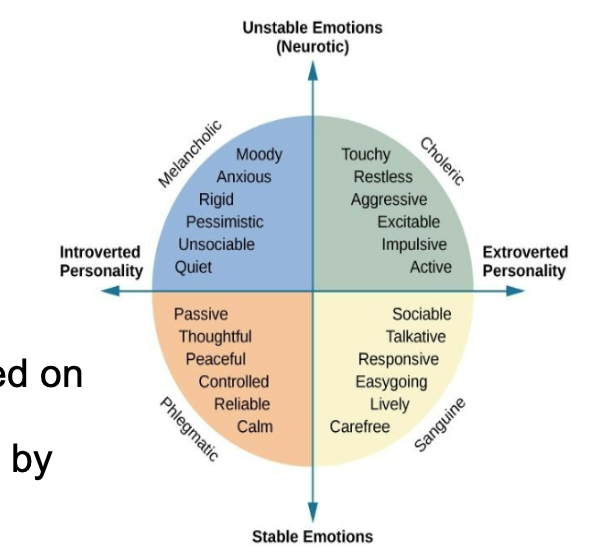
Eysneck’s Three-Dimensional Model
Hands and Sybil Eysenck focused on temperament and believed that personality traits are influenced by genetic inheritance
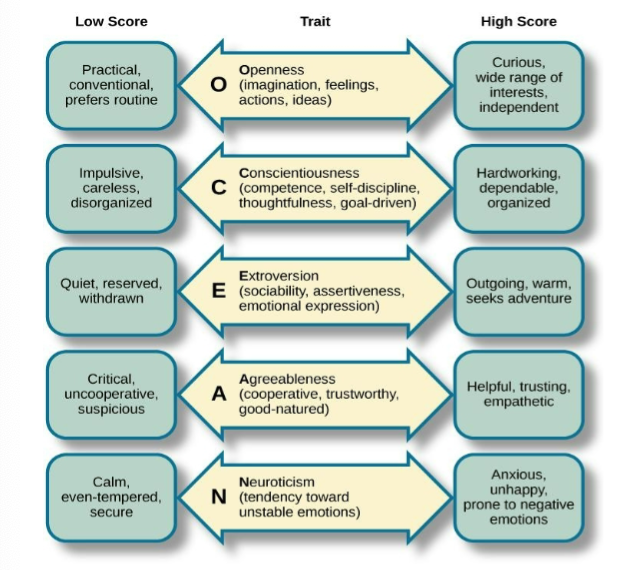
FIVE FACTOR MODEL
Each trait is scored on a continuum
O- Openness to experience
C - Conscientiousness
E - Extroversion
A - Agreeableness
N- Neuroticism
(OCEAN)
HEXACO Model
Trait:
(H) Honesty-Humility
(E) Emotionality
(X) Extraversion
(A) Agreeableness
(C)Conscientiousness
(O) Openness
Cultural Influences on Personality
Culture — beliefs, customs, arts, traditions of a particular society
most important environmental influences on personality
Universal and culture specific aspects account for variation in personality
Individualistic and Collectivist Cultures
Individualist Cultures
value independence, competition, personal achievement
display more personally oriented personality traits
Collectivist Cultures
value social harmony, respectfulness, group needs over individual needs
display more socially oriented personality traits