anatomy and physiology of lymphatic system
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
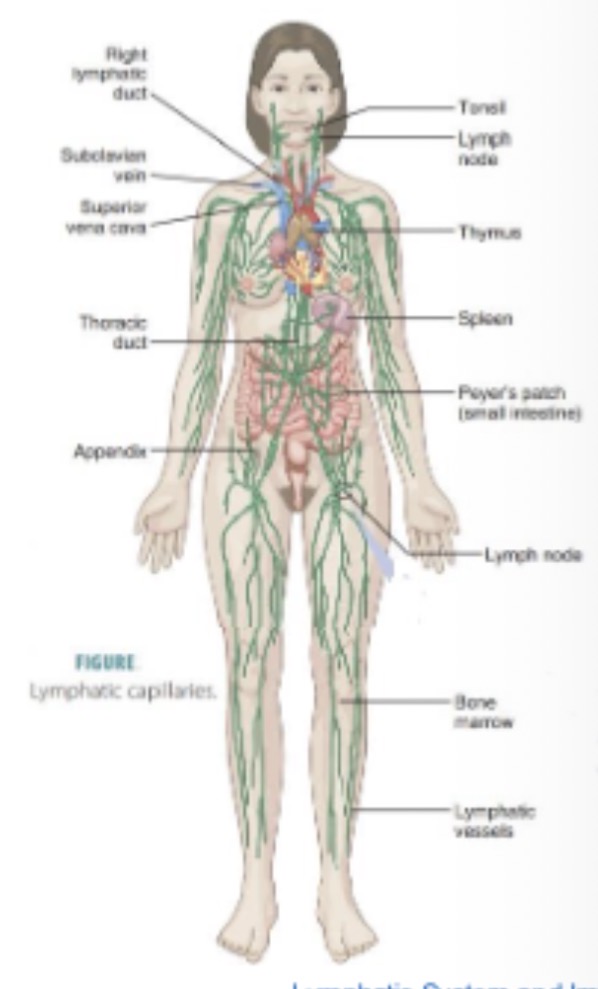
What is the lymphatic system?
A: A network of vessels and nodes that collect excess tissue fluid (lymph), filter it, and return it to venous circulation.
What fluid does the lymphatic system collect?
Excess interstitial tissue fluid (lymph).
Into which circulation is lymph returned?
Venous circulation.
What are the two categories of lymphatic organs?
Primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Which organs are primary lymphoid organs?
Thymus and red bone marrow.
What is secreted by the thymus to mature T lymphocytes?
Thymosin and thymopoietin.
What happens to the thymus after puberty?
It atrophies and is replaced by fatty tissue.
What is the main function of red bone marrow in immunity?
Production of blood cells including lymphocytes.
Which organs are secondary lymphoid organs listed here?
Spleen
tonsils (waldeyers ring)
appendix (GALT)
What immune tissue classification includes the appendix?
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT).
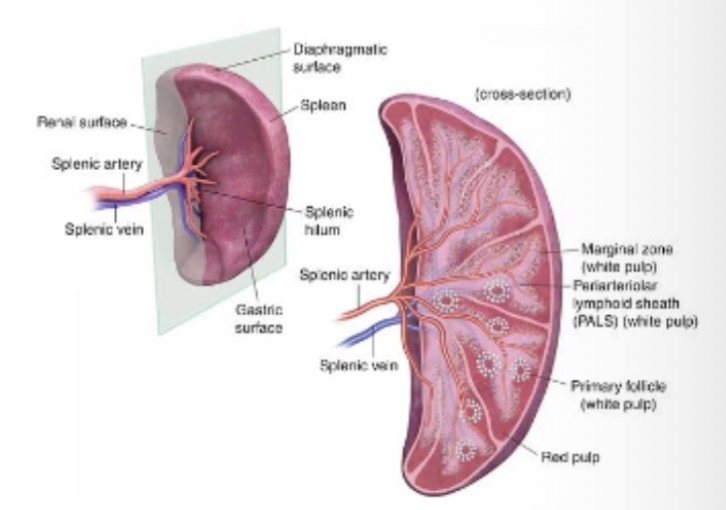
What structure surrounds the spleen?
Fibrous capsule forming lobules.
What structures are found in the splenic hilum?
Splenic artery, splenic vein, efferent lymphatic vessel.
What immune cells are abundant in the spleen?
.
Lymphocytes
Does the spleen filter lymph or blood?.
Blood
What does the spleen remove from circulation?
Pathogens and old red blood cells.
What happens to iron from degraded RBCs in the spleen?
Sent to bone marrow for new RBC production.
Where is bilirubin from RBC breakdown transported?
Liver
What was the splenic function during embryonic development?
RBC production.
When does the spleen stop producing RBCs?
After birth.
What is the function of splenic red pulp?
Blood filtration cavities.
What is the function of splenic white pulp?
Lymphocyte masses surrounding arterioles.
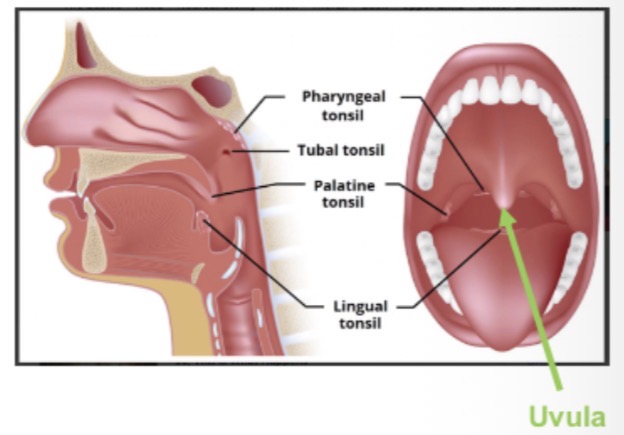
What type of immune tissue are tonsils classified as?
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT).
What is Waldeyer’s ring?
Ringed arrangement of lymphatic tissue in tonsils.
Name the tonsil types in Waldeyer’s ring.
Palatine, tubal, pharyngeal, lingual.
Which immune cells are present in tonsils?
T cells, B cells, macrophages.
Primary defensive role of tonsils?
First line defence against pathogens entering mouth/nose.
When are tonsils largest?
Around puberty.
What happens to tonsils with age?
.
Atrophy
How is lymph fluid classified?
Transudative fluid.
Visual characteristics of lymph?
Transparent and yellow.
Composition of lymph relative to plasma?
Similar; mostly water with ~5% proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, ions.
Why does lymph composition vary?
.
Depends on site of production
Define chyle.
GI-derived lymph rich in fats
How is lymph mainly formed?
Fluid from capillary beds due to high hydrostatic pressure
Structural feature of lymphatic capillaries?
Blind-ended tubes
Why can pathogens enter lymph?
High capillary permeability.
What prevents lymph backflow?
.
Overlapping endothelial mini-valves
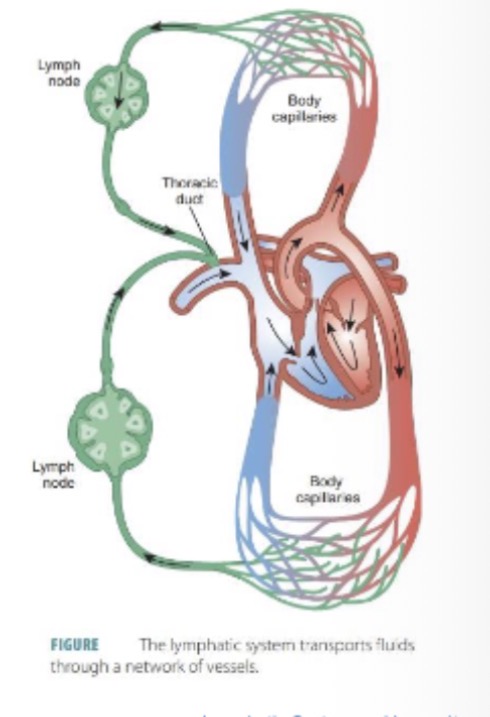
Where is lymph returned to circulation?
A: Left side venous circulation
Homeostatic purpose of lymph return?
: Prevents loss of blood volume.
Where are lymphatic vessels absent?
Bone marrow and avascular tissues
Two lymphatic vessel systems?
Superficial and deep
Origin and drainage of superficial vessels?
Subcutaneous t issue → - drain into deep vessels.
Structures drained by deep vessels?
Internal organs and deeper tissues
What do deep vessels accompany?
Deep arteries.
: Where does lymph drainage begin
Lymph channels.
Compare lymph vessel structure to veins.
Larger lumen, less smooth muscle
Why less smooth muscle present?
Lower pressure than blood vessels
Shared feature between veins and lymph vessels?
A: Valves.
Mechanisms moving lymph flow?
A: Skeletal muscle contraction, arterial pulsation, vessel smooth muscle, limb/trunk movement
Overall route of lymph flow relative to circulation?
A: Follows similar pathways.
Approximate size of lymph nodes?
0.1–0.25 cm.
Function of lymph nodes?
Filter foreign particles.
Where are most lymph nodes located?
Abdomen.
Immune cells present in nodes?
T cells, B cells and other immune cells.
Why are nodes palpable during infection?
Immune activation causes swelling.
Approximate number of nodes in adults?
Several hundred.
Where are nodes found anatomically?
Along lymphatic vessels.
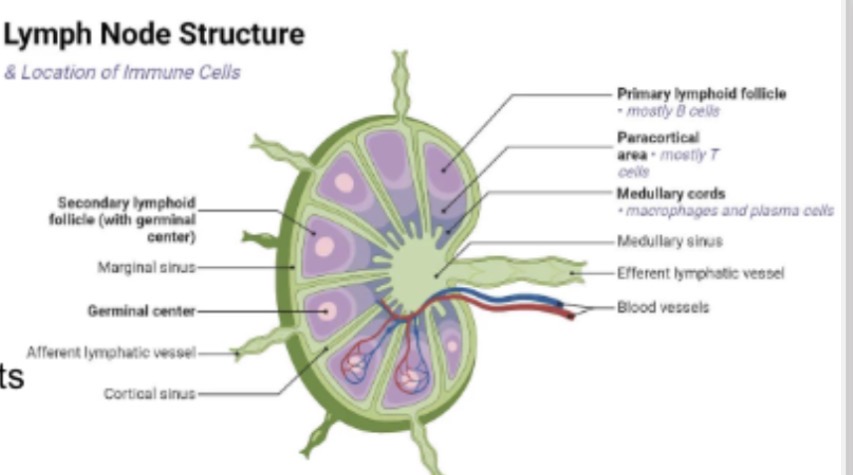
.Outer structure of lymph node?
Fibrous capsule.
Internal structural supports in lymphatic nodes?
Trabeculae (fibrous strands) from compartments
Vessel bringing lymph into node?
Afferent vessel
Vessel carrying lymph out?
A: Efferent vessel.
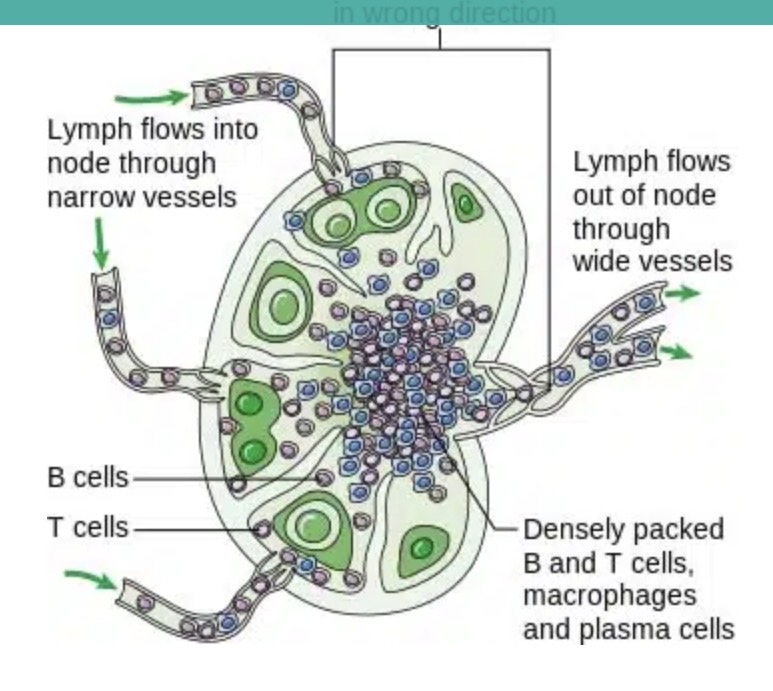
What do lymphatic nodes contain?
Lymphocytes
Macrophages
Act as fibres and defend against foreign pathogens
Cells filtering particles in node sinuses?
Macrophages
Major lymph node cluster sites?
Axilla, groin/femoral, neck/cervical, tracheal, bronchial.
After nodes, lymph drains into what?
Lymphatic trunks.
Name the lymphatic trunks.
Lumbar,
intestinal,
bronchomediastinal,
subclavian,
jugular.
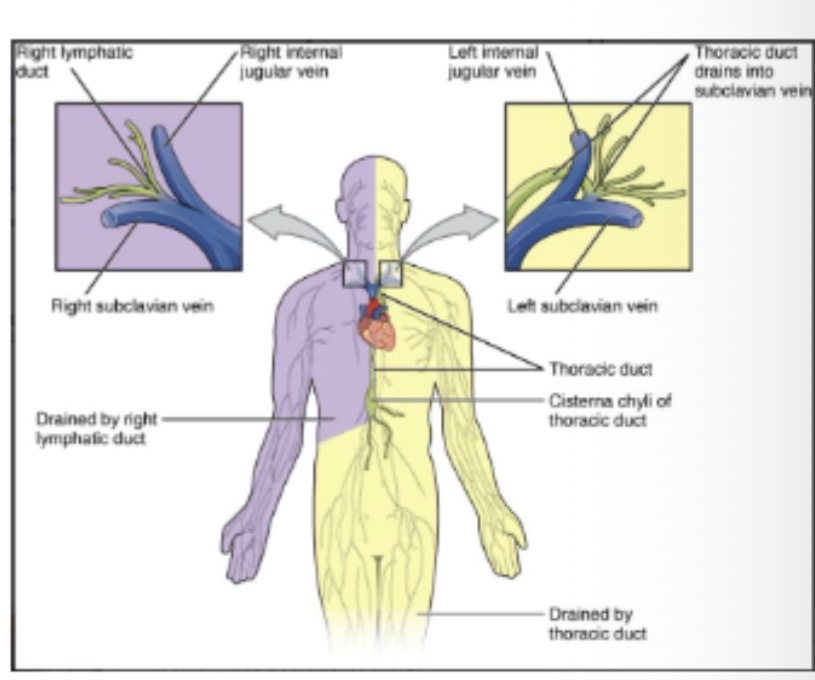
Define lymphatic ducts.
Largest lymph vessels draining lymph into veins.
Where does right lymphatic duct drain?
Right subclavian vein.
Regions drained by right lymphatic duct?
Upper right quadrant — right head, neck, thorax, upper limb.
Where does thoracic duct drain?
.
Left subclavian vein.
Regions drained by thoracic duct?
Remainder of the body. (Larger)
Where do both ducts empty lymph finally?
Venous angles at subclavian veins.