Cell Compartmentalization and Specialization CSA Paper 1A - HL
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
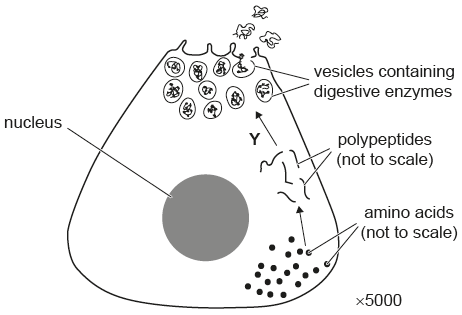
Which cell organelle is involved at Y?
Golgi apparatus
What structures are shown in the electron micrograph below and what is their function?
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum; Synthesis of proteins
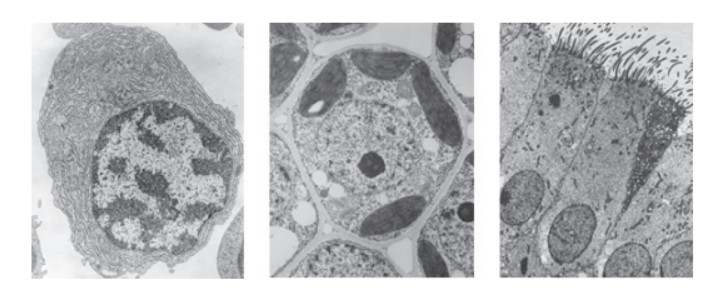
What feature distinguishes striated muscle fibres from the three cell types shown in the images?
Multinucleate structure
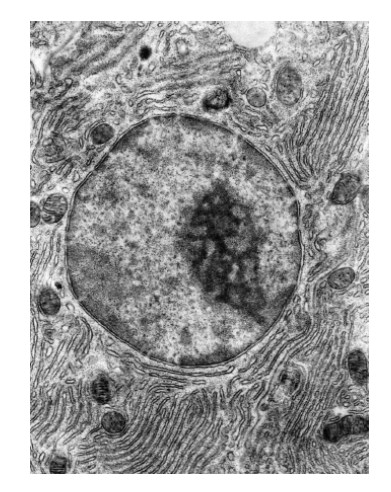
What describes this nucleus?
It contains chromatin and is surrounded by a double membrane.
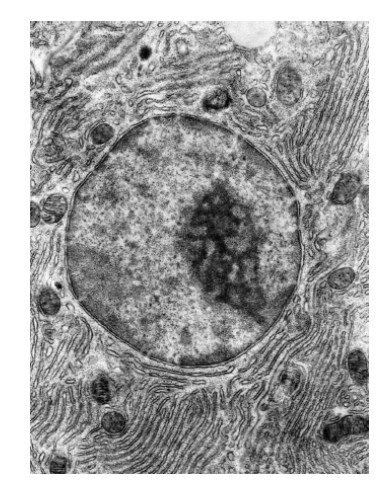
What describes this rough endoplasmic reticulum?
It contains ribosomes and is the main site of protein synthesis in a cell.
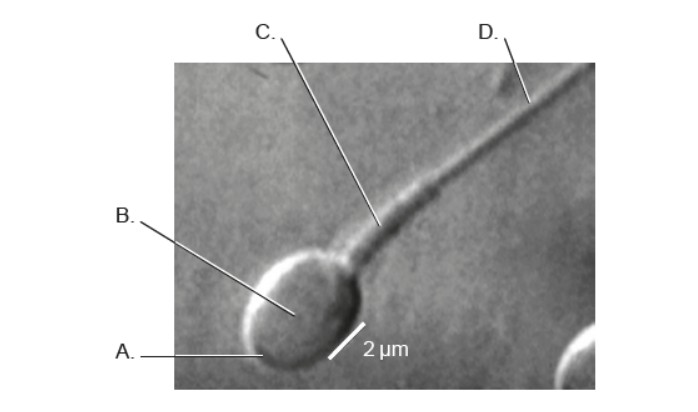
HL The micrograph shows part of a human sperm cell. Which region/regions of the cell is responsible for the cell's need for a large production of ATP?
C
Which of the following are roles of stem cells in adult living organisms?
I. Growth of new organs.
II. Replacement of damaged cells.
III. Production of cells which could differentiate.
IV. Produce new stem cells by mitosis.
II and III only
What are essential properties of stem cells?
They can divide by mitosis and differentiate
Which of the following are advantages of the presence of a nuclear membrane surrounding the nucleus of eukaryotic cells?
I. Separation of the DNA from the cytoplasm.
II. Separation of gene transcription from translation.
III. Concentration of enzymes for DNA replication and transcription.
IV. Increased efficiency of nuclear division.
All of the above.
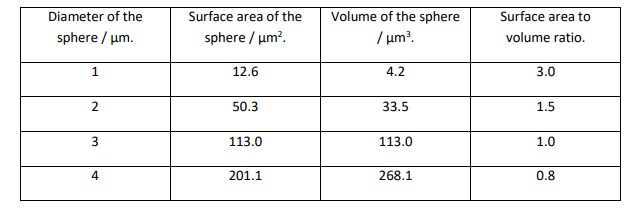
Explain why a large surface area to volume ratio can increase cell effeciency
It increases the rate at which materials can enter and leave the cell relative to its metabolic needs.
Which of the following could be a channel protein used for facilitated diffusion across a cell membrane?
Integral protein
Why are glycoproteins important in tissues?
Cell to cell binding
Which of the following can affect the rate of transport of a substance across a cell membrane by passive transport?
I. Temperature.
II. Channel proteins.
III. Size of the molecule.
IV. Pump proteins.
I, II, and III only
Why is the cell wall not conisdered to be an organelle?
It is not surrounded by a membrane
Which of the following apparatus and techniques was used in determining the function of individual organelles?
I. Fractionation
II. Ultracentrifugation
III. Electron microscopy
IV. Light microscopy
I only
Which of the following explains the advantage to the cellular function of organelles being surrounded by a membrane?
I. Organelles can contain high concentrations of enzymes
II. Organelles permit the separation of (incompatible) functions
III. The cell can maintain conditions in an organelle different to the cytoplasm
IV. Organelles can imitate other organelles
I, II, and III only
What is a function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
To regulate fluidity
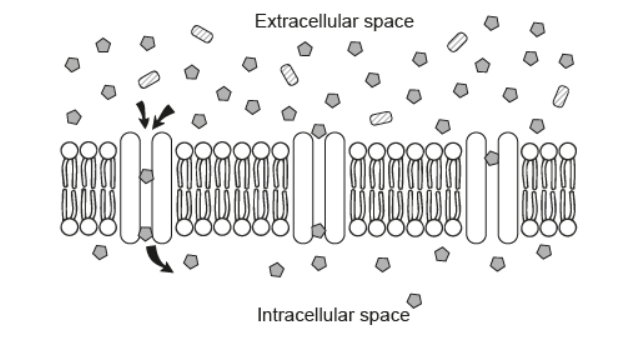
What describes this movement?
Net movement occurs until the concentrations in and out of the cell are equal.
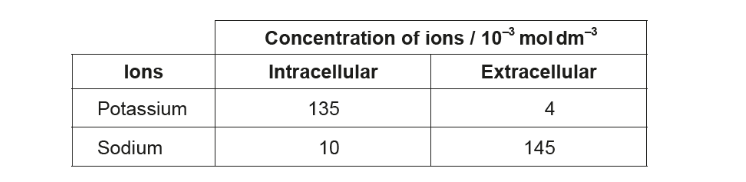
What explains these concentrations?
Active transport using a protein pump
What explains the movement of glucose molecules down a concentration gradient across the cell surface membrane?
They can diffuse between phospholipids due to their flexibility.
Cells use a variety of methods to move particles across membranes. What is a similarity between facilitated diffusion and active transport?
Both are carried out by proteins in the membrane.
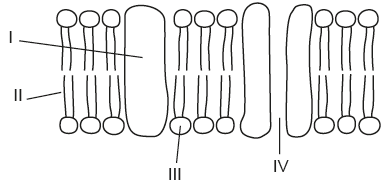
The diagram shows the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes. Which labelled regions are hydrophilic?
III and IV
Which of the following organelles would not be found in the photosynthetic cell of a leaf?
Lysosome
Which statement best explains how the fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the cell membrane?
The membrane consists of phospholipids and proteins that can move laterally, allowing flexibility and dynamic function.