Bio 181 Module 3
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
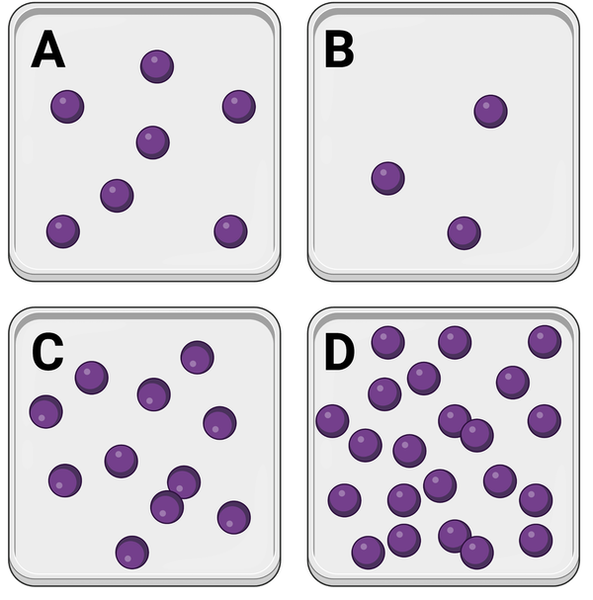
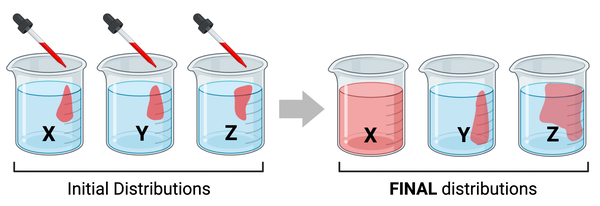
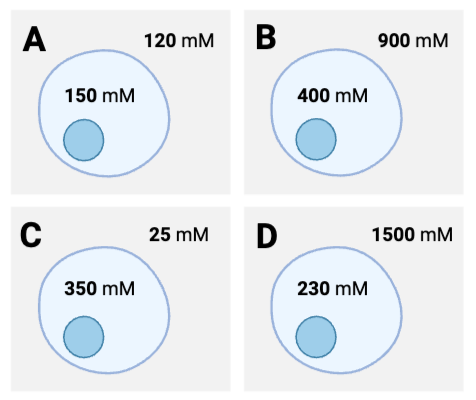
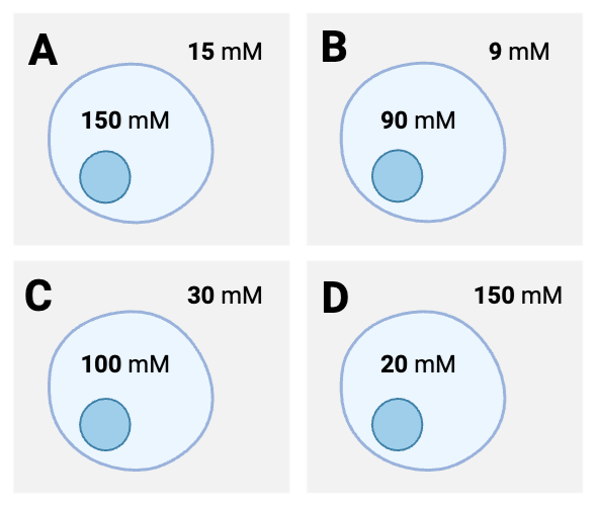
Which container has the lowest concentration of molecules?
Container B
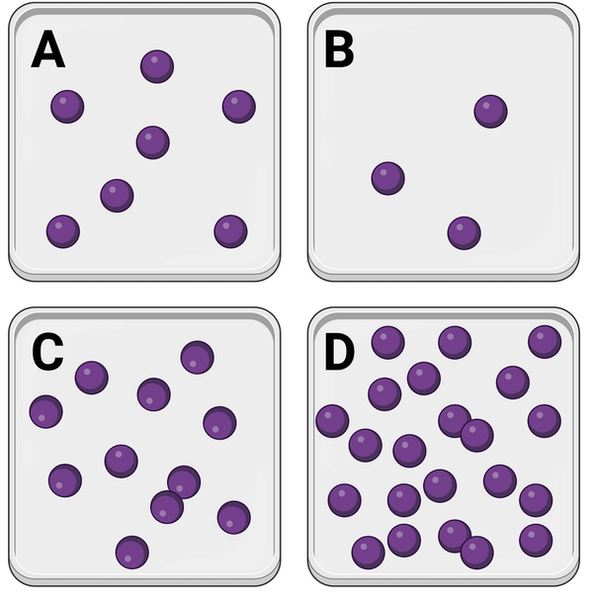
Which series lists the containers in order of their concentrations of molecules, from lowest concentration to highest concentration?
B, A, C, D
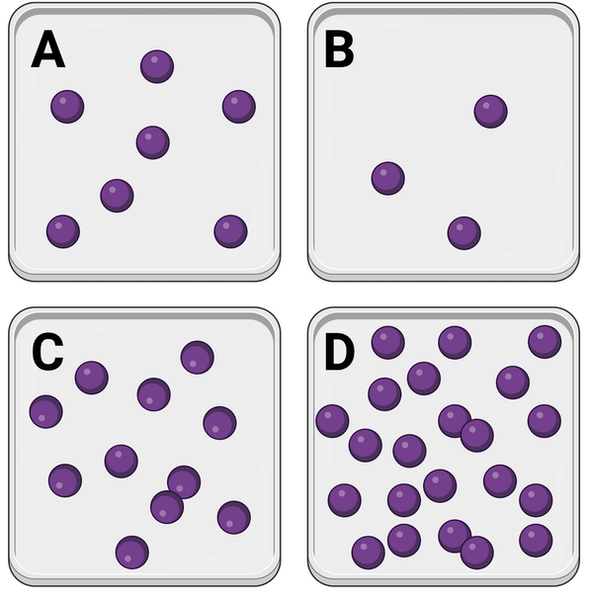
In which container would you expect to observe the greatest number of interactions between molecules?
Container D
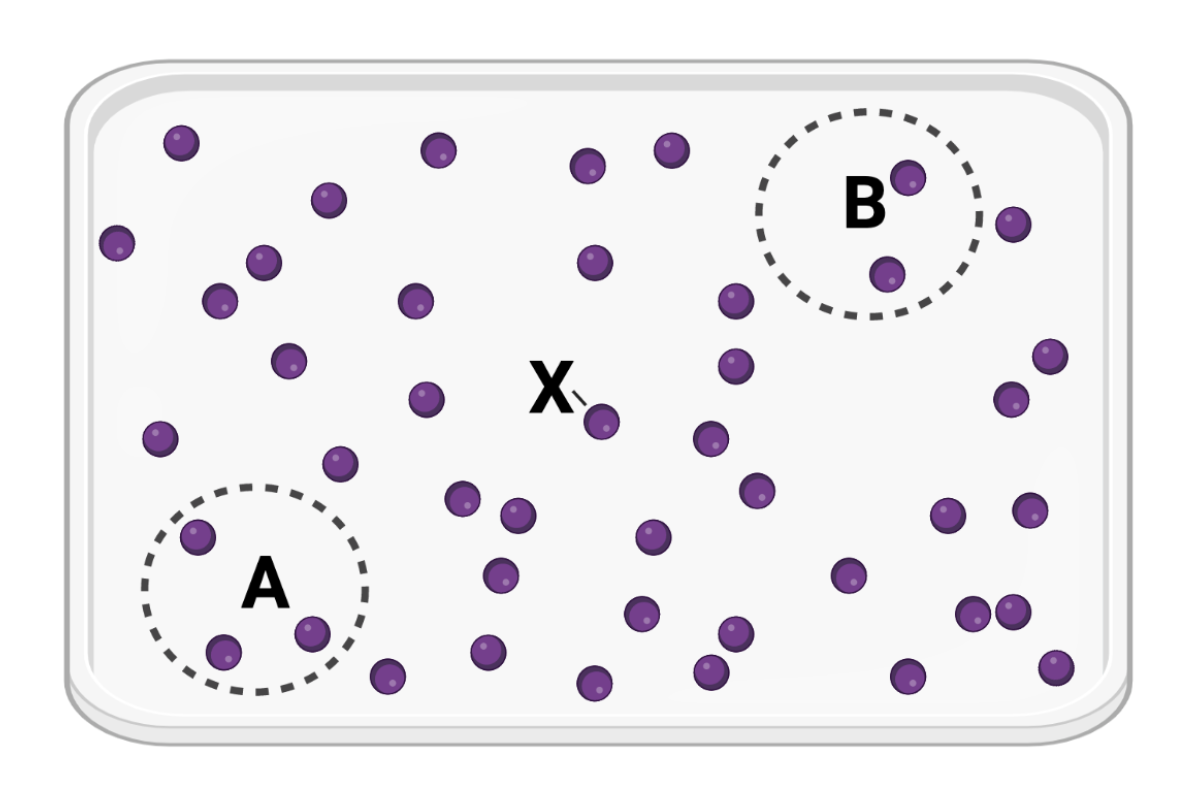
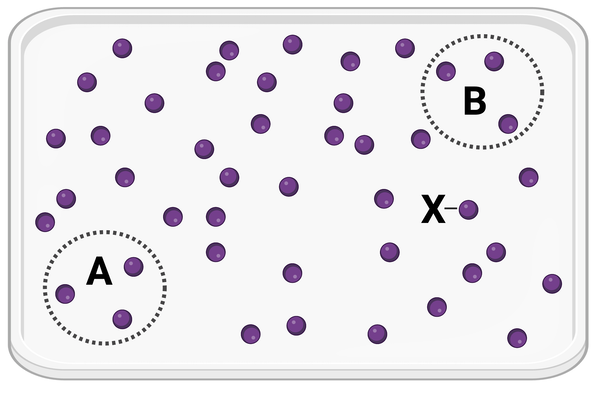
Which statement is correct?
a. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area A before diffusing to area B.
b. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area B before diffusing to area A.
c. Molecule X is equally likely to diffuse to area A or area B.
c. Molecule X is equally likely to diffuse to area A or area B.
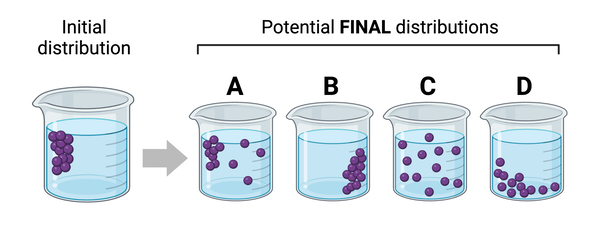
Which of these potential distributions is most likely to be observed?
Distribution C
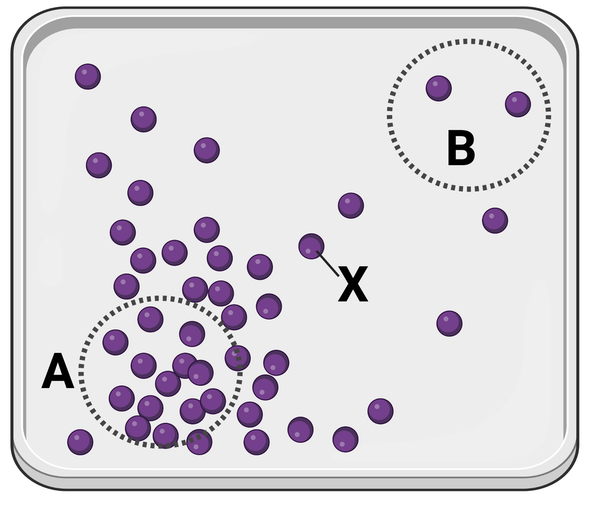
Which statement is correct?
a. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area A before diffusing to area B.
b. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area B before diffusing to area A.
c. Molecule X is equally likely to diffuse to area A or area B.
b. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area B before diffusing to area A.
Which statement is correct?
a. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area A before diffusing to area B.
b. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area B before diffusing to area A.
c. Molecule X is equally likely to diffuse to area A or area B.
b. Molecule X will more likely diffuse to area B before diffusing to area A.
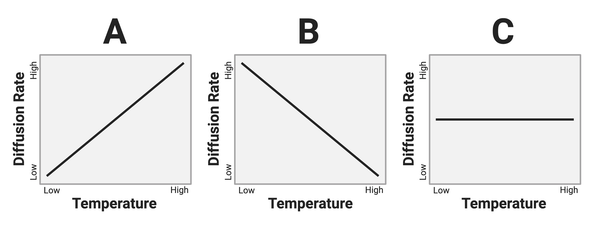
Which graph shows the most likely relationship?
Graph A
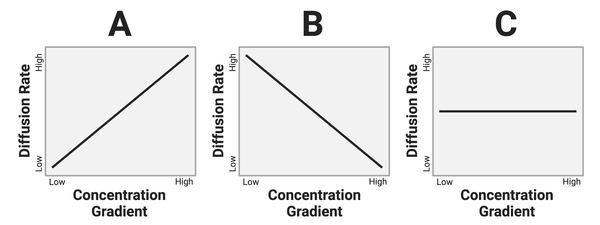
Which graph shows the most likely relationship?
Graph A
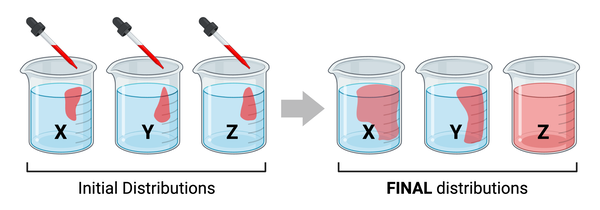
Which series lists the beakers in order of the molecular masses of the molecules, from highest mass to lowest mass?
a. X > Y > Z
b. Y > Z > X
c. Z > X > Y
b. Y > Z > X
What are the most likely temperatures of the three beakers?
a. X= 0℃, Y= 50℃, Z= 95℃
b. X= 95℃, Y= 0℃, Z= 50℃
c. X= 50℃, Y= 0℃, Z= 95℃
c. X= 50℃, Y= 0℃, Z= 95℃
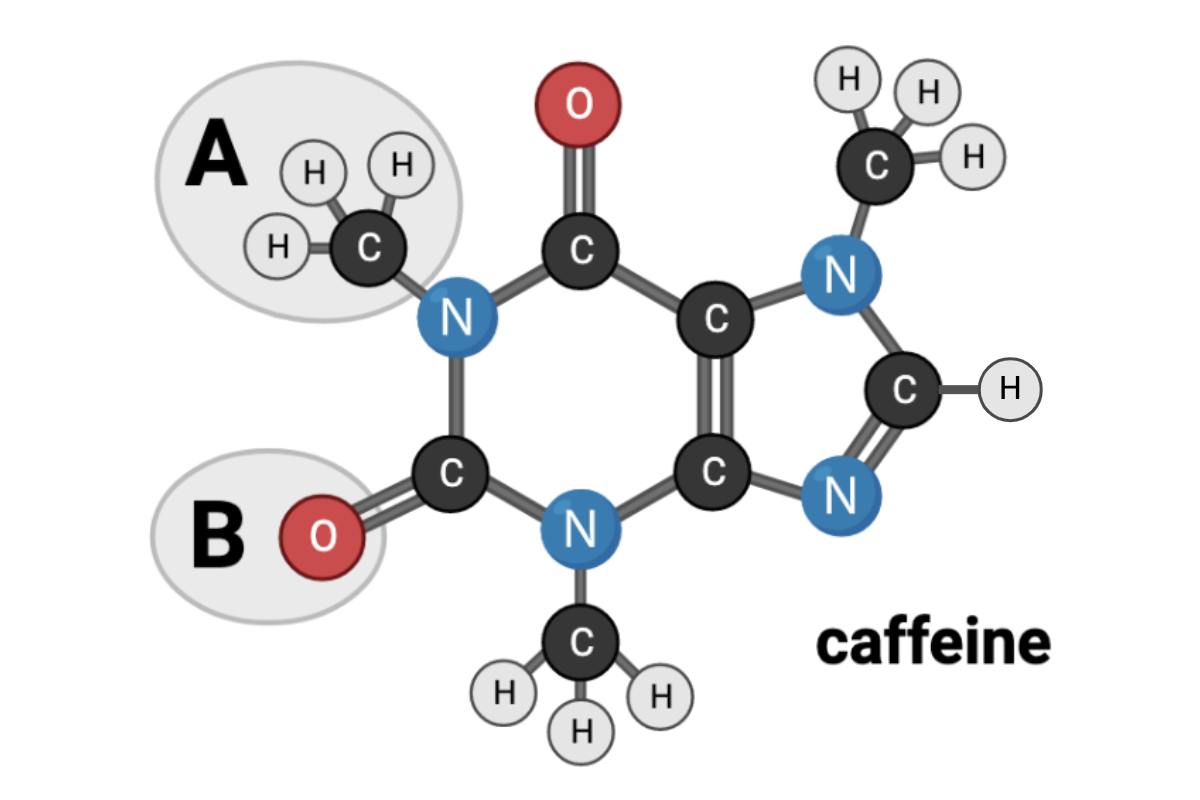
Which terms accurately describe the chemical nature of Region A? Select all that apply.
a. nonpolar
b. polar
c. hydrophobic
d. hydrophilic
a. nonpolar
c. hydrophobic
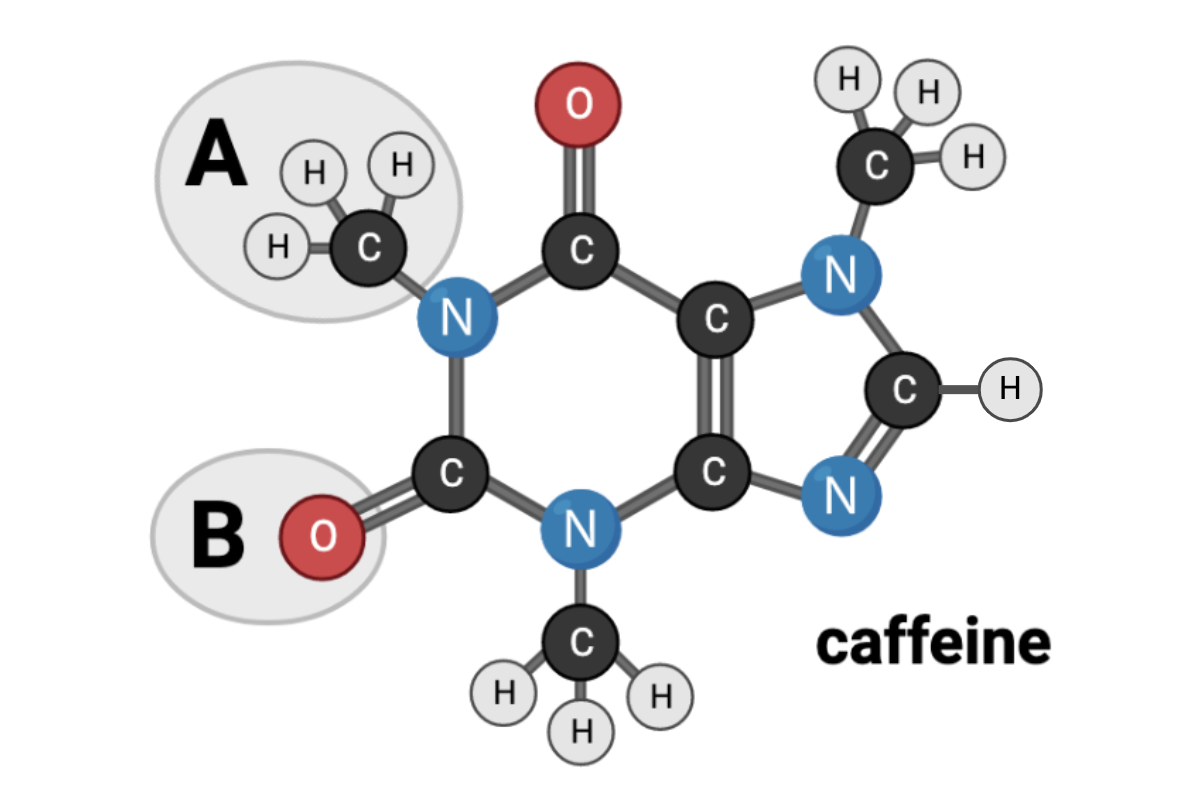
Which terms accurately describe the chemical nature of Region B? Select all that apply.
a. nonpolar
b. polar
c. hydrophobic
Should not have been checked.
d. hydrophilic
b. polar
d. hydrophilic
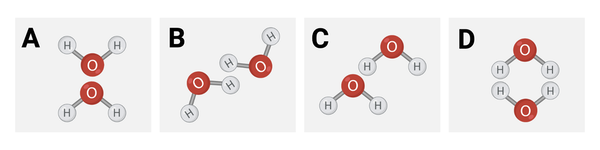
Which diagram shows how water molecules are most likely to interact?
Diagram C
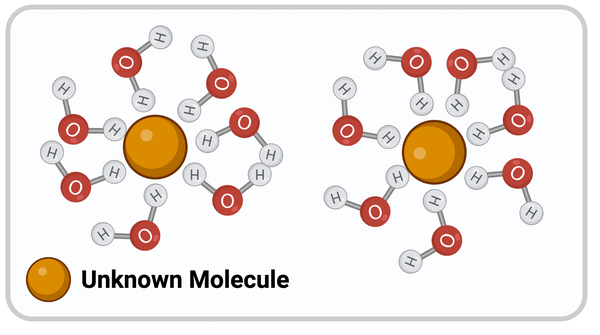
Which chemical property most likely describes the unknown molecule?
negatively charged
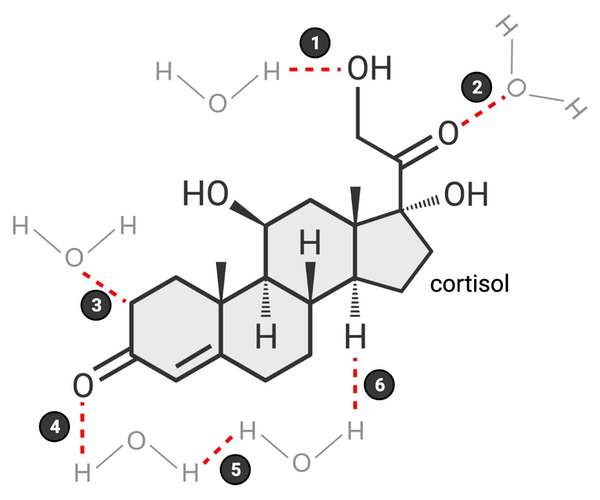
Which of these bonds accurately represents a hydrogen bond? Select all that apply.
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
e. 5
f. 6
a. 1
d. 4
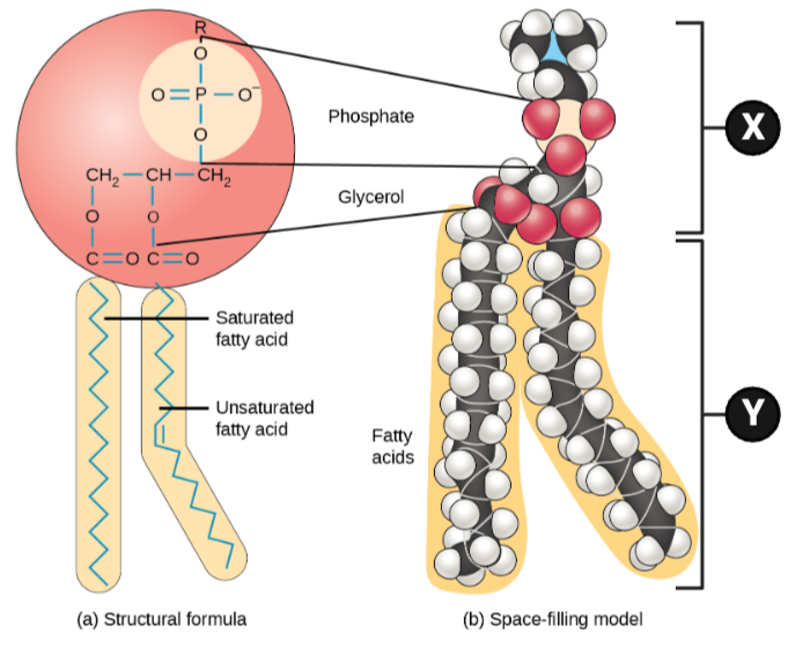
Which chemical properties apply to Region X? Select all that apply.
a. water soluble
b. water insoluble
c. polar
d. nonpolar
e. charged
f. uncharged
g. hydrophobic
h. hydrophilic
a. water soluble
c. polar
e. charged
h. hydrophilic
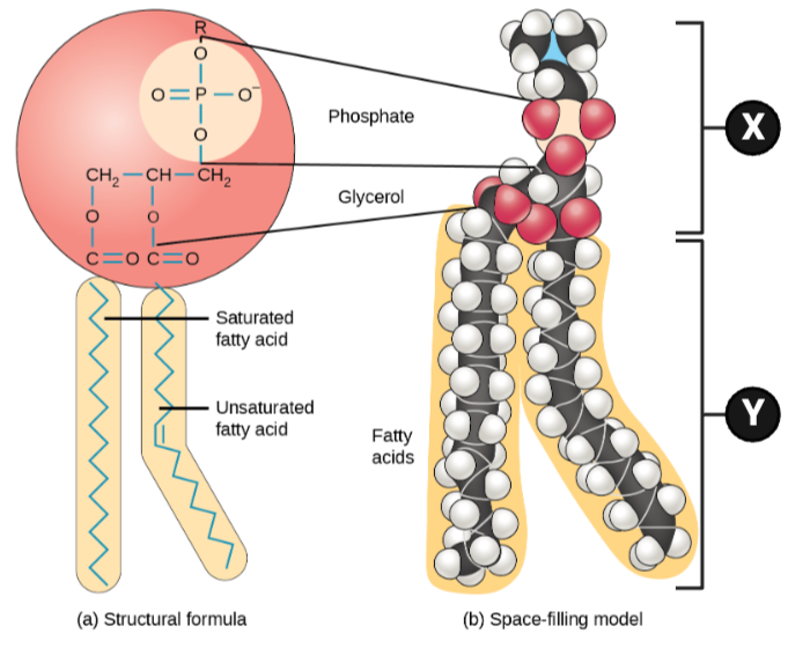
Which chemical properties apply to Region Y? Select all that apply.
a. water soluble
b. water insoluble
c. polar
d. nonpolar
e. charged
f. uncharged
g. hydrophobic
h. hydrophilic
b. water insoluble
d. nonpolar
f. uncharged
g. hydrophobic
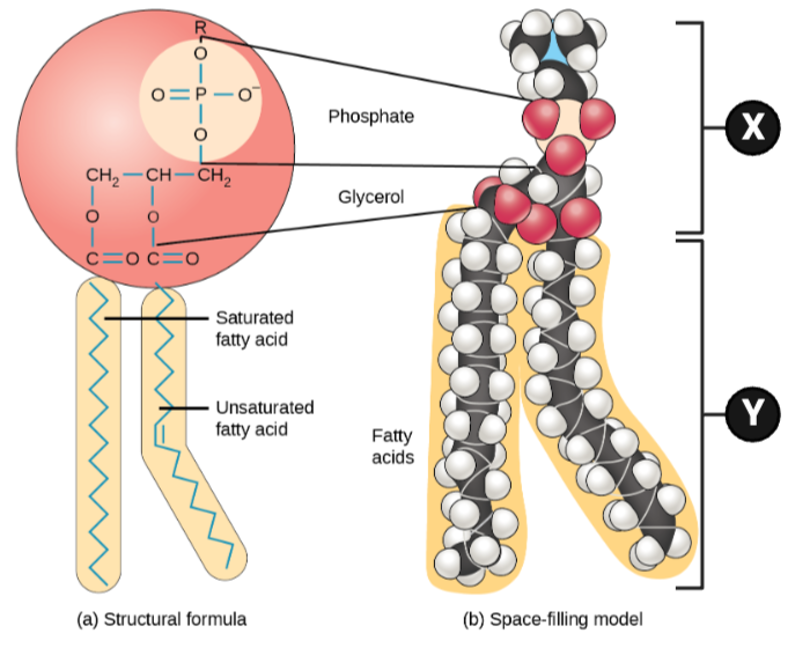
Which region is likely to interact with a molecule of water, and why?
a. Region X, because this region contains charged and polar molecules.
b. Region X, because this region contains only uncharged molecules.
c. Region Y, because this region contains charged and polar molecules.
d. Region Y, because this region contains only uncharged molecules
a. Region X, because this region contains charged and polar molecules.
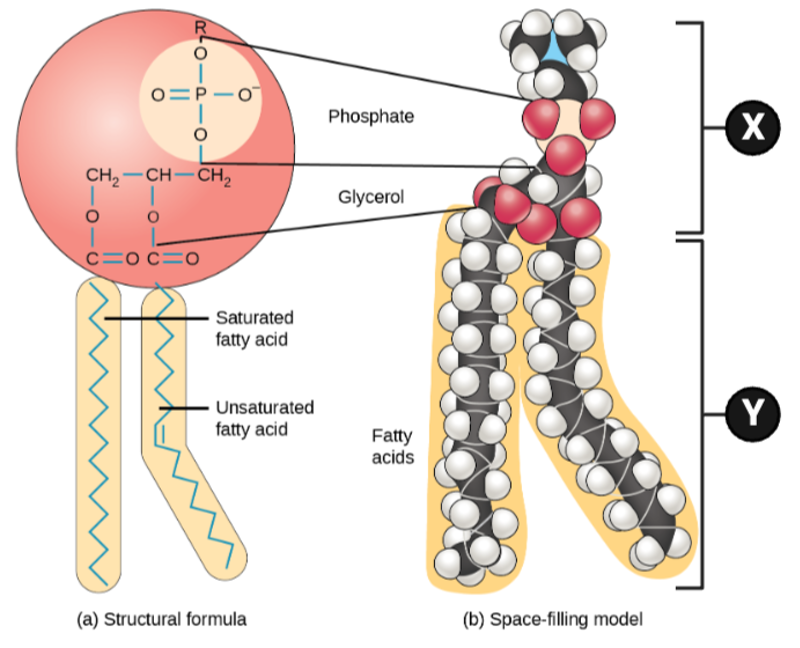
Which region is unlikely to interact with water, and why?
a. Region X, because this region contains charged and polar molecules.
b. Region X, because this region contains only uncharged, nonpolar molecules.
c. Region Y, because this region contains charged and polar molecules.
d. Region Y, because this region contains only uncharged, nonpolar molecules.
d. Region Y, because this region contains only uncharged, nonpolar molecules.
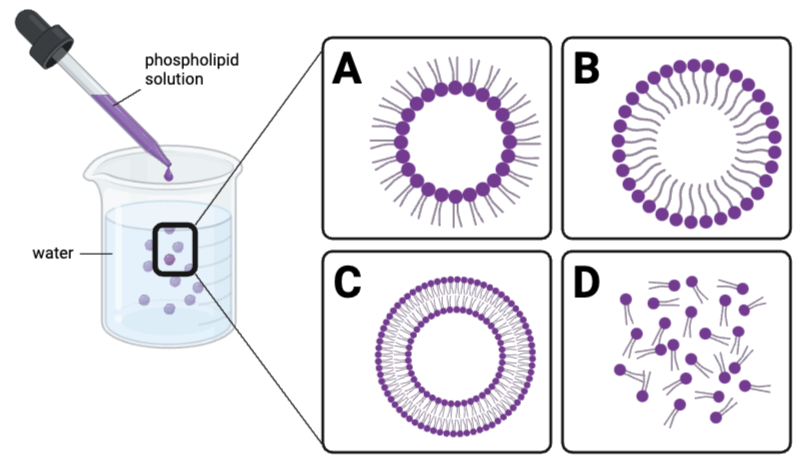
Which structure would be the most stable and likely to occur?
Structure C
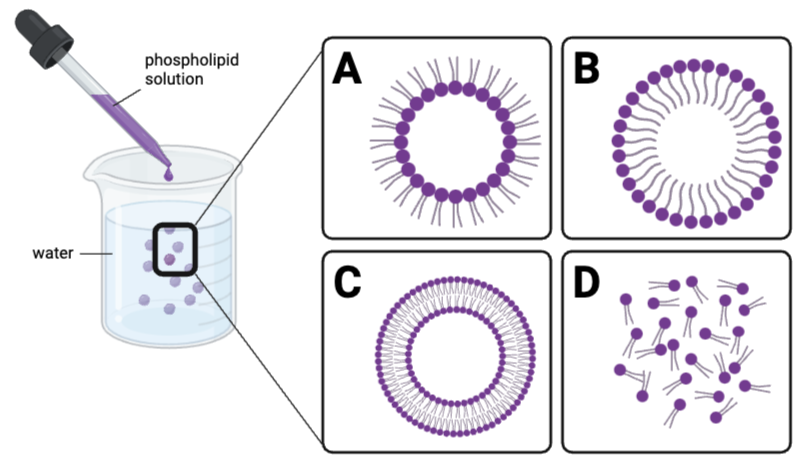
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The phosphate region of a phospholipid has high affinity to water molecules and to the phosphate regions of other phospholipids.
b. The fatty acid region of a phospholipid is repelled by water molecules and by the phosphate regions of other phospholipids.
c. Both the phosphate region and the fatty acid region have high affinity to water molecules and to other phospholipids.
d. Both the phosphate region and the fatty acid region are repelled by water molecules and by other phospholipids.
e. The affinity between the phosphate regions of phospholipids is greater than the affinity between the fatty acid regions of phospholipids.
f. The affinity between fatty acid regions of phospholipids exceeds the affinity between the phosphate regions of phospholipids.
a. The phosphate region of a phospholipid has high affinity to water molecules and to the phosphate regions of other phospholipids.
b. The fatty acid region of a phospholipid is repelled by water molecules and by the phosphate regions of other phospholipids.
e. The affinity between the phosphate regions of phospholipids is greater than the affinity between the fatty acid regions of phospholipids.
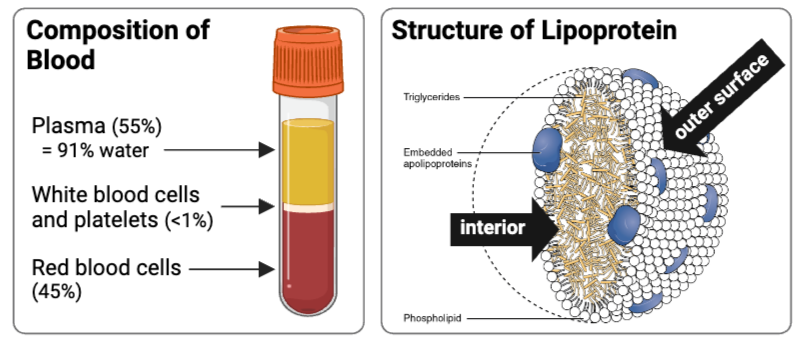
Given that water is the most abundant molecule in blood, predict the chemical properties of a lipoprotein by filling in the blanks of the following statement.
The outer surface of a lipoprotein is ___________, and the interior is ___________.
a. hydrophilic; hydrophilic
b. hydrophobic; hydrophobic
c. hydrophilic; hydrophobic
d. hydrophobic; hydrophilic
c. hydrophilic; hydrophobic
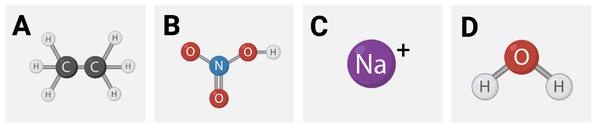
Which series lists the molecules in order of hydrophilicity, from most hydrophilic to least hydrophilic?
a. C > B > D > A
b. A > D > C > B
c. A > D > B > C
a. C > B > D > A
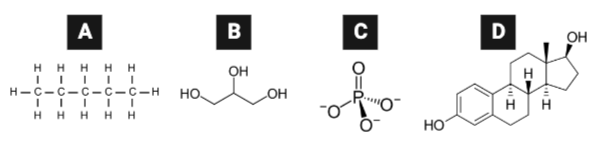
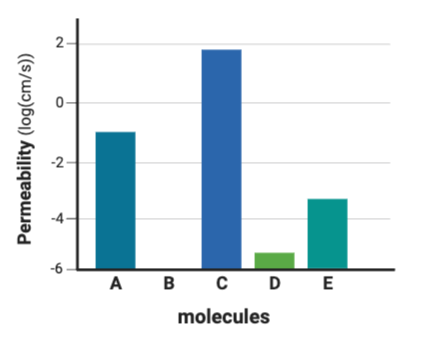
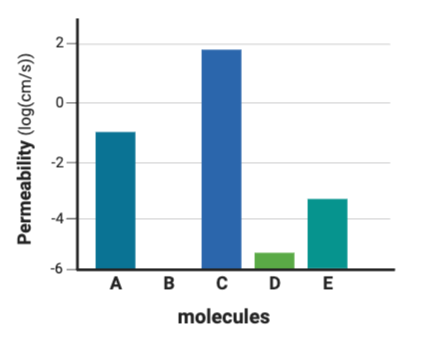
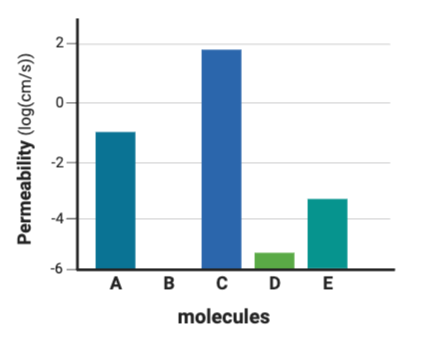
Which series lists the molecules in order of their likelihood to diffuse through a phospholipid bilayer, from most likely to least likely?
a. C, B, A, D
b. A, D, B, C
c. D, A, C, B
d. B, A, C, D
b. A, D, B, C
Which molecule is likely the most charged or polar?
Molecule B
Which molecule is likely the least charged or polar?
Molecule C
Which molecule is likely the most hydrophilic?
Molecule B
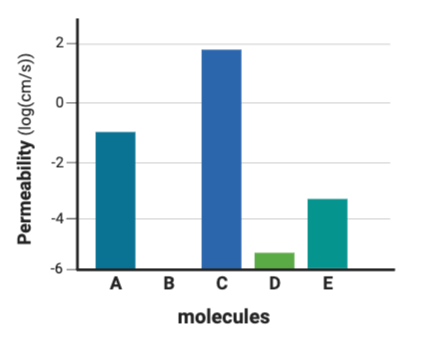
Which molecule is likely the least hydrophilic?
Molecule C
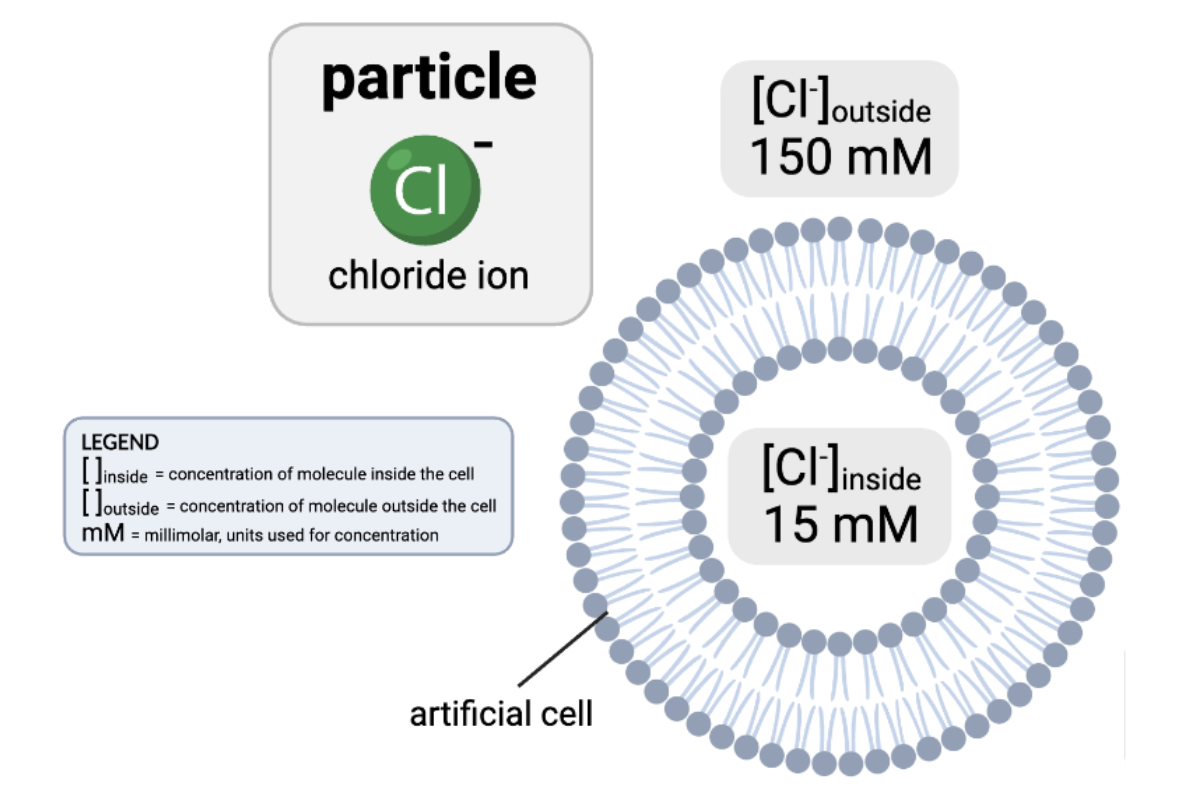
How would osmosis affect the concentration of Cl- in the cell?
a. The concentration of Cl- inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of Cl- inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of Cl- inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of Cl- inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations of Cl- will remain the same.
a. The concentration of Cl- inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
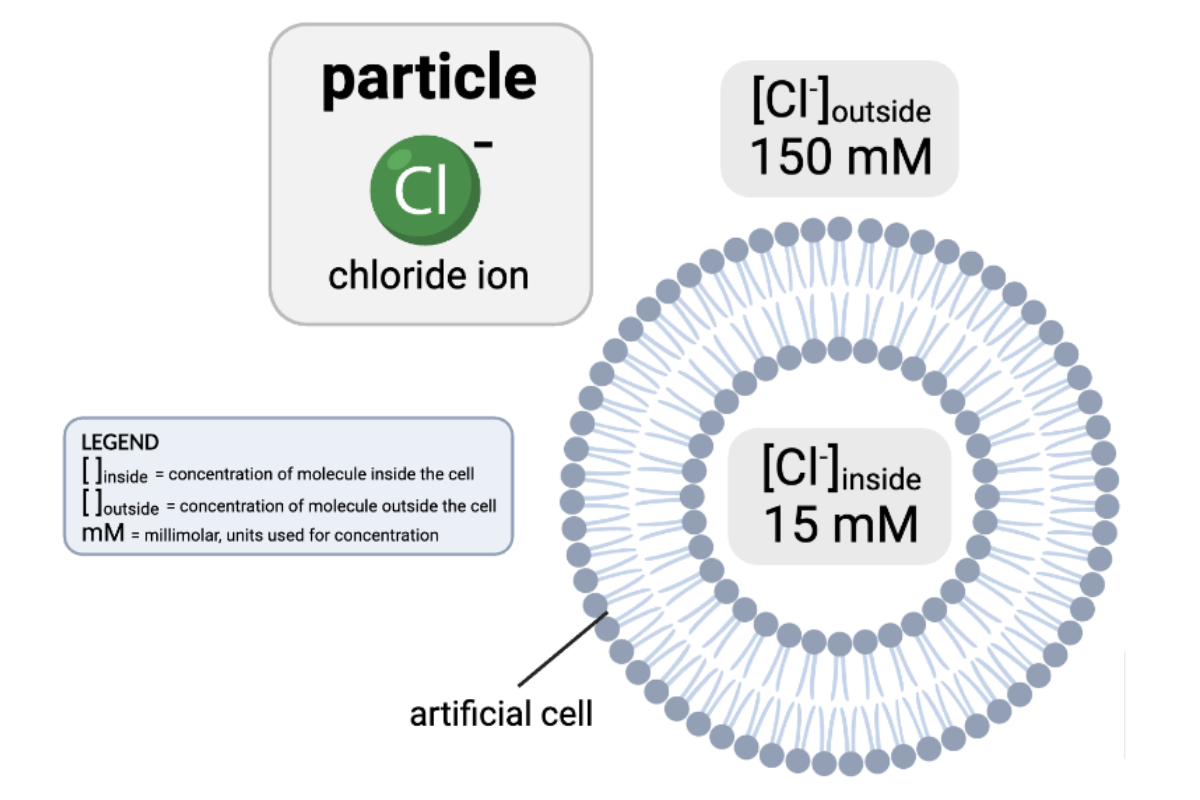
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of Cl- out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of Cl- into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor a net diffusion of Cl- in either direction.
d. Because Cl- is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because Cl- is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because Cl- is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of Cl- into the cell.
d. Because Cl- is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
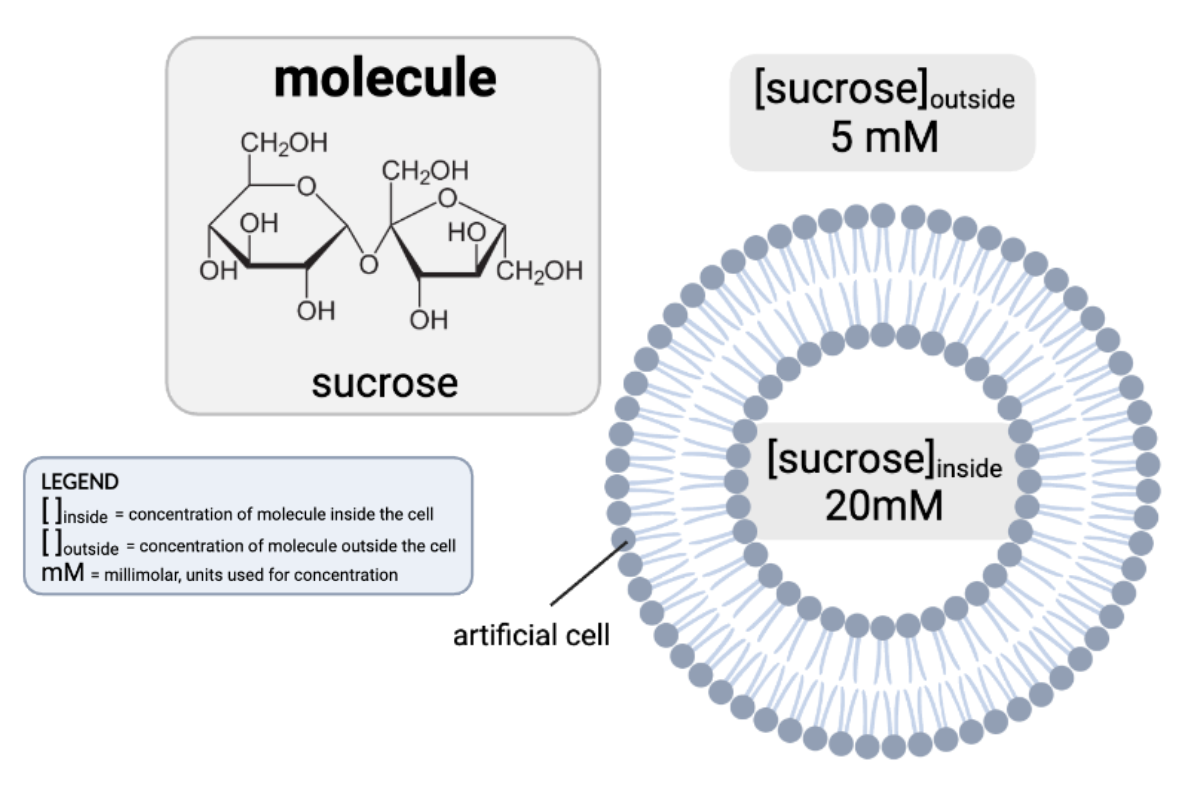
How would osmosis affect the concentration of sucrose in the cell?
a. The concentration of sucrose inside the cell will increase because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of sucrose inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of sucrose inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of sucrose inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations of sucrose will remain the same.
d. The concentration of sucrose inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
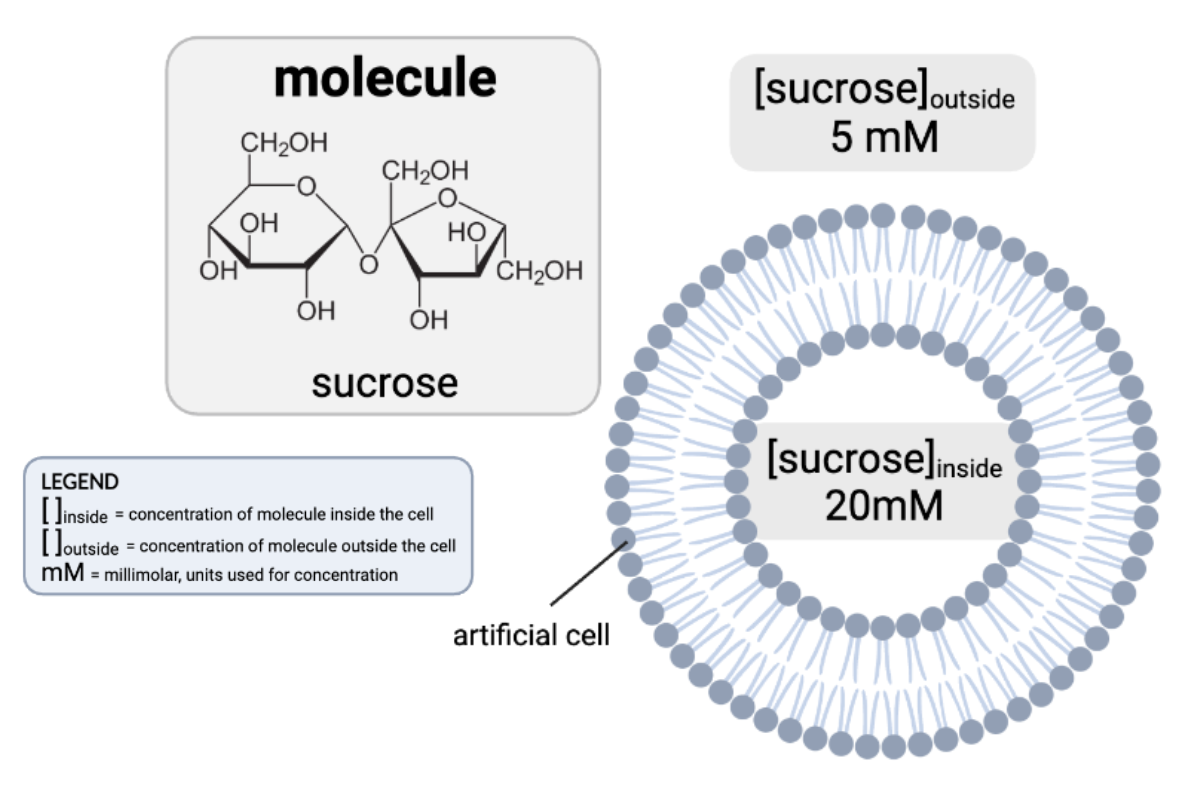
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of sucrose out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of sucrose into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor a net diffusion of sucrose in either direction.
d. Because sucrose is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because sucrose is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because sucrose is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of sucrose out of the cell.
e. Because sucrose is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
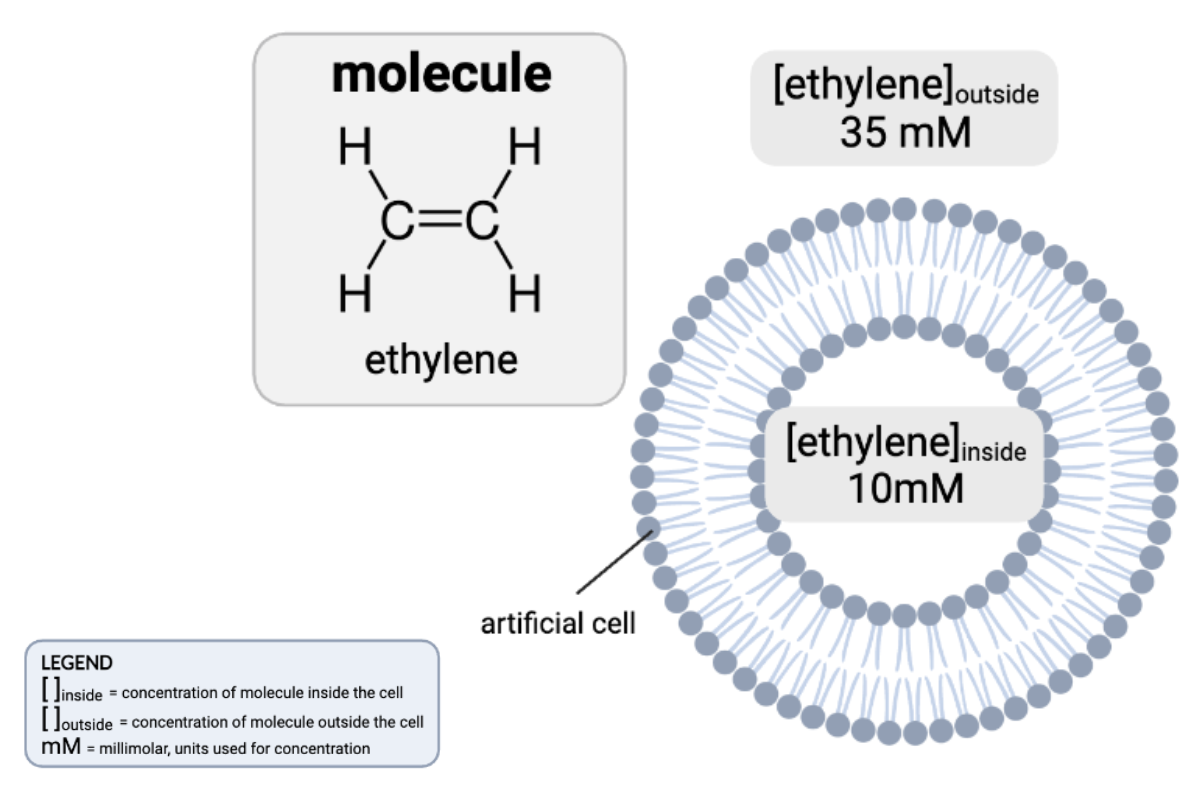
How would osmosis affect the concentration of ethylene in the cell?
a. The concentration of ethylene inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
b. The concentration of ethylene inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
c. The concentration of ethylene inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
d. The concentration of ethylene inside the cell will decrease, because water will diffuse from the outside of the cell to the inside.
e. The concentrations of ethylene will remain the same.
a. The concentration of ethylene inside the cell will increase, because water will diffuse from the inside of the cell to the outside.
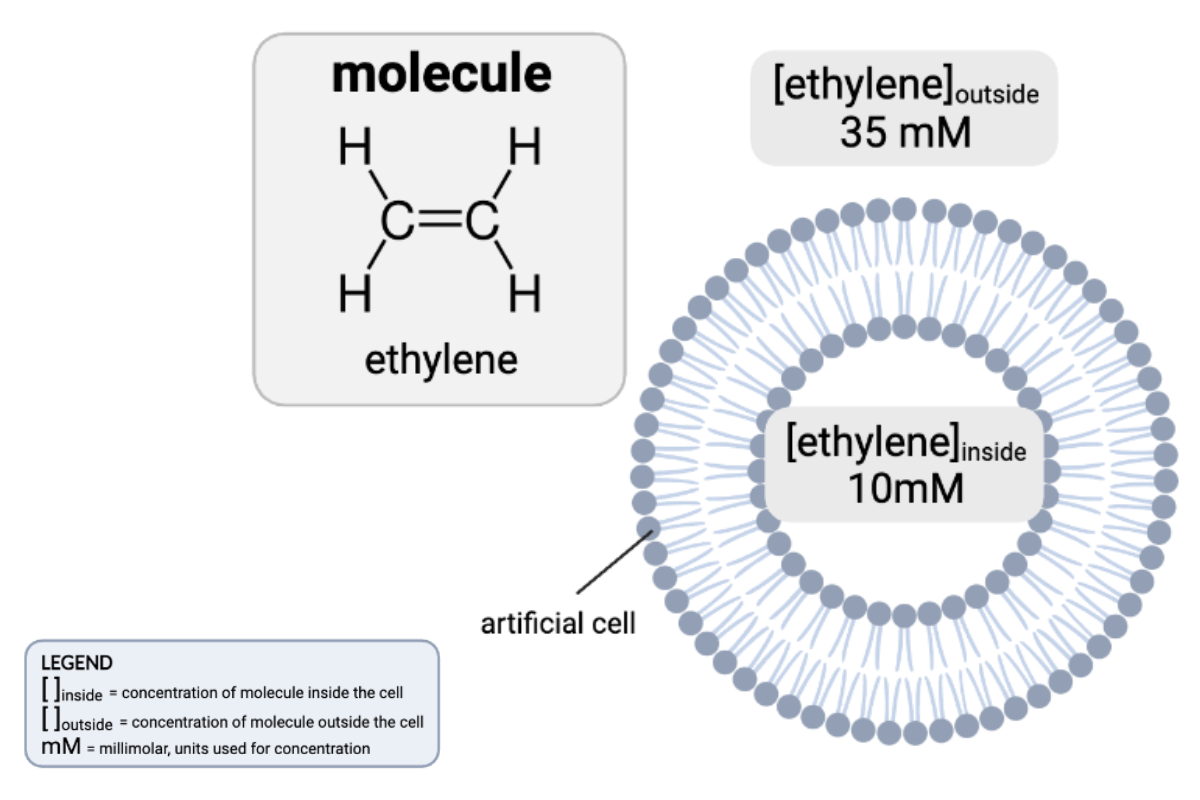
Which claims are accurate? Select all that apply.
a. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of ethylene out of the cell.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of ethylene into the cell.
c. The concentration gradient would not favor a net diffusion of ethylene in either direction.
d. Because ethylene is charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
e. Because ethylene is partially charged, it cannot pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
f. Because ethylene is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
b. The concentration gradient would favor the net diffusion of ethylene into the cell.
f. Because ethylene is uncharged, it can pass through a phospholipid bilayer by simple diffusion.
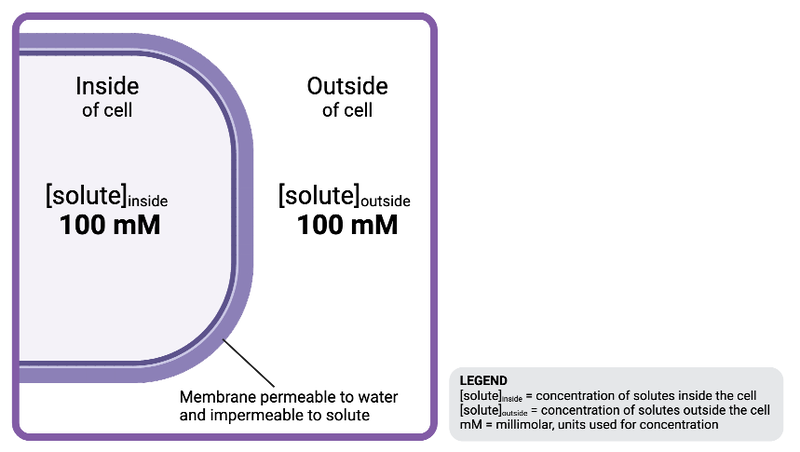
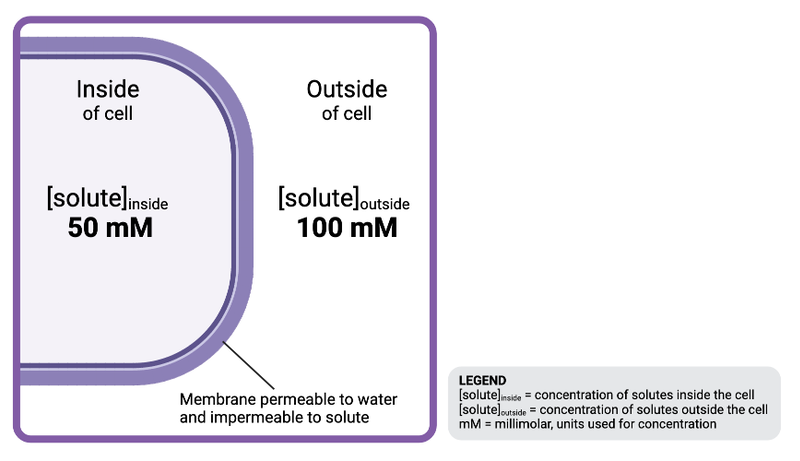
The solution outside the cell is ______________ to the solution inside the cell.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
b. isosmotic
The solution outside the cell is ______________ to the solution inside the cell.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
a. hyperosmotic
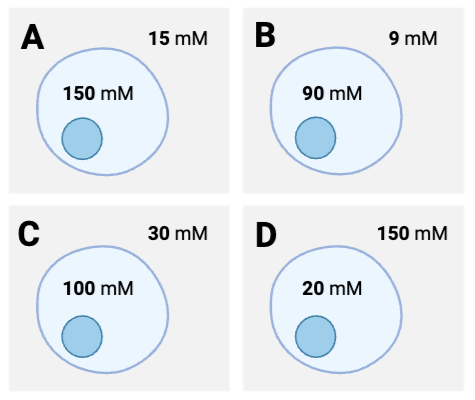
For which cells will the net diffusion of water be out of the cell? Select all that apply.
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
d. Cell D
Which condition causes a net diffusion of water out of the cell?
a. The concentration of water inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
b. The concentration of water inside the cell is less than the concentration outside the cell.
c. The concentration of water inside the cell equals the concentration outside the cell.
a. The concentration of water inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
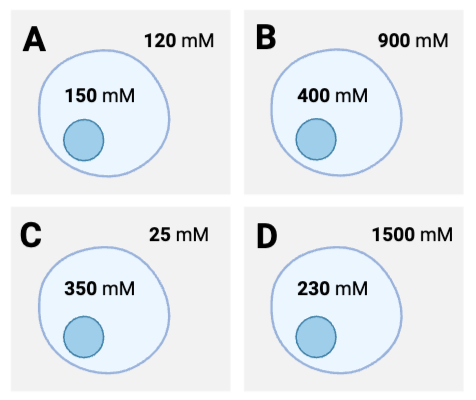
For which cells will the net diffusion of water be into the cell? Select all that apply.
a. Cell A
b. Cell B
c. Cell C
d. Cell D
a. Cell A
c. Cell C
Which condition causes a net diffusion of water into the cell?
a. The solute concentration inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
b. The solute concentration inside the cell is less than the concentration outside the cell.
c. The solute concentration inside the cell is equal to the concentration outside the cell.
a. The solute concentration inside the cell is greater than the concentration outside the cell.
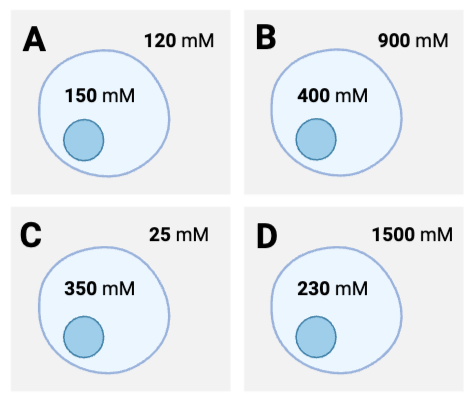
Which cell will experience the greatest net diffusion of water from inside to outside?
Cell D
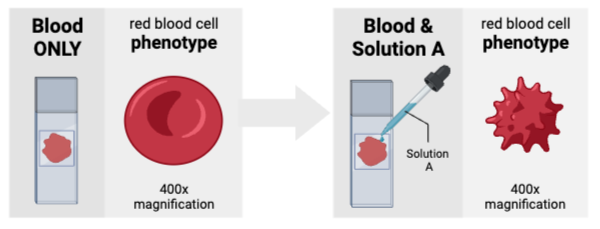
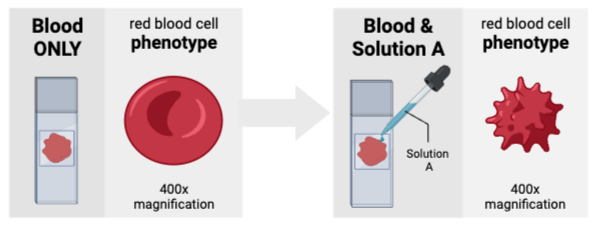
Which cell will experience the greatest net diffusion of water from outside to inside?
Cell C
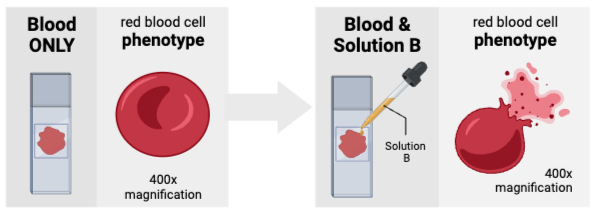
The cells were most likely suspended in a _________ solution.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
a. hyperosmotic
The concentration of solutes outside of the cells was likely _________ the concentration of solutes inside the cells.
a. greater than
b. less than
c. equal to
a. greater than
The cells were most likely suspended in a ________ solution.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
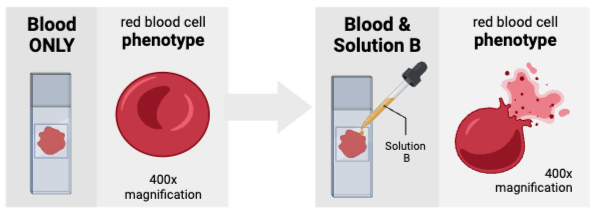
The concentration of solutes outside of the cells was likely _________ the concentration of solutes inside the cells.
a. greater than
b. less than
c. equal to
b. less than
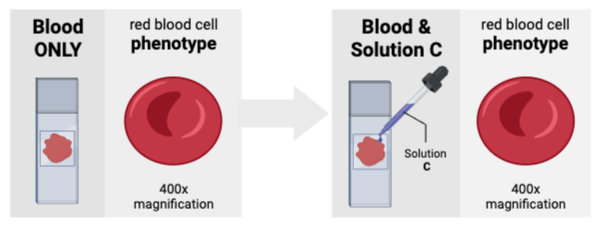
The cells were most likely suspended in a ________ solution.
a. hyperosmotic
b. isosmotic
c. hypoosmotic
b. isosmotic
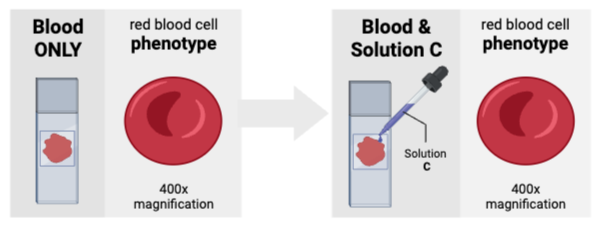
The concentration of solutes outside of the cells was likely _________ the concentration of solutes inside the cells.
a. greater than
b. less than
c. equal to
c. equal to
How would the rate of net diffusion change if the concentration gradient across the membrane were to increase from 20 mM to 40 mM?
a. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one quarter of the previous rate.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one half of the previous rate.
c. The rate of net diffusion would increase to twice the previous rate.
d. The rate of net diffusion would increase to four times the previous rate.
e. The rate of net diffusion would remain the same.
c. The rate of net diffusion would increase to twice the previous rate.
How would the rate of net diffusion change if the concentration gradient across the membrane were to decrease from 150 mM to 50 mM?
a. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one quarter of the previous rate.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one third of the previous rate.
c. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one half of the previous rate.
d. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to three quarters of the previous rate.
e. The rate of net diffusion would remain the same.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one third of the previous rate.
How would the rate of net diffusion change if the area of the membrane were doubled?
a. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one quarter of the previous rate.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease to one half of the previous rate.
c. The rate of net diffusion would increase to twice the previous rate.
d. The rate of net diffusion would increase to three times the previous rate.
e. The rate of net diffusion would remain the same.
c. The rate of net diffusion would increase to twice the previous rate.
How would the rate of net diffusion change if the thickness of the membrane were to increase by 10%?
a. The rate of net diffusion would decrease by approximately 20%.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease by approximately 10%.
c. The rate of net diffusion would increase by approximately 20%.
d. The rate of net diffusion would increase by approximately 10%.
e. The rate of net diffusion would remain the same.
b. The rate of net diffusion would decrease by approximately 10%.
The diffusion of sodium ions through the cell membrane was observed for two cells. The rate of net diffusion for the first cell was three times greater than that for the second cell.
Which statements could explain this difference? Select all that apply.
a. The area of membrane that is permeable to sodium ions for the first cell was three times greater than the area for the second cell.
b. The area of membrane that is permeable to sodium ions for the first cell is one third of the area for the second cell.
c. The concentration gradient of sodium ions across the first cell was one half of the concentration gradient across the second cell.
d. The concentration gradient of sodium ions across the first cell was three times greater than the concentration gradient across the second cell.
e. The thickness of the membrane for the first cell was one half of the thickness of the membrane for the second cell.
f. The thickness of the membrane for the first cell was twice the thickness of the membrane for the second cell.
a. The area of membrane that is permeable to sodium ions for the first cell was three times greater than the area for the second cell.
d. The concentration gradient of sodium ions across the first cell was three times greater than the concentration gradient across the second cell.
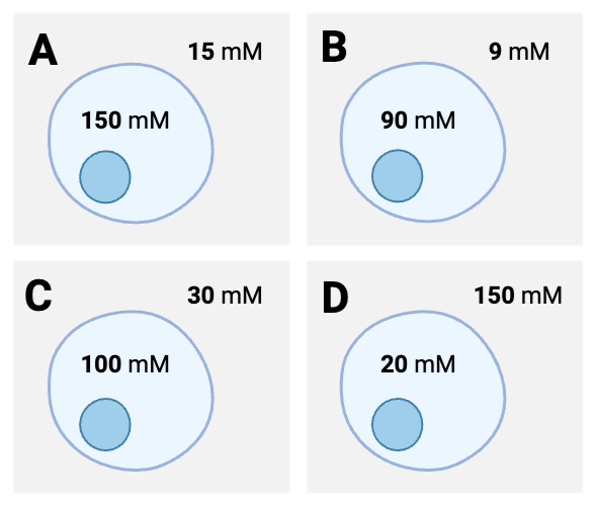
According to Fick's equation, which cell would experience the fastest rate of net diffusion of solutes through the membrane?
Cell A
According to Fick's equation, which cell would experience the slowest rate of net diffusion of solutes through the membrane?
Cell C
Which statements accurately describe simple diffusion? Select all that apply.
a. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. Molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
c. No energy is required for this process to occur.
d. Only kinetic energy is required for this process to occur.
e. A protein transporter is not required.
f. A protein transporter is required.
g. Molecules move directly through the phospholipid bilayer.
h. Molecules move directly through proteins called channels or carriers.
a. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
d. Only kinetic energy is required for this process to occur.
e. A protein transporter is not required.
g. Molecules move directly through the phospholipid bilayer.
Which statements accurately describe facilitated diffusion? Select all that apply.
a. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. Molecules move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
c. A protein transporter is not required.
d. A protein transporter is required.
e. Molecules move directly through the phospholipid bilayer.
f. Molecules move directly through proteins called channels or carriers.
g. This process transports nonpolar molecules.
h. This process transports polar molecules.
i. This process transports charged molecules.
a. Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
d. A protein transporter is required.
f. Molecules move directly through proteins called channels or carriers.
h. This process transports polar molecules.
i. This process transports charged molecules.
Carrier proteins transport molecules across the cell membrane by _________.
a. creating a pore for the molecule to diffuse through
b. using energy in the form of ATP
c. binding the molecule and changing shape to allow passage through the membrane
d. using ion gradients to move the molecule across the membrane
c. binding the molecule and changing shape to allow passage through the membrane
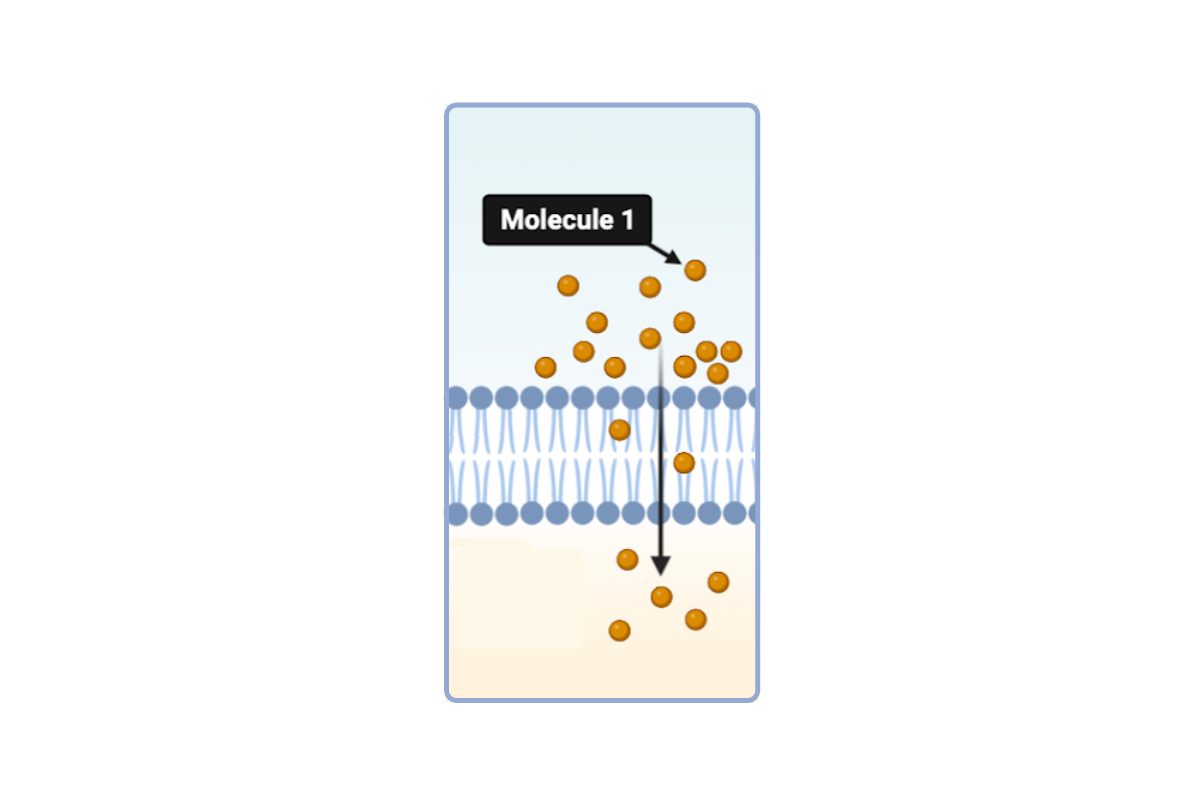
Which statement(s) could accurately describe Molecule 1? Select all that apply.
a. This molecule is hydrophobic.
b. This molecule is small and hydrophilic.
c. This molecule is large and hydrophilic.
d. This molecule is nonpolar.
a. This molecule is hydrophobic.
b. This molecule is small and hydrophilic.
d. This molecule is nonpolar.
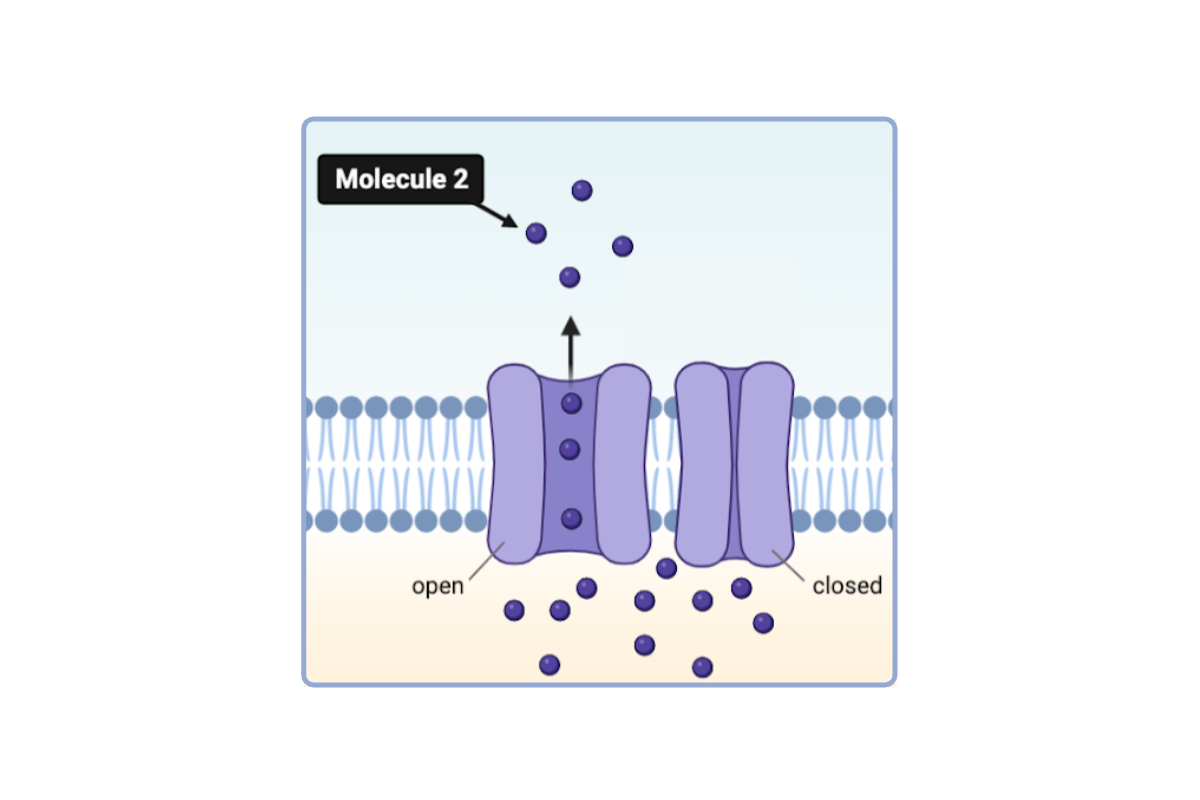
Which statement(s) could accurately describe Molecule 2? Select all that apply.
a. This molecule is hydrophobic.
b. This molecule is hydrophilic.
c. This molecule is nonpolar.
d. This molecule could have a polar region.
e. This molecule could have a charged region.
b. This molecule is hydrophilic.
d. This molecule could have a polar region.
e. This molecule could have a charged region.
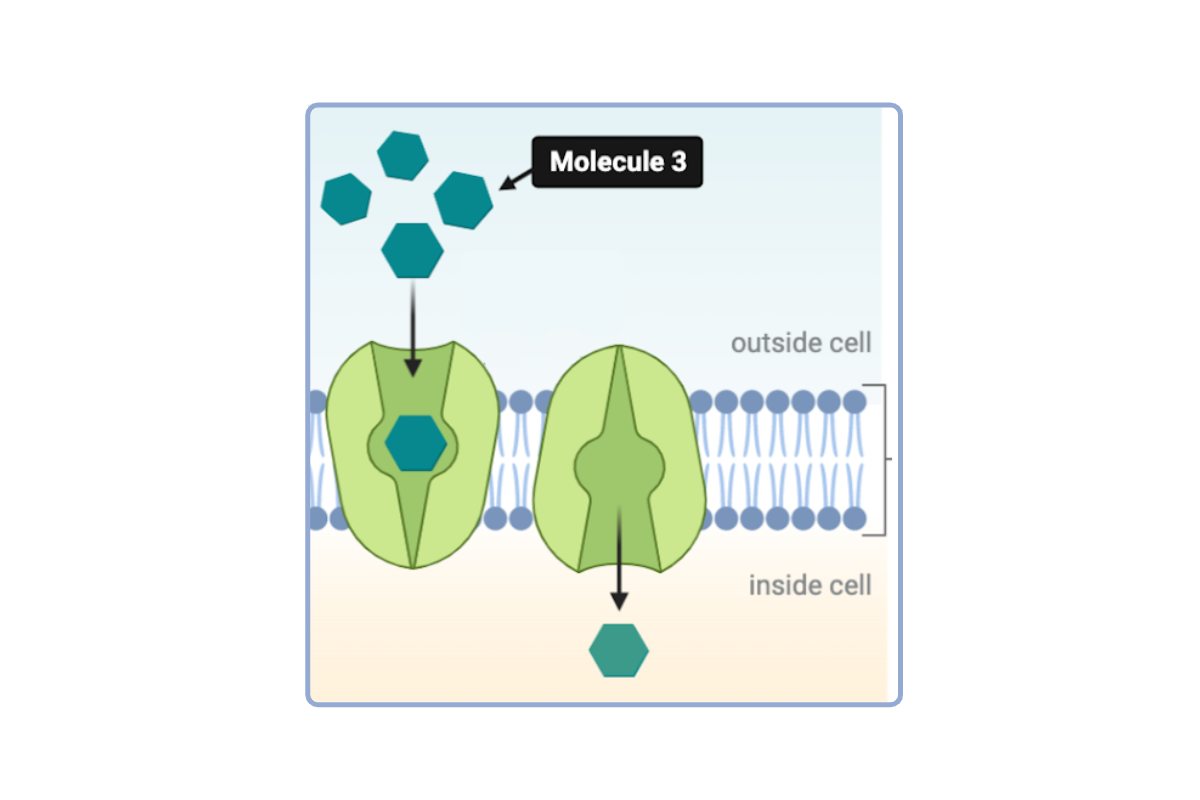
Which statement(s) could accurately describe Molecule 3? Select all that apply.
a. This molecule is hydrophobic.
b. This molecule is hydrophilic.
c. This molecule is nonpolar.
d. This molecule has a polar region.
e. This molecule has a charged region.
b. This molecule is hydrophilic.
d. This molecule has a polar region.
e. This molecule has a charged region.
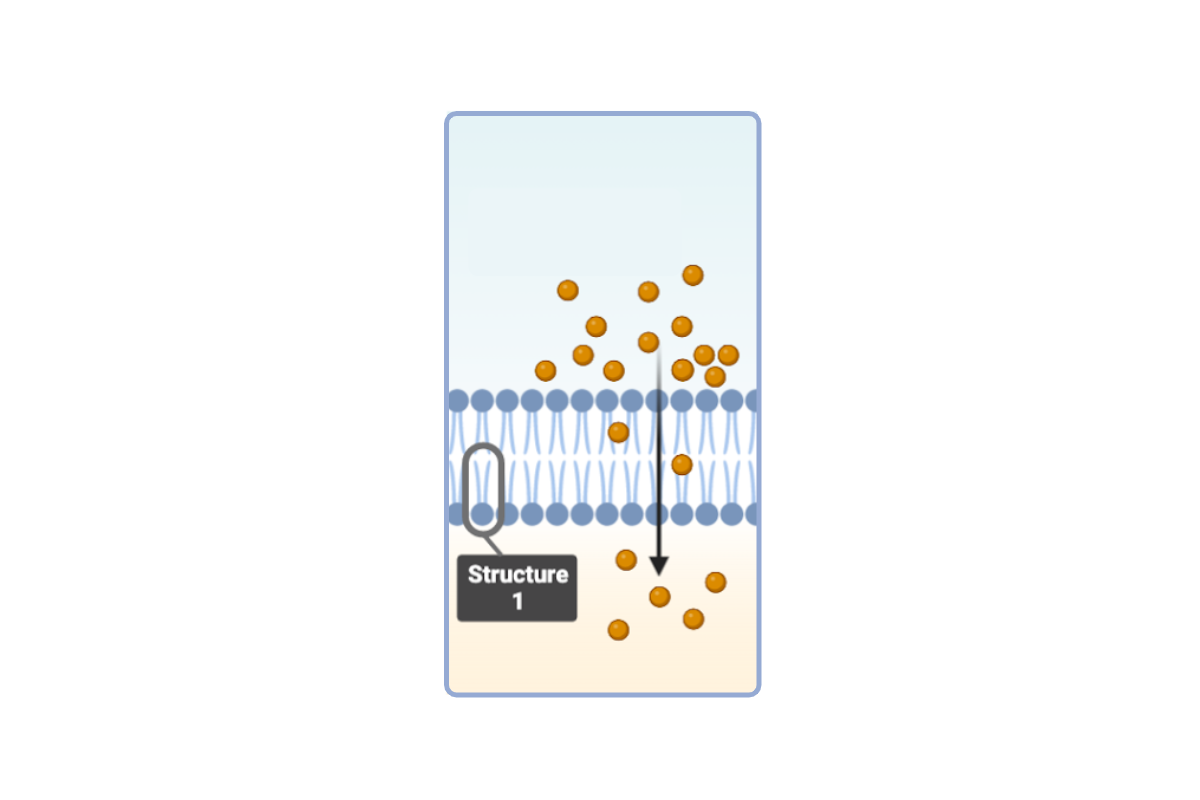
Which statement(s) accurately describe Structure 1? Select all that apply.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure has a hydrophobic region.
e. This structure has a hydrophilic region.
f. This structure is amphiphilic.
g. This structure has a nonpolar region.
h. This structure has a polar region.
i. This structure has a charged region.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
d. This structure has a hydrophobic region.
e. This structure has a hydrophilic region.
f. This structure is amphiphilic.
g. This structure has a nonpolar region.
h. This structure has a polar region.
i. This structure has a charged region.
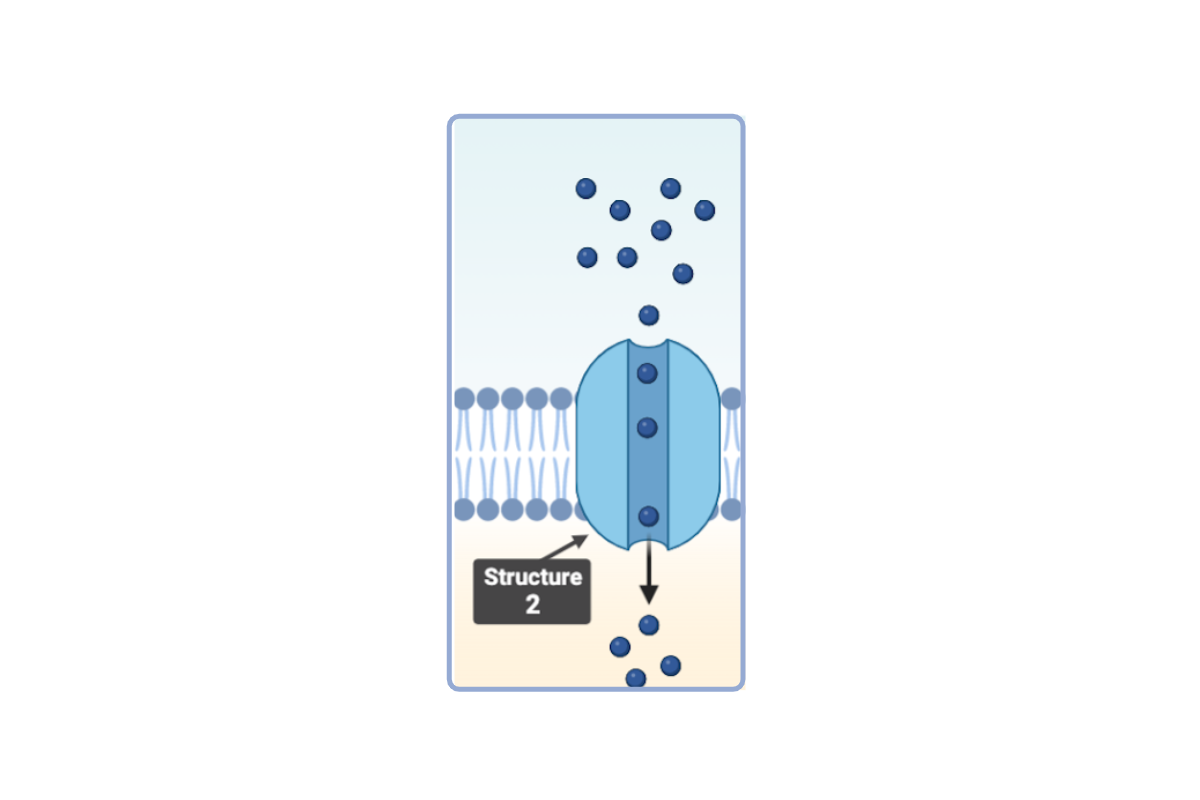
Which statement(s) accurately describe Structure 2? Select all that apply.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
e. This structure is a carrier protein.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
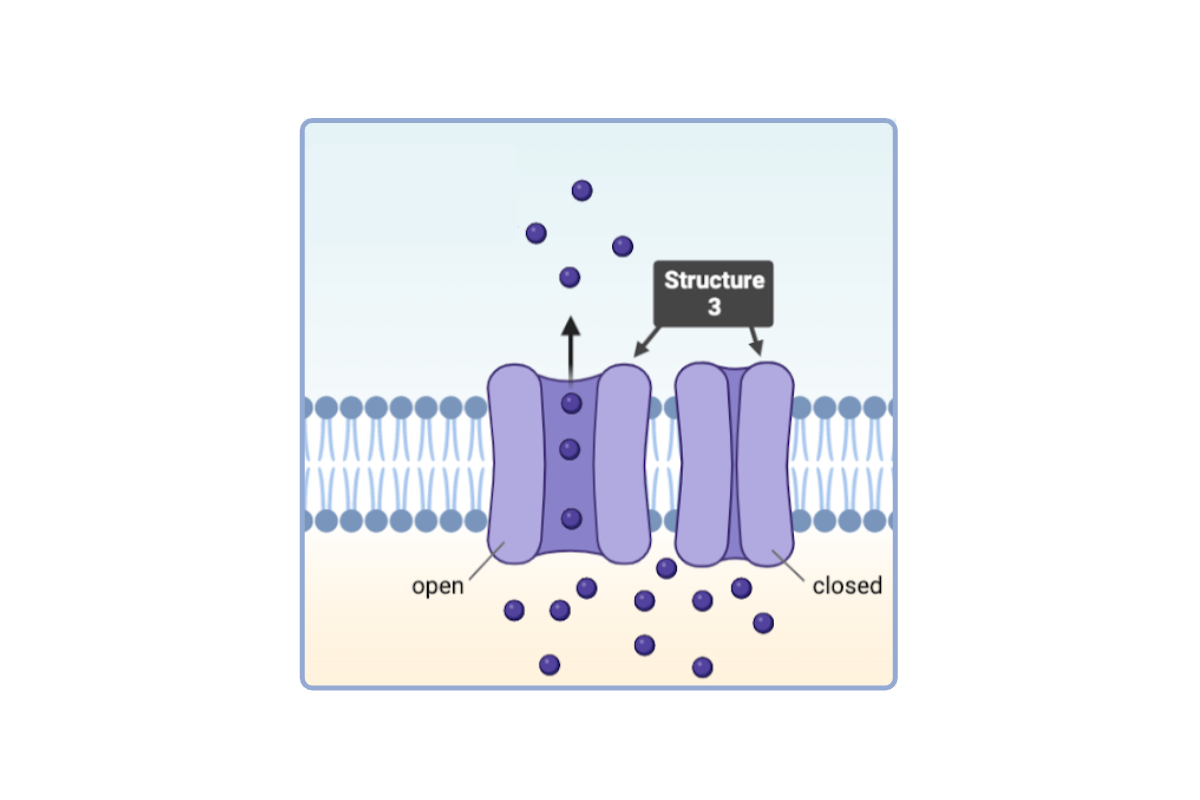
Which statement(s) accurately describe Structure 3? Select all that apply.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
e. This structure is a carrier protein.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
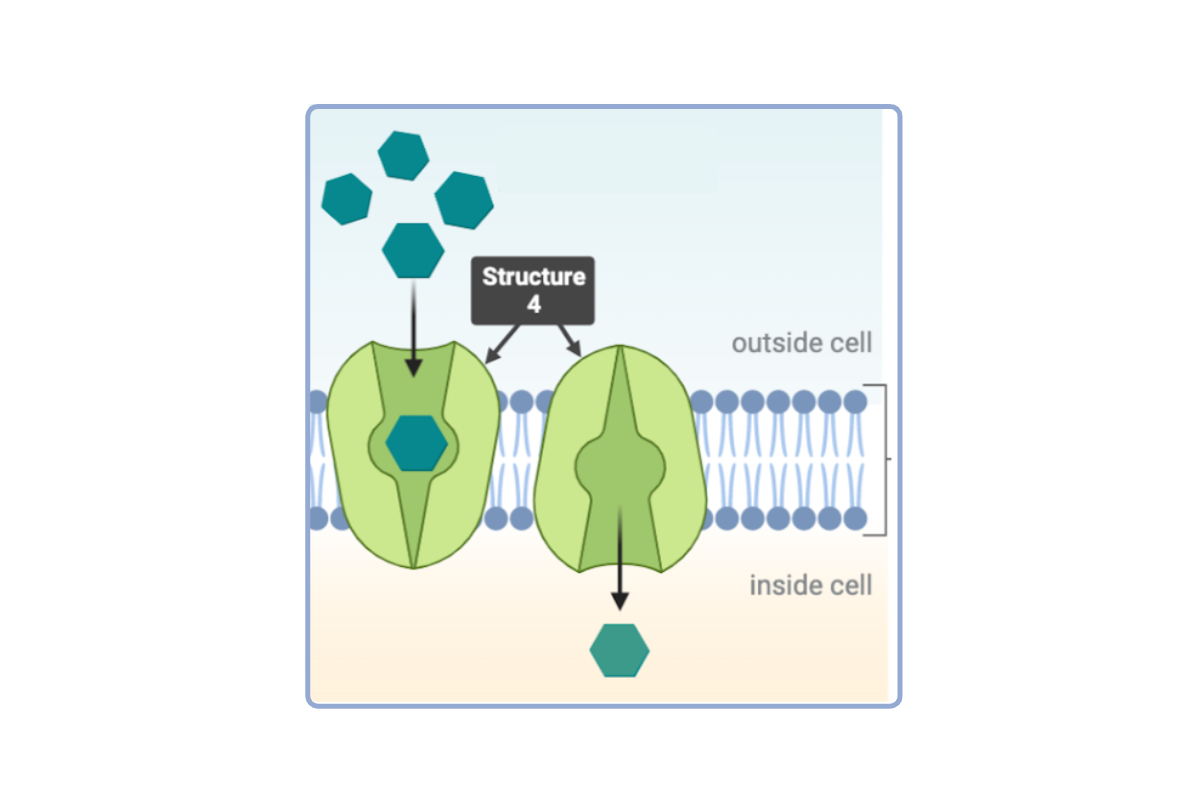
Which statement(s) accurately describe Structure 4? Select all that apply.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
e. This structure is a carrier protein.
c. This structure is a protein.
e. This structure is a carrier protein.
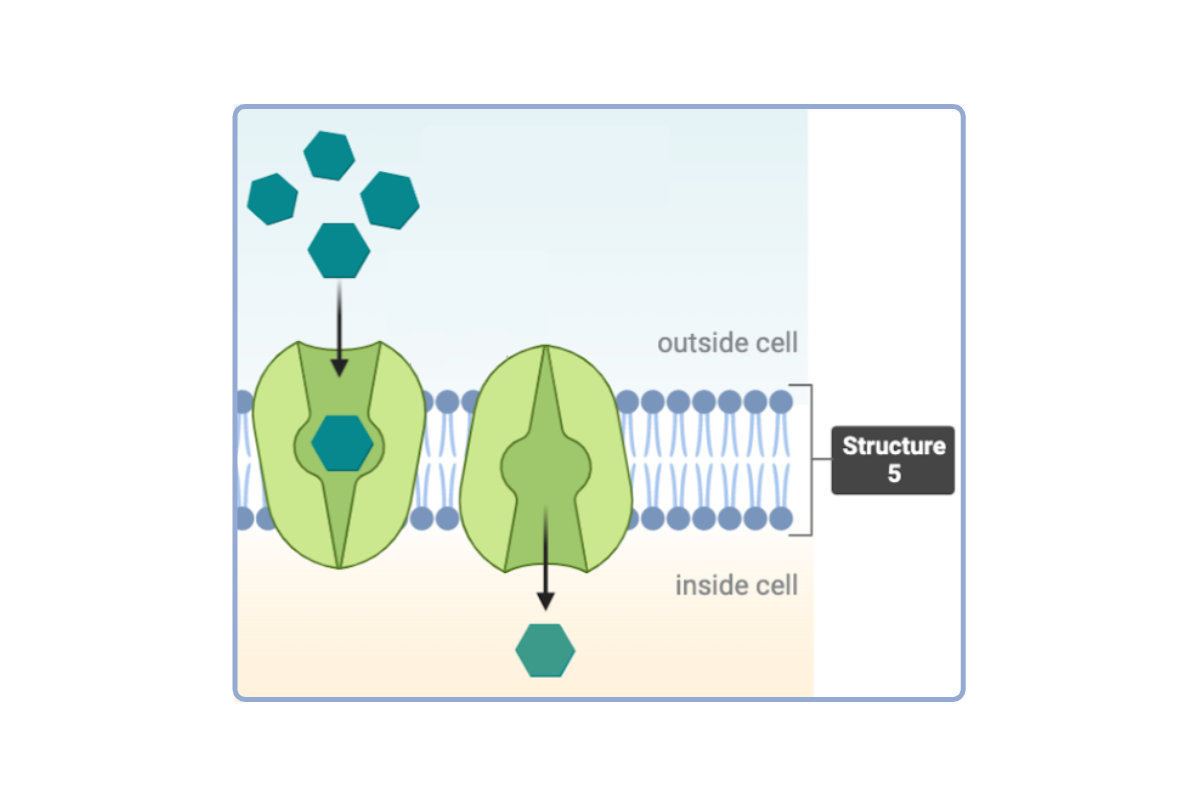
Which statement(s) accurately describe Structure 5? Select all that apply.
a. This structure is a phospholipid.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
c. This structure is a protein.
d. This structure is a channel protein.
e. This structure is a carrier protein.
b. This structure is a phospholipid bilayer.
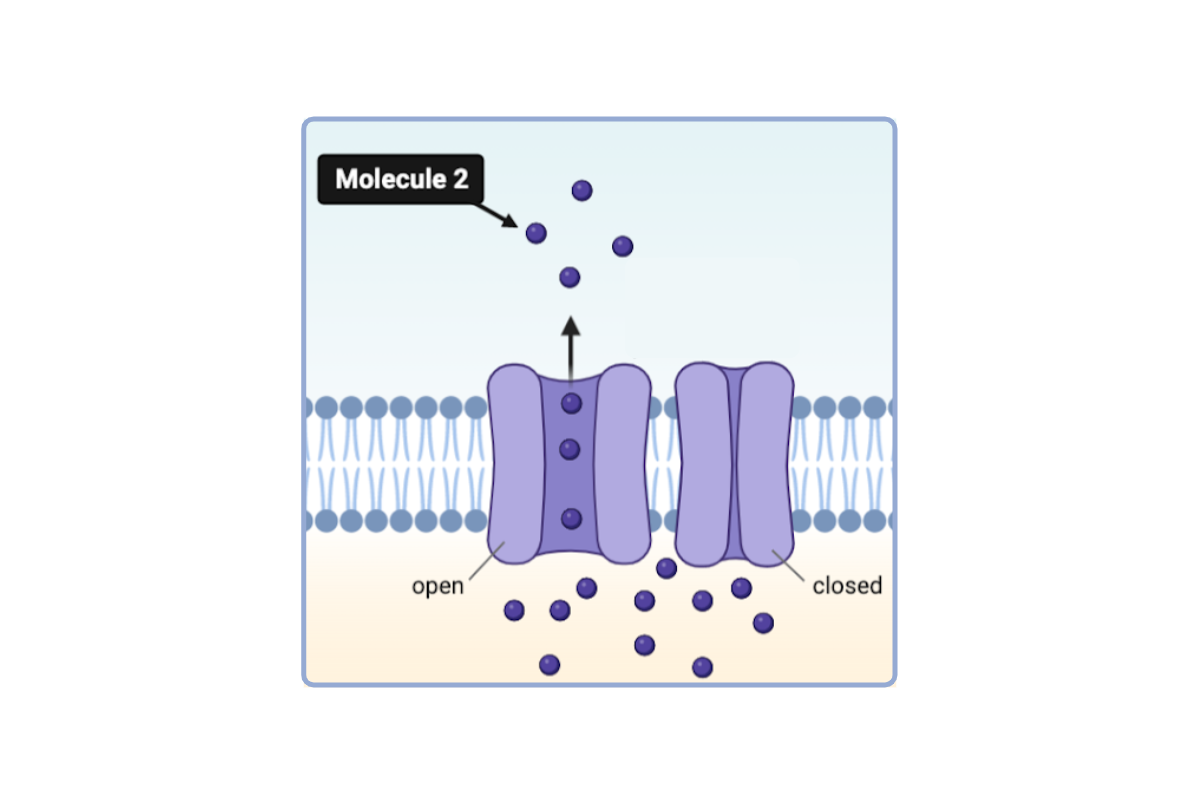
Based on the direction of flow depicted in the model, the concentration of Molecule 2 must be _________ of the cell.
a. higher on the outside than the inside
b. lower on the outside than the inside
c. the same on the outside and the inside
b. lower on the outside than the inside
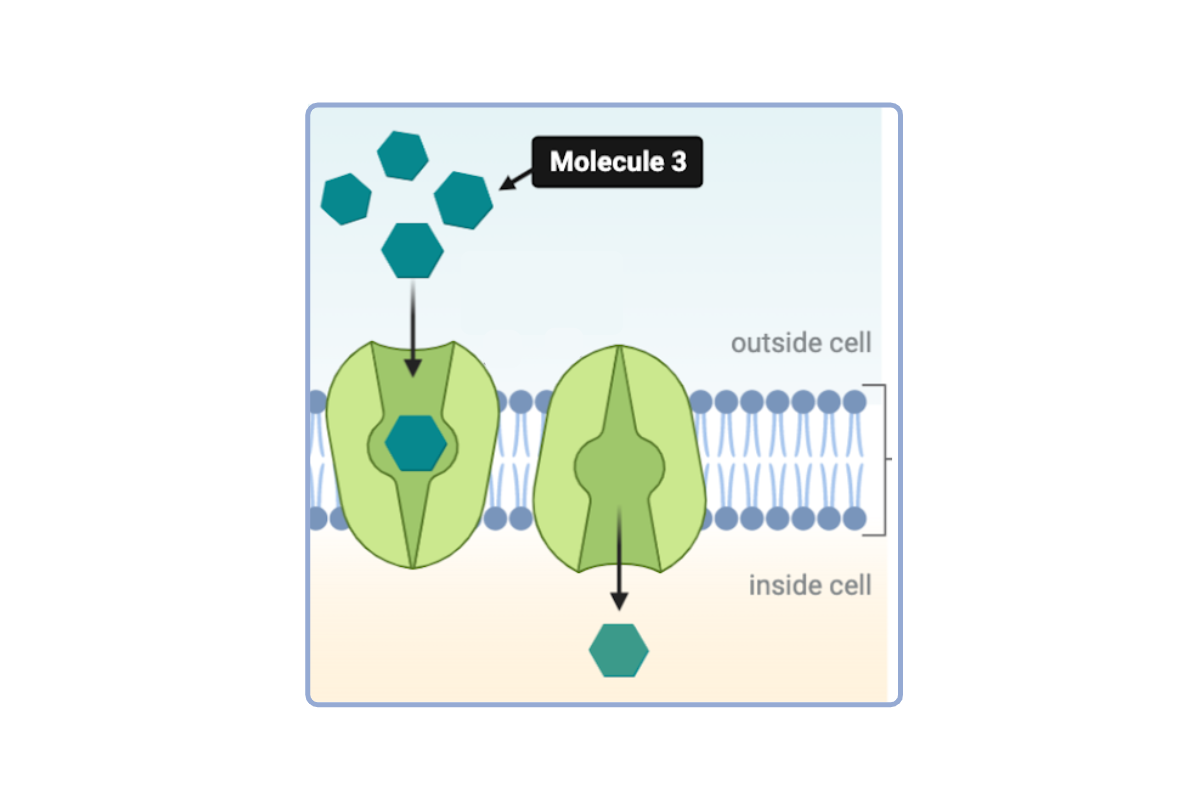
Based on the direction of flow depicted in the model, the concentration of Molecule 3 must be _________ of the cell.
a. higher on the outside than the inside
b. lower on the outside than the inside
c. the same on the outside and the inside
a. higher on the outside than the inside
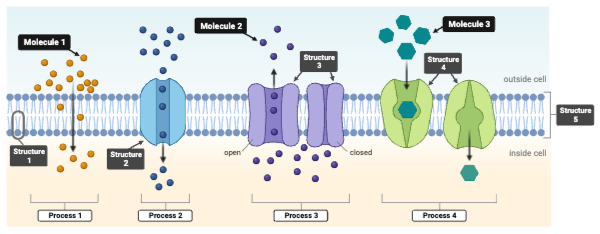
Which process requires a concentration gradient to drive molecules across the plasma membrane, with or without a protein transporter? Select all that apply.
a. Process 1
b. Process 2
c. Process 3
d. Process 4
a. Process 1
b. Process 2
c. Process 3
d. Process 4
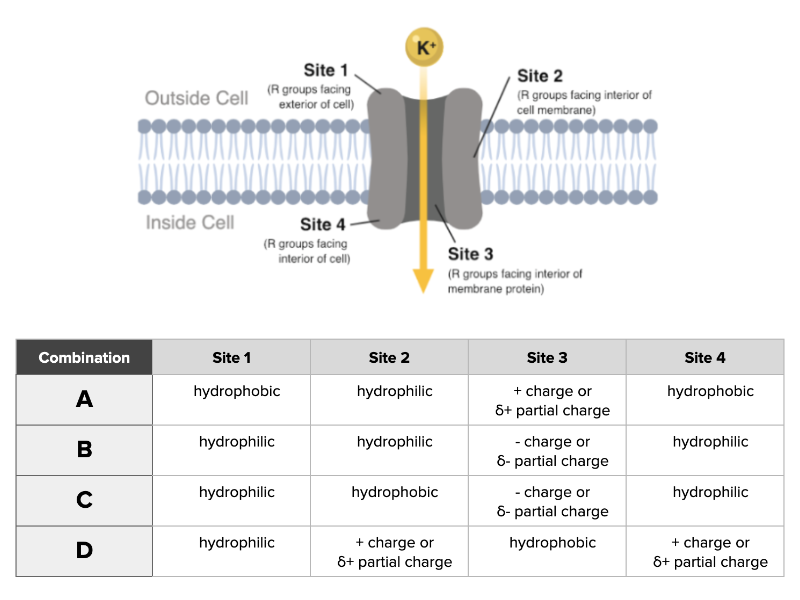
Which combination of chemical properties accurately describes a channel capable of transporting K+ ions through a membrane?
Combination C
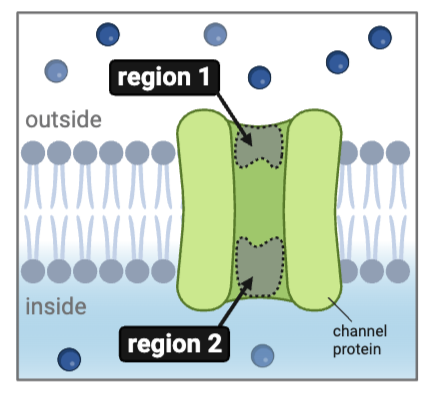
Which types of ions could diffuse through this channel? Select all that apply.
a. K+
b. Na+
c. Ca2+
d. Cl-
e. HCO3-
d. Cl-
e. HCO3-
You are studying how a molecule called BD11 moves through the membrane of a red blood cell. Through some measurements, you observe the following points:
- BD11 is a large, polar molecule.
- BD11 can move through the membrane in either direction.
- BD11 always moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
- No ATP is required for BD11 to move through a membrane.
- BD11 cannot pass through the membrane in the presence of a drug called FR14, but movement through the membrane resumes when the drug is removed.
Based on these observations, BD11 is most likely transported by ________.
a. simple diffusion
b. a channel protein
c. a carrier protein
c. a carrier protein
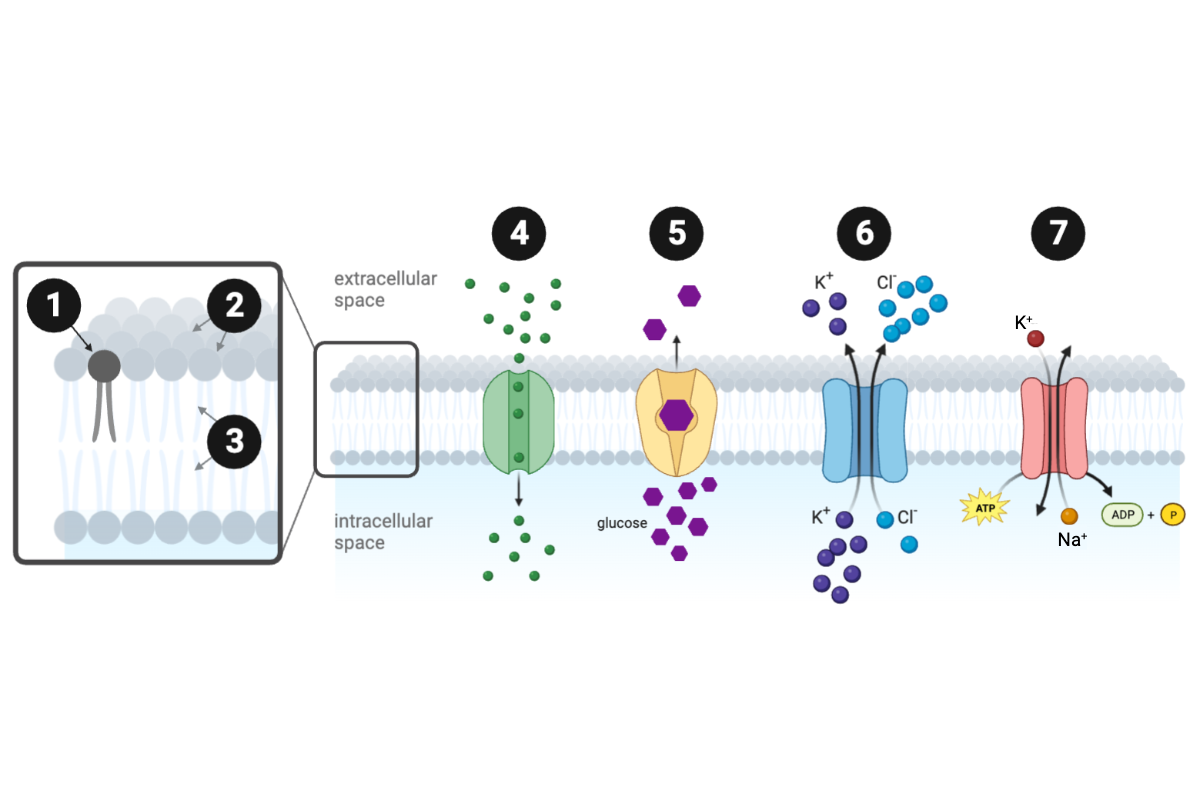
Which structure or protein is labeled number 1?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
f. phospholipid
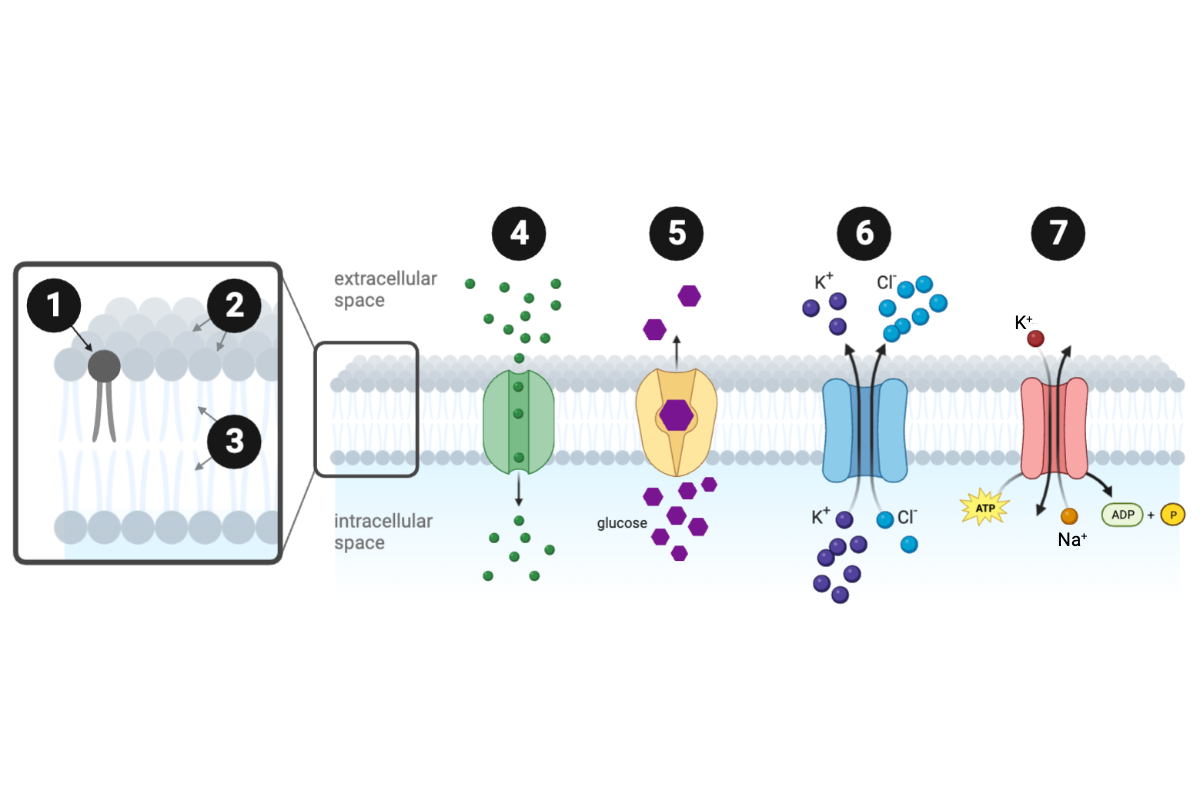
Which structure or protein is labeled number 2?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
d. hydrophilic region
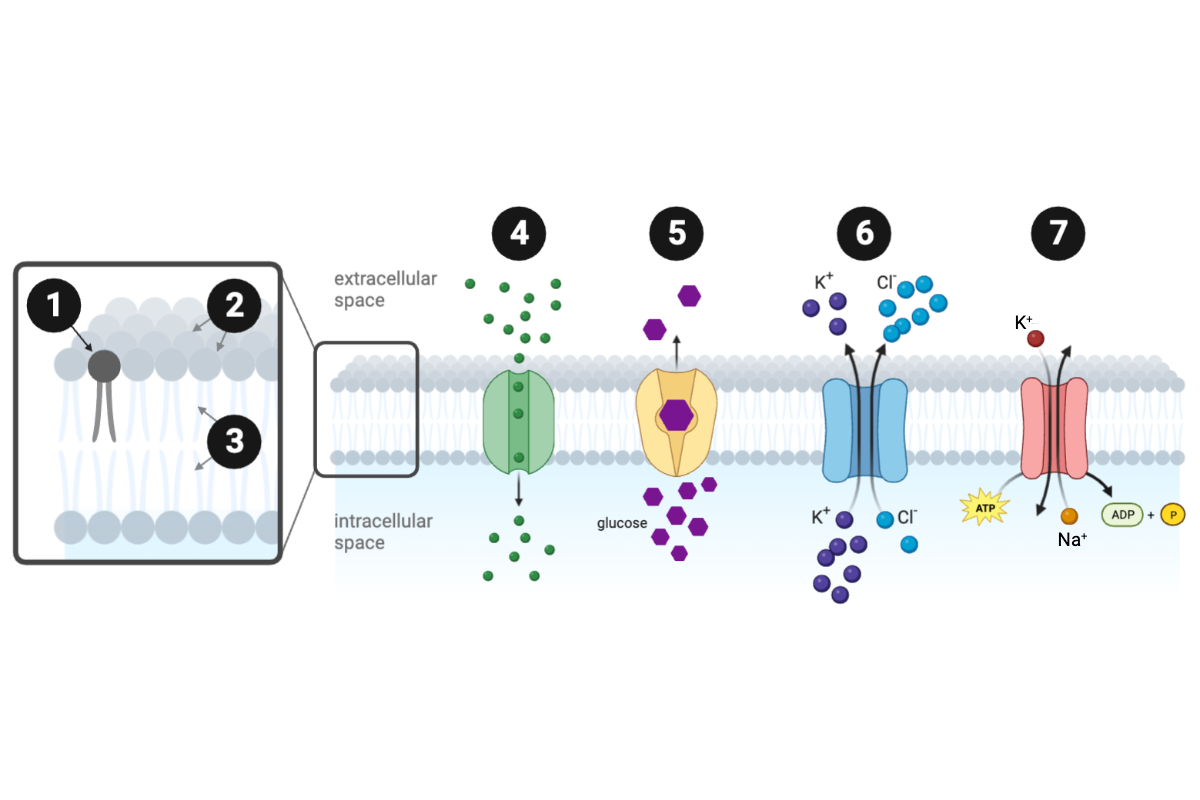
Which structure or protein is labeled number 3?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
e. hydrophobic region
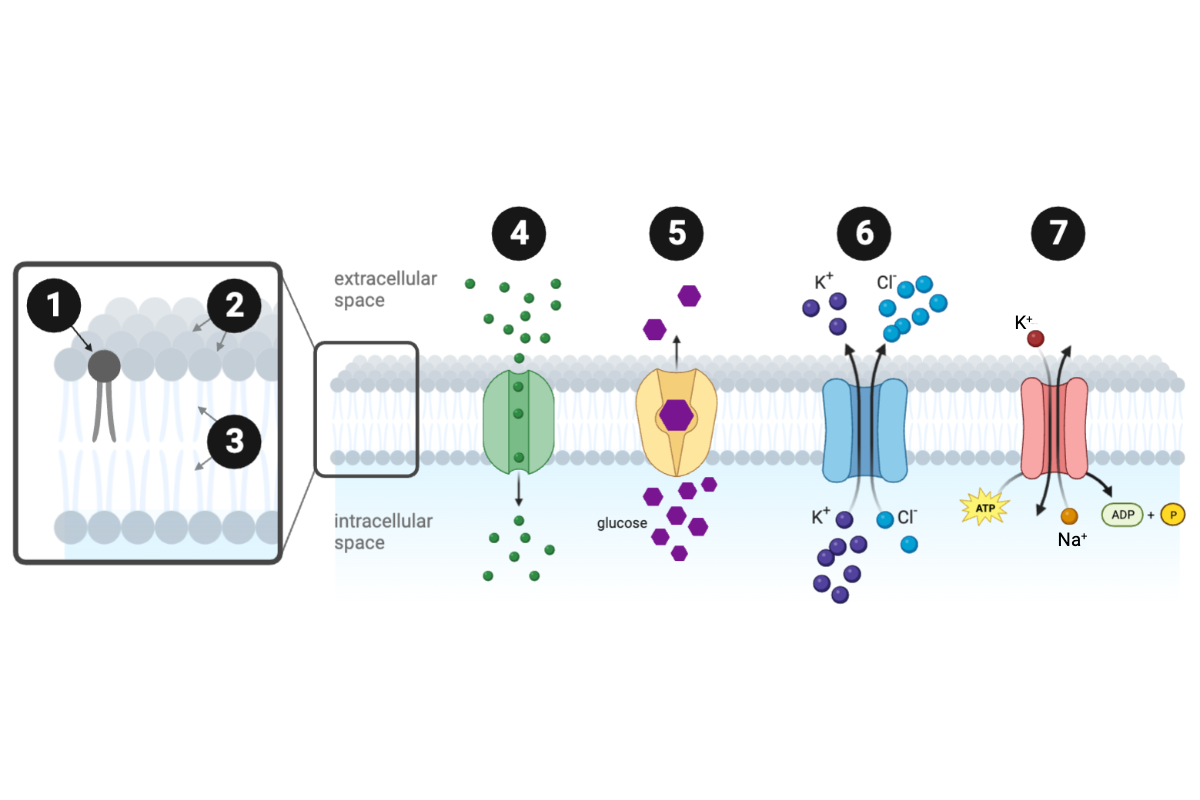
Which structure or protein is labeled number 4?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
b. channel protein
Which structure or protein is labeled number 5?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
a. carrier protein
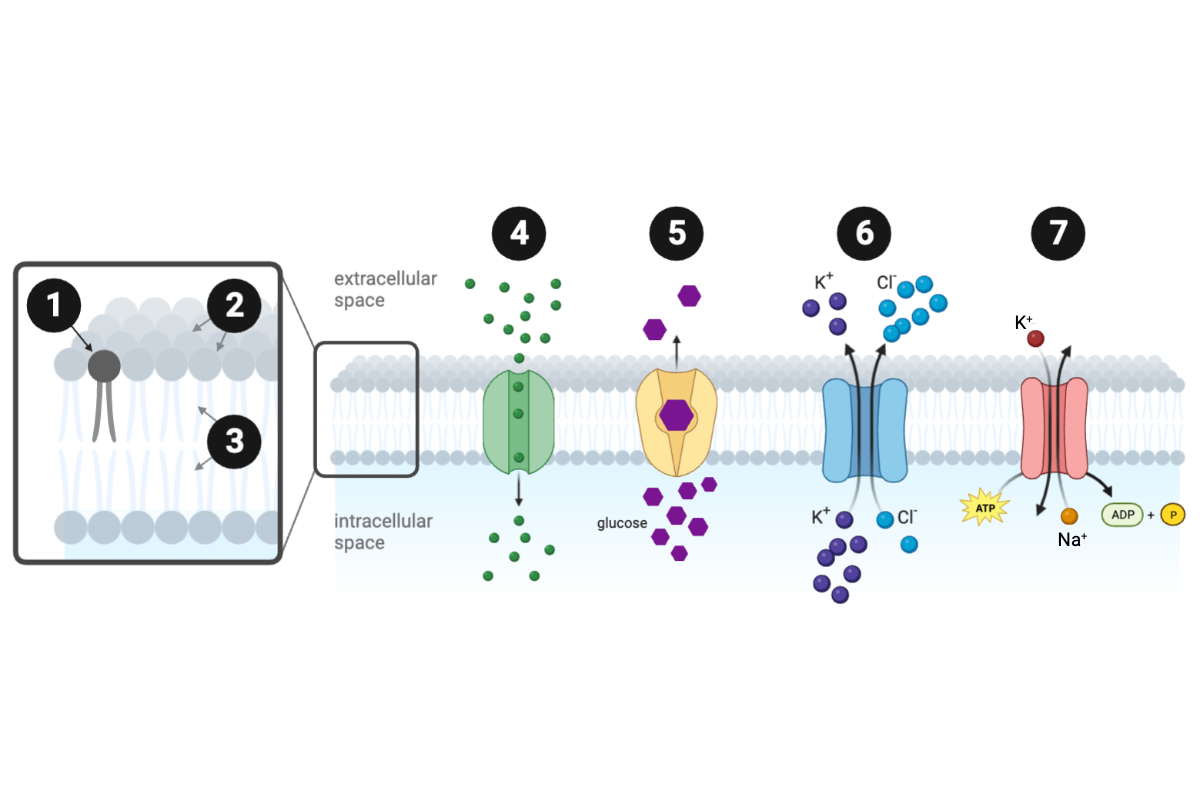
Which structure or protein is labeled number 6?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
c. symporter protein
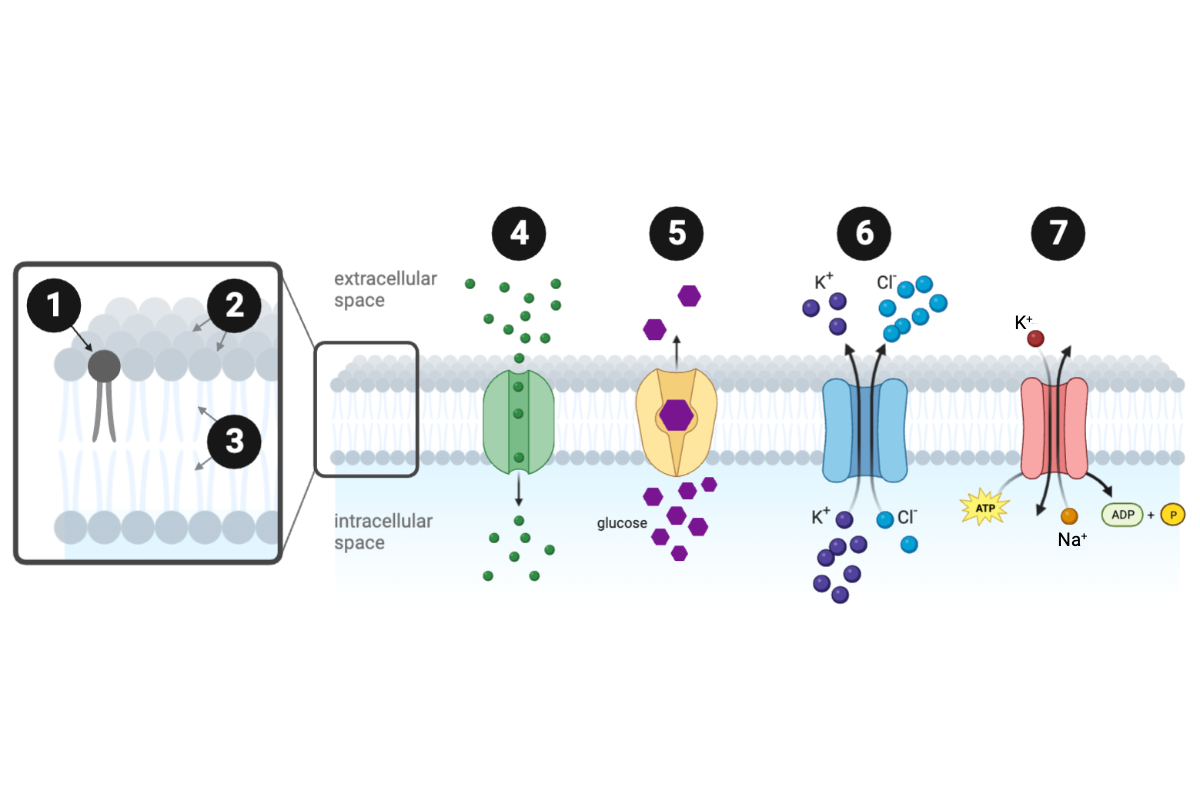
Which structure or protein is labeled number 7?
a. carrier protein
b. channel protein
c. symporter protein
d. hydrophilic region
e. hydrophobic region
f. phospholipid
g. ATPase
g. ATPase
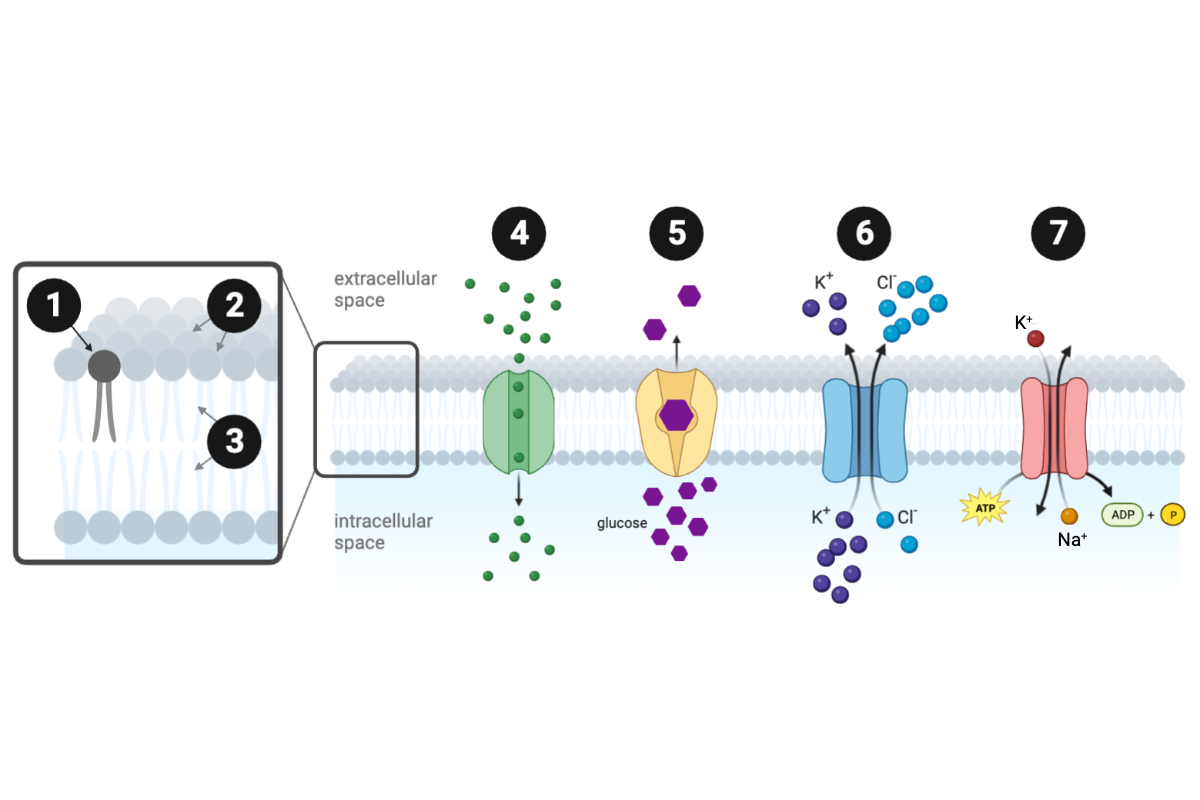
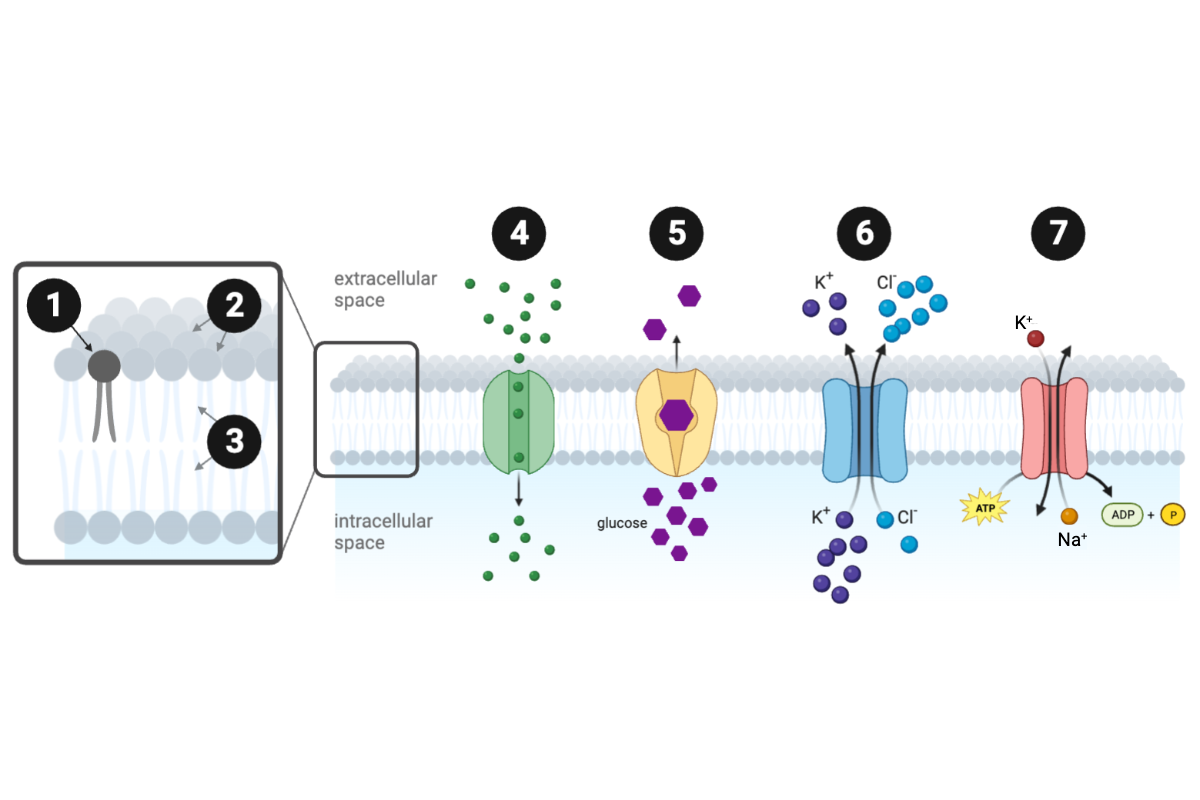
Which protein transporter(s) can move molecules across the membrane against a concentration gradient? Select all that apply.
a. Protein 4
b. Protein 5
c. Protein 6
d. Protein 7
c. Protein 6
d. Protein 7
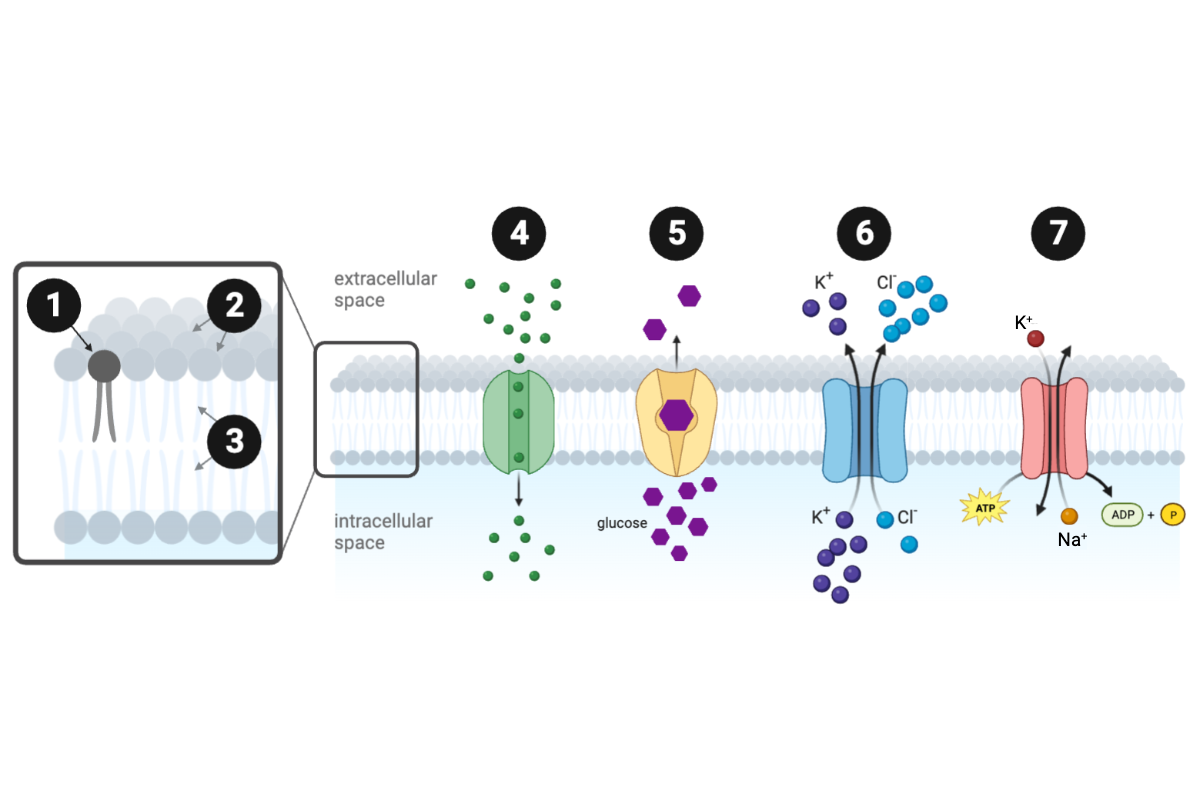
Which protein is a primary active transporter?
a. Protein 4
b. Protein 5
c. Protein 6
.
d. Protein 7
d. Protein 7
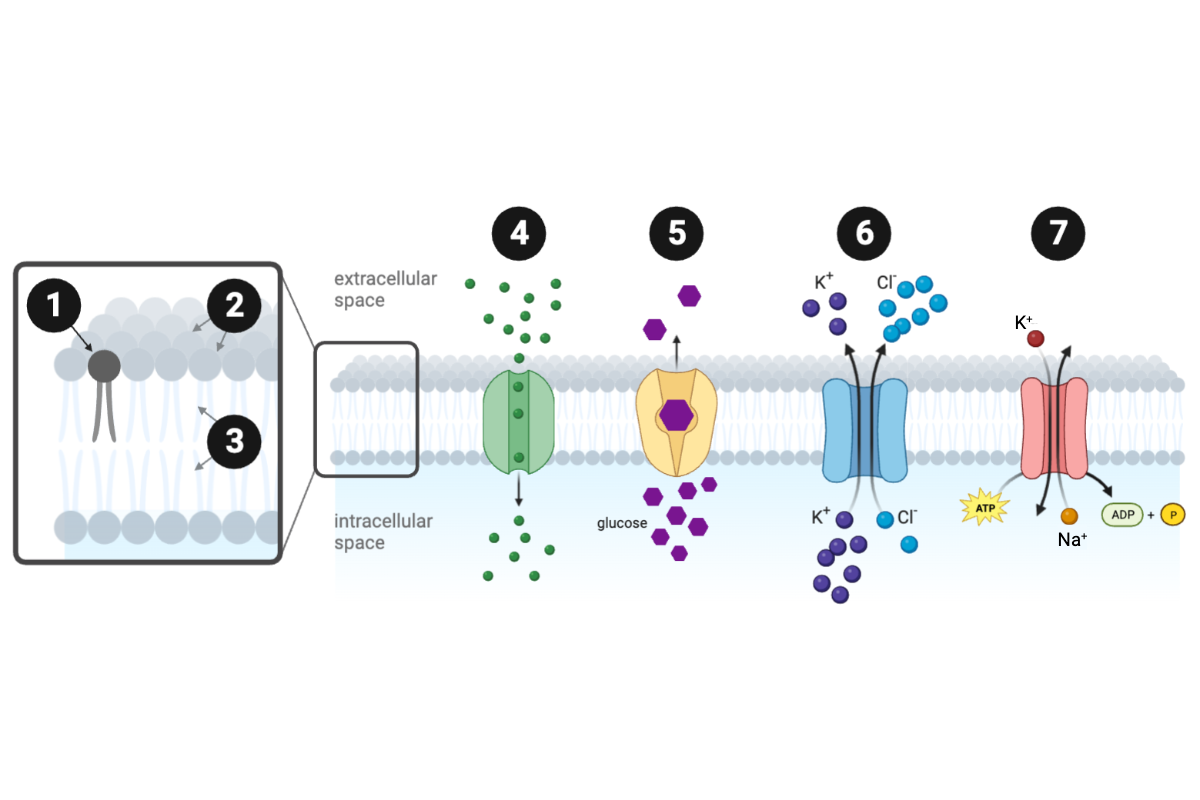
Which protein is a secondary active transporter?
a. Protein 4
b. Protein 5
c. Protein 6
d. Protein 7
c. Protein 6
Which statements accurately describe facilitated diffusion? Select all that apply.
a. This process requires that molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. his process requires channel or carrier proteins.
c. This process requires energy in the form of ATP.
d. This process requires energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient.
e. This process enables nonpolar molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
f. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
a. This process requires that molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. his process requires channel or carrier proteins.
d. This process requires energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient.
f. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
Which statements accurately describe primary active transport? Select all that apply.
a. This process requires that molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. This process requires carrier proteins.
c. This process requires channel proteins.
d. This process requires energy in the form of ATP.
e. This process requires energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient.
f. This process enables nonpolar molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
g. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
b. This process requires carrier proteins.
d. This process requires energy in the form of ATP.
g. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
Which statements accurately describe secondary active transport? Select all that apply.
a. This process requires that some molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. This process requires either carrier proteins or channel proteins.
c. This process requires energy in the form of ATP.
d. This process requires energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient.
e. This process enables nonpolar molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
f. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
a. This process requires that some molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
b. This process requires either carrier proteins or channel proteins.
d. This process requires energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient.
f. This process enables polar or charged molecules to pass through a cell membrane.
Which statement best describes the difference between primary active transport and secondary active transport?
a. Primary active transport moves solutes directly through the membrane, but secondary active transport requires a carrier protein.
b. Primary active transport moves solutes from high concentration to low concentration, but secondary active transport moves solutes from low concentration to high concentration.
c. Primary active transport requires ATP, but secondary active transport requires an electrochemical gradient.
c. Primary active transport requires ATP, but secondary active transport requires an electrochemical gradient.
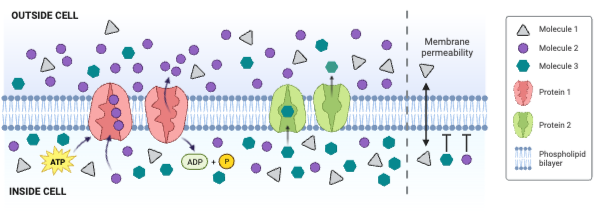
The concentration of Molecule 1 is ___________.
a. greater outside the cell than inside the cell
b. greater inside the cell than outside the cell
c. the same inside and outside of the cell
c. the same inside and outside of the cell
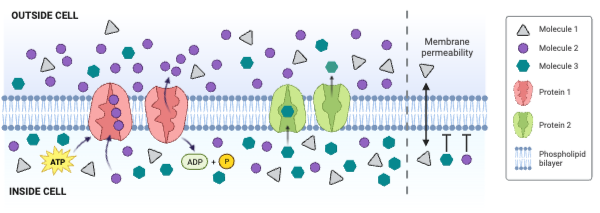
The concentration of Molecule 3 is ___________.
a. greater outside the cell than inside the cell
b. greater inside the cell than outside the cell
c. the same inside and outside of the cell
b. greater inside the cell than outside the cell
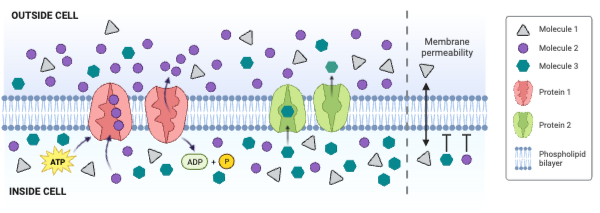
The net movement of Molecule 2 is from ___________.
a. low concentration to high concentration
b. high concentration to low concentration
c. There is no net movement of Molecule 2.
a. low concentration to high concentration
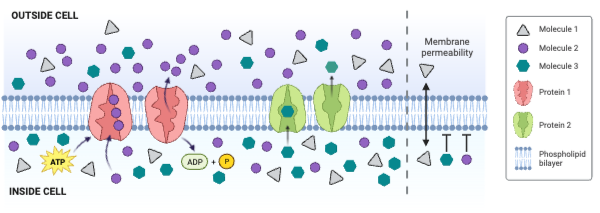
Molecule 2 could be ____________. Select all that apply.
a. charged
b. large and partially charged
c. small and partially charged
d. nonpolar
a. charged
b. large and partially charged
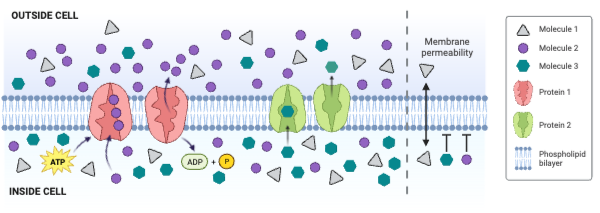
Molecule 3 could be ____________. Select all that apply.
a. charged
b. large and partially charged
c. small and partially charged
d. nonpolar
a. charged
b. large and partially charged
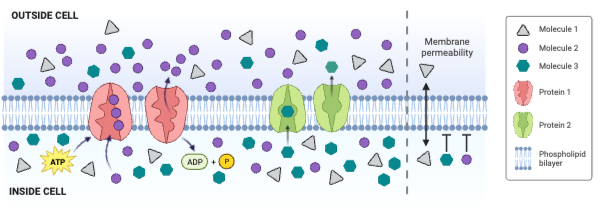
Which molecule moves through the membrane by facilitated diffusion involving a channel protein?
a. Molecule 1
b. Molecule 2
c. Molecule 3
d. None of the molecules move through a channel protein.
d. None of the molecules move through a channel protein.
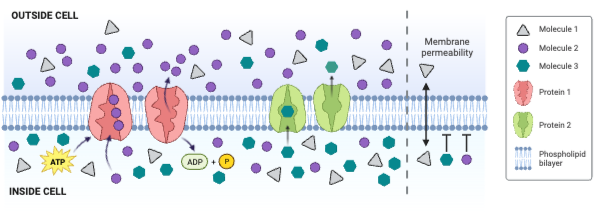
Which molecule moves through the membrane by secondary active transport?
a. Molecule 1
b. Molecule 2
c. Molecule 3
d. None of the molecules move through the membrane by secondary active transport.
d. None of the molecules move through the membrane by secondary active transport.
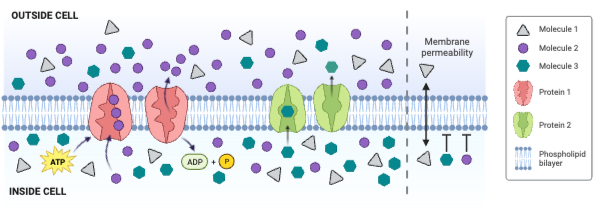
Which protein is a carrier engaged in facilitated diffusion?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. Neither protein is a carrier engaged in facilitated diffusion.
b. Protein 2
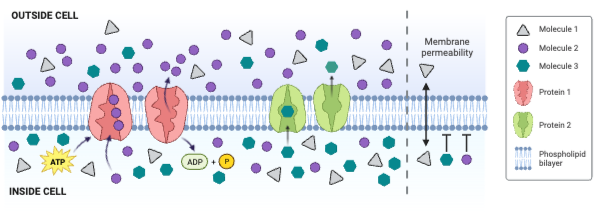
Which protein is an ATPase engaged in primary active transport?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. Neither protein is an ATPase engaged in primary active transport.
a. Protein 1
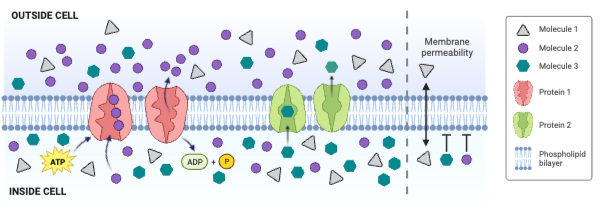
Which protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. Neither protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1.
c. Neither protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 1.
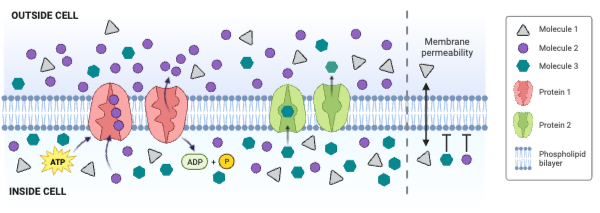
Which protein increases the concentration gradient of Molecule 2?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. Neither protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 2.
a. Protein 1
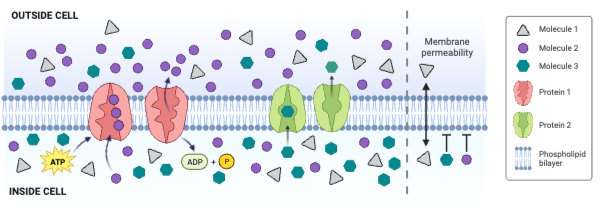
Which protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 3?
a. Protein 1
b. Protein 2
c. Neither protein decreases the concentration gradient of Molecule 3.
b. Protein 2
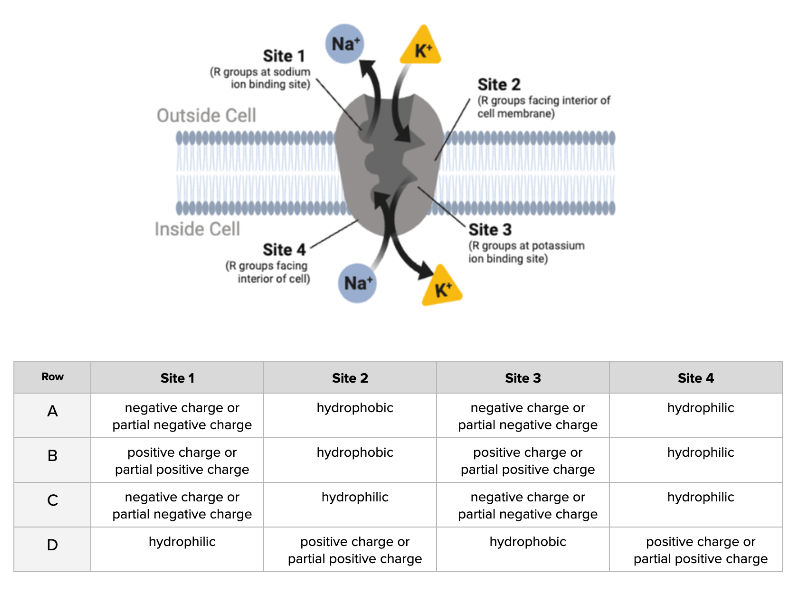
Which combination of characteristics would produce a protein that can move Na+ and K+ through the membrane?
Row A