GenChem1 - 1A Discovering Atoms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what did john dalton do?
discovered existence of atoms
what did jj thompson do?
discovered internal structure of atoms
what did robert millikan do?
found value of e in e/m using an apparatus to view tiny electrically charged oil drops
what did ernest rutherford do?
discovered alpha particles and used his students to conduct the metal foil experiment
what were the names of the students that conducted rutherford’s experiment?
hans geiger and ernest marsden
how did the atom get discovered?
through thompson’s cathode ray experiment
what was the cathode ray experiment?
rays generated from high voltage between 2 electrons. rays were bent by electric field, meaning there must have been charged electrons
what does e in e/m represent?
magnitude of charge on electron
if electrons are negative but atoms are neutrally charged, where do the positive charge come from?
protons
what is the plum pudding model, and is it accurate?
the theory that an atom was a blob of positively charged material. not entirely correct because that material is concentrated in the nucleus.
describe rutherford’s experiment
tested the plum pudding model to see if it was true. if it was, alpha particles would pass through the positive charge in the foil. although most alpha particles behaved this way, a few deflected a significant amount.
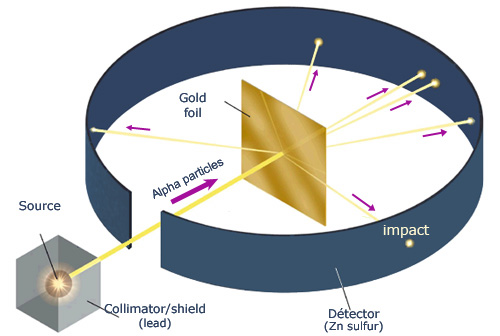
what discovery came from the rutherford experiment?
the nuclear model and the existence of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by empty space with electrons
what are 5 key aspects of the nuclear model?
protons and neutrons located in the nucleus; proton mass = neutron mass, electrons have a significantly smaller mass; mass of atoms comes from nucleus; # protons = atomic #; # protons = # electrons
what is spectroscopy?
analysis of light emitted/absorbed by substance
how does spectroscopy help with study of atoms?
light (electromagnetic radiation) can be emitted/absorbed by atoms, and different elements have unique emission/absorption spectra, allowing spectroscopy to assist in the determination of element composition.
what equation can be used to determine wavelength (λ) or frequency (v)?
(λ) (v) = c (speed of light)
which rays have higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths than visible light?
gamma, x-ray, uv
which rays have lower frequencies and longer wavelengths than visible light?
radio waves, microwaves, infrared
what did johann balmer do?
first to recognize pattern in visible lines of hydrogen spectrum
what formula can be used to find v?
rydberg formula
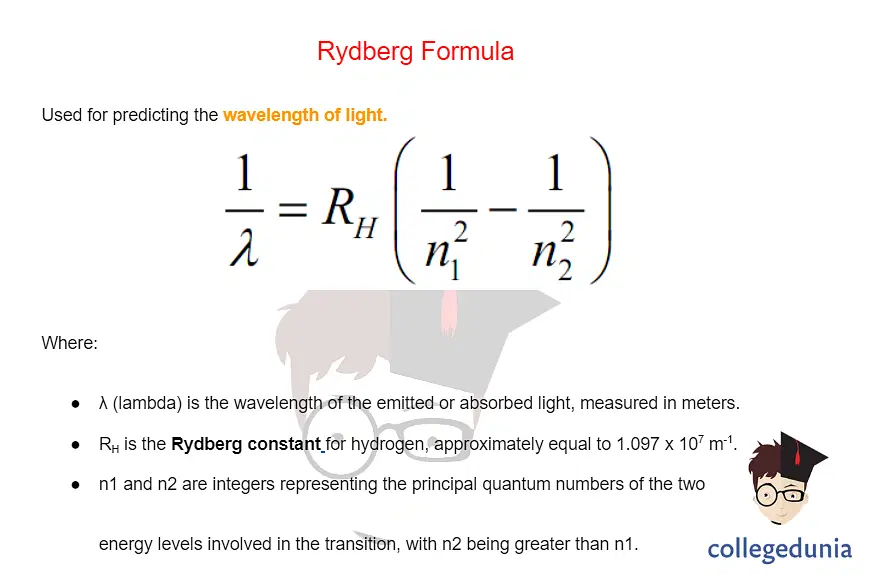
what series are there in terms of different spectra?
lyman series (uv), (n1 = 1); balmer series (visible), (n1 =2)
what are 2 key spectra of light? does v change based on which spectrum is being discussed?
emission and absorption; v stays the same for both because atoms absorb as much as they emit.
what is the problem with rydberg’s formula?
it does not explain why the pattern exists
how can the pattern described by rydberg’s formula be explained?
lights = energy; hydrogen emitting lights = - energy, hydrogen absorbing lights = + energy; electron energy changes based on the how much light is emitted/absorbed
what does the existence of spectral lines suggest?
elections can only have discrete energy values, giving to the existence of energy levels

how do spectral lines form?
come from transition (based of rydberg’s formula) from high to low energy (emission) or low to high energy (absorption)
in what range should λ be for light to be considered visible?
420-700 nm
what is the relationship between λ and energy?
longer wavelengths = lower energy, shorter wavelengths = higher energy; smaller λ value = more energy, higher λ value = less energy.
what is E and what is its equation?
E = energy of photon of light; E = (n)(v)
how does the discharge tube work in regards to hydrogen?
H2 gas —> H atoms —> higher energy H atoms —> energy released, relaxed H atoms
what makes electrons quantized?
electrons can only have certain energies