Reproductive Health Chapters 4
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
common menstrual disorders
-Amenorrhea
-Dysmenorrhea
-Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
-Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
-Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD)
-Endometriosis
MENO=
menstrual rleated
meto=
time
oligo=
few
a=
without/none/lack of
rhagia=
excess or abnormal
dys=
not or pain
rhea=
flow
common womens reproductive disorders
-Menstrual disorders
-Infertility
-Contraception
-abortion
-Menopause

any miscarrage before 16 weeks is considered an
abortion even though you do not actually take out the baby
menstrual cycle lasts
21 days
count for menstrual cycle starts
the first day of your period
menstrual cycle
follicle falls, you shed, you bleed
-fluctuation of hormones
amenorrhea is the
absence of menstruation
2 types of ammenhorea
primary and secondary
2 types of primary amenorrhea
1. absence of menstruation age 14 without development of secondary sex characteristics
2. absence of menstruation by age 16 with normal development of secondary sexual characteristics
-Primary amenorrhea is defined as the failure to reach menarche in females of reproductive age
secondary characteristics
-protruding breasts
-hair on body
what is the difference between the two primary amenorrhea
-at 14 with no development of secondary characteristics
-at 16 with normal development of secondary characteristics
by 16 if a women hasn't had a menses what happens
-endocrinologist and womens health dr
-not normal
secondary amenorrhea
the absence of regular menses for three cycles or irregular menses for 6 months in women who have previously menstruated regularly
a women has had periods but missed them 3 months in a row, or irregular for 6 months
-secondary amenorrhea
ammenorrhea therapeutic management
-primary and secondary
Primary therapeutic management
-involves the correction of any underlying disorders
-estrogen replacement therapy
secondary therapeutic management
-cyclic progesterone
-treatment of hyperprolactinemia
-eating disorder
-obesity
-hypothalamic failure
-hypothyroidism
amenorrhea nursing assessment
-Tanner stages of breast development
-Laboratory testing
tanner stages
by 9: breast buds
by 11: menses
dysmenorrhea is
painful menstruation
DYSMENORRHEA risk factors
younger age, smoking, and stress
types of dysmenorrhea
primary and secondary
primary is what type of pain
spasmotic
primary dysmenorrhea is
-spasmodic
-caused by increased prostaglandin production
primary dysmenorrhea meds
-midol or ibuprophen
-stops prostaglandin production
secondary dysmenorrhea pain is
all over, parts begin to hurt
secondary dysmenorrhea
-congestive
-pelvic or uterine pathology
-endometriosis most common cause of secondary dysmenorrhea
most common cause of secondary dysmenorrhea
endometriosis
nursing assessment for dysmenorrhea includes
-Past medical history
-sexual history
-menstrual history: when was your last period
-bimanualpelvic examination
client with dysmenorrhea will have these mabifestation
-nausea/vomiting/diarrhea
-fatigue
-fever
-headache
-dizziness
-bloating
-water retention
-weight gain
-muscle aches
-food cravings
-breast tenderness
First-line treatment measures for dysmenorrhea usually include
-nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-hormonal contraceptives
dysmenorrhea client education includes
-Comfort measures
-heat
-lifestyle changes
-pain relief
-ask dr for meds for patient
tips for managing dysmenorrhea
-excercise to decrease prostaglandin release
-decrease salty food
-cut alcohol and smoking
-fiber
ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING (AUB) is
-Painless endometrial bleeding that is prolonged, excessive, and irregular and not attributed to any underlying structural or systemic disease
-Similar to and may overlap with other uterine bleeding disorders
AUB patient will be
going through several pads and bleeding for more than 5 days
AUB occurs most often when?
at beginning and end of reproductive years
-when hormones are put of wack
etiology of AUB
hormone disturbance
tx for AUB includes
treating the underlying cause
nursing management for AUB includes
-client education
-explain what is going on
goal for treatment of AUB
-Goal is to normalize the bleeding
-correct the anemia
-prevent or diagnose early cancer
-restore quality of life
PERSON WITH AUB bleeds alot so we need to watch for
Anemia
pharmacotherapy for AUB
meds or insertion of a hormone-secreting intrauterine system
surgical intervention for AUB
-dilation and curettage (D&C)
-endometrial ablation
-uterine artery embolization
-hysterectomy
dilation and curettage (D&C)
-dilate the os and go in to scrape and clean out stuff like old blood cells
-we wake up with cramps and bleeding (scant and spotty due to procedure)
endometrial ablation
-cut the bleeding sources
-arteries connected to uterus get cut and stop the sources where blood can come through
uterine artery embolization
-cut, tie, snip uterine artery
hysterectomy
uterus removed surgically
nursing assessment for AUB
-pain
-anemia
-full assessment
-labs to rule out any pathology
why is it important to stop AUB
-we want to avoid anemia, which can lead to arrhythmia due to blood loss
-heavy bleeding can also lead to clots
-we need to stop this
premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
-WIDE RANGE OF RECURRENT SX
-more severe varient is premenstrual dysphoric disorder
etiolofy for PMDD is
unknown
therapeutic management for PMDD
-Multidimensional approach
-Vitamin supplements
-diet changes
-exercise
-Lifestyle
-medications
when do you treat PMDD
-treated before and during
-before menses load up on ibuprophen
NURSING ASSESSMENT FOT PMS will reveal
-irritability
-tension
-dysphoria (most prominent and consistent symptoms)•
A: anxiety• C: craving• D: depression• H: hydration• O: other
ACOG criteria goes with ACDHO
A: anxiety• C: craving• D: depression• H: hydration• O: other
main sx of PMDD
mood disorders
endometriosis etiology
risk factors; exact cause unknown
-Tall height
-Lower BMI
-Family history of endometriosis in a first-degree relative -Short menstrual cycle (<27 days apart)
-Heavy menstrual flow
-Late menopause
-Obstruction of menstrual flow
-young age of menarche (younger than 11 to 13 years of age)
-No pregnancies (nulliparity)
therapeutic management fot endometriosis
-Medication therapy
-pain relief
-hormonal suppression
-surgery
endometriosis is caused when
-it is caused when tissue similar to that of the endometrium implants outside of the uterus, most commonly throughout the abdominal cavity including the bowel, bladder, ovary, uterosacral ligaments, diaphragm, and pleural cavity.
-Although it is a benign process, it can cause dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, infertility, and chronic pelvic pain
endometriosis Nursing assessment:
-infertility and pain
-nonspecific pelvic tenderness
-tender nodular masses on uterosacral ligaments, posterior uterus, or posterior cul-de-sac
grade 1
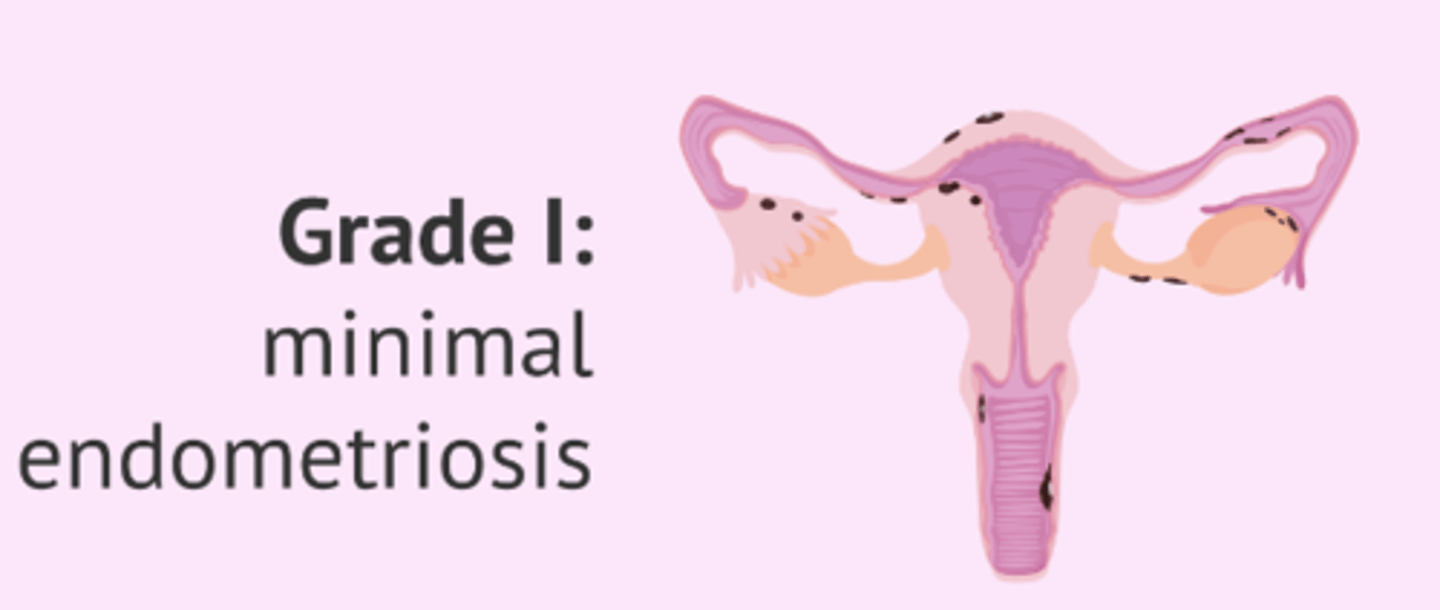
grade 2
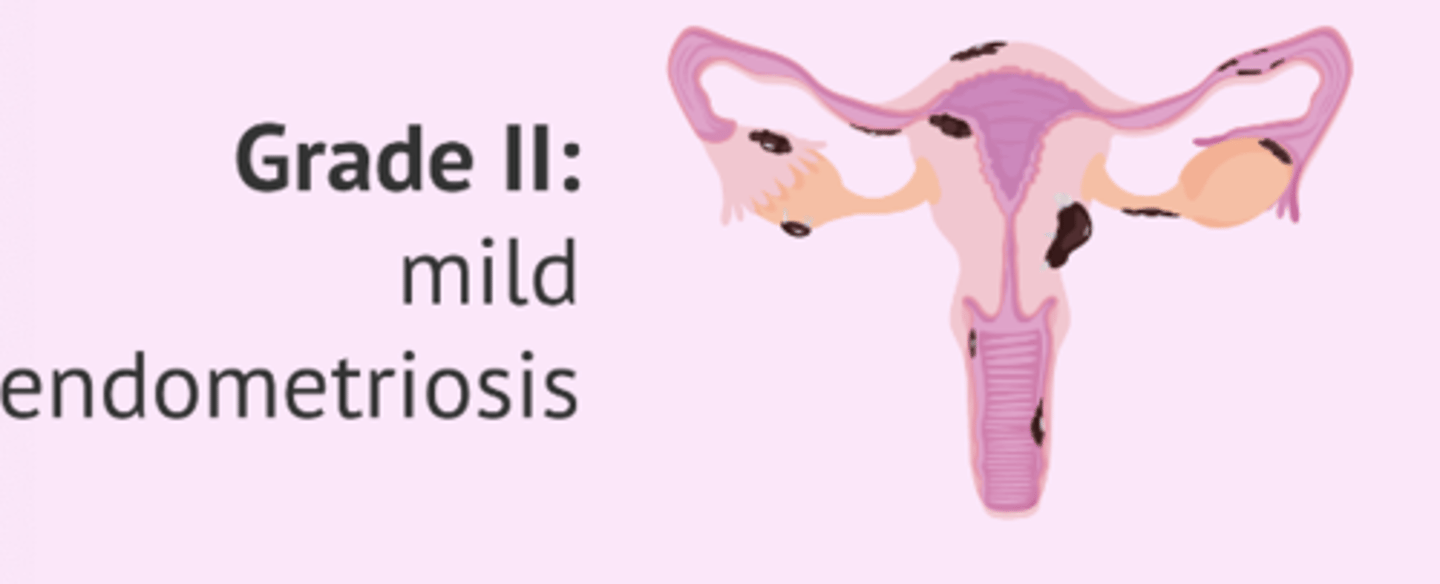
grade 3

grade 4
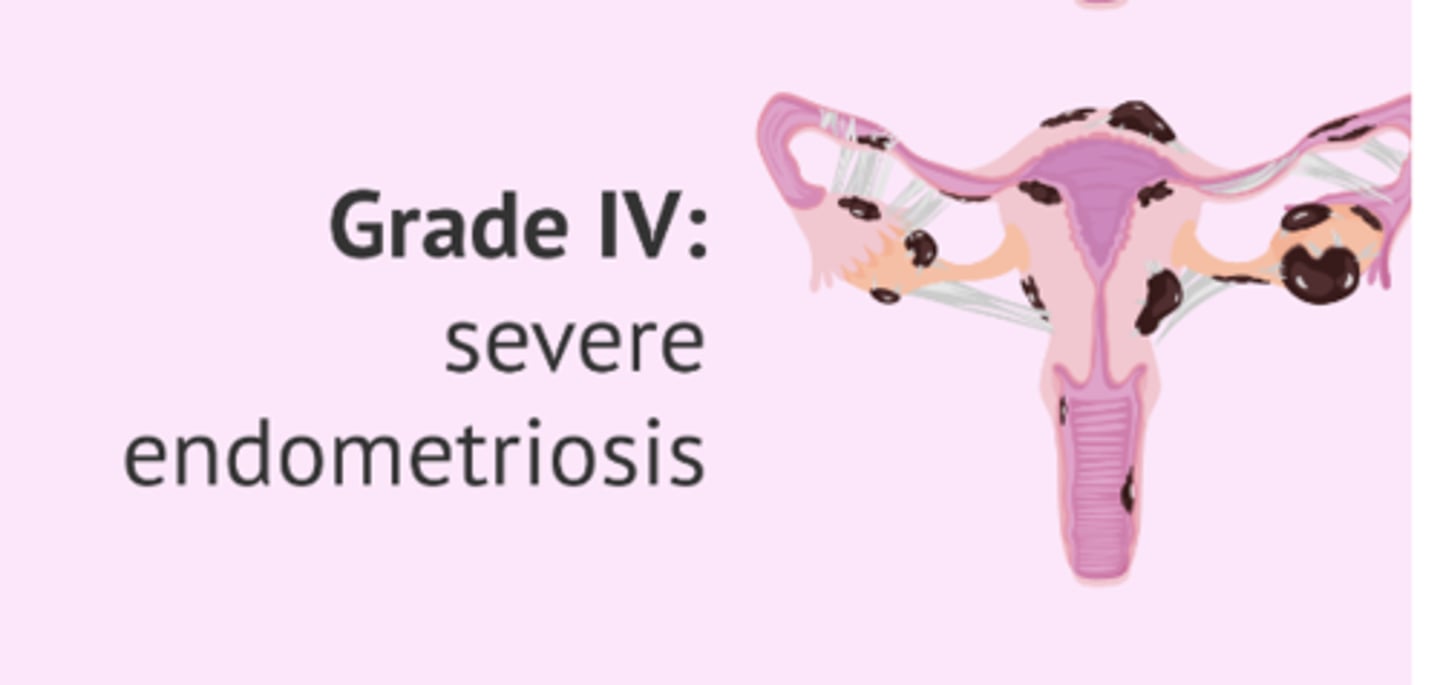
Can you still bleed with endometriosis
yes because those black things are big and can cause bleeding
-At the beginning of the menstrual cycle, when the lining of the uterus is shed and menstrual bleeding begins, endometriosis implants swell and bleed as well.
-In short, the person with endometriosis experiences several "mini-periods" throughout their abdomen, wherever this endometriosis tissue exists.
process of becoming pregnant begins where
fallopian tube, endometriosis can ruin tube causing infertilitry
egg becomes embryo
when its fertilized
endometriosis nursing management
-Education: make sure they understand issues
-Healthy lifestyle habits
-Support groups
infertility can be 2 types
primary or secondary
how does culture go with infertillity
-Cultural expectations for reproduction
-Impact of culture, ethnicity, and religion on perceptions and management of infertility
risk factors for infertility
-Multiple known and unknown factors affecting fertility
-Male and female risk factors
male risk factors
-mumps can cause them to become sterile
-injury
-testicular cancer
therapeutic managagement of infertility
drugs or surgery
how do we assess infertility
-male factor assessment
-female factor assessment
-lab/diagnostic tests
-drugs and alcohol
male factor assessment
-semen analysis
-sexual characteristics
-external and internal reproductive organ examination
-digital prostate examination
female factor assessment
-ovarian function
-pelvic organs
Laboratory and diagnostic testing
-home ovulation predictor kits
-clomiphene citrate challenge test
-hysterosalpingogram
-laparoscopy
hysterosalpingogram
-checks uterus and fallopian tube
-shoot dye that contrasts female organs
-laying in lithotomy position and the table moves
-they want to make sure dye flows through both tubes and uterus
-done by a maternal fetal specialist OBGYN
-done when your ovulating or about to ovulate
NURSING MANAGEMENT OF INFERTILITY
-Respect for couple
-Education
-anticipatory guidance
-stress management
-counseling
-Assistance in decision-making; advocacy
-Assistance with financial strategies
selected treatment options for infertility
-table 4.3
-donor eggs
-donor sperm
contraception behavioral methods
-Abstinence
-Fertility awareness
-Withdrawal (coitus interruptus)
-Lactational amenorrhea method
Fertility Awareness Methods
• Cervical mucus ovulation method
• Basal body temperature
• Symptothermal method
• Standard days method: im busy
withdrawal
pull out
-Lactational amenorrhea method
your mind thinks there is a baby you dont ovulate as you should, some do ovulate when they breast feed and get pregnant right after having a baby
-dont get period while breast feeding but still ovulate
basal body temp is spiked higher during
ovulation
contraception barrier methods
-Condoms
-Diaphragm
-Cervical cap
-Contraceptive sponge
condoms are ______
99.9 percent effective
-can break, or tear
internal condom
-flexible ring
-female
internal condom is ____
95% effective
diaphragm
-reusable dome made of silicone that covers cervix
-does not stop from STI
-similar to cap
after missing one day of birth control what do you do
double up
after missing 2 days of birth control what do you do
-back up methods
-you missed the hormones and your body thinks its free
CONTRACEPTION: HORMONAL METHODS
-Oral contraceptives
-Injectable contraceptives
-transdermal patches
-Vaginal rings
-Implantable contraceptives
-Intrauterine contraceptives• Emergency contraception