Cheat Sheet 2: Cells & Organelles
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Nucleus
Contains DNA; coordinates cell activities.
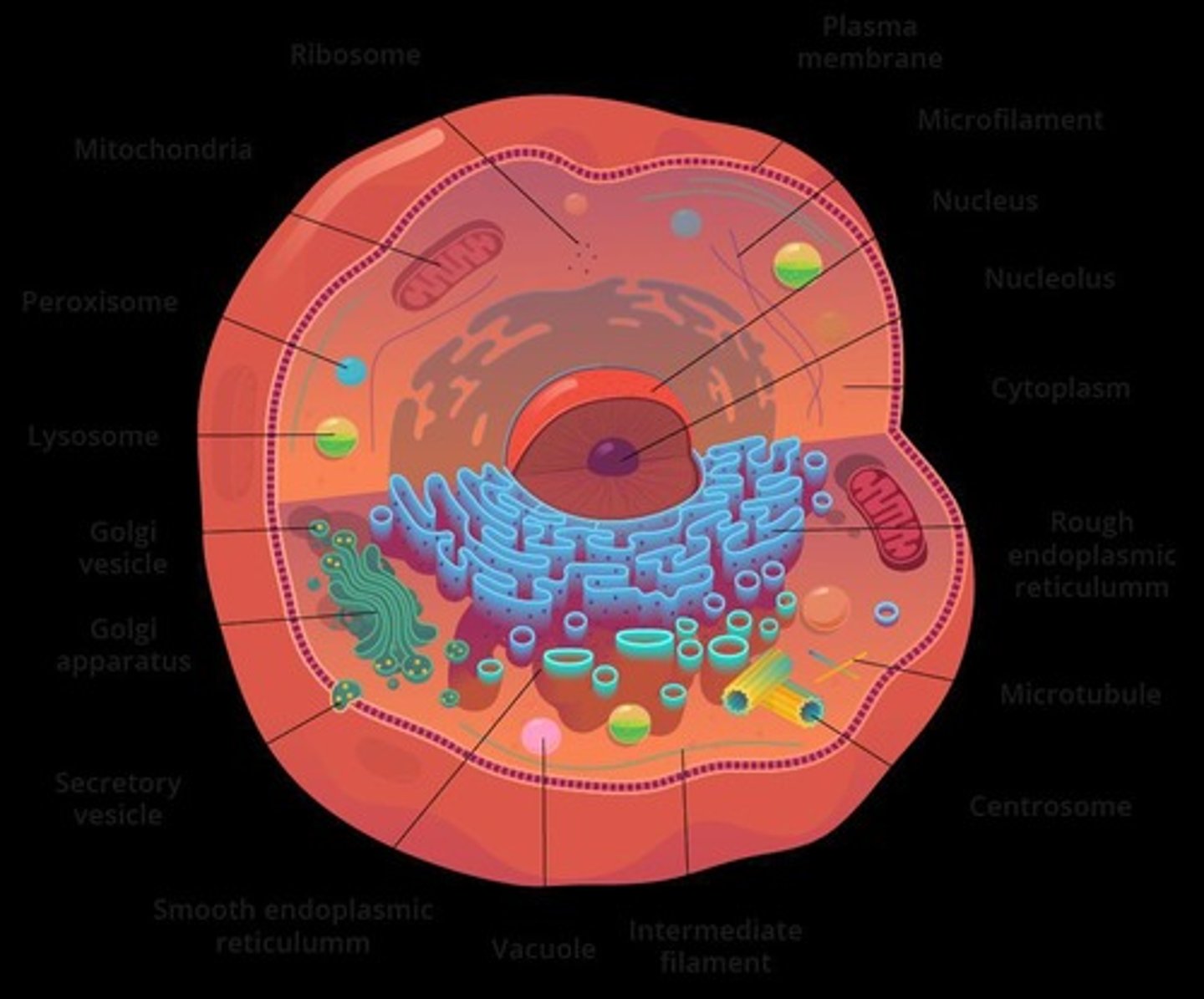
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes and stores proteins; has ribosomes.
Cytoskeleton
Provides mechanical support and cell movement.
Extracellular Matrix
Binds adjacent cells; primarily collagen.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Synthesizes lipids and steroid hormones.
Nucleolus
Site of ribosome synthesis (rRNA).
Microtubules
Composed of tubulin; supports cell structure.
Centrioles
Develop spindle fibers for cell division.
Cilia
Short extensions for cell movement.
Flagella
Thread-like extensions for cell motility.
Cytoplasm
Fluid area for metabolic activities.
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies and packages proteins for export.
Lysosomes
Break down waste and cellular debris.
Mitochondria
Produces ATP; site of fatty acid catabolism.
Peroxisomes
Break down fatty acids and detoxify.
Vacuoles
Membrane-bound vesicles for material transport.
Ribosomes
Made of rRNA; synthesize proteins.
Cholesterol
Regulates fluidity of the cell membrane.
Passive Transport
Movement without ATP; down concentration gradient.
Active Transport
Uses ATP to move substances against gradient.
Endocytosis
Process of engulfing substances into the cell.
Membrane Proteins
Facilitate transport across the cell membrane.
Junctions
Connect cells; includes tight and gap junctions.
Hypertonic
Higher solute concentration outside cell. Causes cell to shrivel
Hypotonic
Lower solute concentration (distilled water), causes cell to burst.