A&P Vocabulary Flashcards: Directional Terms, Cavities, Planes, Organ Systems, Microscope, and Tissues
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering directional terms, body cavities and membranes, quadrants/regions, planes, organizational levels, organ systems, microscope parts, and tissue types.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Anterior (Ventral)
Toward the front of the body.
Posterior (Dorsal)
Toward the back of the body.
Superior (Cranial)
Toward the head (top).
Inferior (Caudal)
Toward the tail or lower part.
Proximal
Closer to the point of origin, usually the trunk.
Distal
Farther from the point of origin, usually the trunk.
Medial
Closer to the midline of the body.
Lateral
Farther from the midline; toward the outer side.
Superficial
Closer to the surface.
Deep
Farther below the surface.
Dorsal body cavity
Cavity subdivided into the cranial cavity and the vertebral (spinal) cavity.
Cranial cavity
Houses the brain.
Vertebral (spinal) cavity
Houses the spinal cord.
Ventral body cavity
Divided by the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity.
Thoracic cavity
Contains mediastinum and pleural cavities.
Mediastinum
Contains esophagus, trachea, bronchi, and heart.
Pleural cavity(s)
Cavities that contain the lungs (pleura covers lungs).
Pericardial cavity
Encloses the heart.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Divided into abdominal and pelvic cavities.
Abdominal cavity
Contains digestive organs.
Pelvic cavity
Contains urinary bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum.
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
the upper right quadrant of the four abdominal quadrants
Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
the upper left quadrant of one of the four
Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
lower right abdominal quadrant
Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
the left lower abdominal quadrant
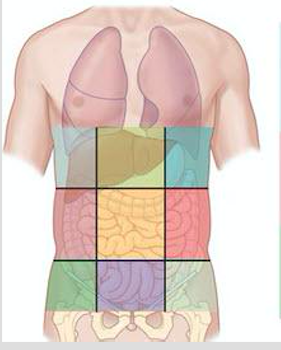
Right hypochondriac region
One of the nine abdominal regions (top-right).
Epigastric region
Upper central abdominal region.
Left hypochondriac region
Top-left abdominal region.
Right lumbar region
Middle-right abdominal region.
Umbilical region
Central abdominal region around the navel.
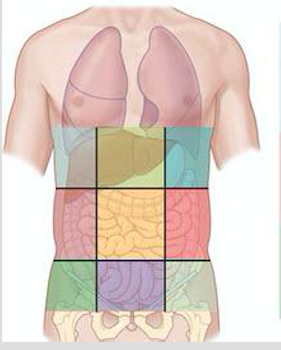
Left lumbar region
Middle-left abdominal region.
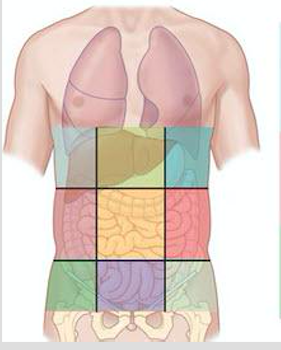
Right iliac (inguinal) region
Lower-right abdominal region.
Hypogastric (pubic) region
Lower central abdominal region.
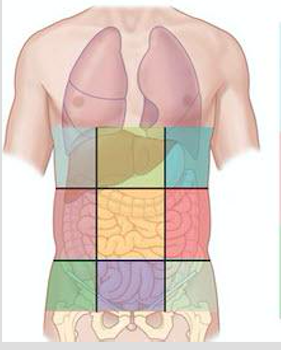
Left iliac region
Lower-left abdominal region.
Right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac (nine regions)
Top row regions of the nine-region grid.
Frontal (coronal) plane
Divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts.
Sagittal plane
A plane parallel to the body’s longitudinal axis; divides into right and left parts.
Midsagittal (median) plane
Divides the body into equal right and left parts.
Parasagittal plane
Divides the body into unequal right and left parts.
Transverse plane (cross sections)
Perpendicular to the body's longitudinal axis; divides into superior and inferior parts.
Chemical level
The smallest level; atoms and molecules.
Cellular level
Levels formed by groups of molecules making cells.
Tissue level
Two or more cell types plus extracellular matrix combining to form tissues.
Organ level
Two or more tissue types form an organ with a recognizable function.
Organ system level
Two or more organs working together for a broad body function.
11 organ systems
Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular, Nervous, Endocrine, Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary (and often Reproductive in many lists).
Integumentary system
Protects the body, produces vitamin D, retains water, regulates temperature.
Skeletal system
Supports the body, protects organs, provides leverage, produces blood cells, stores calcium.
Muscular system
Produces movement, controls openings, generates heat.
Nervous system
Regulates body functions; enables sensation, movement, automatic functions, higher mental activity.
Endocrine system
Regulates body functions via hormones.
Cardiovascular system
Pumps/delivers blood, transports substances, removes wastes.
Lymphatic system
Returns excess tissue fluid to the blood; provides immunity.
Respiratory system
Delivers oxygen to the blood and removes CO2; maintains acid-base balance.
Digestive system
Digests food, absorbs nutrients, removes waste; maintains fluid/electrolyte balance.
Urinary system
Removes metabolic wastes; maintains fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance; stimulates blood cell production.
The Microscope: Head
Upper part that supports ocular and objective lenses.
Base
Broad, flat, lower part that supports the instrument.
Arm
Vertical part connecting head to base.
Ocular lenses
Lenses in the eyepieces; magnify 10x typically.
Monocular/Binocular
Monocular has one ocular lens; binocular has two.
Ocular magnification
Usually 10x.
Objective lenses
Magnifying lenses on the rotating nosepiece; common: 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x.
Rotating nosepieces
Link objective lenses to head; rotate to switch lenses.
Mechanical stage
Flat stage where the slide sits, moved by knobs.
Condenser
Concentrates light on the specimen; adjusted with a knob.
Iris diaphragm lever
Regulates light entering the condenser.
Focus knobs
Coarse adjustment moves stage in large steps; fine adjustment for precise focusing.
Substage light
Light source under the stage; brightness controlled by a knob.
Ocular lenses magnification
Typically 10x.
Objective lenses magnifications
4x (scanning), 10x (low power), 40x (high power), 100x (oil immersion).
Tissue
Group of cells similar in structure and function.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Polarity
Epithelial cells have apical and basal surfaces.
Specialized contact
Cells form sheets with specialized junctions.
Basement membrane
Connective tissue layer that anchors epithelial cells to underlying tissue.
Avascular
Lacks its own blood supply.
Highest mitotic rate
Epithelium regenerates quickly.
Connective tissue
Protects, supports, binds, and transports; contains a matrix and cells.
Matrix
Noncellular, nonliving material between cells; may be liquid, gel, or solid.
Fibers
Collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers in the matrix.
Ground substance
Fluid components and proteoglycans in the matrix.
Highly vascularized
Most connective tissue has good blood supply (except cartilage and poorly vascularized tendons/ligaments).
Cartilage (avascular)
Cartilage has no direct blood supply.
Tendons and ligaments (poorly vascularized)
Connective tissues with limited blood supply.
Muscle tissue
Cells are elongated and specialized for contraction.
Myogenic
Contract without nervous input.
Neurogenic
Require nervous system input to contract.
Voluntary control
Contractions under conscious control.
Involuntary control
Contractions not under conscious control.
Nervous tissue
Transmits impulses; contains neurons and neuroglia.
Neurons
Nerve cells that receive and transmit impulses.
Neuroglia
Supportive cells that protect, nourish, and insulate neurons.
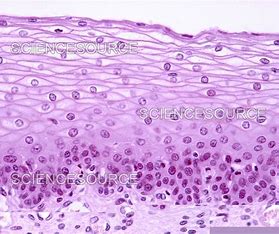
Subcategories of Epithelium: Shape - Squamous
Flattened epithelial cells.
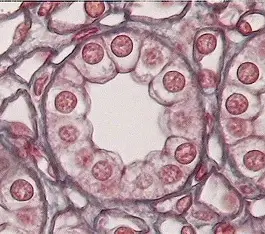
Subcategories of Epithelium: Shape - Cuboidal
Cube-shaped epithelial cells.
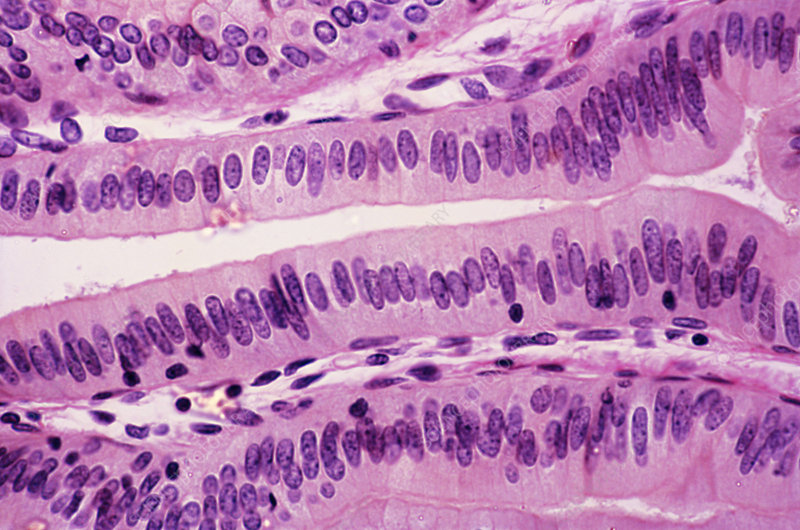
Subcategories of Epithelium: Shape - Columnar
Tall, column-like epithelial cells.
Subcategories of Epithelium: Layers - Simple
Single cell layer.
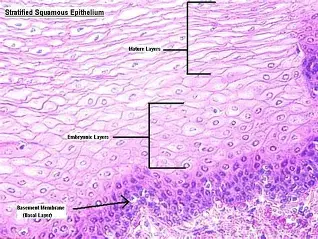
Subcategories of Epithelium: Layers - Stratified
Two or more cell layers.
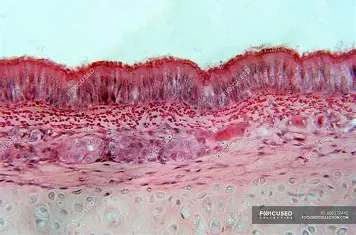
Subcategories of Epithelium: Layers - Pseudostratified
Appears multi-layered but is a single layer; may be ciliated.
head region
cephalic