RSM100 Midterm 1: Study
1/346
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
347 Terms
What is a Business
All profit seeking activities and enterprises that provides goods and services necessary to an economic system
How does businesses improve the standards of living?
Drives the economy, nation’s engine for economic growth and prosperity, countries depends on the wealth businesses generate (income for businesses, employees, + taxes to governments)
To succeed a business must..
know what their customers want and supply it quickly and efficiently
Products firms produce reflects:
changes in consumer tastes and promotes technology and other changes
“When a business succeeds, everybody wins” because
they organize resources, know-hows, and finances for new technologies, medicinal breakthroughs, environmental improvements etc.
Key for long term success + growth of a business
flexibility: ability to change with times and marketplace
Every Business has what type of Interaction?
One between a buyer and seller
The reward for people who take on the risk of business is..
Profits
Profits serve as an ____ to start and maintain businesses
Incentive
Quest for profit =
central focus of business
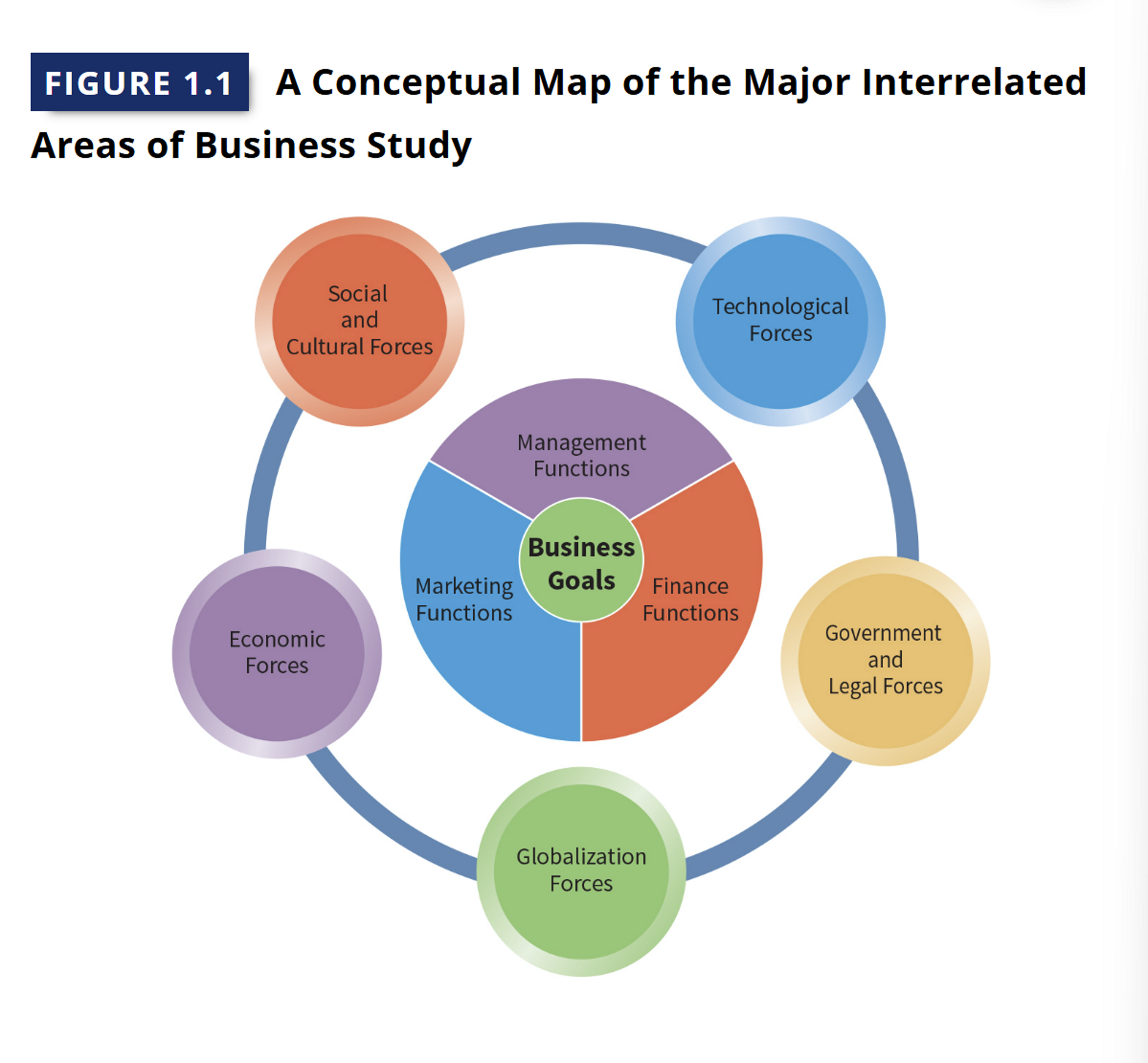
Functional Areas of Business Activity (3)
Management: planning organizing resources to achieve goals (sales, profits)
Marketing: handling customers, building long term relationships, understanding concern and buying behavior
Financial: accounting process, keeping financial records, documents for analysis and use, knowing product sales behavior is critical info with pricing
Non-profit Organizations place what above profits?
Public Service
The Two Types of Non-profits
Private Sector
Public Sector
Examples of Private Sector Non-profits
museums, libraries, charitable organizations
Examples of Public Sector Non-profits
government agencies, political parties, labor unions
How many Non-profits are there in Canada, their revenue, and jobs they provide?
160 000 non profits with $112 billion revenue, 2 million job and 2 billion volunteer hours
Economic requires ___ inputs for successful operations
Four basic inputs: Factors of Production
What are the 4 Factors of Production
Natural resources
Capital
Human resources
Entrepreneurship
**Government must make sure these inputs are good and exist for economies to reach full potential
Factors of Production: Natural Resources Definition
All production inputs useful in their natural states, therefore places with more natural resources have an economic advantage
Factors of Production: Natural Resources Examples
Agricultural land, building sites, forests, water, mineral deposits
Factors of Production: Capital Definition (4 types)
Technology, tools, information, and physical facilities
Technology helps companies operate and improve products —>
To be competitive firms need to continuously acquire, maintain, and upgrade its capital (needs $$)
Factors of Production: Human Resources Definition
Anyone who works, inputs physical labor and intellectual effort
companies rely on employee idea, innovation, and physical inputs
Talents employees are harder to acquire than smth like technology, can be your best assets
Factors of Production: Entrepreneurship definition
Willingness to take risks to create and operate a business
Entrepreneurs sees opportunities to make profits and create plan to earn those profits successfully
Most business activities are about..
securing four-key inputs or developing substitutes
Canadian Businesses operate on an economic system called..
the private enterprise system/capitalism
the type of economic system a business is in affects patterns of resources they use
No business operates completely freely on its own it:
operates within larger economic system of rules + constraints, directs how goods and services are produced, distributed, and consumed
Characteristics of a Private Enterprise System/Capitalism (4)
rewards firms meeting and identifying consumer demands
minimal government interference needed
businesses that meet consumer = gain access to necessary means of productions and profits
success depends on business and ppl involved
Who and What: Adam Smith
Father of Capitalism
Invisible Hand Concept
the economy is regulated by the “invisible hand”
The basic principle of the private enterprise system
that being, competition (the battle among businesses for consumer acceptance
Benefit of Competition
competition forms the best possible products and prices as less efficient firms are driven out
Competitive Differentiation
Unique combo of organization abilities, products, and approaches, sets companies apart
Combining Business and Tech in Fashion: Nordstrom
set up a tech lab with IT professionals to coming up with innovative ideas to change the way customers chop
TextStyle: messaging app between salesperson and customers
known for outstanding service + tech integration (competitive differentiation)
Basic Rights in the Private Enterprise System (4)
1) Private Property
2) Profits
3) Right to Freedom of Choice
4) Right to fair competition
Basic Rights in the Private Enterprise System: Private Property
right to own, use, buy, sell, and hand down property (land, buildings, patents, possessions and intangible properties
Basic Rights in the Private Enterprise System: Profits
right to all after-tax profits earned through activities, legally and ethically entitled to any income greater than costs
Basic Rights in the Private Enterprise System: Freedom of Choice
maximizes individual wealth by providing options
citizens choose own employment, purchases, investments
able to change jobs, choose amongst difference brands for goods + service, etc.
Basic Rights in the Private Enterprise System: Fair Competition
public sets rules for competitive activity, CAD gov. passed laws to prohibit excessively aggressive competitive practices designed to remove competition
the following is illegal (price discrimination, fraud in financial markets, deceptive advertising and packaging)
All Parties can’t be satisfied with gov. decisions: Canadian Radio Television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC)
increased costs to charged to small internet service providers buying access to larger ISP networks of Bell, Bell Aliant
allowed larger ISPs to control network traffic
began charging “usage based bills”
smaller ISPs, forced to introduce limits and charge more, ended competitive advantage over larger ISPs which typically charge more for high volume users
Smaller ISP complained, compromise pricing model was introduced but.. limits usuage but allows them to unlimited use packages to the demanded
complicated marketplace
Canada pays among the highest cellphones rates in the world, 13x higher than France
Canadian economy depends on small businesses for..
growth and strength
of all new businesses created in Canada, 99% are small businesses
98% of businesses in Canada are small businesses (1.2 million)
Entrepreneurship can.. (3)
create jobs and sells products
leads to innovation (less competitors, more flexible)
bring values existing companies with enhanced flexibility, improved innovation, new market opportunities (exp: Apple gets entrepreneurships to design stuff for them)
Canada’s largest technology hub
Toronto-Waterloo Corridor, 100km, 200 000 employees, 15 000 tech. companies, 5 000 recent start ups
Seven Eras on the History of Business
1) Colonial Period (1600s-1700s)
2) Industrial Revolution (1750s-mid-1800s)
3) Age of Industrial Entrepreneurs (late 1800s)
4) Production Era (late 1800s-1920s)
5) Marketing Era (1930s-1950s)
6) Relationship Era (late 1900s-today)
7) Social Era (2000s today)
Seven Era in the History of Business: Colonial Period
rural and agricultural production, small towns
marketplaces of farmers an craft men
Economic focus: rural area, output of farms = success
British investors provided money to developed North American business system —> trade of furs, fish, old-stock large timber —> sought in Europe —> close relationships with Indigenous people (North West Company, Hudsons Bay)
Seven Era in the History of Business: Industrial Revolution
factory system, mass production from numerous skilled workers (improved production through limiting workers to specific tasks)
savings from large-scale production (raw material cheaper in larger quantities), increase machine use
England industrialization —> Canada
mechanized agriculture, factories in cities
railroads opened up transported goods and people
Seven Era in the History of Business: Age of Industrial Entrepreneaurs
Industrial revolution created opportunities for entrepreneurship in Canada
new production methods, + commercially useful products
Alexander Graham Bell + Bell Canada
Eli Whitney: interchangeable parts —> mass productions
entrepreneurship raised living standards, boosted demand for manufactured goods
Alexander Graham Bell (Industrial Entrepreneurs)
Alexander Graham Bell + Alexander Melville Bell + Reverend Thomas Henderson
(1877) short-distance telephone services between office buildings + warehouses
Later became Bell Canada Inc.
Seven Era in the History of Business: The Production Era
↑ demand for manufactured goods
business focused more on production activities
work: more specialized, huge, labor intensive
Henry Ford: assembly lines
new managers: produce goods at higher efficiency + speed
marketing was rare, focus on internal processes, not much focus on what customers wanted/needed
businesses decided what products were available for purchase
Seven Era in the History of Business: The Marketing Era (1930s - 1950s)
Great Depression of early 1930s
incomes drop, business can’t sell supply —> managers paid more attention to markets —> sales and marketing = important
atp: selling = marketing
After WW2 —> demand + consumerism grew, competition increased
Marketing is now more than just selling —> designing products to meet needs (consumer orientation)
Consumer Orientation
a business philosophy that focuses on the unmet wants + needs of consumers, produces to meet those needs
The Marketing Era Introduced Branding which is..
process of creating in consumer’s minds an identity for a good, service, or company
important marketing in contemporary business
a brand can be a name, term, sign, symbol, design, or combination that identifies products/firms
Transaction Management
transaction management: building and promoting products so customers buys products and cover costs + generate profits
Seven Era in the History of Business: Relationship Era (late 1900s - today)
actively promote customer loyalty
long-term customers: reduces advertising and sales costs + customer spendings increase over time = firms revenue grow + understand what they want and prefer = increased chance of competitiveness
age of connections between customers, employer employees, technology + manufacturing, separate companies —> interconnectedness, people expand internationally
new techniques for managing networks of people, businesses, information, tech.
Seven Era in the History of Business: The Social Era (2000s - Today)
new approach to interaction, connection, communication, and exchange of info. w virtual communities + networks
organizations create value though connections with groups or networks of people with similar goals and interests (immense opportunities thru use of technology for relationship maintenance)
Social media: social-professional networks (LinkedIn), blogs, picture sharing platforms, content communities —> mobile strategies using real-time data and location —> market research, communications, sales promotions, loyalty programs, etc.
Current Trends Related to Business (3)
partnerships between businesses = taking full advantage of available opportunities —> strategic alliance
aging population, those with experience and expertise are retiring
more diverse workforce —> more effective performance + better solutions
Strategic Alliance
partnership between organization to create a competitive advantage for the businesses involved
Oursourcing
hiring external company to handle task, produce goods, or provide services that were previously done in-house
who is doing the work?
Offshoring
relocating certain business operations or production to another country, usually because costs are lower there
where is the work done?
Nearshoring
Moving outsourced activities to a nearby country rather than one far away
outsourcing closer geographically and culturally (sometimes)
Changes in the Workplace (3)
increasing focus on collaboration (less individual work)
employees are less loyal to one company or would hold a position for their entire career
employers encourage teamwork, problem solving, innovation
Modern Managers must be
intelligent, motivated, capable of creating/sustaining a vision for organizational success
Qualities of Managers: Vision
ability to perceive marketplace needs and what an organization must do to meet them
exp: James Cameron with Titanic and Avatar
Danny Meyer: cult following for shake shack dining experience
Vision: Danny Meyer and Shake Shack
“enlightened hospitality”
warmer, friendlier, more engaging customer service experience
identify and serve needs and demands of customers: all-natural menu, great customer service
Qualities of Managers: Critical Thinking
Ability to analyze and assess information to pinpoint problems or opportunities
look at a variety of information, develop future-oriented solutions, draw connections between dissimilar information
Qualities of Managers: Creativity
capacity to develop novel solutions to perceived organizational problems
being able to see better and different ways of doing business
crisis calls for creative leadership
Creative Managers: Captain Chesley Sullenberger
guided US airways Flight 1549 to safe landing in Hudsons River
both engines quit after hitting birds on takeoff
quick thinking saved lives
Qualities of Managers: Ability to Lead Change
Business leaders must guide employees and organization through changes from tech., marketplace demands, global competition
managers must be skilled at recognizing employee strengths + motivating people towards common goals + able to make tough decisions
Sources for organizational change: External
feedback from customers, developments in the international marketplace, economic trends, new technologies
Sources for organizational change: Internal
new company goals, emerging employee needs, labor union demands, production problems
Business traits that bring upon admiration (5)
Businesses brings products and services that satisfy consumer needs in a socially responsible manner
solid profits,
stable growth
safe and challenging work environment,
high-quality goods and services,
business ethics and social responsibility
Business Ethics
standards of conduct and moral values involved in decisions made in the work environment
Social Responsibility
management philosophy that includes contributing resources to the community, preserving natural environment, developing or participating in not-for-profit programs that better society
Volkswagen Emissions Scandal
Second largest automobile manufacturer in the world behind Toyota
was “cheating on emissions tests”: placed in cars software’s that turn off emissions controls when driving normally and turns them on when the car is undergoing an emissions test
diesel cars were emitting up to 40x more pollution that allowed under US standards, when car recognizes its being tested, adjusts how car is running to reduce emissions to legal levels
Results of Volkswagen Emmissions Scandal
CEO abruptly resigned
Fines ($18 Billion penalties EPA) and lawsuits (criminal prosecutions)
11 million loyal customers loss
stock price drop 20%
Fortune Publications of Most-admired companies
yearly, US based firms
complied from surveys and research of the Hay Group (global human resources and organizational consulting firm)
Criteria: innovation. people management, use of corporate assets, social responsibility, quality of management, quality of products and services
Apple ranked #1 in 2022
Economics =
analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services, and the choices people and governments make in allocating scarce resources
affects all of us
Microeconomics
study of the behavior of small economic units, such as individuals, families and businesses in making decisions regarding allocation of limited resources
studies human decision and resource allocation
Heart of Business:
Interaction between buyer and seller
Buyer: need, want good/service willing to pay for it
Sellers: require exchange to earn a profit and stay in business
The Exchange Process Between Buyer and Seller involves
demand and supply
Demand
willingness and ability of buyers to purchase goods and services for sale at different prices
driven by price and consumer preferences
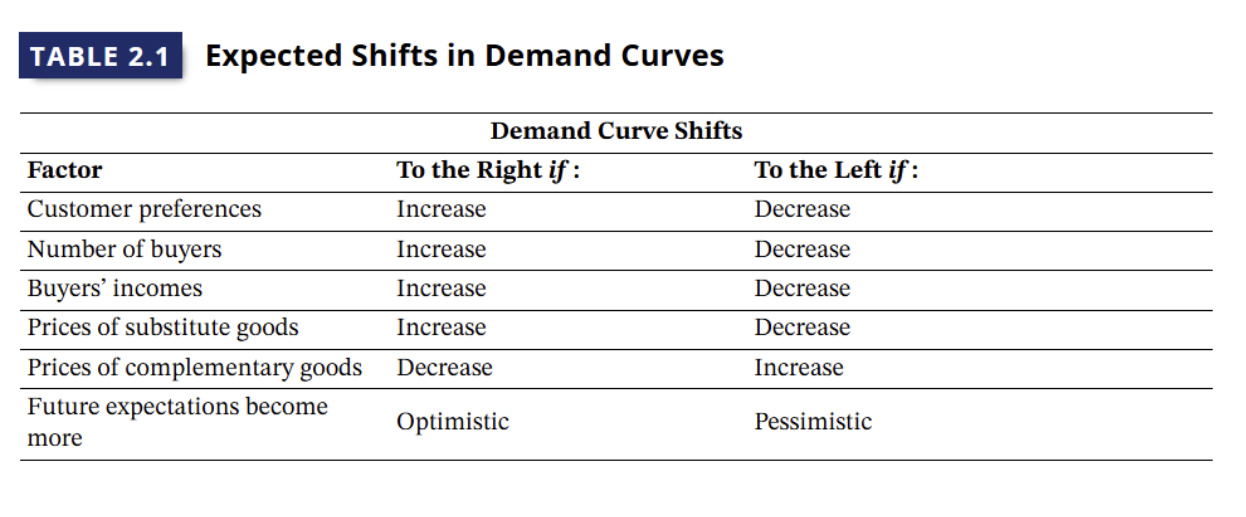
Demand is Affected by (5)
consumer preferences
incomes
prices of substitutes + complementary
number of buyers in the market
strength of the buyers future outlook
Any of these factors can produce a new demand curve
Demand Curve
graphs the amount consumers want to buy at different prices
typically slope downwards, signifying at lower prices consumers are willing to buy more
change in quantity demanded = movement along the curve
change in market demand = shift of curve
Supply
amount of goods and services for sale at different price
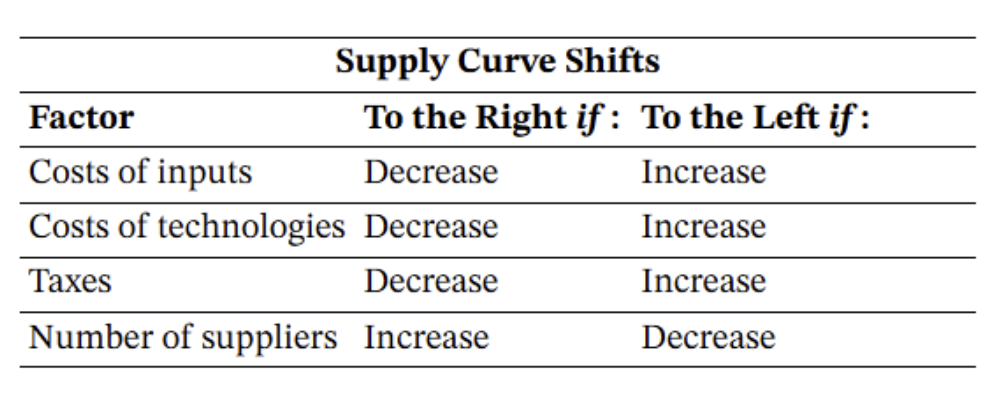
Factors Driving Supply
willingness and abilities of sellers to provide goods and services at different prices affected by:
costs of inputs
costs of technologies
taxes
number of suppliers
Economics Dilemma
what we want VS what we can afford
decide what to spend and save + what to spend on (which good? which service)
Macroeconomics
study of a country’s overall economic issues
how economy as a whole uses its resources and how government policies affect people’s standards of living
Macroeconomic issues
help shape the decisions made by individuals, families, and businesses
gross domestic product, unemployment rates, national income, inflation, price indexes
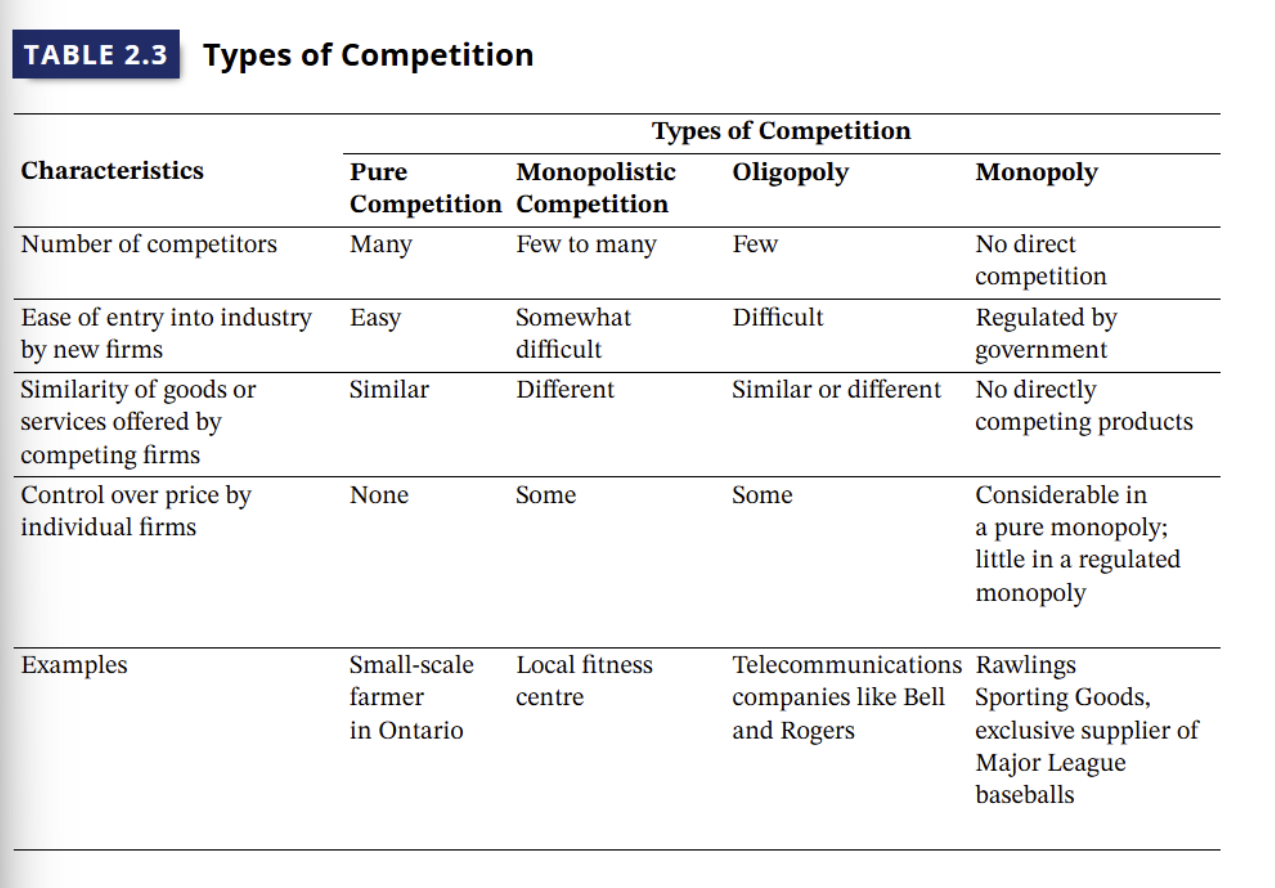
Types of Competition in a Private Enterprise System(4)
pure competition
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
monopoly
The Private Enterprise System also known as..
capitalism/market economy
rewards businesses for meeting the needs and demands on consumers
governments more hands-off
competition regulate economic life, creating opportunities and challenges for business people
Pure Competition
Large number of buyers and sellers exchange homogenous products, no on e has a significant influence on price
prices are set by the market, bc no one dominates
buyers see little difference between goods and services offered by sellers
Exp: agricultural products: wheats, grains
Monopolistic Competition
Large numbers of buyers and sellers exchange differentiated/heterogeneous products, sellers has some control over price of own goods/services
differentiates products bases on price, quality, etc.
Exp: Pet food, different flavors, prices, health benefits
Oiligopoly
Few sellers compete and high start up costs = barriers of entry for new competitors
some may offer similar products (steel), some not (cars, aircrafts)
limited number of sellers = more firm control over price
competitors usually sell at similar prices, price cuts by one firms are met by competitors
prices may vary between markets (e.g. geographically)
Monopoly
Single seller dominates trade in a good or service, buyers have no close substitutes
firm has such unique characteristics, no other can enter
full price control
many companies have short-term monopolies (google, FaceBook)
lacks benefits of competition —> regulated by governments
How Canadian Government Regulate Monopolies
issues patents for new applications
limits lifes of patents
pure monopolies are illegal (Antitrust legislation: Competition Act)
now allowing big companies to merge
some monopolies are allowed, given government regulation
Regulated Monopoly
local, provincial, or federal government grants exclusive rights in a certain market to a single firm, a monopoly heavily controlled by the government
pricing decisions controlled by regulatory authorities
Ontario Energy Board sets electricity and natural gas rates
Deregulation of Regulated Monopolies
starting 1980-1990s by US gov.
transportation, energy, and communications industries
idea: increased competition to improve customer service and reduce prices
Not as followed in Canada
Planned Economy
gov. controls determine a businesses ownership, profits and resource allocation to accomplish government goals rather than those set by individual firms
Two Forms of a planned economy
communism
socialism
Socialism
characterized by government ownership and operation of major industries (energy, communications)
argue major industries are too important to a society to be left in private hands, governement better serves interests
allows private ownership in less crucial industries (retail, resturants)
Exp: Denmark, Sweden, Finland, some African Nations, India
Communism
all property shared equally by people in community under the direction of a strong central government
K