Clinical Bacteriology - Laboratory - Isolation of Pure Culture of Organisms
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Pure culture technique
This culture technique is done to identify the etiologic species/causative agent of a certain disease in a patient.
Pure culture technique
It will demonstrate how organisms grow as small distinct group in the medium. Small spots that occur in the medium present the growth of culture as distinct group.
Culture
act of cultivating or growing of organisms.
Pure culture
culture cultivating only a single species of organism.
Liquid
Broth
Liquid form of culture media
Agar
Solid form of culture media
Turbidity
What is the indication of the presence of bacteria in broth?
Colony
What is the indication of the presence of bacteria in agar?
Agar
It is the solidifying agent of solid culture media
It is not easily degraded by the microorganisms
Why do we use agar as our solidifying agent in solid culture media?
95°C or more
At what temperature does agar melt?
Below 50°C
At what temperature does agar solidify?
Colony
This is a bacterial population derived from a single bacterial cell (same genus and species)
Pure culture
What is the goal of isolating bacteria using culture media?
Pure culture
What culture is required for subsequent procedures used to identify and characterize bacteria?
Organism of interest
It is the organism we want to grow in the culture media
99.99%
When organisms from pure culture clone each other (asexual reproduction), how identical are the other organisms from each other?
Low
Pure culture multiplication rate (qualitative)
single
Pure cultures are composed of cells or microorganisms arising from a _x_ progenitor cells? (How many?)
Colony forming unit
CFU meaning
Colony forming unit
The progenitor from which a particular culture is derived
Aseptic technique
A technique performed under sterile conditions.
Streaking
It is the process of spreading the microbial culture with an inoculating needle on the surface of the media
Four quadrant streak plate method
Identify the setup
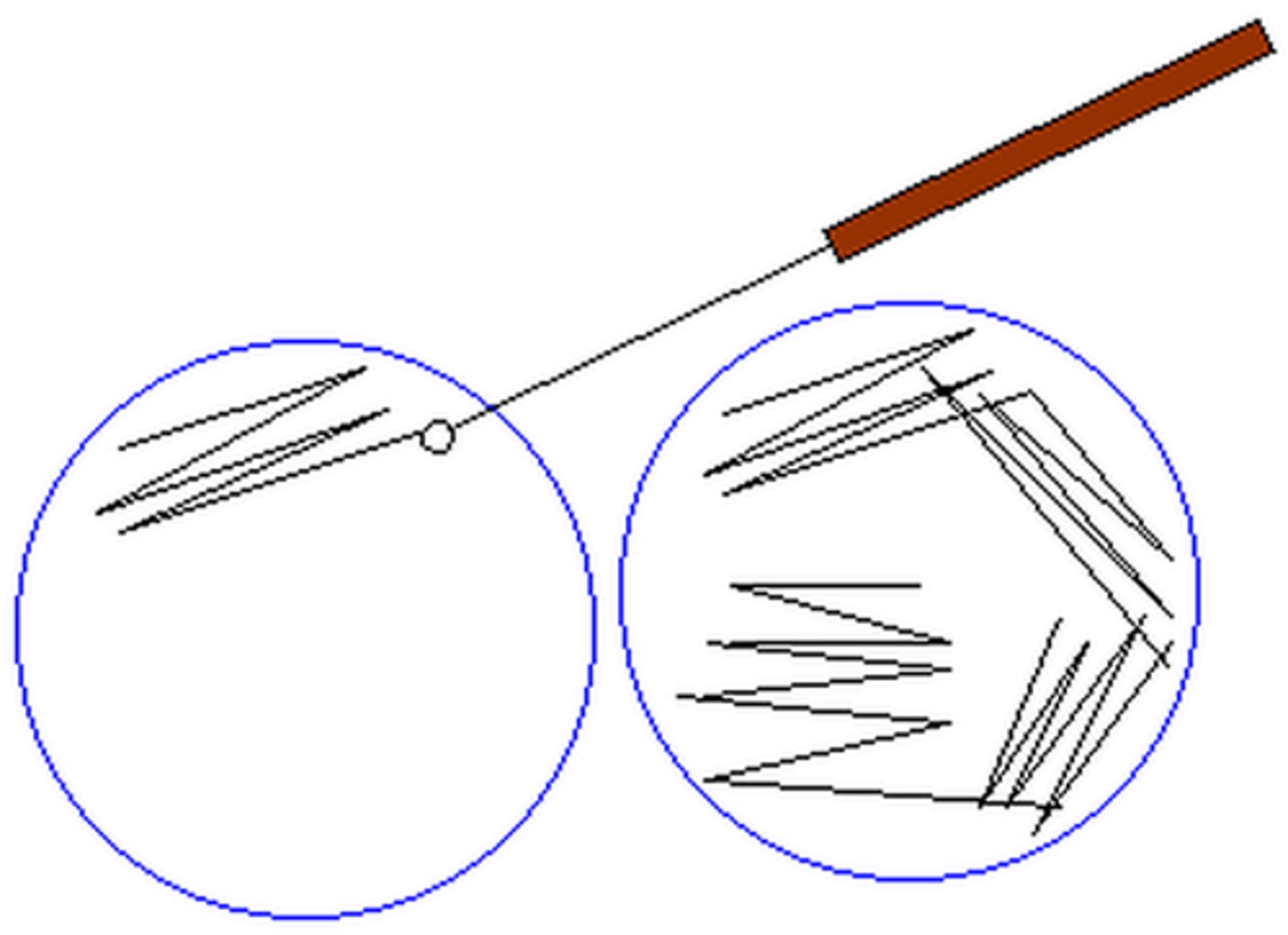
Qualitative
Four quadrant streak plate method: Qualitative or Quantitative?
To thin out inoculums to get separate colonies
What is the purpose of streaking the plate?
Four quadrant streak plate method
By streaking, a dilution gradient is established on the surface of the plate as cells are deposited on the agar surface.
Sterilized wire loop
What equipment is used to streak the bacterial suspension onto the agar?
Subculture
This is done by streaking well-isolated colonies from the primary streak plate to a new plate.
Nutrient agar
Enrichment and non-selective solid culture media
3
How many loopfuls of the bacterial suspension are placed onto the agar?
Petri dish
a shallow dish used to culture bacteria
1/4
How much of the agar plate do you streak for the 1st quadrant?
2-3
When streaking the 2nd quadrant, how many times do you touch the 1st quadrant?
2-3
When streaking the 3rd quadrant, how many times do you touch the 2nd quadrant?
1
When streaking the 4th quadrant, how many times do you touch the 3rd quadrant?
24-48 hours at 37°C
Incubation time and temperature
Heat in-between quadrants
In the hospital setting, when we receive mixed culture, what is done during the streaking of agar plates in order to prevent contamination growing on the plates?
Biosafety cabinet
What equipment is required to streak the agar with the petri dish cover fully opened? (Not slightly opened)
30 degrees
How many degrees should you rotate your
Heavy confluent growth
1st quadrant growth
Less dense growth
2nd quadrant growth
Weak growth
3rd quadrant growth
Isolated single colonies
4th quadrant growth
4th quadrant
Which quadrant is pure culture obtained from?
1st quadrant
Which quadrant has tight streaks and heavy growth?
2nd and 3rd quadrants
Which quadrants have decreased density but may still contain mixed culture?
4th quadrant
Which quadrant is used for the identification of organisms?
Sterile petri dish
It is where the serial dilution and melted nutrient agar are poured together
Melted nutrient agar
What is poured together with the serial dilution for the serial dilution pour plate method?
Serial dilution pour plate method
Identify the setup
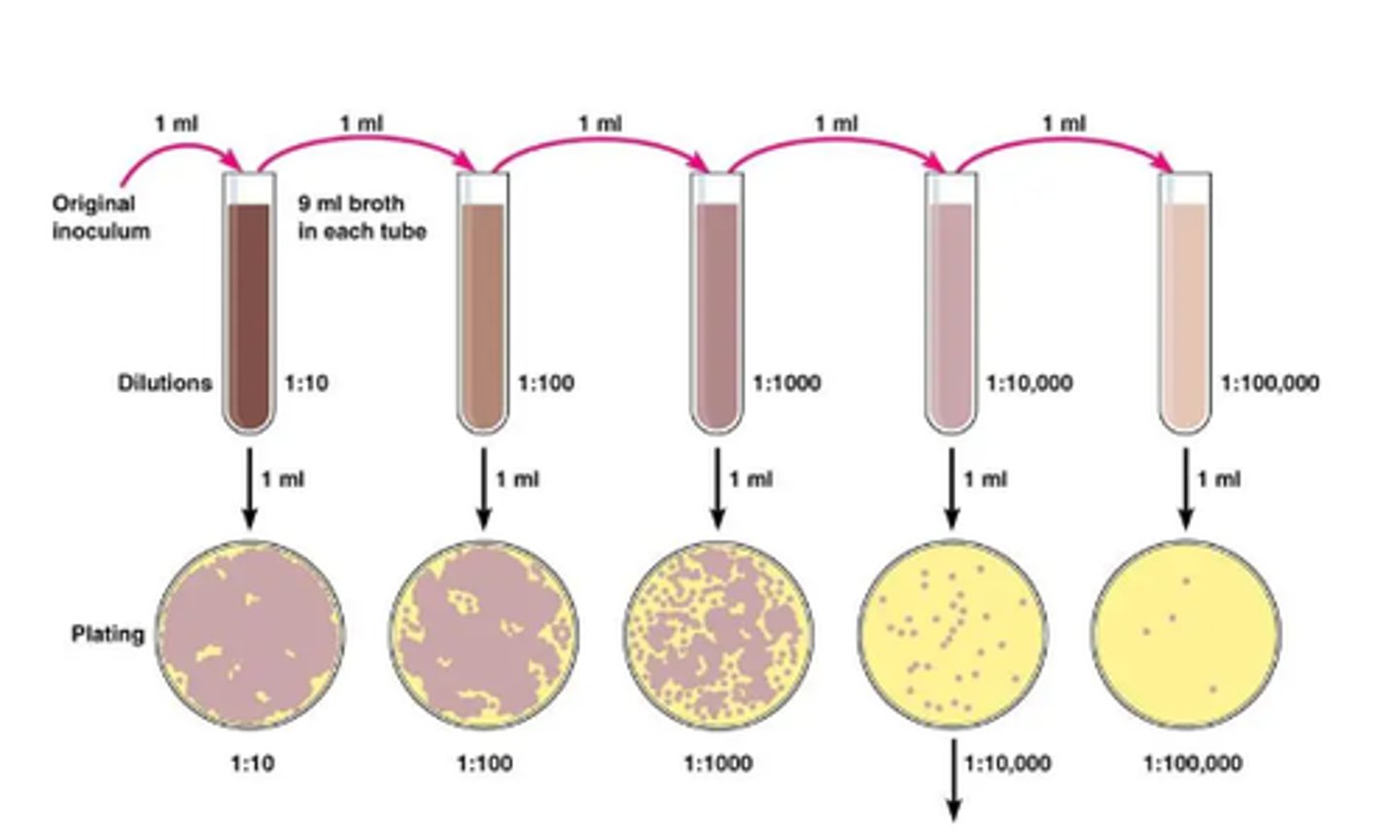
Quantitative
Serial dilution pour plate method: Qualitative or Quantitative?
Serial dilution pour plate method
In this method, the original sample is diluted several times, to reduce population sufficiently to obtain separate colonies.
Psychrophilic or cryophilic organisms
What organisms will not be able to grow using the serial dilution pour plate method?
Heat shock
What do the organisms in serial dilution pour plate method experience when mixed with melted nutrient agar?
45-50°C
At what temperature is melted nutrient agar maintained at?
1mL of inoculum, 9mL NSS
How is a 1:10 serial dilution made in a test tube?
1mL
What volume of bacterial suspension from the serial dilution is dispensed onto the serial dilution petri dish?
Quebec colony counter
What instrument is used to count colonies on the agar plate from the serial dilution plate?
1:10, 1:100, 1:1000
Which serial dilutions are "too numerous to count"?
1:10,000, 1:100,000, 1:1,000,000
Which serial dilutions produce single colonies on agar plates?
Pressure sensing device
Quebec colony counter principle
Felt-tipped pen
What equipment is used to count colonies on an agar plate on the Quebec colony counter?
Agar-side up
What is the orientation of the agar plate when it is incubated?
Moisture
What is the reason why an agar plate is incubated agar-side up?
Swirl on a flat surface
How is the 1mL bacterial suspension and melted nutrient agar mixed in the petri dish for preparation of the serial dilution plate?
Electronically
How do modern colony counters count colonies?
Felt-tipped pen
When counting colonies using the Quebec colony counter, what is used to mark the colony so that it is considered counted?
CFU/mL
Unit of measurement for colony count
Colony count x reciprocal of dilution
What formula (CFU/mL) is used for small number of colonies?
280,000 CFU/mL
Solve:
What is the colony count for a plate with 28 colonies on a plate of 1:10,000 dilution?
Colony count x reciprocal of dilution
What formula do you use for this situation?
Colony count: 15
Serial dilution of plate: 1:1,000,000
Average number of colonies in 5 squares x 62.5 x reciprocal of dilution sample
What formula (CFU/mL) is used for serial dilutions that are too numerous to count?
62.5
Which portion of the formula pertains to the area of the petri dish?
Average number of colonies in 5 squares x 62.5 x reciprocal of dilution sample
Colonial characteristics
It is the color, size, shape, surface appearance, changes in agar media, and odor of the colonies from the incubated agar plate.
Color
Which colonial characteristic refers to the pigmentation?
Size
Which colonial characteristic refers to the diameter?
Shape
Which colonial characteristic refers to the form, elevation, and margin?
Surface appearance
Which colonial characteristic refers to the appearance of the surface of the colony?
Changes in agar media
Which colonial characteristic refers to the changes resulting from bacterial growth?
Changes in agar media
Which colonial characteristic is not applicable to nutrient agar?
Odor
Which colonial characteristic refers to the smell?