Unit 7: The Cold War in America 4/28
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms

Battle of Dien Bien Phu
A significant battle in 1954 between the French forces and the Viet Minh, marking the end of French colonial rule in Indochina.
The battle culminated in a decisive victory for the Viet Minh, leading to the Geneva Accords and the division of Vietnam.

Draft Dodgers
Individuals who evaded military conscription during the Vietnam War, often by fleeing to Canada or seeking deferred status.
Their actions were often controversial and sparked debates about patriotism and obligation.

Agent Orange
A herbicide used by the U.S. military during the Vietnam War to eliminate forest cover and destroy crops, leading to severe health issues for veterans and local populations.
This chemical caused long-term environmental damage and health problems, including cancer and birth defects, impacting countless lives even years after its use.

Kennedy Doctrine
A foreign policy approach by President John F. Kennedy that aimed to contain communism in the Western Hemisphere, including support for anti-communist regimes and measures like the Bay of Pigs invasion.
A key component of U.S. foreign policy during the Cold War, focusing on the prevention of communism's spread in Latin America. The doctrine emphasized military aid to allied governments and interventions to support pro-U.S. regimes.

Alliance for Progress
A foreign policy initiative aimed at fostering economic development and political stability in Latin America during the Kennedy administration.
It promoted social reform and countered communism by investing in infrastructure, education, and health care.
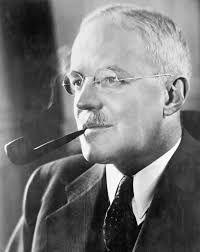
Allen Dulles
Director of the CIA from 1953 to 1961, instrumental in U.S. covert operations during the Cold War.
He played a significant role in the Bay of Pigs invasion and the Cuban missile crisis, shaping U.S. intelligence and foreign policy.

Cuban Missile Crisis
A 13-day confrontation in October 1962 between the United States and the Soviet Union over Soviet ballistic missiles deployed in Cuba, which brought the world close to nuclear war.
It highlighted the dangers of nuclear war and led to increased diplomatic communication between the US and the Soviet Union.

Mann Doctrine
The Mann Doctrine suggested that the U.S. would prioritize stable, pro-business governments over democratic reform, even if it meant supporting dictatorships that aligned with American economic interests.
This policy was seen as a departure from the Alliance for Progress, which had emphasized economic and social development in Latin America

National Sandinista Liberation Front
A Marxist political organization in Nicaragua that sought to overthrow the Somoza dictatorship and was influential in the Sandinista revolution.
A leftist revolutionary group in Nicaragua that led the uprising against the Somoza dictatorship in the late 20th century, promoting socialist policies and significant social reforms after coming to power.

Bay of Pigs
A failed invasion of Cuba in April 1961 by Cuban exiles, supported by the U.S. government, aiming to overthrow Fidel Castro's regime.
The invasion aimed to establish a anti-communist government in Cuba but resulted in a significant embarrassment for the Kennedy administration.

Salvador Allende
The first Marxist president of Chile, Salvador Allende served from 1970 until he was overthrown in a military coup in 1973.
He implemented socialist reforms and faced opposition from both domestic and foreign entities, leading to his eventual demise.

Augusto Pinochet
A Chilean military general who led the coup that overthrew Salvador Allende and ruled as a dictator from 1973 to 1990, known for his authoritarian regime and human rights violations.
Pinochet's government implemented neoliberal economic reforms and suppressed political dissent, leading to significant social and economic changes in Chile.

Rockefeller Report
A report issued in 1975 by the Rockefeller Commission that investigated the CIA's activities, including domestic espionage and controversial programs.
The report aimed to assess and address abuses of power within the CIA and restore public trust.
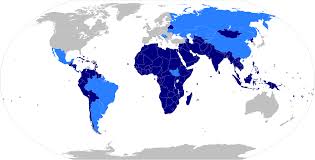
Non-Aligned Movement
An international organization founded during the Cold War that aimed to maintain independence from both the Western and Eastern blocs, promoting peace and cooperation among developing nations.
The Non-Aligned Movement seeks to provide a platform for countries that chose not to formally align with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact, advocating for sovereignty and mutual respect among nations.
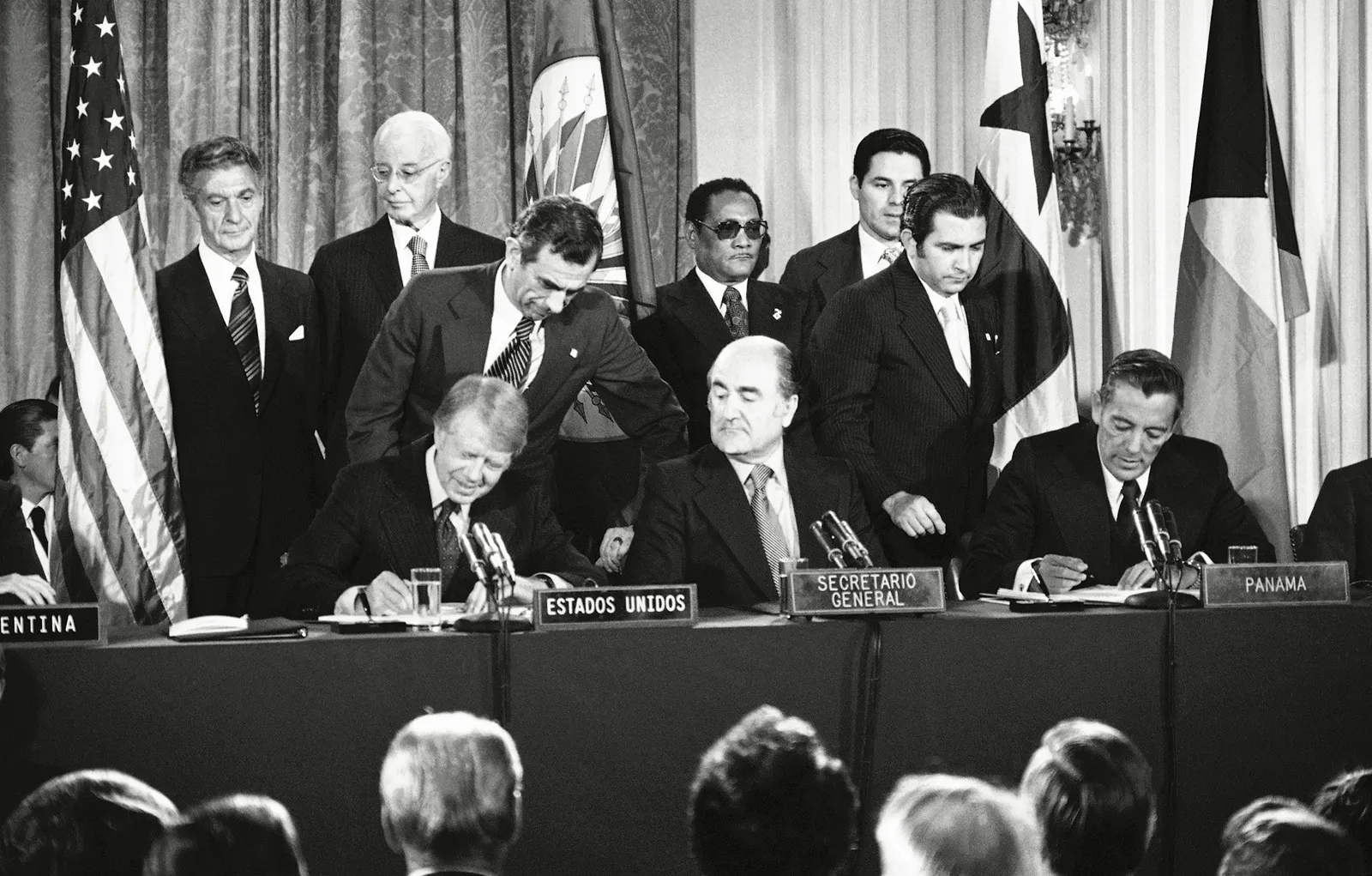

Panama Canal Treaties
Treaties signed in 1977 that stipulated the transfer of control of the Panama Canal from the United States to Panama by the end of 1999.
These treaties aimed to establish a framework for the gradual handover while ensuring the canal remained open to maritime traffic.

Gouzenko Affair
The Gouzenko Affair was a pivotal event in 1945 when Igor Gouzenko, a Soviet cipher clerk, defected to Canada and revealed extensive Soviet espionage activities in the West, effectively marking the beginning of the Cold War era.
The affair revealed Soviet espionage operations and heightened tensions, leading to increased suspicion and anti-communist sentiments in the West.

NORAD
A joint defense organization created in 1957 between the United States and Canada to monitor and defend North American airspace against potential threats, particularly from Soviet bombers during the Cold War.
NORAD is responsible for aerospace warning and control and provides vital defense capabilities for North America.

Fidel Castro
Cuban revolutionary leader who established a one-party socialist state in Cuba and became a central figure during the Cold War, particularly in relations with the United States.
He led the Cuban Revolution in 1959 and was a key ally of the Soviet Union, which brought Cuba into direct conflict with the U.S. during events like the Cuban Missile Crisis.

Che Guevara
A revolutionary figure and key ally of Fidel Castro in the Cuban Revolution, known for his role in promoting Marxist ideology and guerrilla warfare.
He played a significant role in the Cuban government and became a symbol of revolutionary movements worldwide, advocating for armed struggle against imperialism.
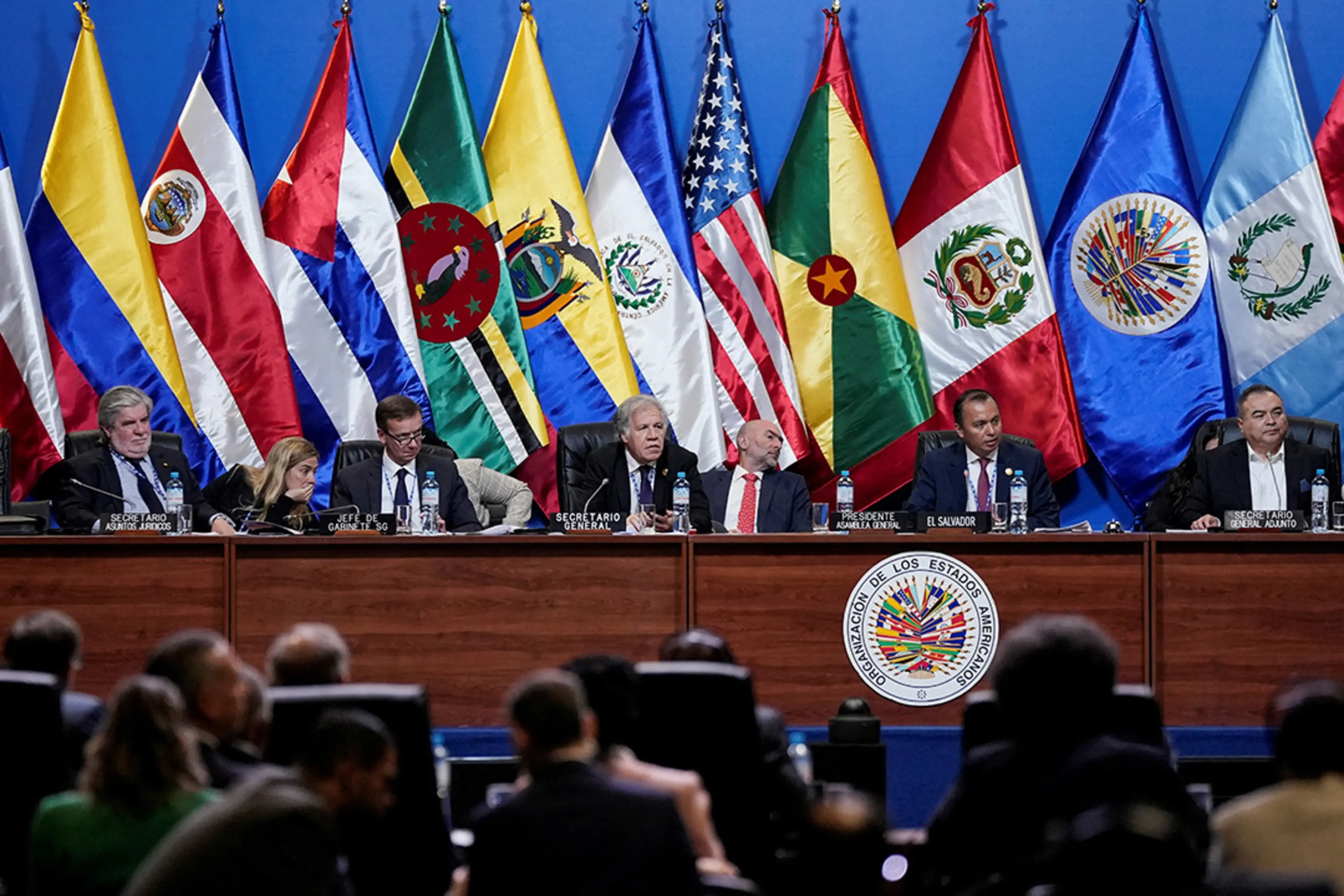

Organization of American States (OAS)
A continental organization founded in 1948 to promote regional solidarity and cooperation among its member states in the Americas.
The OAS works to strengthen democracy, promote human rights, and foster economic development throughout the Americas.