Binomial distribution
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
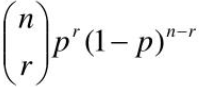
X-B(n,p) then:
p(X=r) =
r = no. of successes out of n
n = no. of trials
p = probability of success
binomial distribution needs …
to have a fixed probability of success, be independent events, have a clear success or fail
null hypothesis
H0. This is the defualt position, e.g. what we expect to happen in an experiment.
alternative hypothesis
H1. This is what we suspect is actually happening
test statistic
this is what we observed when we actually did the test
significance level
the maximum probability where we would reject the null hypothesis
critical region
the range of values of the test statistic that would lead you to rejecting null hypothesis
steps for actually doing a test
find the test statistic and p
write the null and alternative hypothesis
determine the probability of the observed test statistic
two part conclusion: do we reject null hypothesis? put it into context of original problem