Distortion
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Types of distortion
Overdrive, Distortion and Fuzz
Parameters of Distortion
Drive: Amount of Gain
Tone: Shapes frequency response of distorted signal
Level: Volume control (after distortion added)
How was distortion used before the 1950s
it wasn’t used it was actively avoided (but in modern times it often desired)
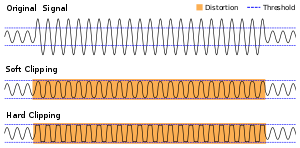
How distortion changes a sound wave
It squares it off its peaks
Willie Kizarts impact on distortion
poked hole in his amp through the cone making it have a distorted sound which he used to play guitar on rocket 88
example of a distortion pedal
Boss DS-1 used by Kurt Cobain of Nirvana and John Frusciante of RHCP
Famous song which uses the boss DS-1 distortion pedal
Nirvana Smells like Teen Spirit (1991)
Distortion in a DAW
-redlight distortion plugin on studio one
= much easier to alter and tweak than other versions of distortion
how fuzz affects the frequency range of the clean signal
cuts away mids and emphasises highs
What does distortion add to a signal which alters its tone
Saturation and alters the signal with harmonic and inharmonic overtones
overdrive
weakest form of distortion which just pushes the signal hard not changing its existing tone
known as crunch on amp settings giving more grit
used in chordal passages and riffs
How distortion was created
In the 1950s Willie Kizart poked a hole in his amps speaker cone in order to create a fuzz sound
when distortion pedals began to be used in music
1962
Types of music which welcome distortion and peaking
Punk, Metal and Rock
How distortion was avoided before 1950s
live mixing engineers would ride the faders to ensure signals didn’t peak
radio broadcasts in 1930s and 1940s would avoid distortion by using compression
Guitar Simulators
used to emulate guitar and amplifier sounds
Jimi Hendrix fuzz pedal
fuzz face
c