Prokaryotic Homework Exam 3
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a general term for when a protein binds to the operator site in an operon to turn off gene expression?
Negative control
Genes that produce products necessary for “housekeeping” functions of the cell are referred to as:
Constitutive genes
What is negative gene regulation?
When a repressor protein binds to the operator of a gene to turn expression off
The presence of glucose will do what to the lac operon?
Prevent induction
The catabolite repression of the lac operon is mediated by:
Catabolite activator protein (CAP) and cyclic AMP
There is a mutant of the lac repressor gene, called IS. This mutant protein can never bind to lactose. What happens in the mutant cell?
The operon cannot be induced
The operon cannot be turned on
The catabolite repression of the lac operon is mediated by catabolite activator protein and cyclic AMP. When glucose is low, cyclic AMP is _______ and CAP is ________
When glucose is low, cyclic AMP is high and CAP protein is bound to the lac CAP site
What would occur if the trp repressor protein could not bind to tryptophan?
Transcription of the trp operon would remain on
There are posttranscriptional mechanisms that regulate polypeptide synthesis. Translational efficiencies can be modified during elongation by the presence or absence of stem loops. This can lead to:
Unequal movement of the ribosome through intervening region
The effector molecules bind to regulator gene products and cause changes in the three-dimensional structures of these proteins. Conformational changes in protein structure resulting from the binding of small molecules is called:
Allosteric transitions
What is ligand bonding?
A ligand is a molecules that binds to a larger target molecule, like a protein or DNA, to initiate or alter a cellular process
What is positive control?
In positive control, the genes are expressed only when an active regulator protein (an activator) is present. Thus the operon will be turned off when the positive regulatory protein is absent or inactive
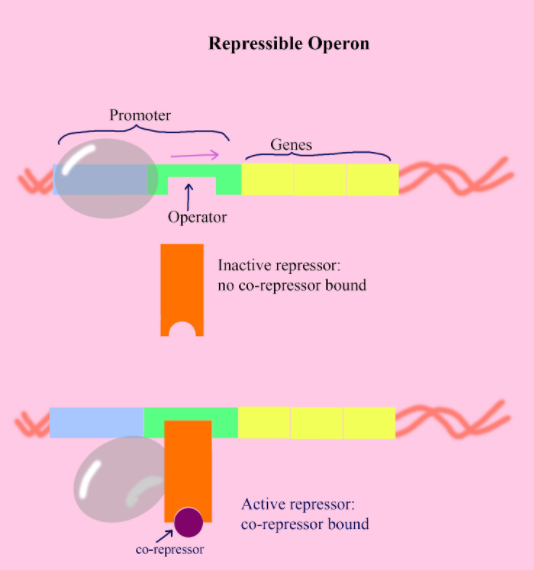
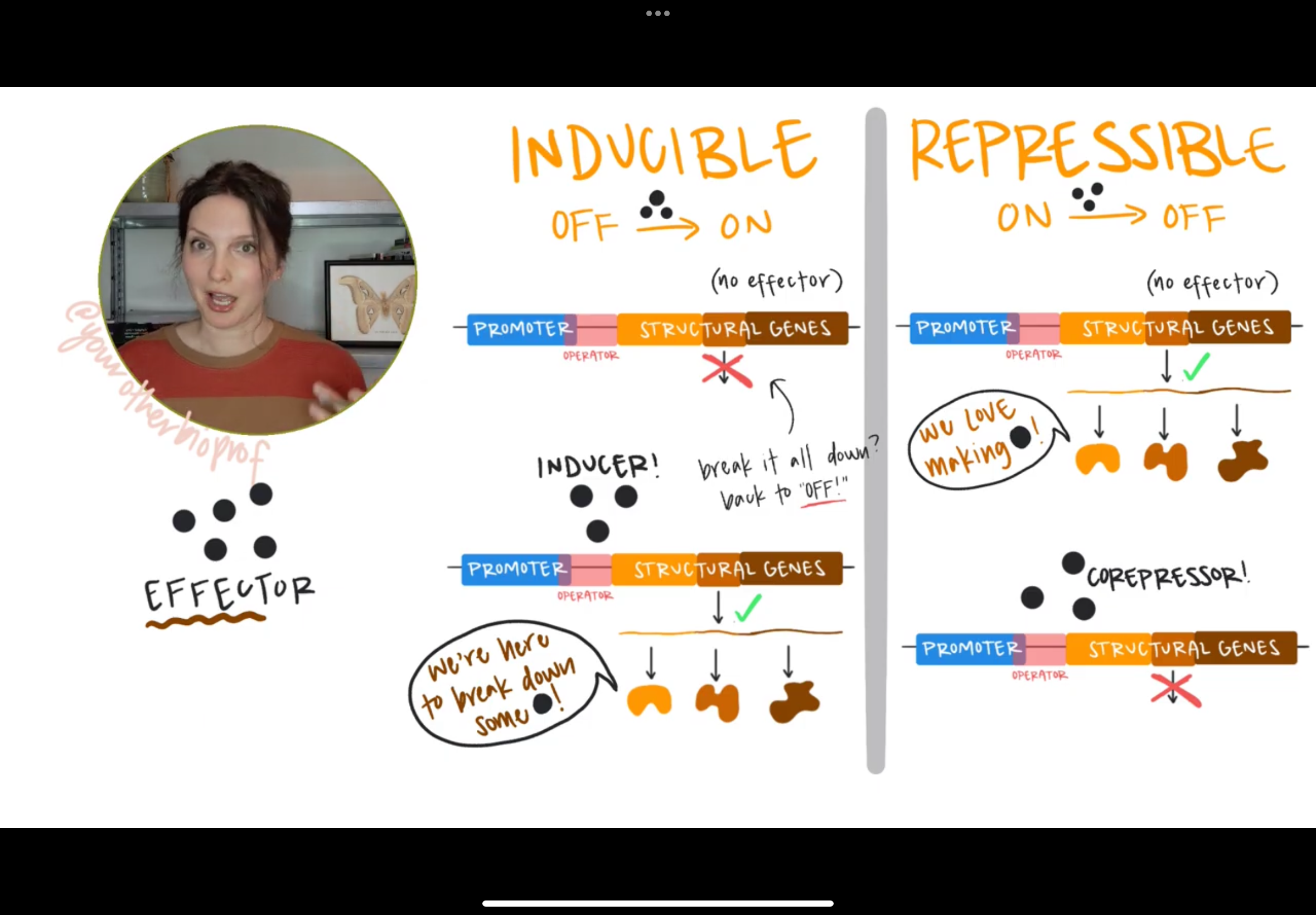
What is repressible regulation?
A mechanism where the activity of a gene or a group of genes is turned off (repressed) in the presence of a specific molecule, often the end product of a metabolic pathway. This type of NEGATIVE regulation, where a repressor protein binds to the operator, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the gene
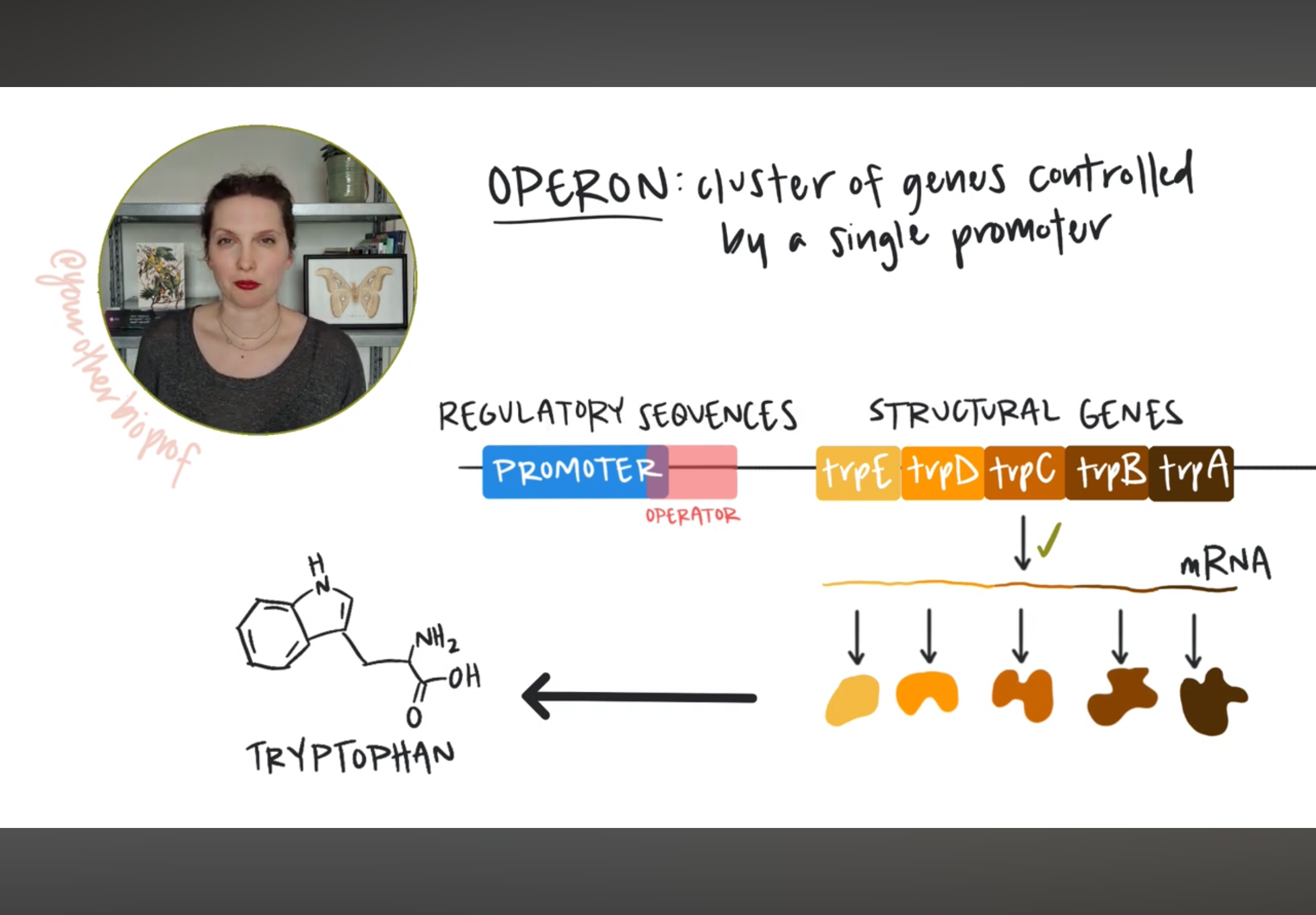
What is a operon?
A cluster of genes organized together controlled by a single promoter
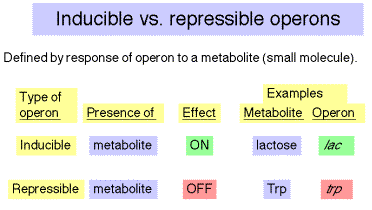
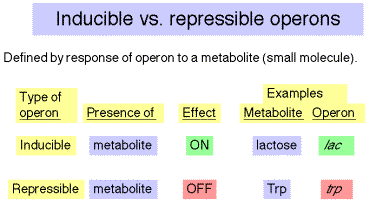
What is inducible regulation?
A type of gene regulation where a gene is normally off but can be turned of in response to an environmental signal (an inducer)
What is positive control?
The genes are expressed only when an active regulator protein (activator) is present
What are attenuated genes?
These are genes that have their expression reduced or turned off, often by a mechanism like premature termination of transcription
What are repressible genes?
These genes are normally “on”, but can be switched off by the presence of a corepressor. Ex: Tryptophan represses the expression of trp genes