Feeding and energy
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
what are feed stuffs
an ingredient in a diet or ration that has one or more purposes
what is apparent digestibility
extent to which a nutrient or feed component is absorbed and utilized by an organism after feeding. It is calculated by measuring the difference between the amount of a nutrient consumed and the amount excreted in feces.
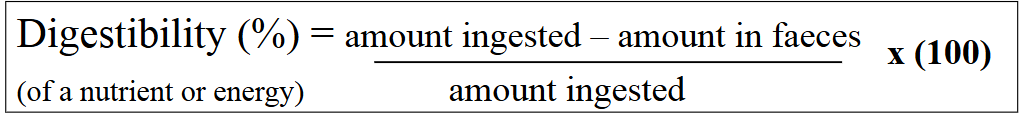
what are six classes of nutrient
1. water (the aqueous medium of life)
2. protein
3. carbohydrates (structural & energy)
4. lipids
5. vitamins (indispensable components elements
6. inorganic elements of diverse cellular processes)
three factors affecting digestibility
1- gut transit time
2- fibre content
3- feed preparation factors
what is gross energy
Sample dried
• Known quantity of DM combusted (completely oxidised) in sealed chamber
• Energy released by oxidation of covalent bonds warms surrounding water
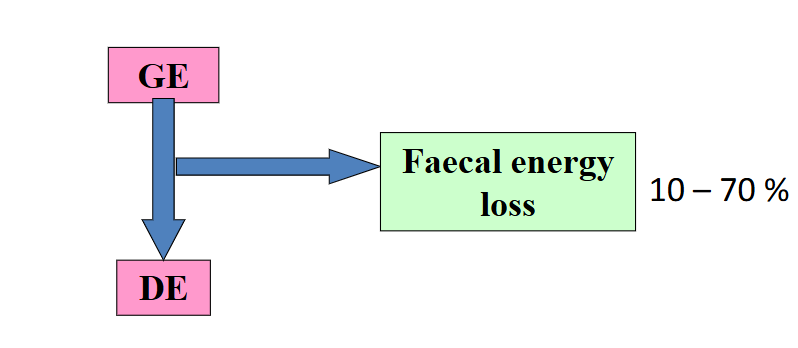
what is digestible energy
amount of energy digested
calculated from faeces lost
GE-faecal energy loss = digestible energy
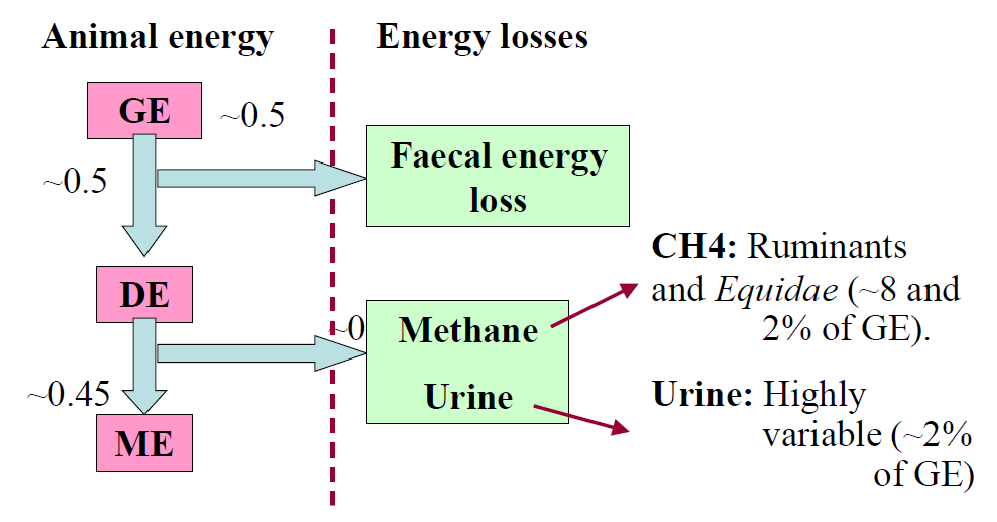
what is metabolizable energy
the energy assimilated by the animal & available to fuel metabolism
GE - FL = DE
DE- other losses = ME
6 factors effecting metabolisable energy
1) digestibility
2) diet quality
3) species
4) nitrogen balance
5) food prep
6) feeding levels
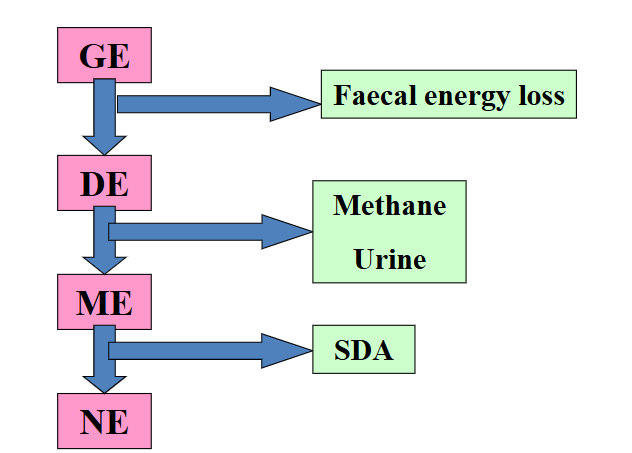
what is net energy
all of the dietary energy available to the animal when the costs of digestion, metabolism & wastage have been accounted for
Thermic energy loss must be subtracted from the
ME to give the Net Energy (NE) of foods
how do you calculate DM from FW
fresh weight (Kg) X dry matter proportion
how do you calculate FW from DM
dry matter weight (Kg) / dry matter proportion