Topic 3 - conservation of energy
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
equation for change is GPE
change is gravitational potential energy (joule, J) = mass (kilogram, kg) x gravitational field strength (newton per kilogram, N/kg) x change in vertical height (metre, m)
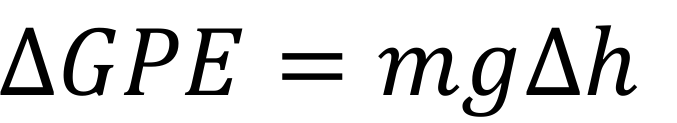
equation to calculate the amount of energy associated with a moving object
kinetic energy (joule, J) = ½ x mass (kilogram, kg) x (speed)2(metre/second2, m/s2)
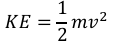
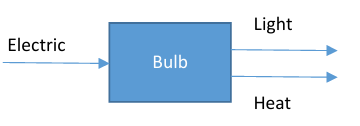
energy transfer
diagrams show energy input, and the energy output
and this forms that the energy takes
this includes the waste output energy too
motors also waste energy as heat
energy changes - object projected upwards
KE transferred to GPE, then vice versa as it falls back down
energy changes - object projected up a slope
KE transferred to GPE (and also to heat if friction is present)
energy changes - moving object hitting an obstacle
KE transferred to sound/KE transferred to obstacle if that moves too
energy changes - object being accelerated by a constant force
object is having work done to it, with it gaining KE
whatever supplies the force is having its energy transferred to KE
energy changes - vehicle slowing down
KE transferred to heat (through brakes)
energy changes - boiling water in kettle
electrical energy to thermal
what is conservation of energy
in physics, conservation of energy means that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant
a ‘closed system’ has no external forces acting on it (eg. no change in gravitational force, no electrostatic attraction, no external magnetic force etc)
in a closed system, the total energy in the system never changes, regardless of the energy transfers that take place
in other words, in a closed system no energy is lost
once it becomes an open system, energy can be transferred out of the system, and therefore the total energy of the system can change
mechanical waste energy
in mechanical processes (ie. where forces are involved on objects)
energy transferred to it can cause a rise in temperature
so energy is dissipated to surroundings (heat is transferred to air)
and this makes the process wasteful
waste energy
forms: light, sound, (most commonly) heat
to reduce waste:
lubricate systems, so less friction and less heat created
thermal insulation, so less heat is lost to surroundings
buildings
thicker walls means greater thermal insulation, so less heat is lost
air cavities between walls cause lots of heat loss by convection - cavity wall insulation fills in this gap and prevents air flow
efficiency equation
ratio of useful output over total input of energy
efficiency = useful energy transferred by the device/total energy supplied to the device
how to increase efficiency
reducing waste output (via lubrication/thermal insulation or other methods)
recycling waste output and using it as input (absorbing heat energy dissipated and used to as input heat energy)
suitable methods depend on each situation
energy sources
fossil fuels
nuclear fuel
bio-fuel
wind
hydro-electricity
tidal
solar
non renewable energy is used more for large scale energy supplies due to the large energy output per kilogram of fuel - renewable resources cannot provide such a large amount of energy as easily
renewable energy has become more important due to the finite lifetime of fossil fuels, and so their development has become more important
patterns and trends in the use of energy resources
during industrial revolution, fossil fuels became an important source of energy as it was easy to mine, and provided a lot of energy
only recently has renewable energy become more suitable - technology has had to develop a lot since industrial revolution to be able to harness such energy sources efficiently