ap macroeconomics review
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
4 key assumptions of PPC
1. only 2 goods can be produced
2. using all resources
3. fixed resources
4. fixed technology
policy economics
applied to fix problems or meet economic goals
Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS)
how much people save rather than consume when there is a change in income
- change in savings/change in disposable income
- 1 - MPC
Long Run Aggregate Supply
wages and resource prices will increase as price levels increase
Shifters of SRAS
1. Change in resource prices
- Inflationary expectations
2. Actions of the government
3. Change in Productivity
- Technology
US progressive income tax system
1. when gdp is down, the tax burden on consumers is low, promoting consumption and increasing AD
2. when GDP is up, more tax burden on consumers, discouraging consumption and decreasing AD
how to measure growth in GDP from year to year
Percent change in GDP = new year - old year / old year X 100
Investment
- Not stocks or bonds
- When businesses b uy capital like machines, resources, and. tools
Labor force participation rate
labor force ( unemployed + employed )/ civilian population rate
Price index
index number that shows how the weighted-average price of a "market basket" of goods changes over time
equation to calculate present value
$X/(1+ir)^N
money demand shifters
1. Changes in price level
2. Changes in income
3. Changes in technology
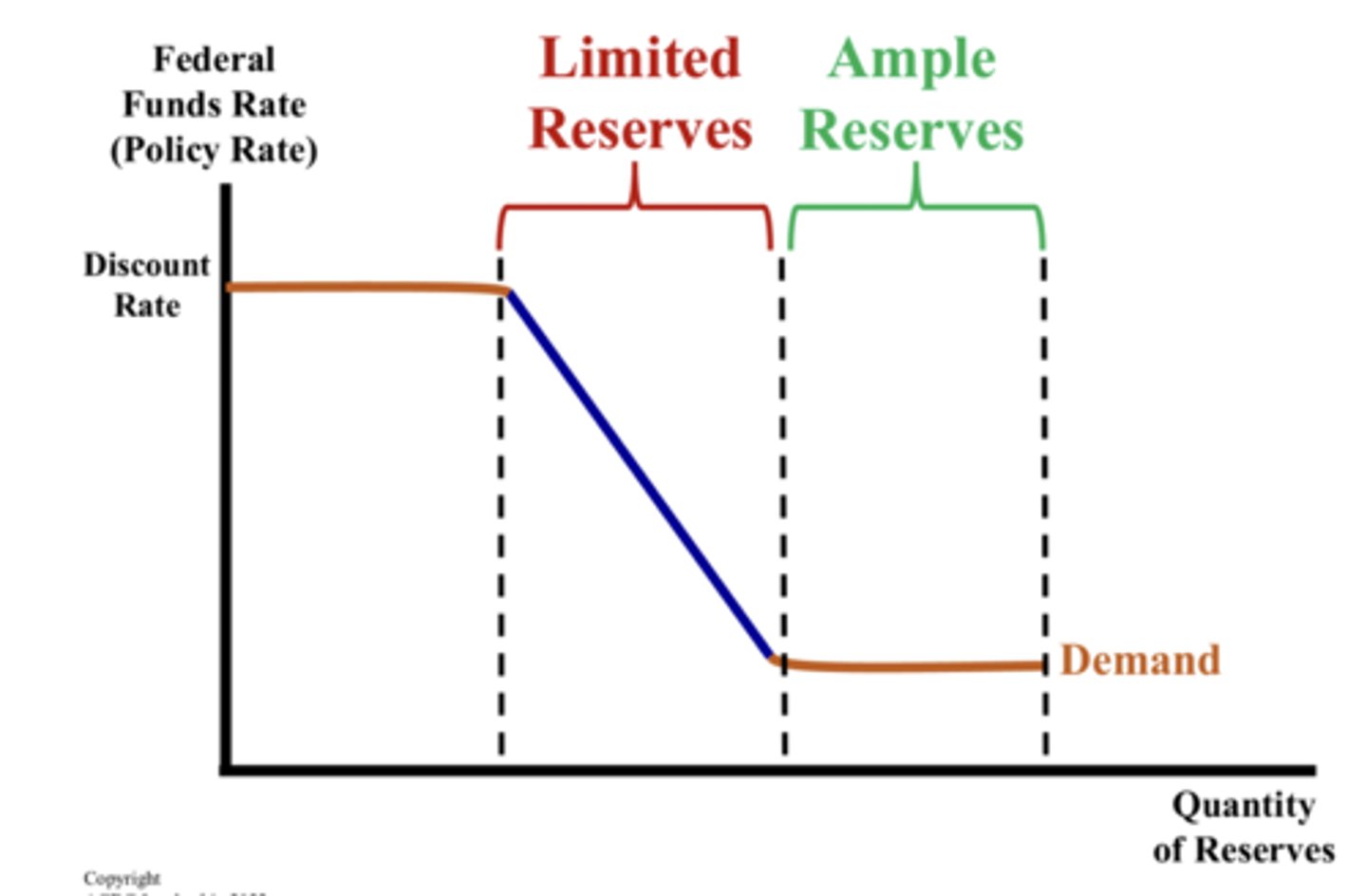
reserve market model graph
Supply Shifters in Loanable Funds Market
1. Changes in private savings behavior
2. Changes in public savings
3. Changes in foreign investment
4. Changes in expected profitability
monetary base
the sum of currency in circulation and bank reserves
Under the curve of the PPC
inefficient/unemployment
complements
two goods that are bought and used together (Ex. Hot dogs and hot dog buns)
supply
the different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices
surplus
Qs > Qd (too much of one good)
Spending multiplier
1/MPS or 1/1-MPC
Fiscal Policy
actions by congress to stabilize the economy
4 factors of production
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
welfare
government aid to the poor
Expenditures Approachj
add up all the spending on final goods and services produced in a given year
- GDP (y)= C + I + G + (X-M)
interest rate
the amount a lender charges borrowers for borrowing money; "price of a loan"
3 functions of money
1. medium of exchange
2. unit of account
3. store of value
demand deposits
money deposited in a commercial bank in a checking account
shifters of money supply
1. reserve requirement
2. discount rate
3. open market operations
administered rates
interest rates set by the Fed rather than determined in a market
- reserves at the fed have no risk
- banks have no incentive to lend money at an interest rate that is lower than what they can get from the fed
interest on reserves (IOR)
The interest rate that the Federal Reserve pays commercial banks to hold reserves.
monetary policy for ample reserves
- the fed would decrease the interest on reserves = demand for reserves in the ample reserves to decrease
- the fed would increase the interest on reserves = demand for ample reserves increases
national savings
public savings + private savings
budget deficit
when annual government spending without raising taxes to close a recessionary gap
Foreign Exchange Graph
shows the relationship between different countries exchange rates and quantities of currency
balance of payments
summary of a country's international trade;
CA and CFA must balance out CA + CFA = 0; Money that leaves a country ust coe back as either foreign purchases of g&s or foreign purchases of financial assets
subsidy
A government payment that supports a business or market; causes a good's supply to increase
National Rate of Unemployment (NRU)
Frictional + Structural unemployment; the amount of unemployment that exists when the economy is healthy and growing
the barter system
Goods and services are traded directly. There is no money exchanged.
production possibilities curve (PPC)
a model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scarce resources; graphically demonstrates scarcity, trade-offs, opportunity costs, and efficiency
the line of a PPC is
efficient
Above the curve of the PPC
impossible/unattainable due to scarce resources
constant oppurtunity cost
Resources are easily adaptable for producing either good
- Results are a straight PPC
law of increasing opportunity cost
As you produce more of any good, the opportunity cost (forgone production of another good) will increase.
- Result is a concave or a bowed out PPC
Why does opportunity cost increase?
Resources are not easily adaptable when producing both goods
3 shifters of the PPC
1. change in resource quantity or quality
2. change in technology
3. change in trade (allows more consumption)
demand
different quantities of goods
that consumers are willing and able to buy at
different prices.
law of demand
There is an INVERSE relationship between
price and quantity demanded.
why does the law of demand occur
1. substitution effect
2. income effect
3. law of diminishing marginal utility
substitution effect
if the price goes up for a product, consumers buy less of that product and more of another substitute product
income effect
if the price goes down for a product, the purchasing power increases for consumers, allowing them to purchase more
law of diminishing marginal utility
The more you buy of ANY GOOD the less satisfaction you get from each new unit consumed.
what to remember when graphing demand or supply
price does not shift the curve, it only moves along the curve
5 shifters of demand
1. Tastes and Preferences
2. Number of Consumers
3. Price of Related Goods
4. Income
5. Future Expectations
substitutes
goods used in place of one another (Ex. Coke and Pepsi)
law of supply
direct relationship between price and quantity supplied
- as price increases, the quantity producers make increases
- as price falls, the quantity producers makes falls
5 shifters of supply
1. Prices/Availability of Inputs (Resources)
2. Number of Sellers
3. Technology
4. Government Actions (Taxes, Subsidies)
5. Expectations of Future Profit
normal good
a good that consumers demand more of when their incomes increase (direct relationship; income falls demand falls)
- Ex. cars, luxury items, jewelry
inferior good
a good that consumers demand less of when their incomes increase (inverse relationship; income falls demand increases)
- Ex. Top ramen used clothes, used cars
shortage
Qd > Qs (shortage of a good)
double shift rule
If two curves shift at the same time, either price or quantity will be indeterminate
price ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold (helps consumer)
price floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold (helps producer)
per unit opportunity cost formula
Per unit opportunity cost = opportunity cost/units gained
absolute advantage
the producer that can produce the most output or requires the least amount of resources/input
comparative advantage
the producer with the lowest opportunity cost
export
to carry out of the country
import
to carry into the country
output questions
OOO - other goes over; inputs are the same for both countries (time, workers, other resources)
input questions
IOU - other goes under; outputs are the same for both countries (the product)
terms of trade
the agreed upon conditions that would benefit both countries
Economics
the science of scarcity; study of decision making of how we should use resources
scarcity
unlimited wants and limited resources
Microeconomics
study of small economic units (individual, market, firms)
macroeconomics
study of the large economy as a whole or economic aggregates
theoretical economics
uses scientific methods to make generalizations and abstractions to develop theories (guesses, supposed to happen)
positive statement
Based on facts. Avoids value judgements (what is).
normative statement
includes value judgements (what ought to be)
5 key economic assumptions
1. Society has unlimited wants and limited resources (scarcity).
2. Due to scarcity, choices must be made. Every choice has a cost (a trade-off).
3. Everyone's goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own "self-interest."
4. Everyone makes decisions by comparing the marginal costs and marginal benefits of every choice.
5. Real-life situations can be explained and analyzed through simplified models and graphs.
marginal analysis
making decisions based on increments (additional benefits or costs)
normative statement example
Pollution is the most serious economic problem
positive statement example
if average temperatures rise, the sales of sunscreen will rise
Aggregate Demand
the amount of goods and services in the economy that will be purchased at all possible price levels
AD: relationship between price level and RGDP
inverse relationship; increases pl inflation -> rgdp demanded falls
decreases pl -> rgdp demanded increases
shifters of AD
C, I, G, Xn
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
how much people consume rather than save when there is a change in income
- change in consumption/change in disposable income
total change in GDP
multiplier x initial change in spending
Tax multiplier
MPC/MPS ; always negative since an increase in taxes decreases GDP
Aggregate Supply
the amount of goods and services (real GDP) that firms will produce in an economy at different price levels
short-run aggregate supply curve
wages and resource prices will not increase as price levels increase
LRAS curve
price level increases but GDP doesnt as real output will always be the same when workers ask for higher wages if output is increased
Shifters of LRAS
1. Change in resource quantity or quality
2. Change in technology
inflationary gap
Output is high and unemployment is less than NRU; equillibrium is after LRAS
recessionary gap
Output is low and unemployment is more than NRU; equillibrium is before LRAS
stagflation
A period of falling output and rising prices; always happens when SRAS shifts left
demand-pull inflation
demand pulls up prices; customers want g&s -> prices go up (AD increase)
cost-push inflation
Higher production costs increase prices. A negative supply shock increases the costs of production and forces producers to increase prices. (SRAS decrease)
Long-Run Self-Adjustment
businesses and workers will adjust their price and wage expectations to bring the economy back into equilibrium
discretionary fiscal policy
Congress creates a new bill that is designed to change AD through government spending or taxation
- takes time for congress to act
Non-Discretionary Fiscal Policy
automatic stabilizers; permanent spending or taxation laws enacted to work counter cyclically to stabilize the economy
- when gdp goes down governmntt spending automatically increases and taxes automatically fall
contractionary fiscal policy (the brake)
Laws that reduce inflation, decrease GDP (Close a Inflationary Gap)
-Decrease Government Spending
-Tax Increases
-Combinations of the Two