Astrophysics
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what is the universe?
The universe is a large collection of billions of galaxies.
what are galaxies?
There are regions within this space known as galaxies where billions of stars are grouped together. There are billions of galaxies distributed throughout the universe.
what is the distance like between stars and galaxies
the distance between the neighbouring stars in the galaxy is often millions of times greater thn the distance between planets in our solar system. The force which keeps the stars toegehter in a galaxy is gravity. Galaxies themselves are often millions of times further apart than the stars are within a galaxy.
what is the sun
The Sun, the Earth's star, is the largest object in the Solar System. The Sun’s huge gravitational field keeps many other objects - planets, dwarf planets, asteroids and comets – in orbit around it.
what are planets
these are large objects that orbit a star.
what are dwarf planets
these are planet like objects that aren’t big enough to be planets
what are moons
these orbit planets with almsot circular orbits. Theyre a type of natural satellite
wahta re artificial satellites?
(ones humans have built) that usually orbit the earth in fairly ciuclar orbits
what are asteriods?
lumps of rock and metal that orbit the sun. They’re suually found in the aesteroid belt
what are comets?
lumps of ice and dust that orbit the sun. Their orbits are usually hihgly elliptical (a very stretched out circle)-soem travel from near to the sun to the outskirts of our solar systems
what ahppens as the distance from teh sun increases?
In general, as the distance from the Sun increases:
the temperature decreases, for example, Mercury is 430°C whereas Neptune is -200°C
the time taken to orbit the Sun increases, for example, Mercury orbits once every 88 Earth days, but Neptune orbits once every165 Earth years
what is weight?
The force acting on an object due to gravitational attraction
effects of weight
Objects stay firmly on the ground
Objects will always fall to the ground
Satellites are kept in orbit
mass in relation to gravitational field strenght
Both the weight of any body and the value of the gravitational field strength g differs between the surface of the Earth and the surface of other bodies in space, including the Moon because of the planet or moon's mass
The greater the mass of the planet then the greater its gravitational field strength
A higher gravitational field strength means a larger attractive force towards the centre of that planet or moon
wht woudl ti eman if gravitaitonal orce is less
it is easier to raise a mass. Its mass will be the same but its weight will be a lot greater
what does gravitaitonal force depend on
masses of the two obejcts
distance between the masses
the greater te attraction the mroe curved paths the obejct follows
what is centripetal force?
if an obejct is travelling in a circle it is cosntntly changing direction so there is a force actign on it. This force is called centripetal force and acts towards the centre of the circle. This force causes obejcts mvoign to change direction. The object keeps accelerating towards what its orbitign but the instantaneous velocity (which is at a right angle to the acceleration) keeps it travelling in a circle. The force that makes thsi happen is provided byt eh gravitational force. Teh graivtational attraction of the sun keeps the palnets and comets in their orbtis aroudn it.
what do planets,comets, moon,esteroids and artificial satellites orbit?

which way does gravitaitonal force act?
The gravitational force exerted by the larger body on the orbiting object is always attractive
Therefore, the gravitational force always acts towards the centre of the larger body
what are artificil satellites used for?
soem are put itno a very high orbit above the earth and are used to help us communicate over large distances
soem satellites out into a much lower orbit and are used to monitor in detail the earths surface, such as the temeprature of the worlds oceas or the progress of forest fires.
what does strogner force mean?
the stronger the force the larger the isntantaneous velocity needed to balance it. So the closer to a star or a planet you get, the faster you need to go to remain in robit. For an object in a stable orbit, if the speed of the obejct changes, teh size (radius) of its orbit must do so too. Faster movign objects will move in a stabel orbit with a smaller radiusthan slwoer movign oens
what are the similarities in teh way planets orbit the sun?
their orbits are slightly eliptical with sun at oen focus
they all orbit in the same plane
they all travel the same direction around the sun
differences in the way planets orbit the sun?
They orbit at different distances from the Sun (different orbital radius)
They orbit at different speeds
They all take different amounts of time to orbit the Sun
The further away a planet is from the Sun, the slower it travels and therefore the longer it takes to orbit
what is orbits of the moon like?
moons orbit planets in a ciruclar path but are slighlty elliptical
some planets have mreo than one moon
the closer the moon is to the planet
-the shorter the time it will take to orbit
the greater the speed of the orbit
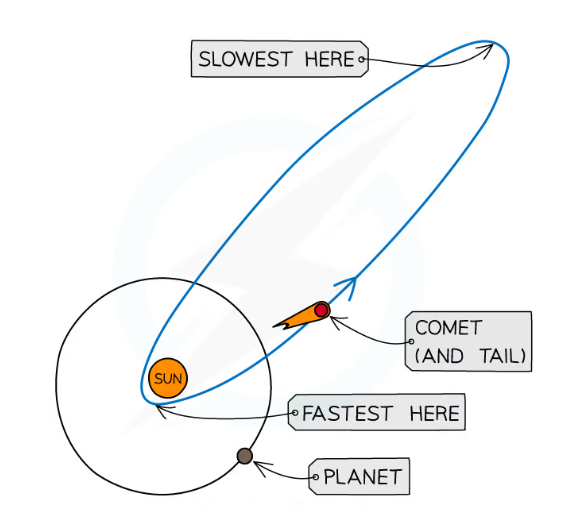
what is orbits of comets like?
Their orbits are highly elliptical (very stretched) with the sun as one focis.
This causes the speed of the comets to change significantly as their distance from the Sun changes
Not all comets orbit in the same plane as the planets and some don’t even orbit in the same direction
As the comet approaches the sun, its speed increases
As it moves further away from the sun, its speed decreases
what are geostationary satellites?
some artificial earth satellites have an orbital period of exactly one day. They’re called geostatioanry satellites and are sueful in communicatiosn because they’re always over teh same part of the planet
hwo to calcualte average speed of orbit?
the average orbital speed of an object can be defined by the equation:
2 (pi) r/ T
Where:
v = orbital speed in metres per second (m/s)
r = average radius of the orbit in metres (m)
T = orbital period in seconds (s)
the orbital period is defined as?
The time taken for an object to complete one orbit
what does teh colour of a star depedn on?
The colour of a star depends on the visible light it emits. All stars emit visible light, but how much it emits of each frequency depedns on its suface temeprature. Warm objects emit infrared and extremely hot objects emit visible light as well. Therefore, the colour they emit depends on how hot they are
what kind of light will a hotter star emit?
the hotter the star the mreo light of higher frequencies it will emit.
what kind of light will a cool star emit?
a cool star will emit most of its visible light at the lowest frequency of visible light (ie red light) so will appear red.
order of temeprature for different coloured stars?
Orange stars are hotter than red stars, yellow stars are hotter than orange stars and white stars are hotter than yellow stars. White stars emit all frequenceis of visible light roughly equally. Blue stars are hotter than white stars . They emit more high frequency light (blue,indigo and violet) than lower freqeucny oens (red and orange) and so they appear blue
what are the different star classification?
There are seven different groups of stars. These groups are called O,B,A,F,G,K,M.
O and B are the hottest stars and K and M are the coolest
what are the different ways an astronomer describes the brightness of a star?
the apparent brightness or magnitude of a star. This is hte easiest method and is simply a measure of how bright a star is as seen from the earth
the absolute brightness or magnitude. this is a measure of how bright stars would appear if they were all placed a fixed distance from earth. Thsi is often a better emasure of brightness becasue it allows scientists to make comparisons between stars wihtout worrying about relative distance form earth.
The luminosity of a star. This measures how much energy in teh form of light is emitted from a stars surface every second
what does lower and hgiehr magnitude mean?
the lower the absolute magnitude, the brighter the str. Very bright strs have a negative value for their absolute magnitudes. For example, the sun has an absolute magnitude of around +5 while the Pole Star, one of the brightest lookign stars in the night sky jad a mgnitude of -4.
what does brightness of a star depend on?
the te,[erature
the size
how is a star born?
stars are formed from large clouds of dust and gas particles we call nebulae or stellar nebulae. These particles are drawn together over a verry long period of time by gravitational forces. The particles are pulled together so tightly that there is a very large increase in temerpature adn pressure. As a result of this nuclear fusion reactiosn begin. Hydrogen nuclei join together to make larger nuclei and huge amounts of energy in teh form of heat and light are released.
life cycle of a star
stars initially form from a cloud of dust and gas called a nebula
the force of gravity pulls the dust and gas together to form a protostar. The temperature rises as the star gets denser and mroe particles collide with each other. When the temperature gets high enough, hydrogen nuclei undergo nucleat fusion to form helium nuclei.This gives out huge amoutns of energy, which keeps the core of the star hot. A star is born
The star enters a long stable period. During this period, the outwars pressure caused by thermal expansion (the energy produced by nuclear fusion tries to expand the star) balances the force of gravity pulling everything inwards. In this stable period period its called a main sequence star and it typically lasts several billion years. The heavier the star, the shorter its time on teh main sequence
Eventually the hydrogen in the core begins to run out and the force due to gravity is larger than the pressure of thermal expansion. The star is compressed until it si dense and hot enough that the energy (and so pressure) created makes the outer layers fo the star expand. The star becomes a red giant (if its a small star) or a red supergiant (if it is a larger star.) It becomes red because the surface cools
A small to medium sized star like the sun then becomes unstable and ejects its outer layer of dust and gas. This leaves behind a hot,dense soild core-a white dwarf-emtis mroe blue and white light as temp because od contraction. As white dwarf cools it changes to cold balck dwarf star
Big stars however start to glow brihgly again as they undergo mroe fusion to make heavier elements. They expand and contract several times, as the balance shifts between gravity and thermal expansion. Eventually, they explode in a supernova
The exploding supernova throws the outer layers of dust and gas into space, leaving a very dense core called a neutron star. If the star is massive enough, it will collapse and becoem a black hole- a super dense point in space that nt even light can escape from
what is the hertzsprung russel diagram?
its a graph of absolute magnitude agaisnt temperature for many many stars. It shows the relationship between brightness,temeprature and classification of a star
characteristics and where stars are palced in hertzspring russel diagram
There are clear groups on the graph that correspond to different periods in a stars life cycle.
Most stars lie on the Main Sequence. This is the band of stars going from top left to bottom right. Since all main sequence stars are roughly the same size, the brighter the star, the higher the temp
Below the main sequence (bottom left) are the White Dwarfs which are very hot but small so are dim
Above the main sequence on the right-hand side are the Red Giants. Tehya re cool and very bright as they are large
Above those are the Red Supergiants
what is the doppler effect?
when a source of waves is moving relative to the observer, the waves will undergo a change in frequency and wavelength when they are observed compared to when they were emitted.
what is red shift?
if the light source is moving away from you, the waves will ahve a longer wavelength and light it emits will be shifted towards teh red end (ie the lwoer frequency end) of the visible part of the EM spectrum-this is the red shift. The stars must be moving away from teh earth. the furhter away a glaaxy is the greater hte red shift and therfeor the faster it is movign away from us.
what is blue shift?
blue shift would indicate that the source of light is moving towards the observer. the wavelenght of ligth also decreases
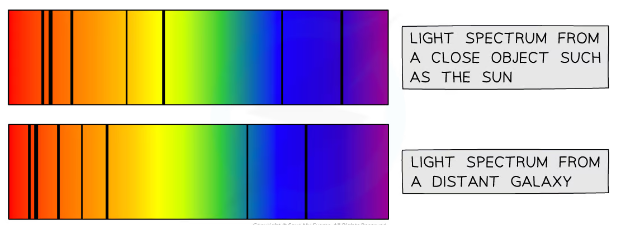
evidence for red shift?
when light is passes throuhg a sample of an element a pattern of dark lines is produced called absorbtion liens in the visbile part of the EM spectrum that the element (hydrogen) absorbs.
when we look at light from distant galaxies we see the sae pattern but at lwoer freq so longer wavelengths than they shoudl be
the pattern has been shifted towards red end of spectrum
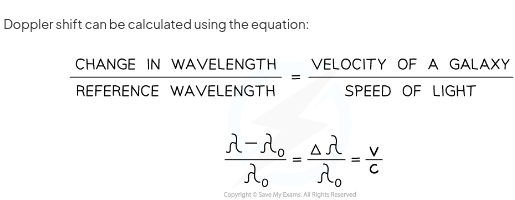
how to calculate red-shift/doppler equation?
change in wavelenght/ reference wavelenght= velocity of a galacy/speed of light
evidense from red shift of teh big band and universe expanding
measurements of the red shift suggest that all the distant galaxies are moving away from us very quickly as they have greater red shifts than nearer ones.
more distant galaxies have greater red-shifts than nearer ones-they show a bigger observed increase in wavelength
. if glaxies all grouped togehter at first this emans that mreo distant galaxies are movign away faster than nearer ones. This supports the big bang theory that hte universe started from one single point
therefore we can say the whoel unviers is expansifn
what si the movement of galaxies ike?
All galaxies are moving away from the Earth
Galaxies are moving away from each other
how does CMB suggest that there was a big bang?
scientists can detect low frequency microwave radiation comign from all directions and all parts of the universe. This implies all parts of univere were in contact a long time ago and started from one focal point
its knwn as cosmic mcirowave background radiation
According to the Big Bang theory, the early Universe was an extremely hot and dense environment
As a result of this, it must have emitted thermal radiation. CMB is the leftover enregy of the initial explosion
Initially this radiation would be high energy in gamma region.
As the unvierse expands and cools this background radiation ‘cools’ and drops in frequency and wavelegnth increased. Those thermal waves red shifted and so now we recieve them as microwaves
what is the big bang theory
initially all the matter in teh universe occupied a singel point
this tiny space was very dense and very hot
thsi single point then exploded’-the big bang
space started expanding coolign as it does so and the expansion is still going on