L14 - male reproductive system
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
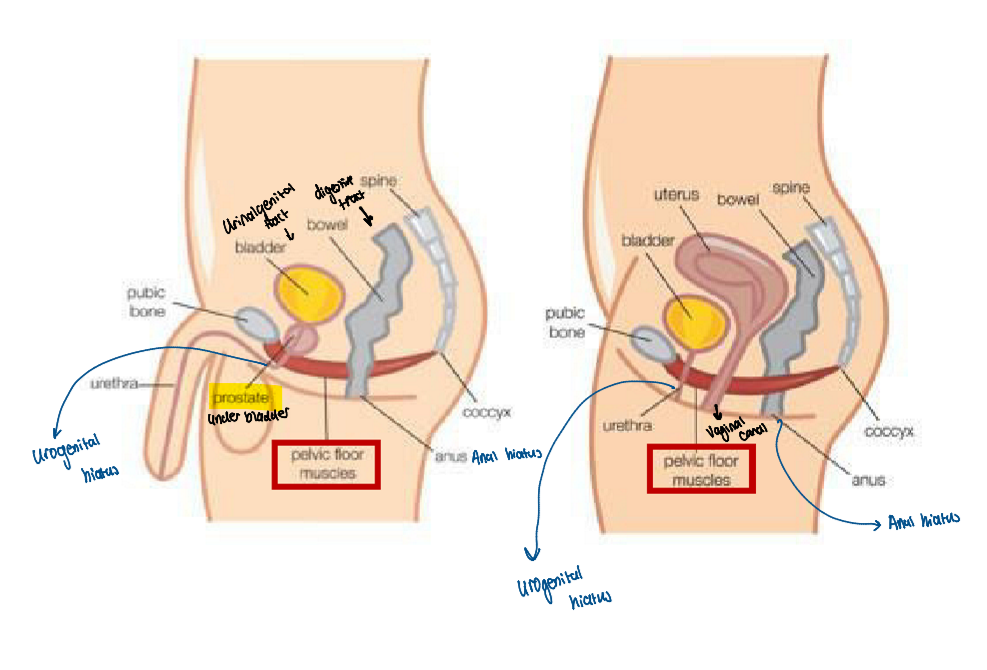
Male and female pelvic floor openings
Males → opening for bladder(urogenital), digestive tract/ bowl
Females → bladder, digestive tract and vaginal opening
Where does the pelvic brim stretch from
From top of pubic symphesis to top of Sacrum above S1 vertebrae
pelvic floor muscles stretch from
Tip of coccyc to pubic rami
What is everything below pelvic floor muscles called
perineum

Peritoneum in relation to male pelvic organs
all retropeitoneal except rectom top 3rd cover by 3 sides of peritonum, middle only 1 side lower part retroperitoneum
What pouch is formed
between rectum and bladder form recto vestibular pouch
Function of the testis
produces sperm and hormones (testosterone)
Structure of testis and layers surrounding
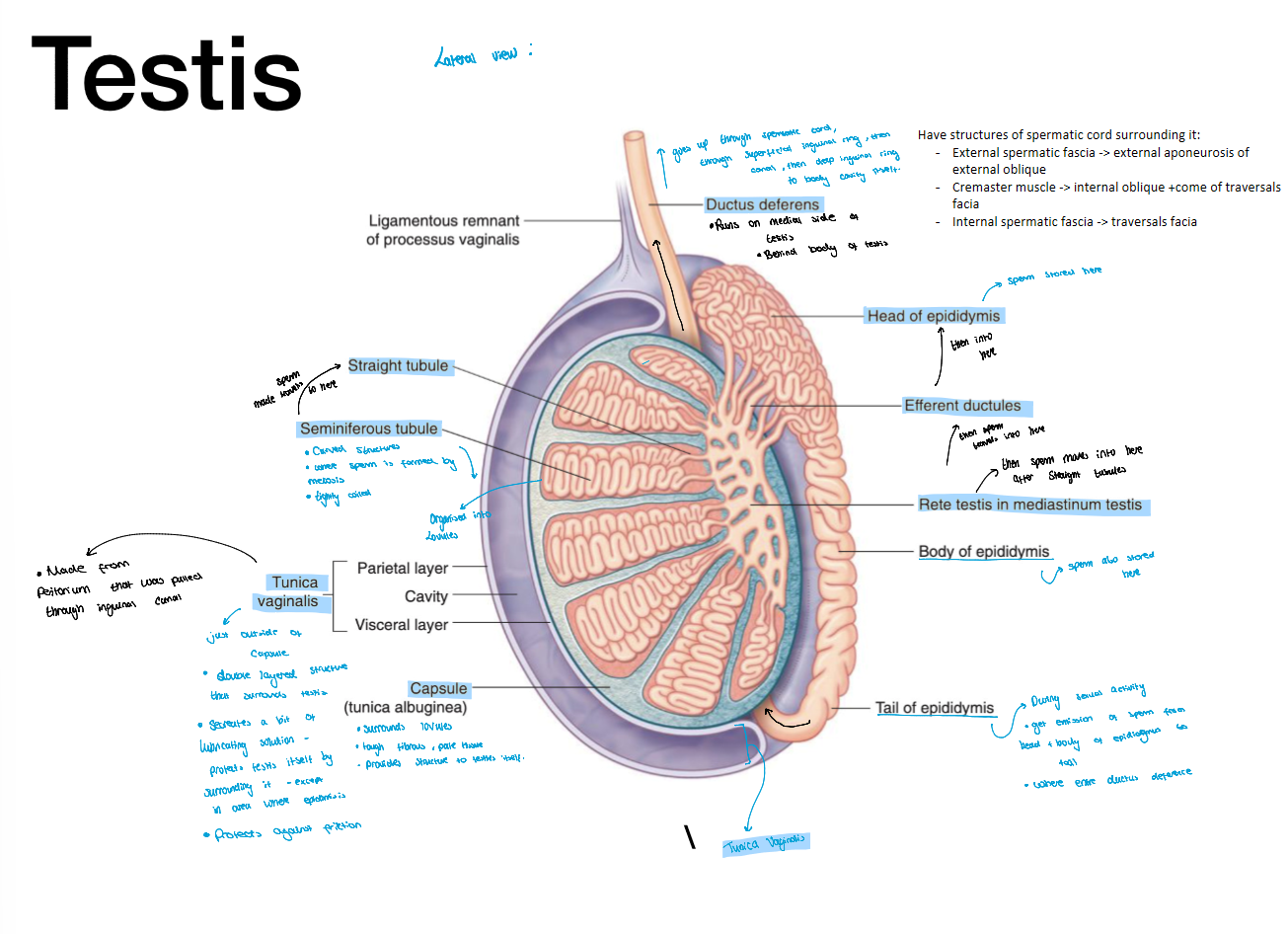
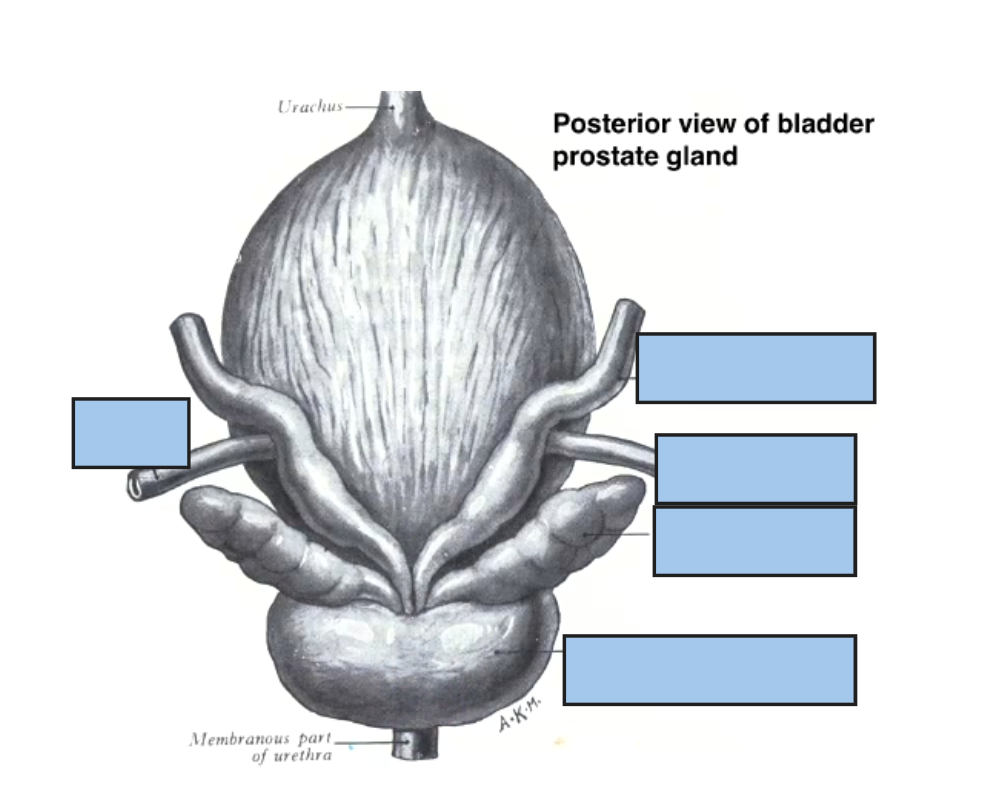
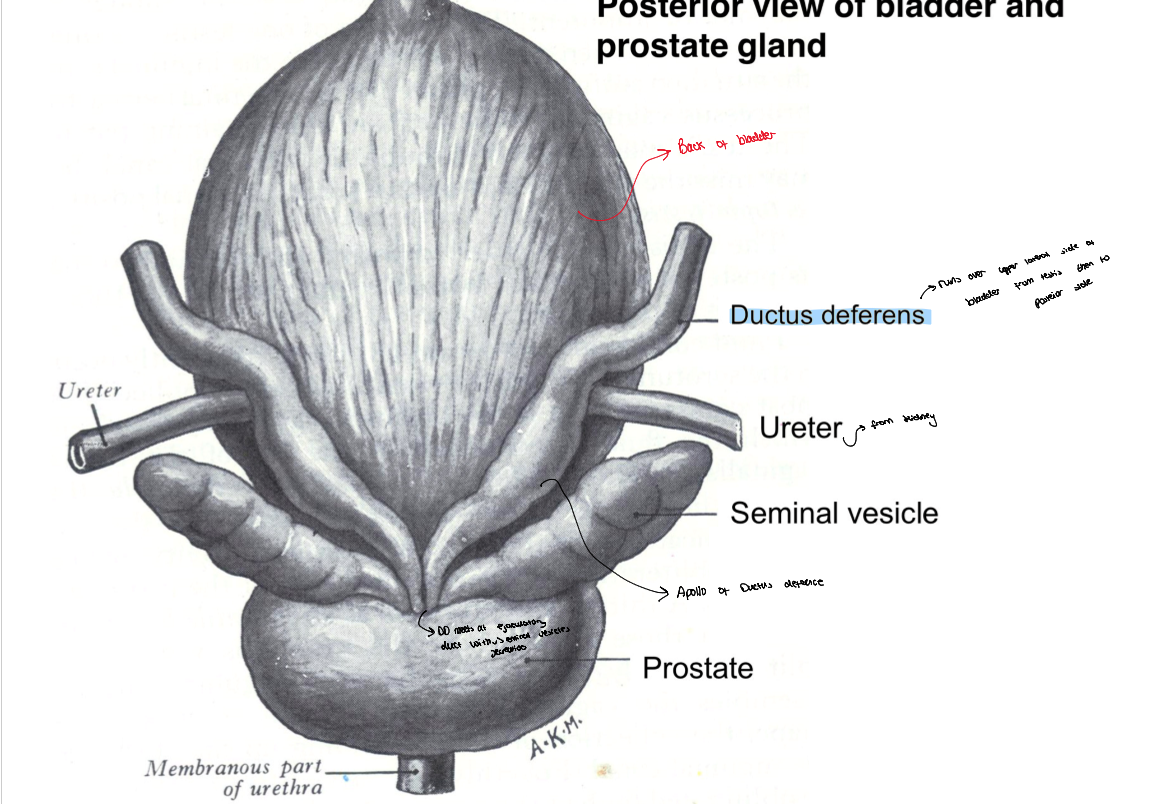
Sperm route
made in semiliferouse tubule
tehn into straight tubule
thene inot rete testis
then into efferent dutules
then head of epidimis where its stored
During maturation of perm or
from head to body then to tail of epididymis
then into ductus defernce (DD)
then thorugh spermatic cord thorugh superfitial ring
then through deep ring
then over the bladder to then over uriter
then connects to an area called apolo DD
where meets with seminal vesicle
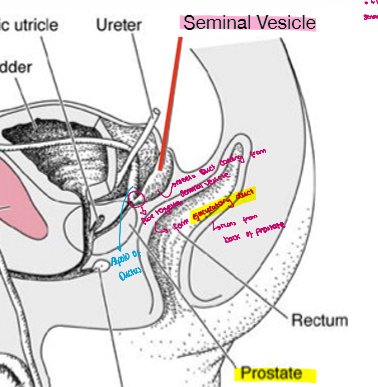
Seminal vesicles
convoluted tubules packed into gland
responsible of 70% of seminal fluid
fluid contains food e.g. fructose, proteins which is needed by spermatazoa , Vitamine C , citric acid
fluid is alkali Ph >7 healthy for sperm
Seminal vesicle and ductus defernce
so ductus deference forms Apollo of ductus which meets seminal duct from seminal vesicle
they fuse together to form ejaculatory duct which is located behind the prostate
Prostate
also an exocrine gland
adds things to sem en
contributes 1/3 to total vol
Adds ; sugars (fructose) enzymes (prostatic specific enzymes) and zinc (stablaises DNA)
What are teh 2 things that help regulate sper m production?
Cremsteric muslce → in spermatic cord, brings tetses towards or away from body to make environment good to make sper m (34 degrees)
Dartos msucle → surrounds testis making skin thinner or thicker deepening of environment
what happens next after prostate
So once sem en form ejaculatory duct gets into prostate is at its full volume after prostte adds more fluid
then in prostate also get urethra form bladder in here
urethra meets elements form reproductive tract and they then fuse together and run through urethra thorugh peni s
benign prostatic hyperplasia
Enlargment of prostate gland on dorsal posterior side
due to growth of epithilum and stroma tissue
causes problems with urination as blocsks internal neck sphincter
have pain during urnation , pee at night , urgency sudden deisre to pee
treatments → alpha blockers relax muscle , surgery
Prostate cancer
slow growing cancer
more comm in erdely men
death due to metastasis
have venous plexus which can cause spread to bony pelvis and vertebrae column
spread through internal iliac veins to heart and lungs
Symptoms → hard to urinate , back pain due to tumor growth on vertebrae column
fist way to check is by pressing on anterior wall of rectum to see if have hardening of prost ate
Bulboreurethral gland
sits next to pelvic floor
secreates mucus and lumbrication into urethra before sem en passes
fluid is alkali - helps remove any urine left in urethra nutralise it as its acidic , helps form low viscosity path in vag ina a for spe rm to pass through
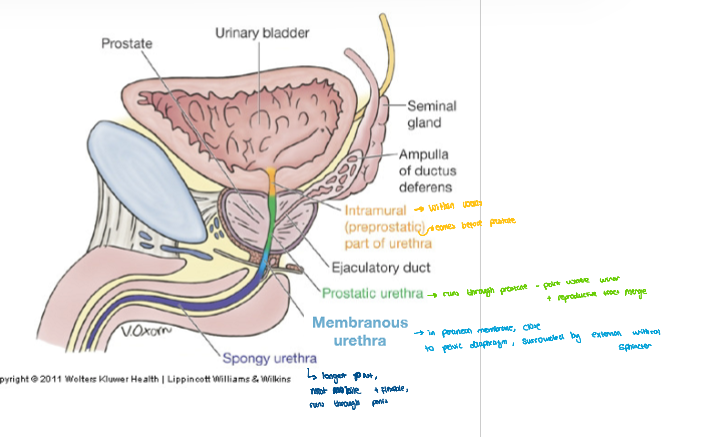
Peni s structure

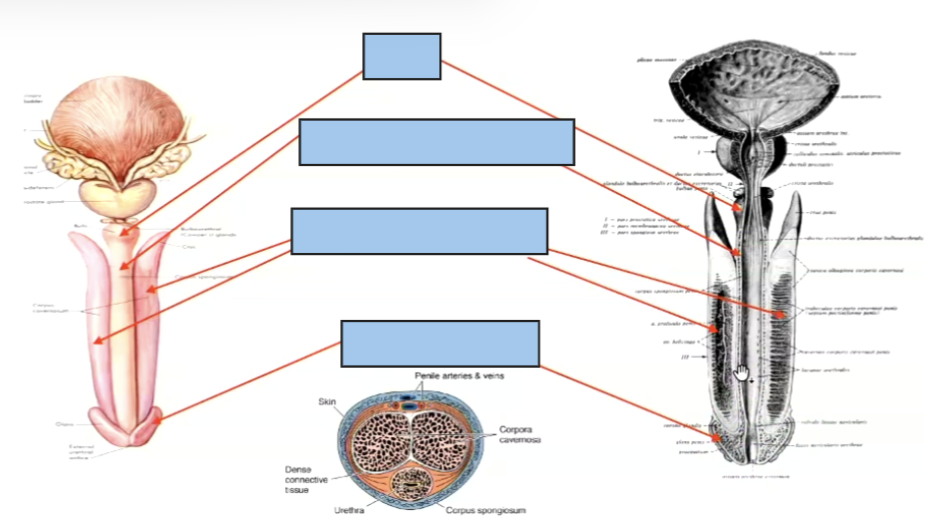
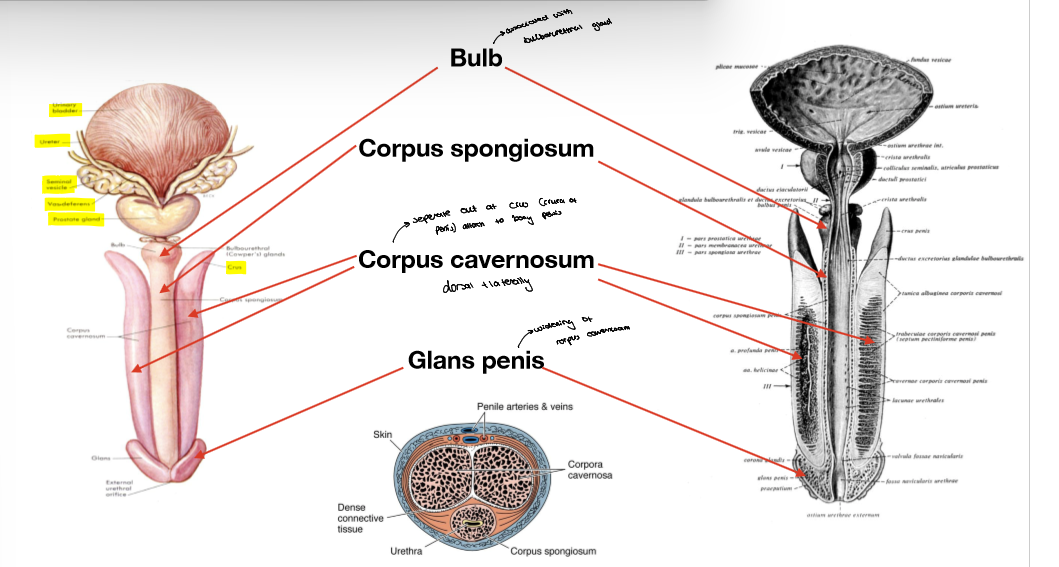
Parts of teh urethra
Intermurinal - before prostate
prostetic urethra - in prostate where uriter and reproductive tracts join
membranous urethra - surrounded by external sphincter
spongy urethra - most flexible part, longest part , rusn through peni s
Urethral sphincter
Internal urethral sphincter
just above prostate
stops urine from leaving bladder
stops back flow of se men - under sympathetic control
smooth muscle
involuntary
Autonomic nerves - Sympathetic and parasympathetic
External urethral sphincter
in membranous urethra
Skeletal muscle
somatic
voluntary control
perineal nerve - branch of pudendal nerve
Flassid state
most of time in this state
most arteriol blood bypasses corposa cavernosa through atriovenouse anastomosis
so most blood goes from arteriol system to veouse system without going through complicated capillary beds
keeps pressure low and so in flassid state
Errection
Parsympathtic innervation (S2-S4) closes arterio venouse ansatomasis
blood is forced through corpus caviosum and corpus somavgiosum
more blood flowing through then causes errection epenis becomes enlaged and turgid
Tonic contraction inhibited, arteries straighten incraease blood to cavionosum spaces
contarction of msucles at base of peni s, vessles become compressed forcing blood to move up the peni s
Pathway of PS fibers in erection
PS nerves from sacrum nerve s2,s3,s4
move out then loop back through splanchnic nerves
then 2nd order reaction with cavernous nerves which increase parasympathetic activity to corpus cavenosam causing errection
what happens after erection
Emission
when seme n and glandular secretions mix together in prostati c urethra
sympathtic repsonce
proximal parts of urethra fill up with se- me
Ejacul-ation
contraction of urethra
increase pressure of urethra
Sympathetic→ cause closure of internal urethral sphincter
somatic nerves cause rhythmic contraction of muscles in base of pe nis bulbospongioses and ischiocavernosis - involved in erection and increasing pressure in urethra and causing ejacu lation
Remission
reversion of errect-ion
increase sympathetic input - return of blood shunts
Less blood to blood to pen is
Allows venous return less coiling of blood vessels at base of pen is
Becomes flaccid again
Sympathetic pathway for ejaculat-ion

Muscles / tissues involved

arterial supply and nerve supply
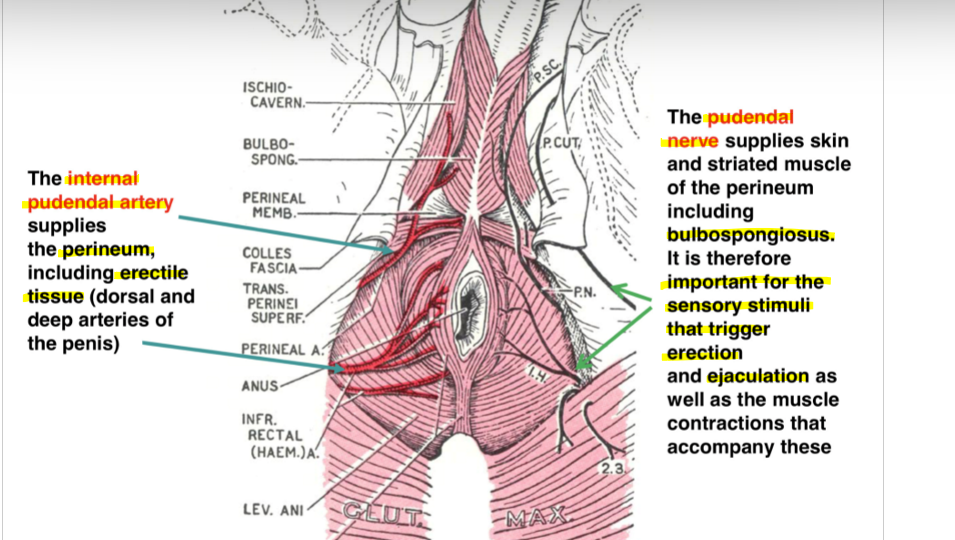
last bit look at notes