Chapter 6 Study Guide: Bone Tissue
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
diaphysis
The long middle part of the bone (like the shaft of a baseball bat).
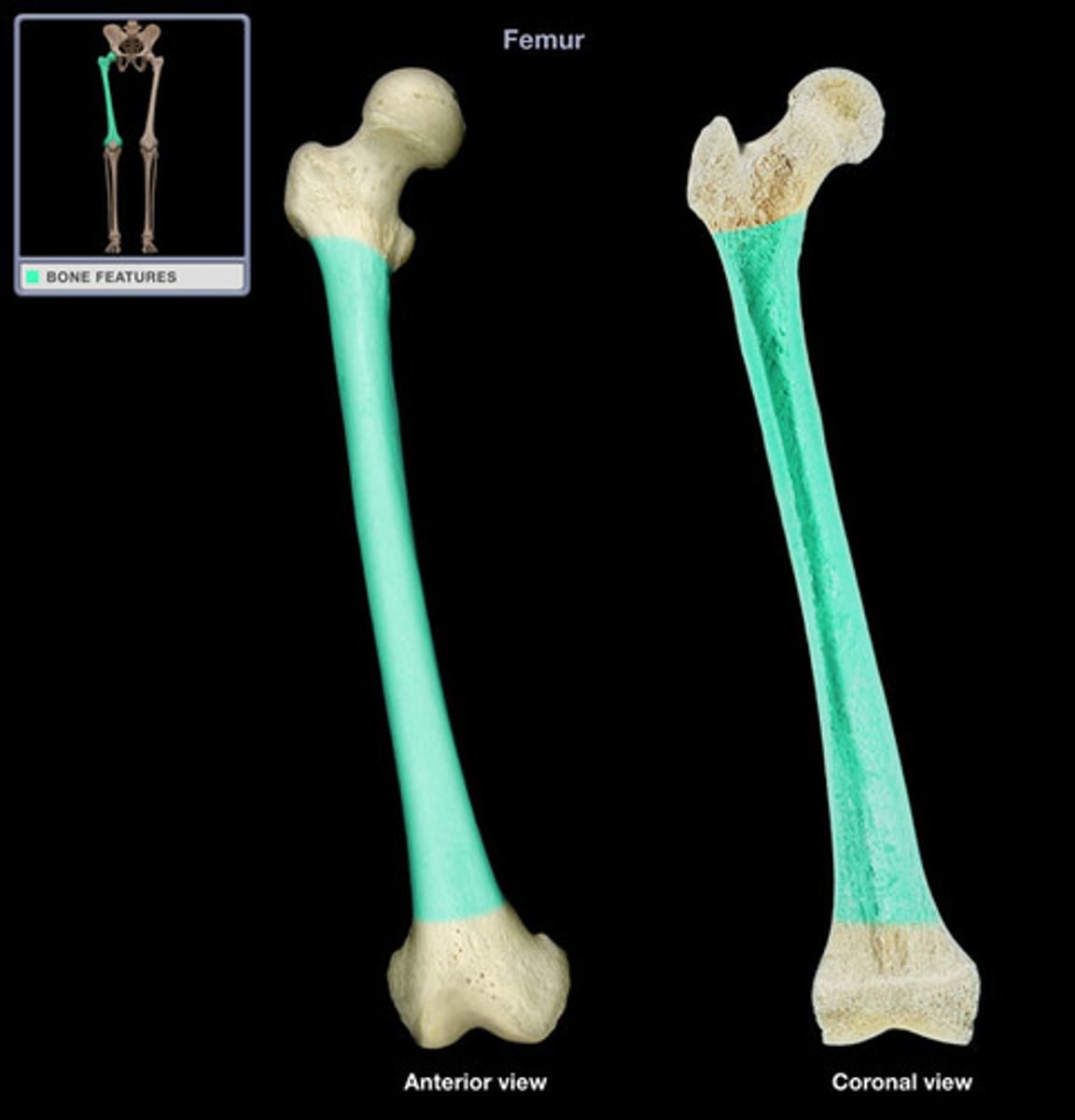
epiphyses
The rounded ends of the bone (like the knob at the end of a drumstick).
metaphyses
The zones between the middle and ends where growth happens (like the stretchy part of a rubber toy).

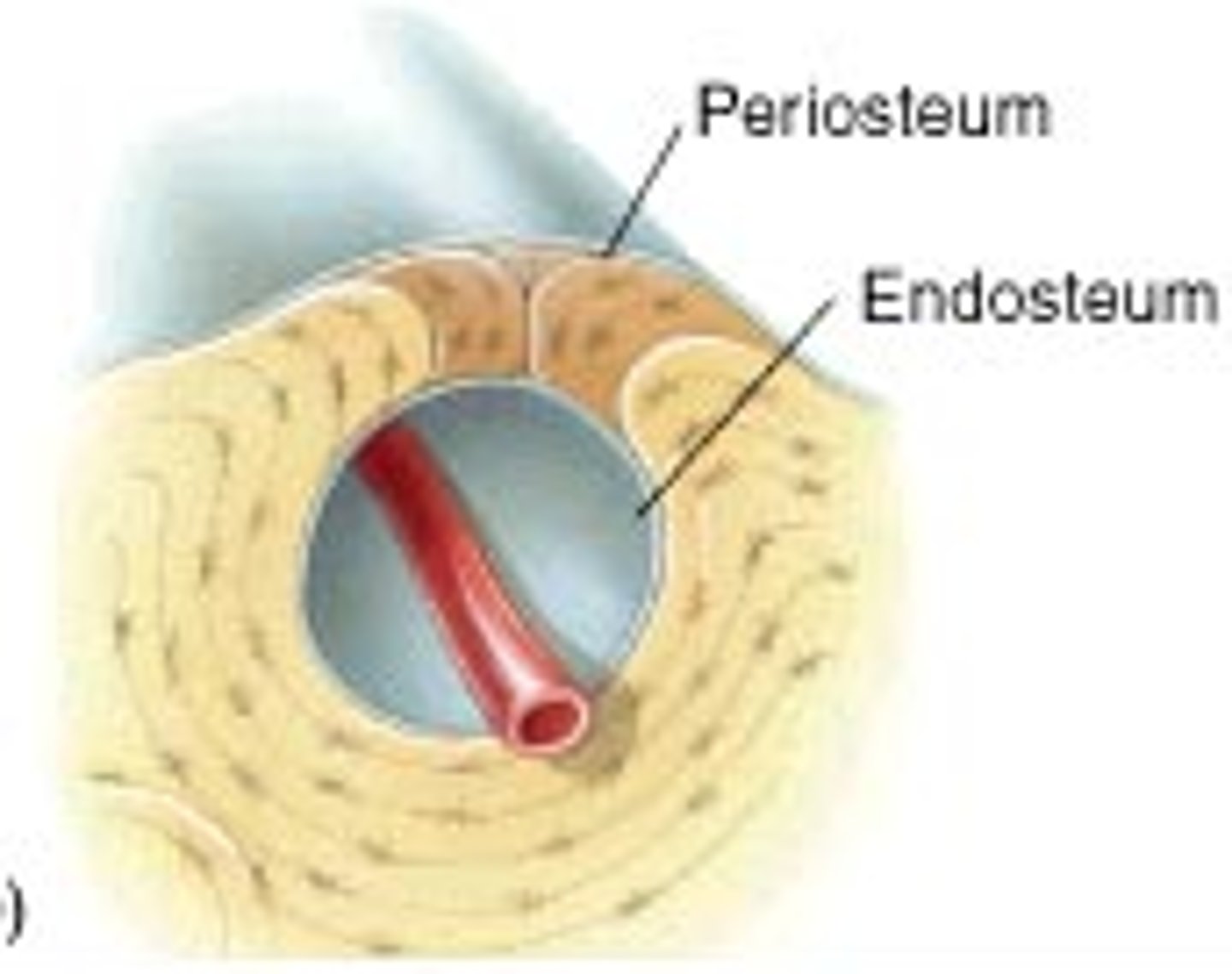
periosteum
The outer layer covering the bone, like skin on a sausage.
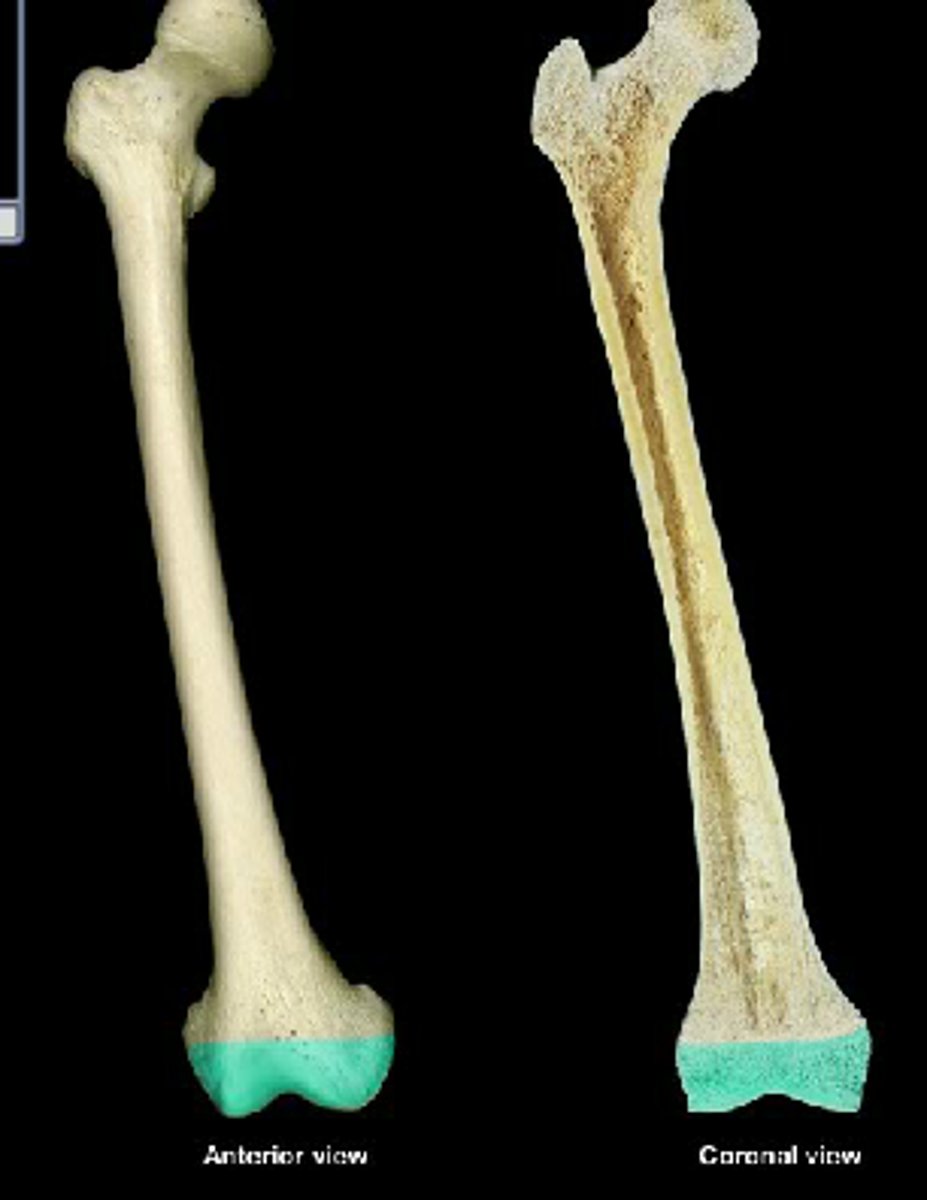
medullary cavity (marrow cavity)
The hollow center of the bone filled with marrow (like jelly in a donut).
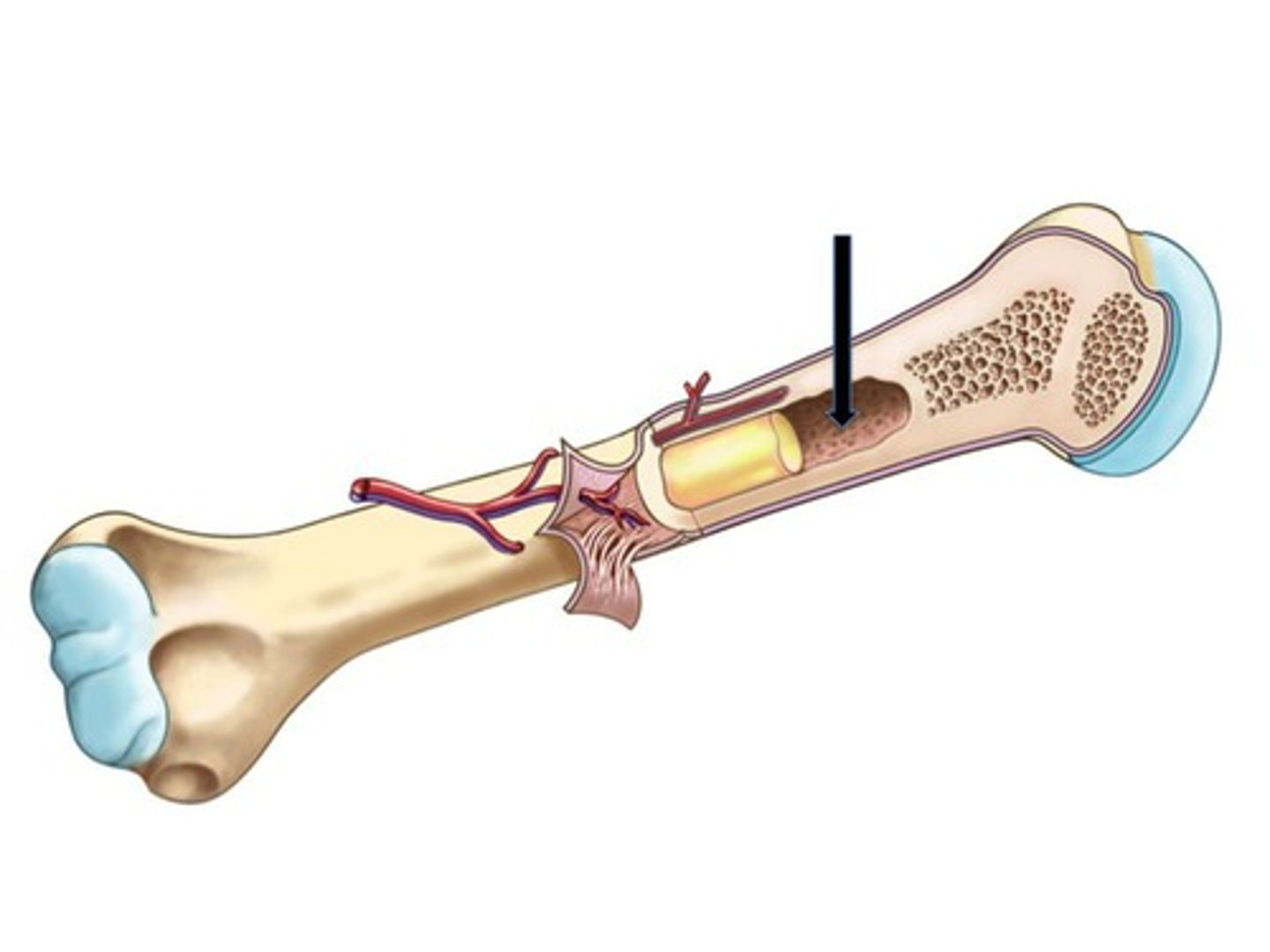
endosteum
The inner lining of the medullary cavity (like the inner wrapper lining a chocolate bar).
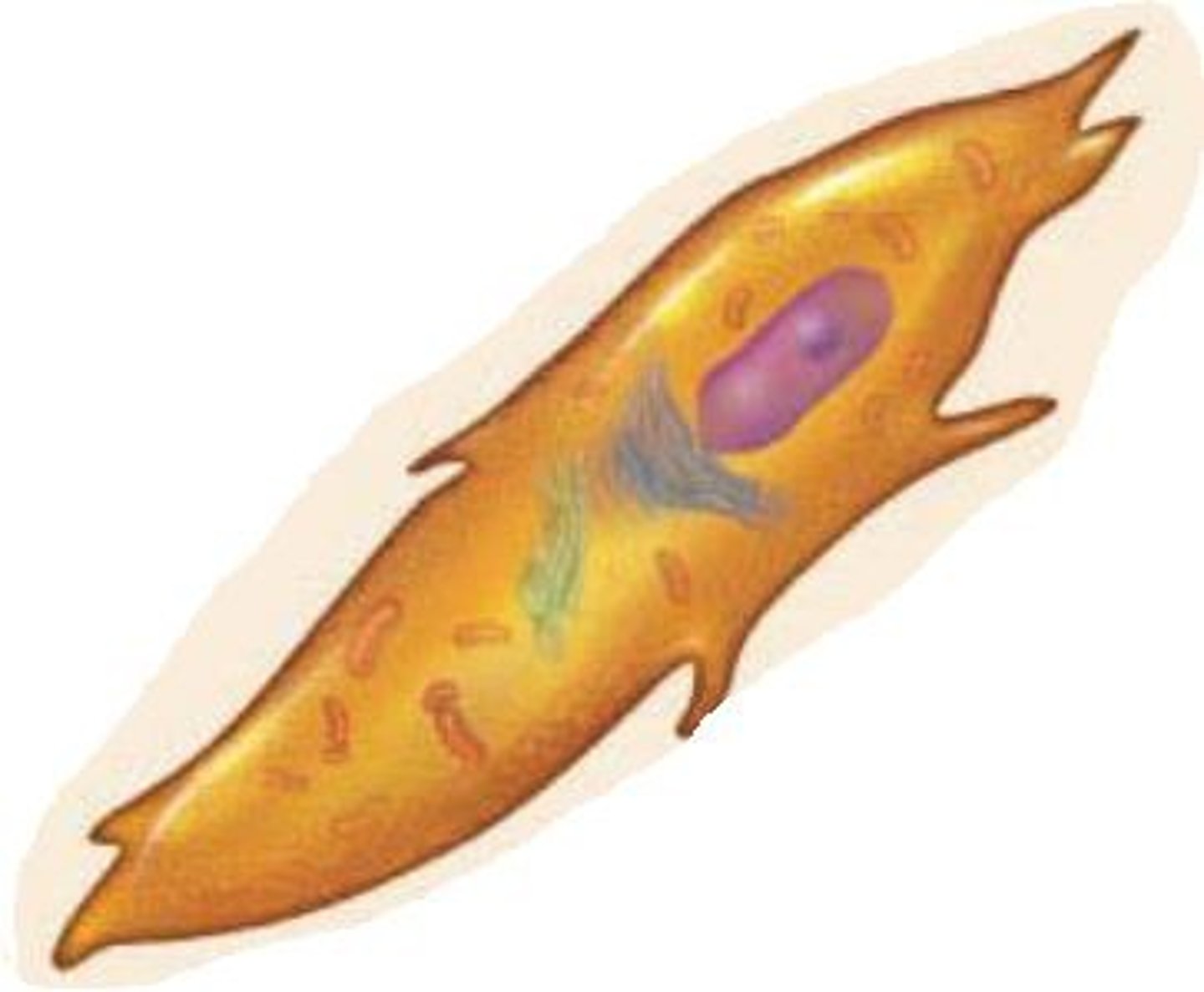
osteogenic cells
Stem cells that develop into osteoblasts. The “baby” cells that can become builders.
osteoblasts
produce the molecules of the bone matrix. The builders – they build new bone.
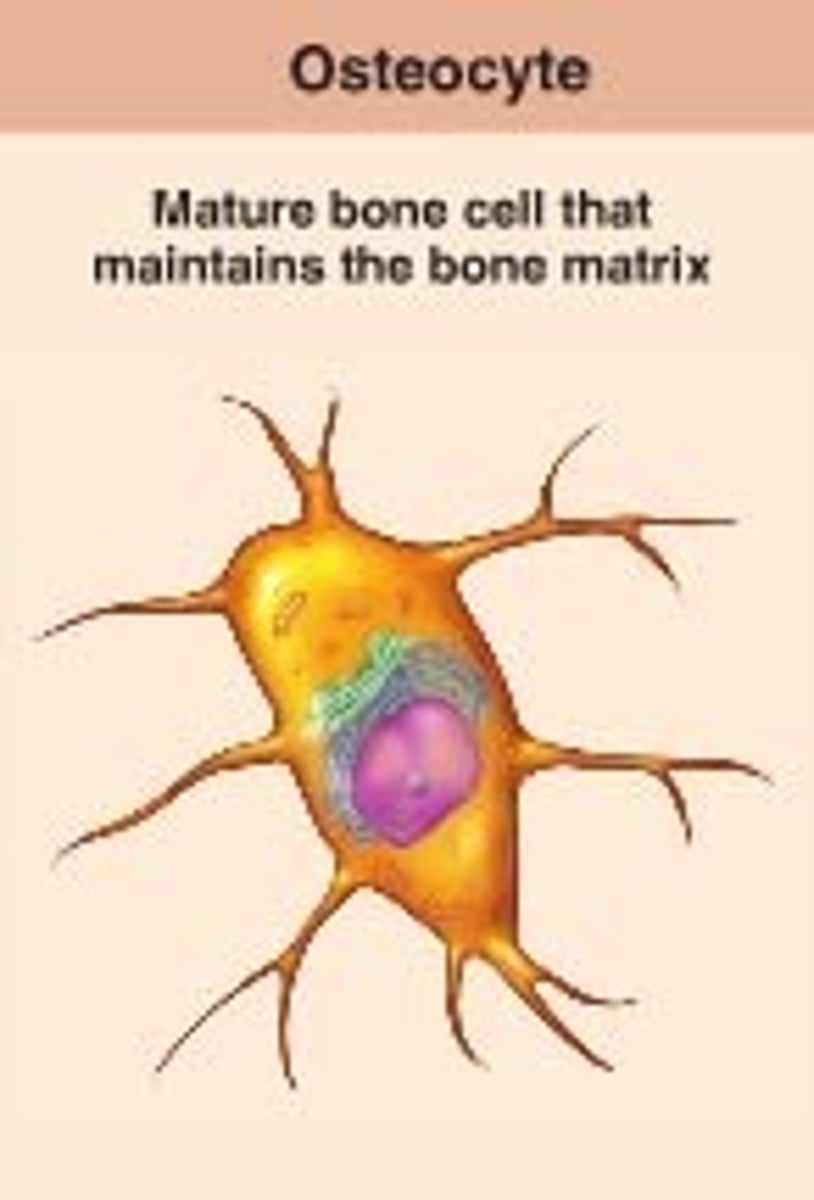
osteocytes
mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix (and bone tissue). The managers they maintain and check on the bone.
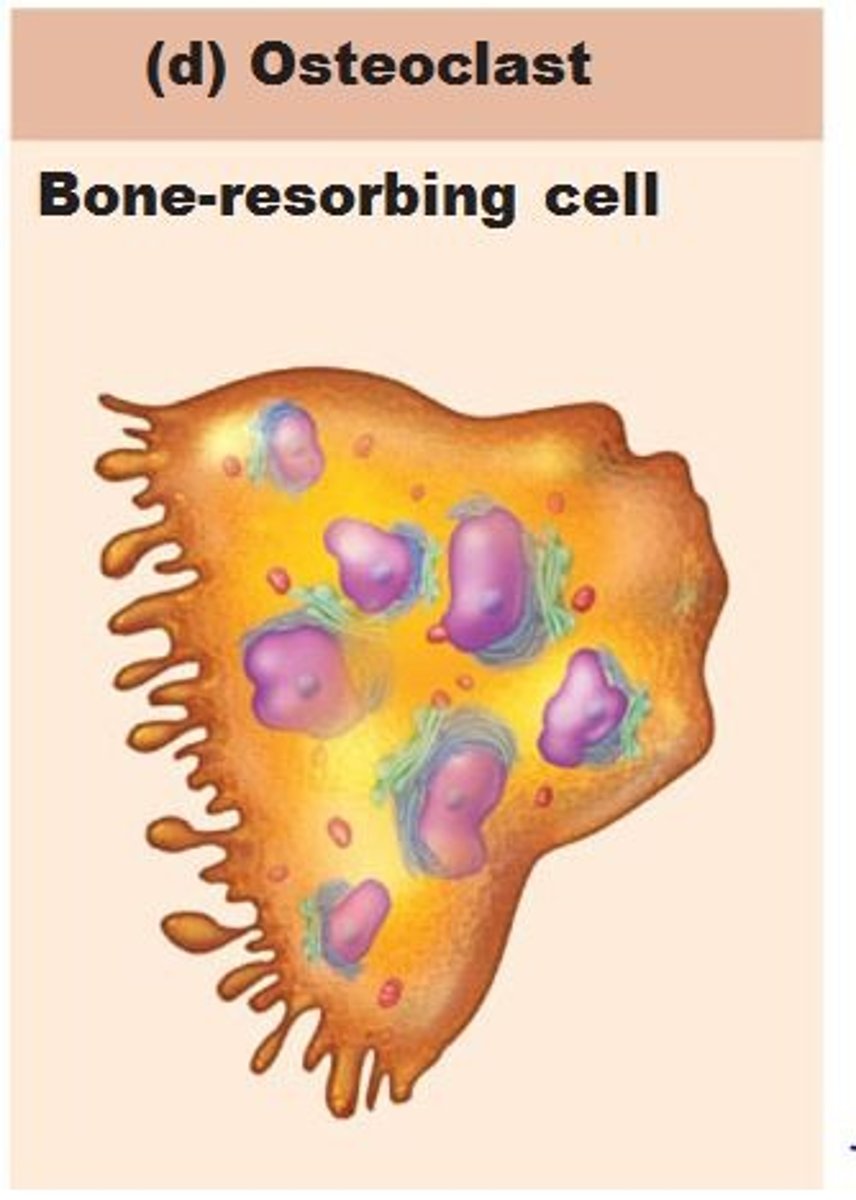
osteoclasts
Cells that destroy the bone matrix (dissolving bone tissue). The demolition crew – they break down bone to release calcium.
compact bone
Hard and solid like concrete (outer layer of bone).
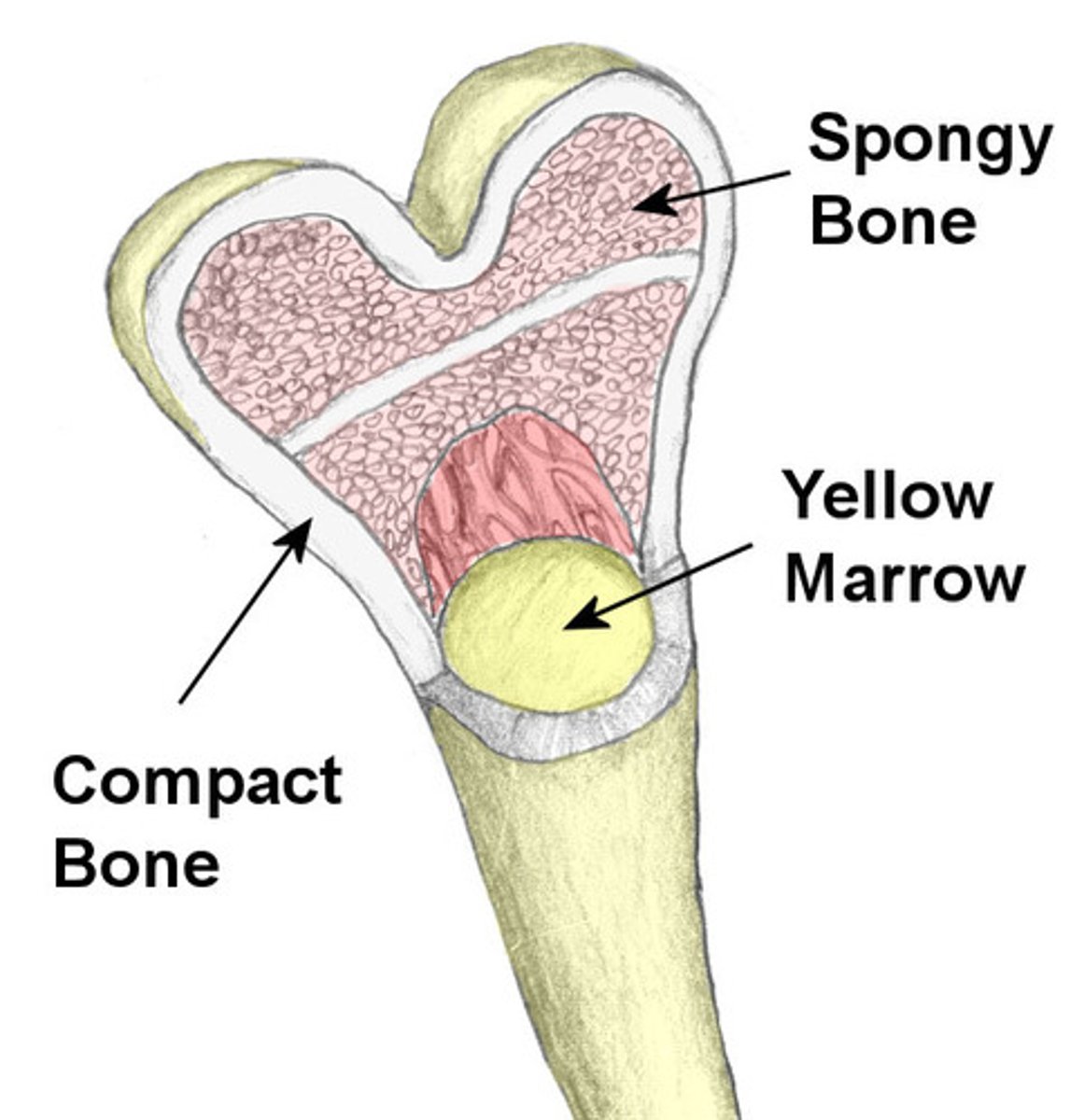
spongy bone
Lightweight and airy like a sponge or honeycomb (inside of bone).
osteons or Haversian systems
Circular building blocks of compact bone (like tree rings).
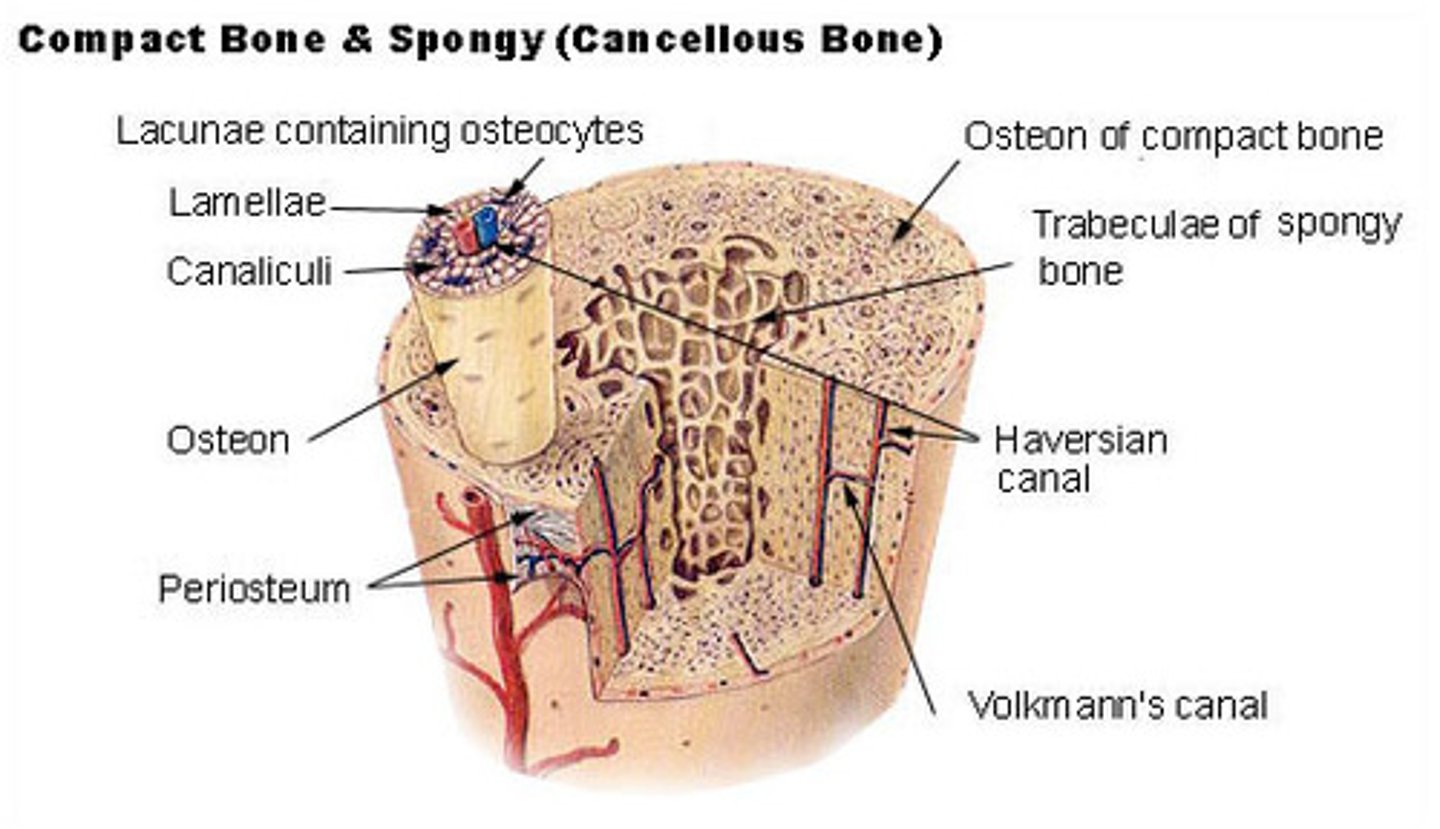
perforating (Volkmann's) canals
Side roads bringing blood from the outside into the bone.
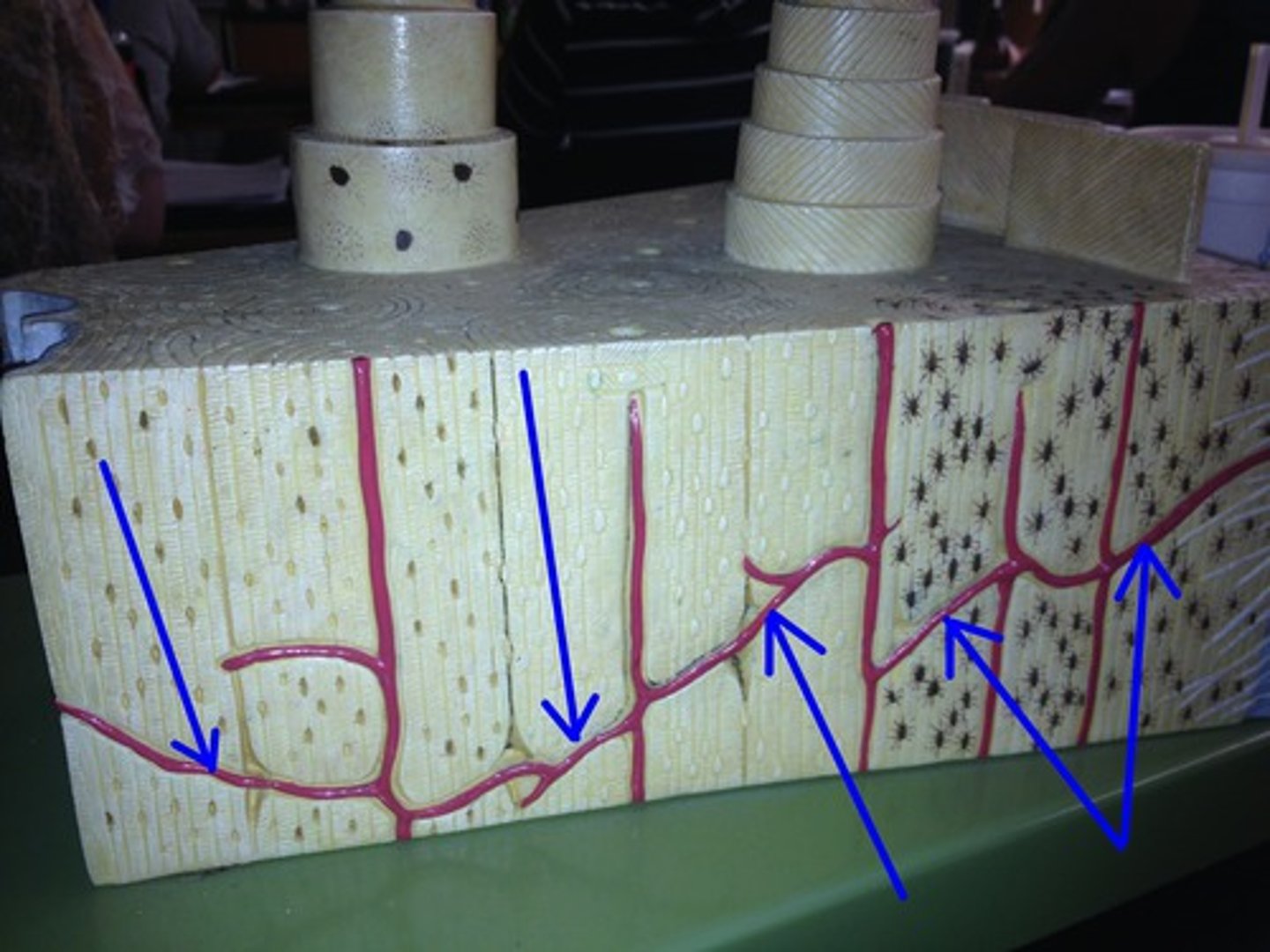
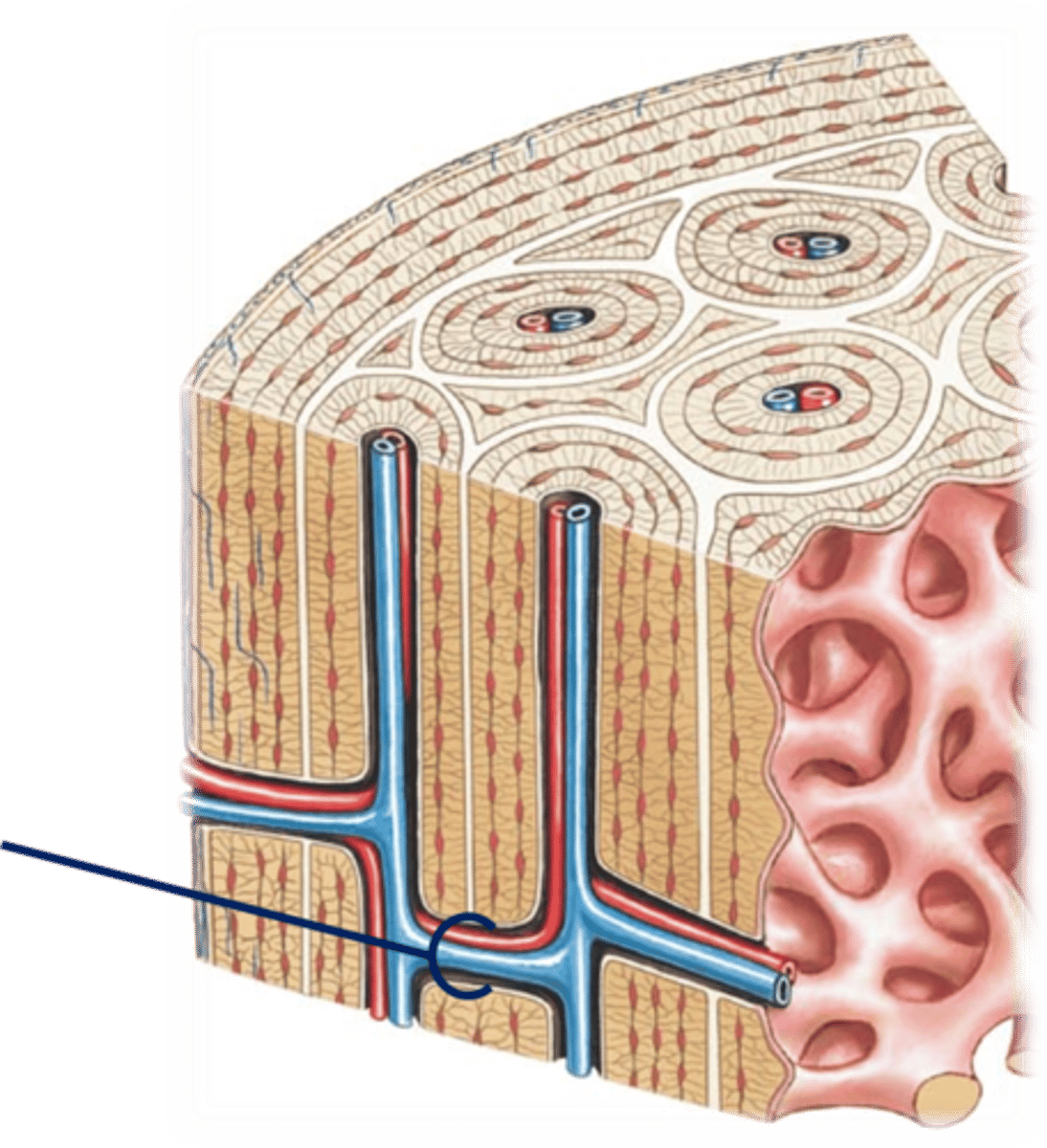
central (Haversian) canals
Main roads running through each osteon for blood vessels.
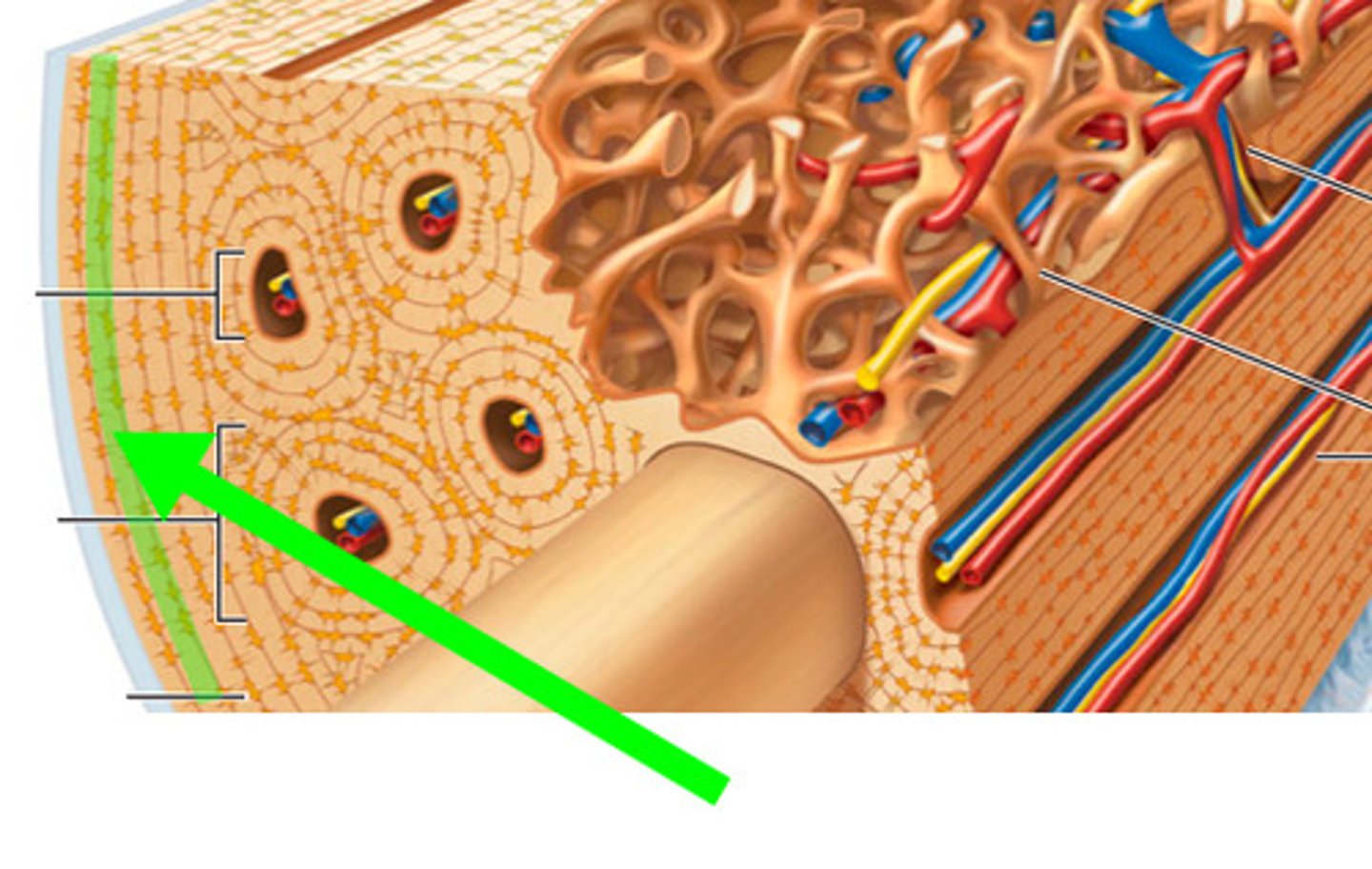
lamellae
Layers or rings in the osteon (like onion layers). Thin (concentric) layers of bone matrix that form the structure of osteons.
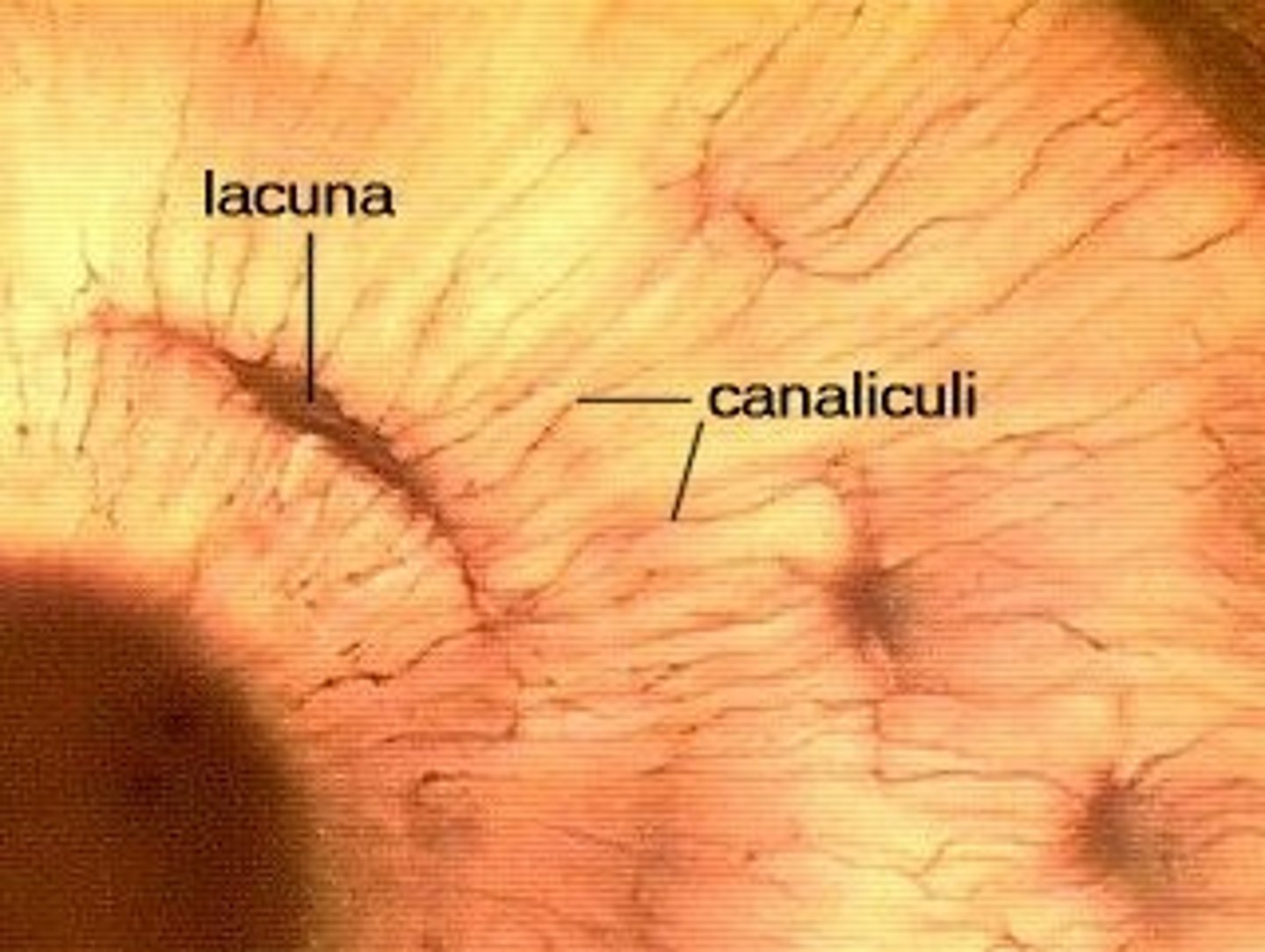
lacunae
Small “rooms” where bone cells (osteocytes) live. Tiny holes or spaces in the bone layers where osteocytes live
canaliculi
Tiny tunnels that connect bone cells so they can talk (like text messages). Microscopic canals that connect lacunae and allow for communication between osteocytes.
trabeculae
The lattice-like beams in spongy bone (like scaffolding in a building. The small, rod-like structures in spongy bone provide support.
ossification or osteogenesis
The process by which bone forms. The process of bone formation (like pouring concrete to make a sidewalk).
intramembranous ossification
The process by which bone develops directly from mesenchymal tissue. Bone forms directly from soft tissue (like a flat bone of the skull forming from a soft sheet).
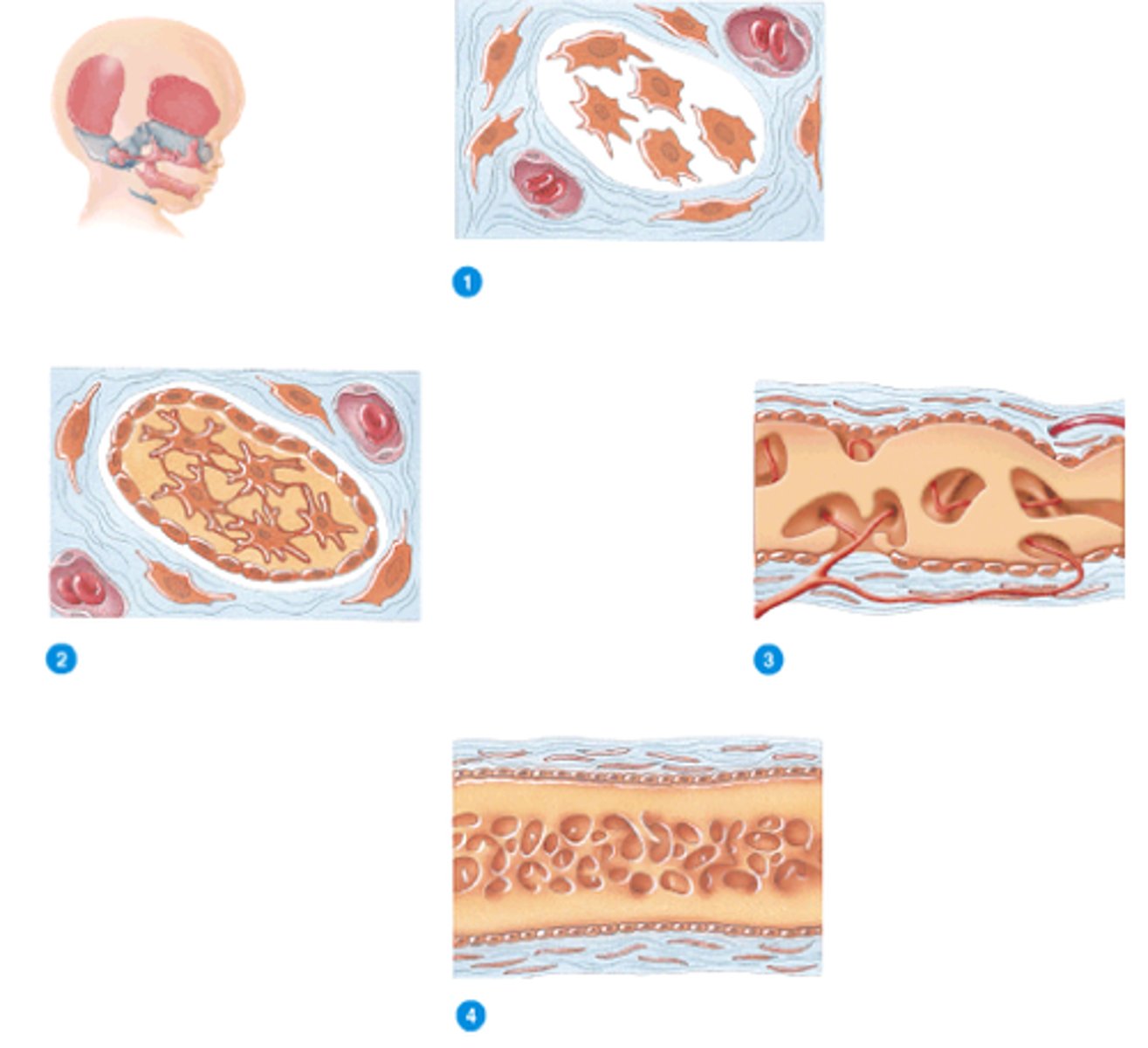
endochondral ossification
The process by which bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage. Bone replaces cartilage (like turning rubber into stone — most bones do this).
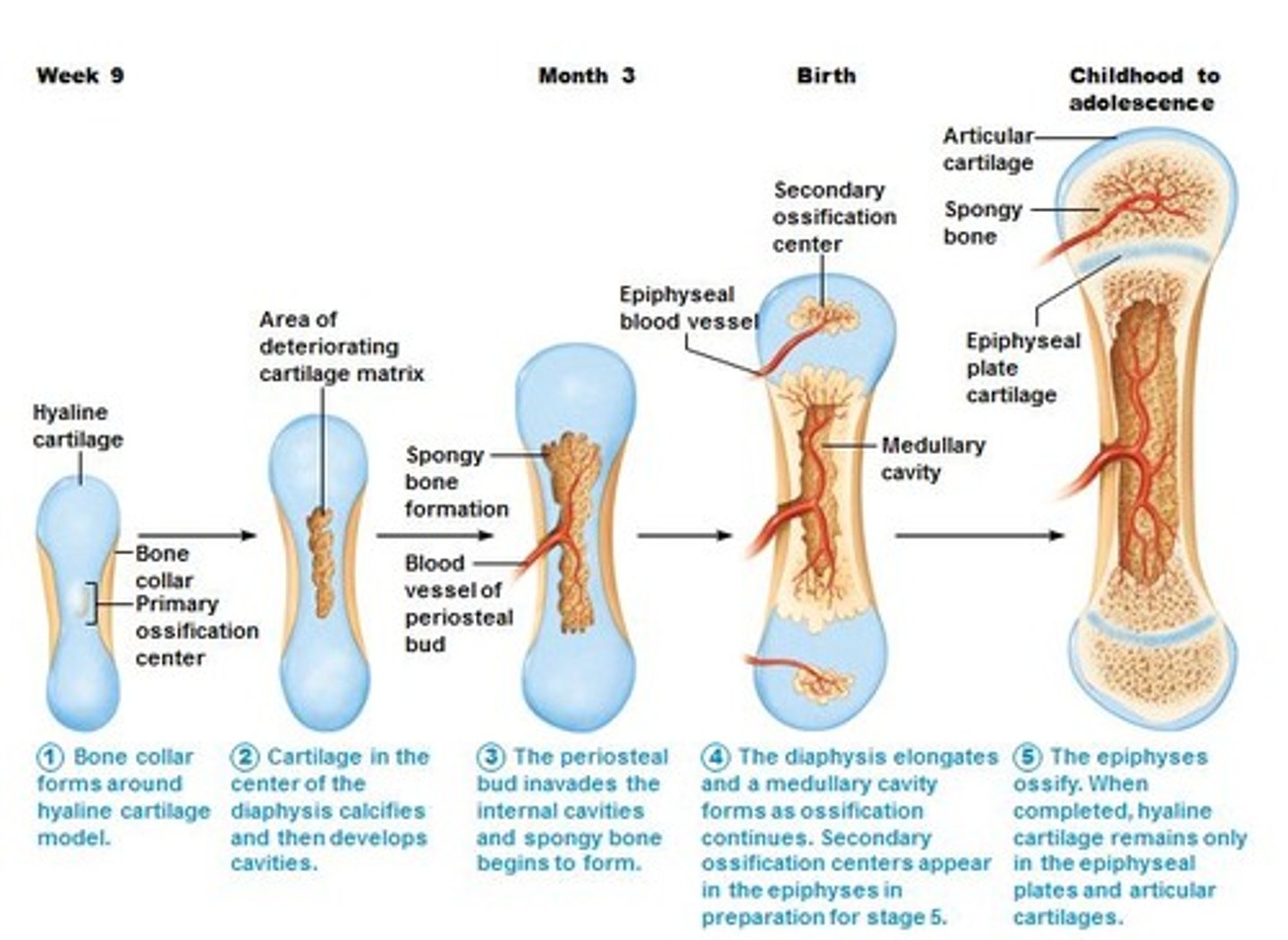
interstitial growth
Growth in length occurs at the growth plate epiphyseal plates. Bones grow longer at the growth plate (like stretching a rubber band).
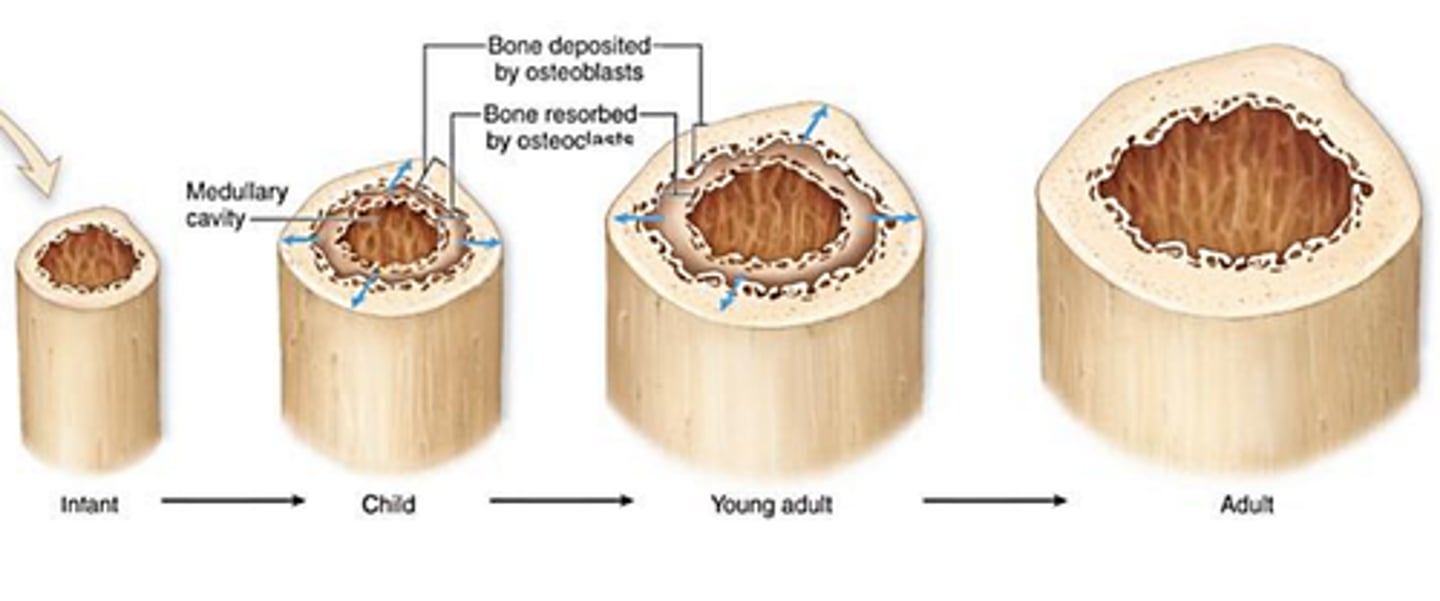
appositional growth
Bones grow thicker by adding layers (like wrapping more tape around a pipe).
primary ossification center
The first spot where bone starts to form (in the middle of the bone).
secondary ossification center
They show up later at the ends of the bone (epiphyses) after the primary center does its thing.
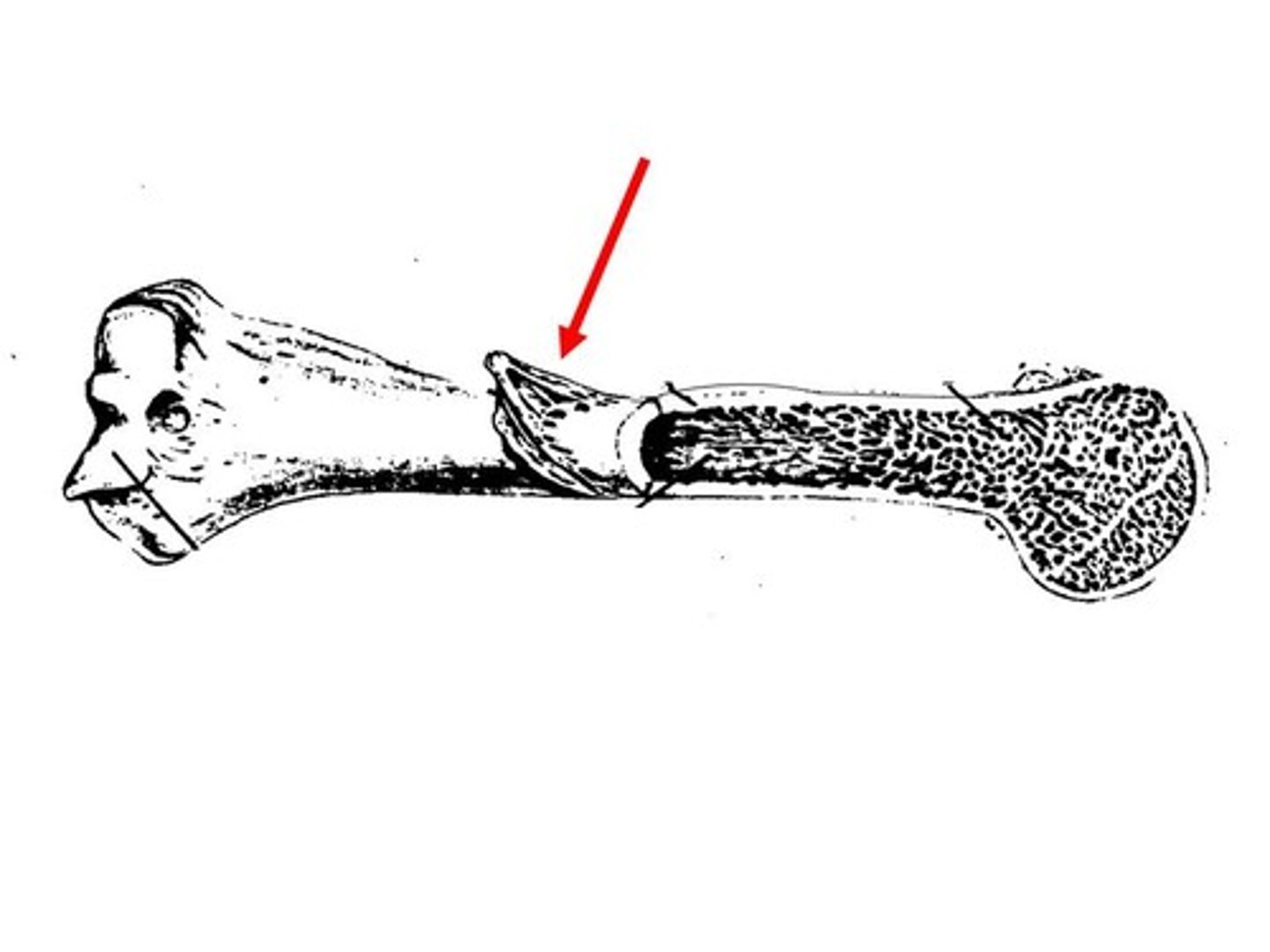
epiphyseal plate
The growth plate is where bone lengthens (like a stretchy band). Where, the cartilage between the diaphysis and epiphysis lets your bone grow longer
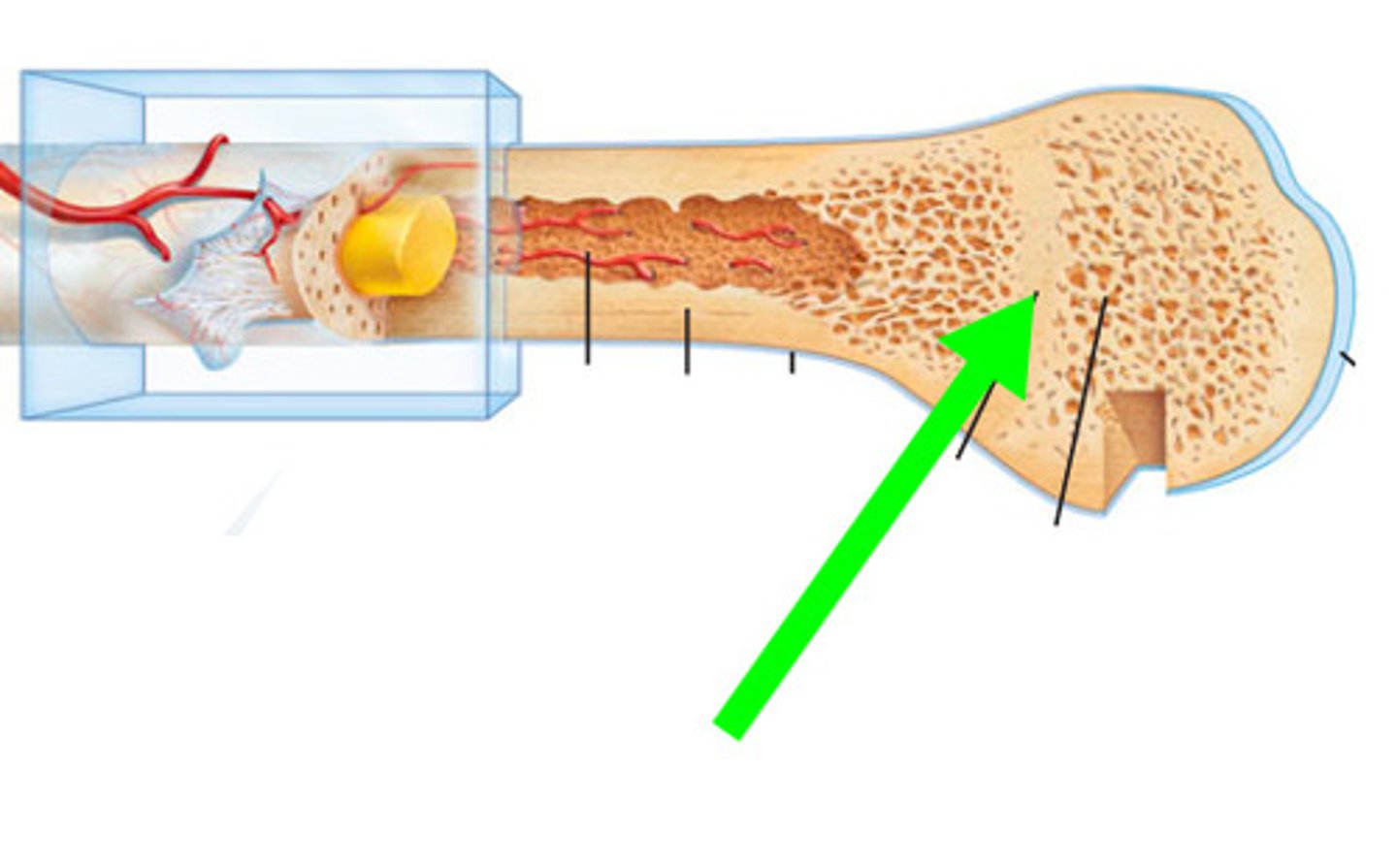
epiphyseal line
What’s left after growth stops (a scar that shows you’re done growing). It means you've stopped growing
bone remodeling
Constantly replacing old bone with new (like renovating your house a little at a time).
bone resorption
Breaking down bone to release calcium (like taking apart a Lego set).
Disuse (like muscles shrinking if you don’t use them)
No use = bone loss
Stress (like lifting weights makes bones denser).
More stress = stronger bones
Cardiac arrest (heart can’t beat right).
Too much blood calcium
Respiratory arrest (muscles can’t contract properly).
Too little blood calcium
Blood calcium levels regulated by control of rate of resorption from bone
Pulling calcium out
Blood calcium levels regulated by control of rate of deposition into bone
Putting calcium in
Turns on the calcium-releasing team.
Increased PTH (parathyroid hormone) production
Decreasing blood calcium levels results. More bone breakdown = more calcium released
Increase the number and activity of osteoclasts
Decreasing blood calcium levels. Kidneys save calcium instead of peeing it out.
Decrease urine calcium loss
Helps absorb more calcium from food in the intestines. Promotes calcium absorption from GI tract
Calcitriol
Rising blood calcium levels. Hormone that stores calcium back in bone
Increased Calcitonin Production
Calcitonin accelerates. Bone “soaks up” extra calcium like a sponge.
Calcium deposition