Cerebellum
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture complete 4/2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
the cerebellum sits within which fossa?
the posterior fossa
the cerebellum sits on the ___, meaning the cerebral tonsils can ___
foramen magnum, press on spinal column
the 4th ventricle is ___ to the cerebellum
ventral
what view of the cerebellum?
posterior
what view of the cerebellum?
anterior

what view of the cerebellum?
inferior

what view of the cerebellum?
superior
list the lobes and functional areas of the cerebellum.
lobes - anterior, posterior, flocculonodular
functional areas - spinocerebellum, cerebrocerebellum, and vestibulocerebellum
the vermis and paravermis are included in which functional area?
the spinocerebellum
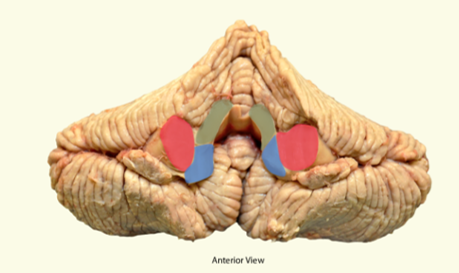
what is highlighted in green?
superior cerebellar peduncle
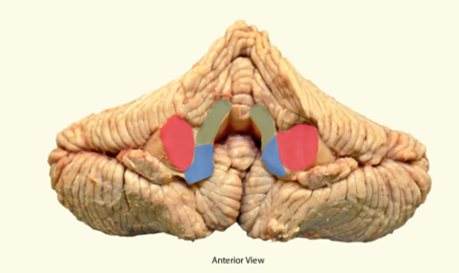
what is highlighted in red?
middle cerebellar peduncle
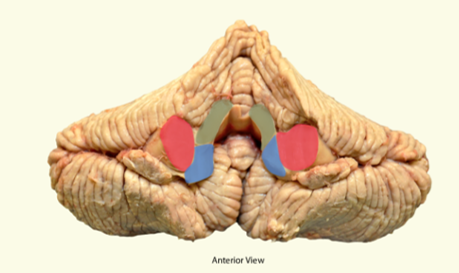
what is highlighted in blue?
inferior cerebellar peduncle
what is the basic flow of info through the cerebellum?
inputs arrive at cerebellar cortex, which projects to deep nuclei, which provide output
input → cerebellar cortex → deep cerebellar nuclei → output
what are the transverse divisions of the cerebellum? what are the longitudinal divisions?
transverse: anterior lobe, posterior lobe, flocculonodular lobe
longitudinal: vermis, paramedian (paravermis), lateral
which longitudinal cerebellar region is specialized for body posture?
vermis
which longitudinal cerebellar region regulates gross movements of ipsilateral extremities (such as walking)?
paravermis
which longitudinal cerebellar region regulates skilled movements of the ipsilateral extremity?
lateral
what separates the anterior and posterior lobes of the cerebellum?
the primary fissure
which lobe of the cerebellum regulates eye movement and body posture?
flocculonodular lobe
which lobe of the cerebellum regulates movements of the legs?
the anterior lobe.
which lobe of the cerebellum regulates movements of the arms?
posterior lobe
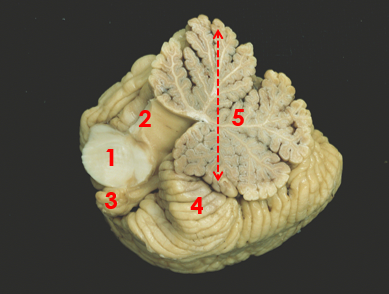
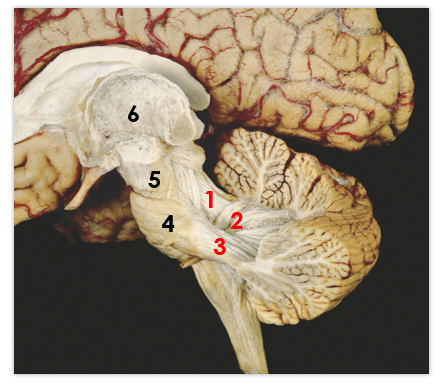
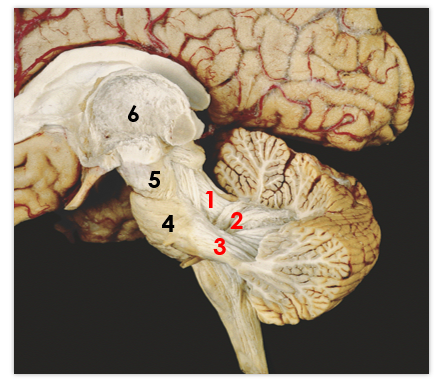
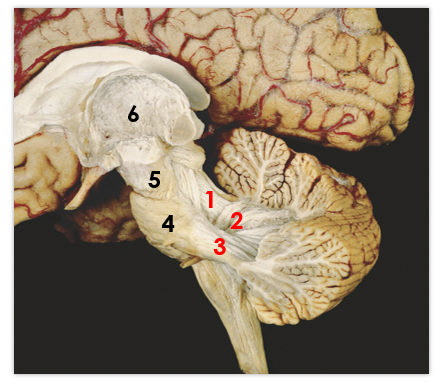
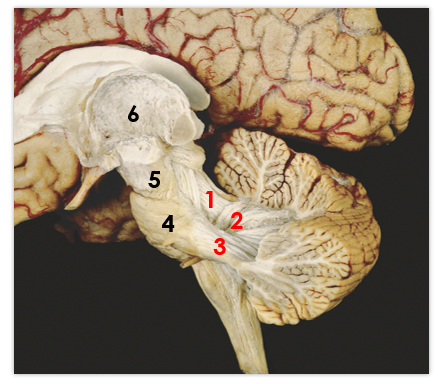
1
middle peduncle
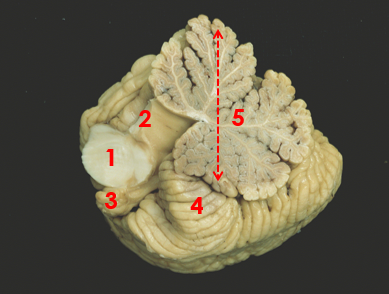
2
superior peduncle
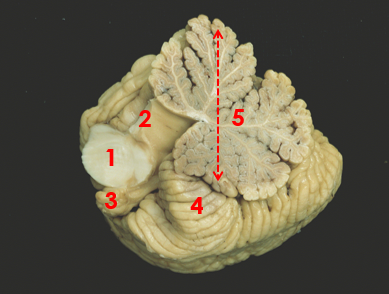
3
flocculus
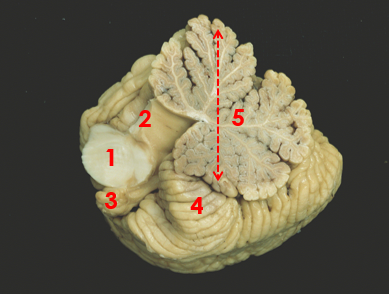
4
tonsil
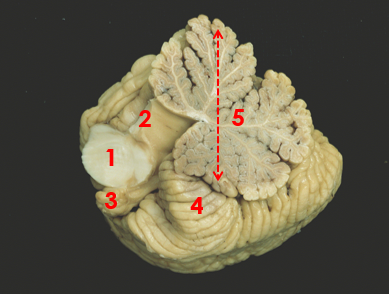
5
vermis
list the 3 deep cerebellar nuclei
dentate nucleus, fastigial nucleus, and the interposed nucleus (emboliform and globose)
do the deep cerebellar nuclei receive inhibitory or excitatory signals from other parts of the brain?
they receive both inhibitory and excitatory signals 👍
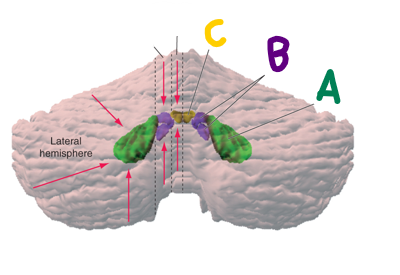
which is the fastigial nucleus?
C (yellow)
which is the interposed nucleus?
B (purple)
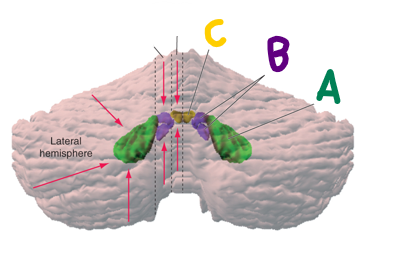
which is the dentate nucleus?
A (green)
largest deep cerebellar nucleus, communicates through cerebellar peduncles
dentate nucleus
what is the function of the dentate nucleus?
coordinating fine limb movements
what is the function of the intermediate/interposed nucleus?
regulates ipsilateral extremity (gross movement)
what is the function of the fastigial nucleus?
regulates body posture via flocculonodular lobe
in terms of information entering/exiting the cerebellum, what does the middle cerebellar peduncle do?
input from pons
in terms of information entering/exiting the cerebellum, what does the inferior cerebellar peduncle do?
input from inferior olive, spinal cord, and vestibular nucleus
how does info from the frontal-motor/parietal cortex get to the cerebellum?
it goes through the VA thalamus, through the pons, through the middle cerebellar peduncle, to the cerebellum
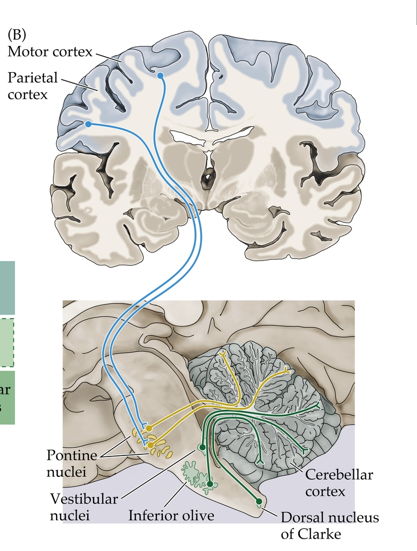
what is the main input to the cerebellum?
the middle cerebellar peduncle
in terms of information entering/exiting the cerebellum, what does the superior cerebellar peduncle do?
output from cerebellum
how does info get from the cerebellum to the primary motor and premotor cortex?
it leaves the cerebellar cortex through deep cerebellar nuclei exiting through the superior cerebellar peduncle, through the VL thalamus → to cortex
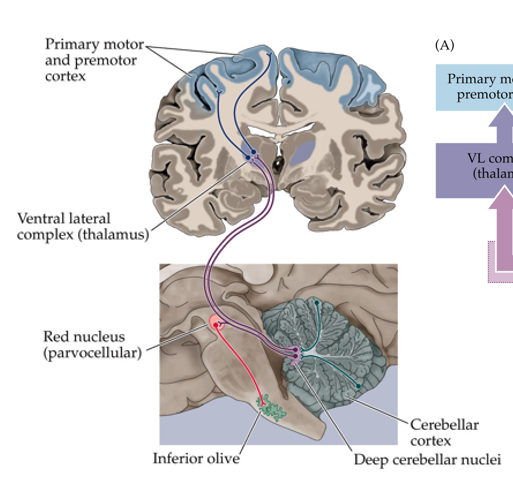
what is the output target of the cerebrocerebellum? list deep cerebellar nuclei, other targets, and function
dentate nucleus → premotor cortex (UMNs) → motor planning
what is the output target of the spinocerebellum? list deep cerebellar nuclei, other targets, and function
interposed and fastigial nuclei → motor cortex and brainstem (UMNs) → motor execution
what is the output target of the vestibulocerebellum (FN lobe)? list deep cerebellar nuclei, other targets, and function
vestibular nuclei → LMNs in spinal cord and brainstem → balance and vestibulo-ocular regulation
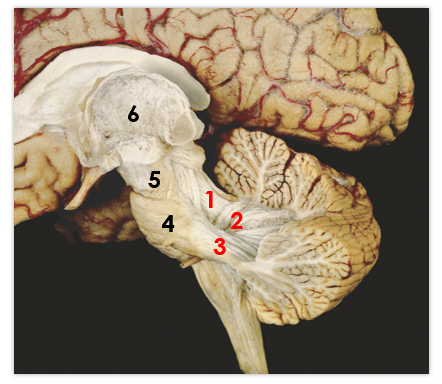
1
superior cerebellar peduncle
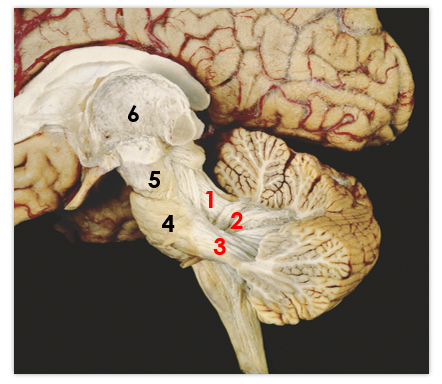
2
inferior cerebellar peduncle
3
middle cerebellar peduncle
4
pons
5
midbrain
6
thalamus
cellularly, what are the output of the cerebellar cortex?
purkinje cells
list the three cerebellar cortex layers from innermost to outermost
granule, purkinje, molecular
cellularly, what are the inputs to the cerebellar cortex?
climbing fibers and mossy fibers
where do climbing fibers originate?
inferior olive (medulla)
climbing fibers (excite/inhibit) purkinje cells
excite
mossy fibers (excite/inhibit) granule cells
excite
granule cells (excite/inhibit) purkinje cells
excite
basket interneurons (excite/inhibit) purkinje cells
inhibit
purkinje cells (excite/inhibit) cerebellar nuclei
tonically inhibit
what are the primary functions of the cerebellum?
control posture, correct rapid movements initiated by cerebral cortex, motor learning, movement control
how does the cerebellum control movement?
cerebellum receives intention from motor cortex to start a voluntary movement. proprioceptors and visual signals inform cerebellum of body position. cerebellum plans best way to perform a movement and sends a “blueprint” to the motor cortex. errors sent to cerebellum for correction
nystagmus
jerky eye movements
ataxia
lack of coordination
dysarthria
speech difficulties
intention tremor
tremor upon movement
titubation
body wavering
dysdiadochokinesia
clumsy alternating movements
dysmetria
under/overshooting
where does the flocculonodular lobe receive input from?
vestibular input from semicircular canals and vestibular nuclei, visual input from superior colliculi and visual cortex
lesions of the ___ disturb eye tracking, balance, and gait
flocculonodular lobe
where does the paravermal region receive input from?
proprioceptive input from spinal cord, trigeminal nerve (CN V), visual and auditory systems
the paravermal region sends fibers to deep cerebellar nuclei, which project to cerebral cortex to ___
modulate descending motor systems
which region contains sensory maps, which track the position of body parts in space?
paravermal region
which region uses proprioceptive input to predict future position of a body part during movement?
paravermal
the lateral cerebellum receives input from ___ via ___
cerebral cortex via pontine nuclei
the lateral cerebellum sends fibers to
the thalamus and the red nucleus
which region is involved in planning movement about to occur and in cognitive functions?
lateral cerebellum
intention tremor, dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, and scanning speech (slow separation of syllables) are all signs of syndrome in the
posterior lobe
ataxia involving lower limbs suggests syndrome of the
anterior lobe
alcoholic degeneration of purkinje cells is associated with which lobe?
anterior lobe syndrome
truncal ataxia (titubation) is a sign of syndrome in which lobe?
flocculonodular
peduncles review: mainly efferents to red nucleus and thalamus
superior cerebellar peduncle
peduncles review: afferents from pons and cortex
middle cerebellar peduncles
peduncles review: mainly afferents and efferents from vestibular nuclei
inferior cerebellar peduncles
afferent vs efferent (in 3rd semester of neuro is crazy 💀)
afferent - towards CNS
efferent - exiting CNS
list the afferent pathways associated with the inferior cerebellar peduncle
olivocerebellar tract, vestibulocerebellar tract, dorsal spinocerebellar tract, cuneocerebellar tract
give the location and function: olivocerebellar tract
from spinal cord through olivary nucleus to contralateral cerebellum
function: source of climbing fibers for direct input to cerebellum
give the location and function: vestibulocerebellar tract
from semicircular canals through inferior peduncle
function: maintains upright posture
give the location and function: dorsal spinocerebellar tract
from reticular nuclei (which regulates sleep, respiration, heart rate)
function: unconscious proprioception from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, and skin
what information does the cuneocerebellar tract carry?
proprioception from the upper limbs and neck
the middle cerebellar peduncle carries info from ___ to ___
from pontine nuclei (from opposite cerebral cortex, visual and auditory inputs), to opposite cerebellar hemisphere
the superior cerebellar peduncle sends outputs to the
contralateral red nucleus (midbrain) and ventral lateral nucleus (thalamus)
ventral spinocerebellar tract
unconscious proprioception from muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs, and skin
is the ventral spinocerebellar tract ipsilateral or contralateral?
ipsilateral, it decussates first through the anterior white commissure (spinal cord) and second through the superior cerebellar peduncle
the vermis gets input from.. (what kind of input?)
spinal cord, somatosensory and kinesthetic information
damage to the vermis leads to
difficulty with postural adjustments
the intermediate zone (paravermis) receives input from
red nucleus and somatosensory information from spinal cord
damage to the paravermis results in
rigidity and difficulty in moving limbs
lateral zone receives input from
motor and association cortices through the pons
damage to the lateral zone leads to
overshooting of movements, lack of coordination of multi-joint movement, and poor muscle learning/movement timing