Glycolysis + Fates of pyruvate/cori cycle
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:46 AM on 10/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
1
New cards
Glycolysis preparatory phase
traps glucose in the cell and modifies it so that it can be cleaved into a pair of phosphorylated 3-carbon compounds. Activate by phosphorylation
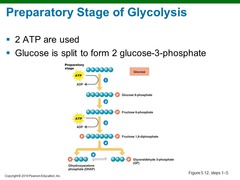
2
New cards
Glycolysis payoff stage
oxidizes the 3-carbon compounds to pyruvate while generating 2 molecules of ATP. Payoff phase. Collect energy from high energy metabolites
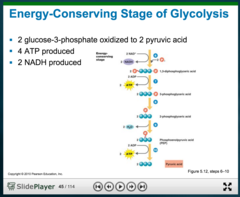
3
New cards
Glucose
Most stable hexose
alpha - down
beta - up
alpha - down
beta - up
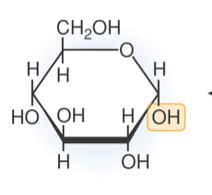
4
New cards
Glucose to G6P
1. hexokinase
2. Favorable (-16.7 kJ/mol) (irreversible)
3. uses ATP + Mg2+
2. Favorable (-16.7 kJ/mol) (irreversible)
3. uses ATP + Mg2+
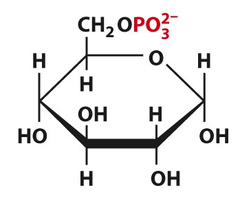
5
New cards
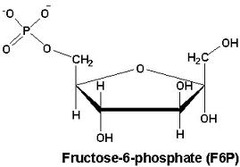
G6P to F6P
1. phosphoglucose isomerase
2. unfavorable (1.7 kJ/mol)
3. glutamate helps with breaking the ring by acting as a base
2. unfavorable (1.7 kJ/mol)
3. glutamate helps with breaking the ring by acting as a base
6
New cards
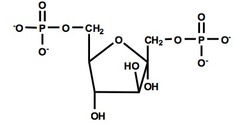
F6P to F1,6BP
1. phosphofructokinase-1
2. favorable (-14.2 kJ/mol)
3. first committed step
4. ATP + Mg2+
2. favorable (-14.2 kJ/mol)
3. first committed step
4. ATP + Mg2+
7
New cards
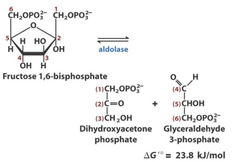
F1,6BP to DHAP + GAP
1. aldolase
2. unfavorable (23.8 kJ/mol)
3. lysine used (schiff base). nucleophile = nitrogen on lys; electrophile = second carbon in F1,6BP
2. unfavorable (23.8 kJ/mol)
3. lysine used (schiff base). nucleophile = nitrogen on lys; electrophile = second carbon in F1,6BP
8
New cards
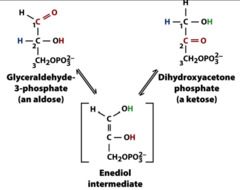
DHAP to GAP
1. TIM
2. unfavorable, but GAP concentration is kept low, allowing reaction to go forward (Le Chatelier)
3. creates enediol intermediate which is unstable
2. unfavorable, but GAP concentration is kept low, allowing reaction to go forward (Le Chatelier)
3. creates enediol intermediate which is unstable
9
New cards
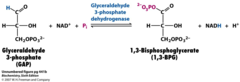
GAP to 1,3-BPG
1. GAPDH/G3P DH
2. unfavorable (6.3 kJ/mol)
3. NAD+ (only oxidation step) + H+
4. uses cysteine (form a thioester and decrease the free energy) and histidine (aid oxidation)
2. unfavorable (6.3 kJ/mol)
3. NAD+ (only oxidation step) + H+
4. uses cysteine (form a thioester and decrease the free energy) and histidine (aid oxidation)
10
New cards
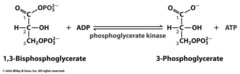
1,3-BPG to 3-PG
1. phosphoglycerate kinase
2. favorable (-18.6 kJ/mol)
3. reversible due to coupling of GADPH
4. 1st ATP produced
2. favorable (-18.6 kJ/mol)
3. reversible due to coupling of GADPH
4. 1st ATP produced
11
New cards
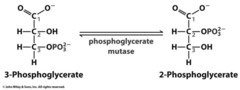
3-PG to 2-PG
1. phosphoglycerate mutase
2. unfavorable (4.6 kJ/mol)
3. uses 2 histidines
2. unfavorable (4.6 kJ/mol)
3. uses 2 histidines
12
New cards
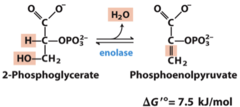
2-PG to PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate)
1. enolase
2. unfavorable (1.7 kJ/mol)
3. reversible, because product concentration is kept low enough to go forward
4. uses lys and hist
5. produces 2 H2O
2. unfavorable (1.7 kJ/mol)
3. reversible, because product concentration is kept low enough to go forward
4. uses lys and hist
5. produces 2 H2O
13
New cards
PEP to pyruvate
1. pyruvate kinase
2. favorable (-31.4 kJ/mol)
3. ATP produced
4. Tautomerizes into ketone
2. favorable (-31.4 kJ/mol)
3. ATP produced
4. Tautomerizes into ketone

14
New cards
Thioester intermediate is ________ in energy
high
15
New cards
Net reaction for glycolysis
Glucose + 2 ADP + 2 NAD+ + 2Pi -> 2 pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP + 2H2O
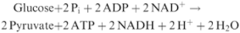
16
New cards
What type of bond is broken in aldolase?
C-C
17
New cards
What product leaves first in aldolase rxn?
G3P
18
New cards
What is the importance of the thioester intermediate?
Higher energy, easier to overcome
19
New cards
Which steps are coupled?
GAP to 1,6BPG
20
New cards
Pyruvate + Pyruvate decarboxylase
Acetylaldehyde + CO2
21
New cards
Acetaldehyde to ethanol
Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADH used to produce NAD+)
22
New cards
Pyruvate to Lactate enzyme
Lactate dehydrogenase (uses NADH + H+)
23
New cards
Purpose of lactic acid fermentation
Lactate does not cause negative feedback of glycolysis and regenerates NAD+ to be used in glycolysis