5. what's in medicine
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
alcohol
ROH group, ends in -ol
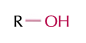
2
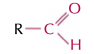
New cards
aldehydes
RCHO group, ends in -al
3
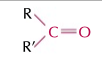
New cards
ketones
RCOR’ group, double bond oxygen, ends with -one
4
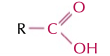
New cards
carboxylic acids
RCOOH group, double bond oxygen, -oic acid
5
New cards
acid anhydrides
(RCO)2O, double bond oxygens, ends in oic anhydride
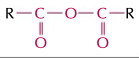
6
New cards
esters
RCOOR’, double bond oxygen, ends in -oate
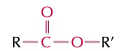
7
New cards
ethers
ROR’, name in middle -oxy-
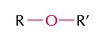
8
New cards
primary alcohols
alcohol attracted to carbon joined to one carbon
9
New cards
secondary alcohol
alcohol attached to carbon attached to two carbons
10
New cards
tertiary alcohol
alcohol attached to carbon attached to three carbons
11
New cards
oxidising agent
used to oxidise alcohol into different compounds eg potassium dichromate (VI) solution
12
New cards
aldehydes then carboxylic acids
primary alcohol oxidised
13
New cards
ketones only
secondary alcohols oxidised
14
New cards
aren’t oxidised
tertiary alcohols oxidised
15
New cards
distillation of primary alcohol
used to oxidise alcohol produce aldehyde
16
New cards
reflux of primary alcohol
vigorously oxidise alcohol to carboxylic acid, excess oxidising agent, heating
17
New cards
reflux of secondary alcohol
oxide alcohol into ketone, uses oxidant agent
18
New cards
dehydration
forming alkene from alcohol by elimination of water
19
New cards
dehydrating alcohols to form alkenes
* reactant vapour pass over hot catalyst (pumice stone or aluminium oxide) creating gas product
* or, reflux reactant with excess conc sulphuric acid at 170 degrees, product collected over water
* or, reflux reactant with excess conc sulphuric acid at 170 degrees, product collected over water
20
New cards
mechanism of dehydration to alkene
* H+ ion joins to alcohol, making it protonated and oxygen having positive charge
* positive oxygen pulls electrons from carbon and water falls off, making a unstable carbocation
* carbocation loses H+ and alkene is formed
* positive oxygen pulls electrons from carbon and water falls off, making a unstable carbocation
* carbocation loses H+ and alkene is formed
21
New cards
form esters
alcohols react with carboxylic acids or acid anhydrides
22
New cards
alcohol and carboxylic acid
produces ester by esterification where water is produced from loss of OH and H
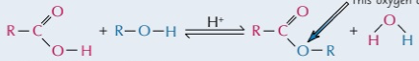
23
New cards
alcohol and acid anhydride
produces both an ester and carboxylic acid, where one reactant splits and gains R
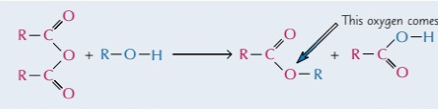
24
New cards
makea haloalkane
alcohol and halide ions (eg HCl) substation of -OH for X, shake
25
New cards
phenol
benzene ring with -OH attached, C6H5OH
26
New cards
test for phenol
positive result with iron iii chloride solution turns purple
27
New cards
weak acids
phenols, allows them to react with strong alkalis
28
New cards
phenol with strong alkalis
produces salt and water
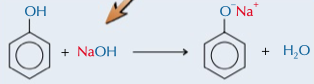
29
New cards
phenols don’t react with
carbonates, allow you to tell them apart from carboxylic acids
30
New cards
phenol mak esters
alcohol which react with acid anhydrides by not carboxylic acids
31
New cards
refluxing
solution is heated and any fumes produced are condensed to re react, typically electronically heated
32
New cards
distillation
reactants heated and fumes produced and separated and condensed, allowing you to collect products by boiling points
33
New cards
redistilation
impure products heated and separated by boiling points
34
New cards
seperation
removes a insuluble product form water and anything desolved in it. usa a serparattor funnel.
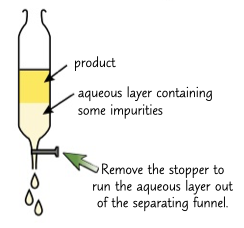
35
New cards
drying a product
removed water from a soluble product. add anhydrous salt like magnesium sulphate or calcium chloride. looks like a snow globe
36
New cards
filtration
separates solid product from liquids, use a funnel, filter paper and vacuum
37
New cards
recrystallisation
organ solid product, dissolve in hot solvent then cool till it forms crystals as it becomes insoluble. wash with ice cold solvent
38
New cards
ideal solvent for recrystalistion
very soluble at high temp but very insoluble at low temp
39
New cards
measure melting point
a simple way to determine purity that happens at one value. measured as a range
40
New cards
thin layer chromatography
chromatography with a glass or metal plate coated in silica or alumina
41
New cards
fluorescent dye
added to plate coating allowing everything but samples to glow
42
New cards
iodine vapour
place plate in jar with crystals and let the vapour turn the samples purple
43
New cards
Rf value
identifies substance in chromatography. spot over solvent

44
New cards
infrared spectroscopy
uses a beam of radiation and a detector to see what’s absorbed. helps determine bonds in a substance and functional groups
45
New cards
mass spectrometry
process which produces a graph showing mass of a compounds fragments, its Mr is typically the 2nd largest peak. helps work our structure
46
New cards
green chemistry
* use renewable resources
* ensure chemicals and process are as safe was possible
* minimise waste and make products biodegradable or recyclable
* ensure chemicals and process are as safe was possible
* minimise waste and make products biodegradable or recyclable
47
New cards
renewable resources
raw materials, energy sources and minimise energy use
48
New cards
safe chemicals and processes
produces non toxic and non harmful substances, minimise chance of accidents and improve use of technology to monitor and control
49
New cards
minimise waste
prevent waste, high atom economy, catalysts, reduce steps and biodegradable or recyclable products