Beam Restricting Devices
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
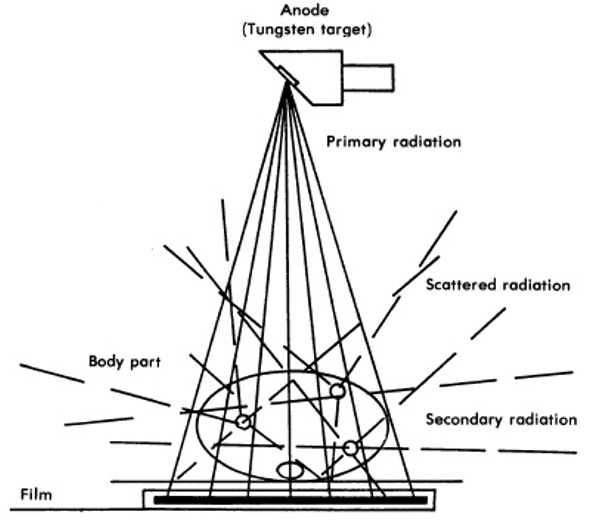
Scatter Radiation
change in direction of the x-ray photon after interaction with the atoms of the patient
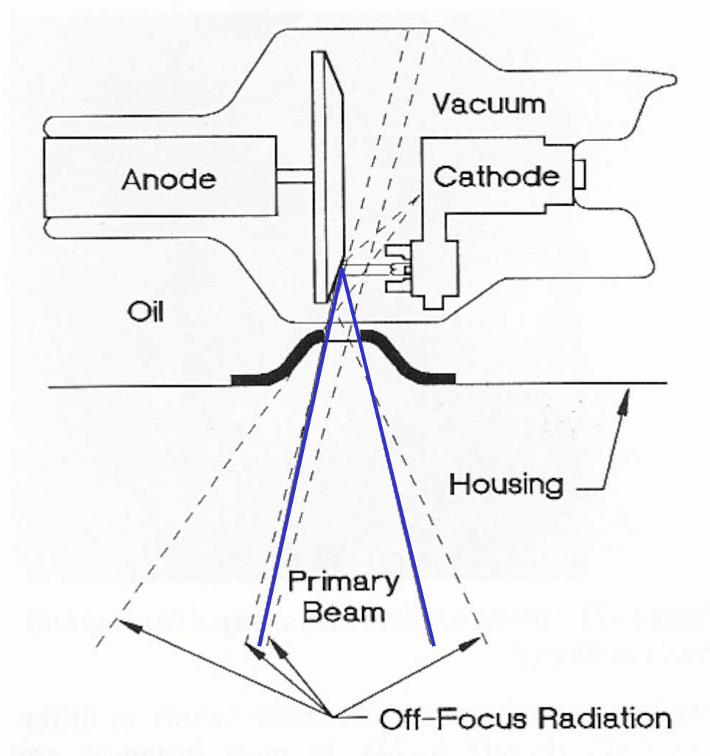
Off-focus, Extra-focal
–Refers to photons not produced at the focal spot of the anode
•tube housing
•evaporate tungsten on envelope
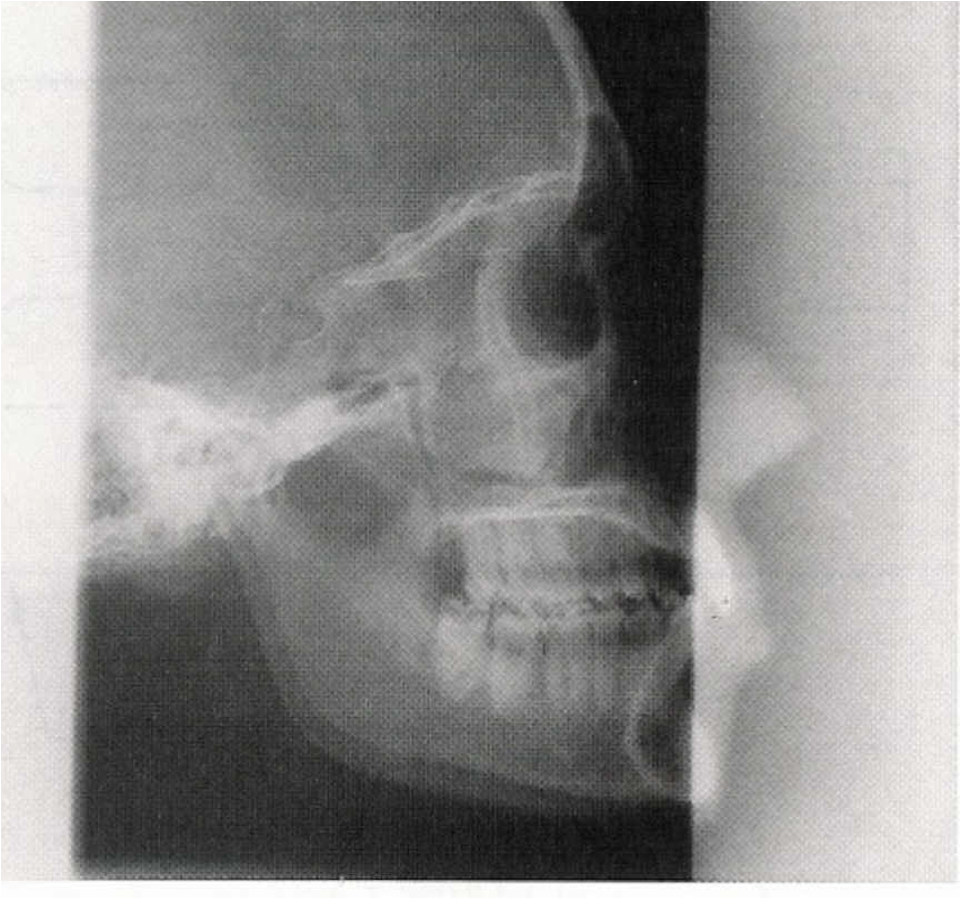
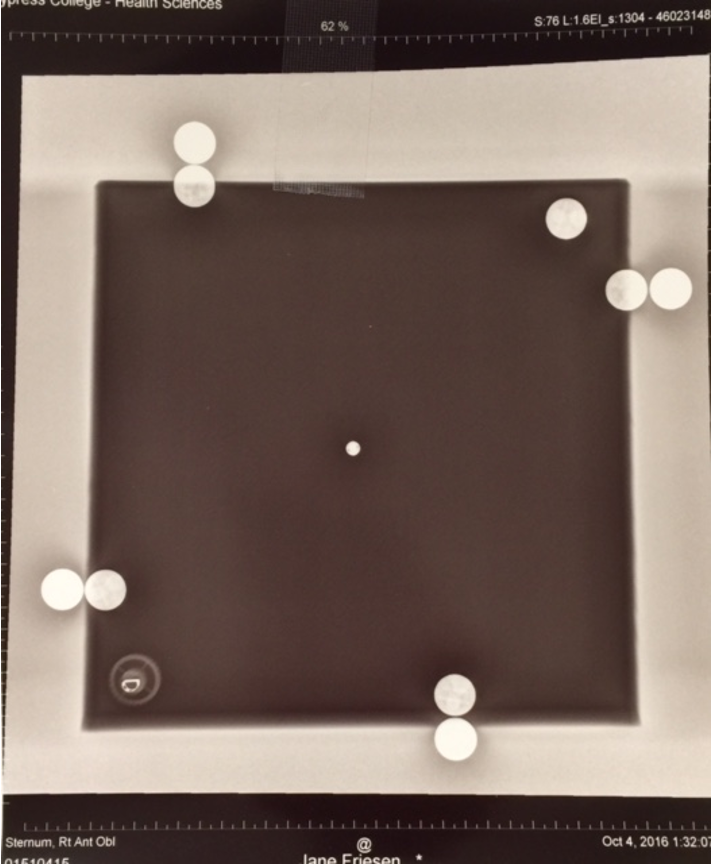
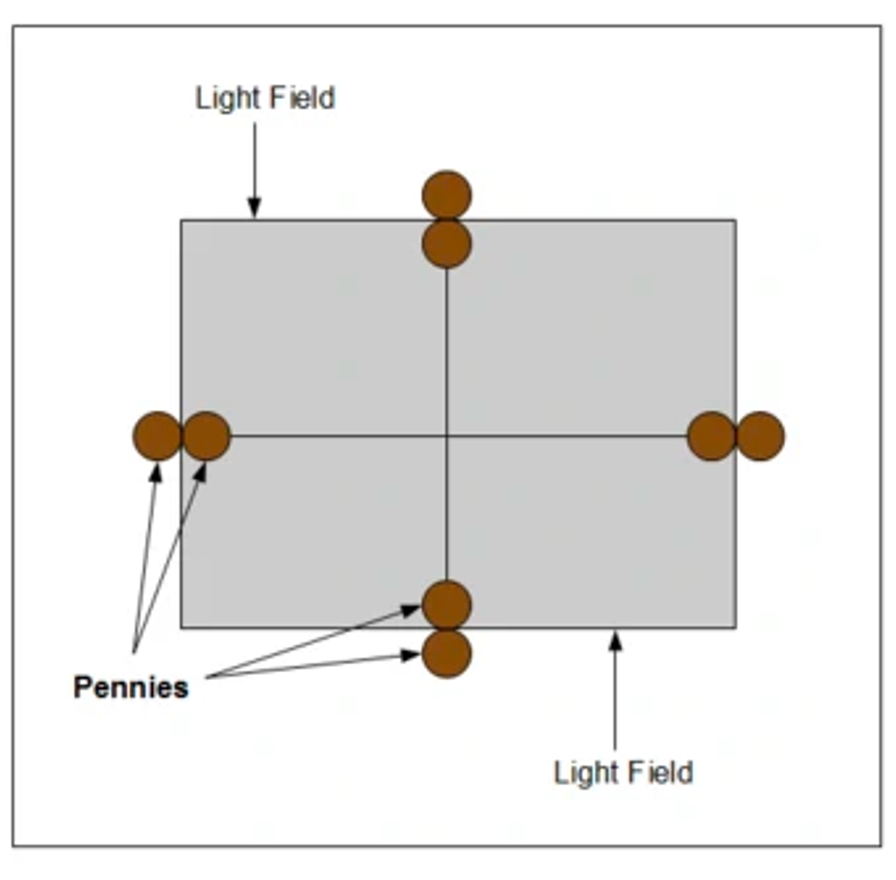
Field Light Congruency
Light field (light bulb and mirror) represents the X-ray field
Cross-hairs represent the CR
How does scatter affect an image?
Increase density, decrease contrast and resolution
This increase in density from scatter is called…
fog. Radiograph will have an overall gray appearance
Primary radiation
–radiation emitted from the x-ray tube
Remnant (exit) radiation
unabsorbed and scattered x-rays that interact with the IR, it carries the aerial image
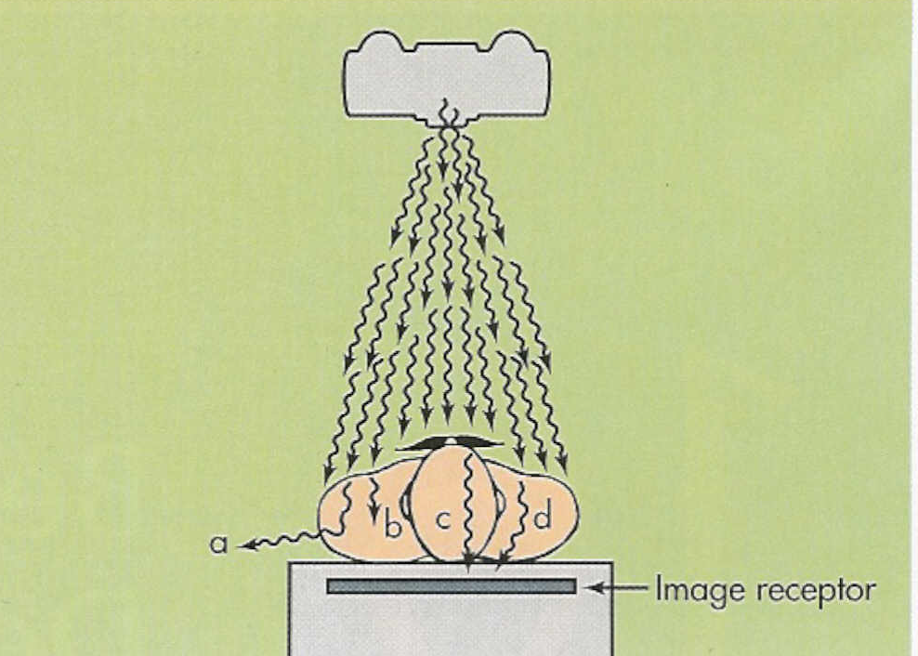
Factors that influence the degree of scatter radiation:
Field size
Thickness of the object
Density (composition) of the object
Tube potential (kV)
Field size-
area of the x-ray beam. Field size is altered by the use of a beam limiting device. Increase field size and scatter
Thickness of the object
more atoms are present in larger object to cause more interactions.
Bigger object, more scatter
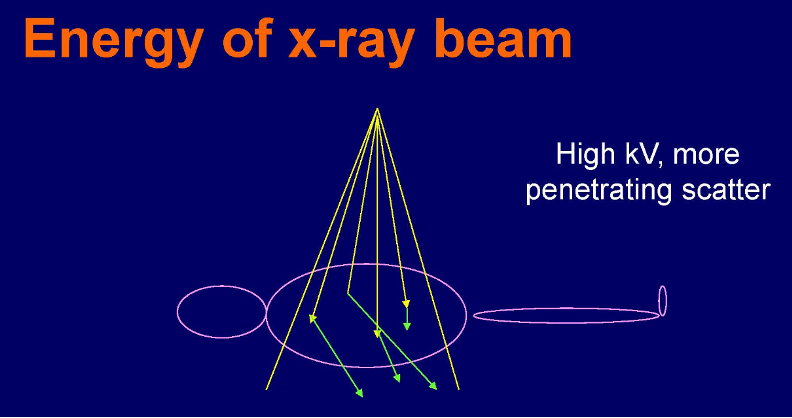
Tube potential (kV)
as kV is increased, the energy of scattered radiation also increases, so scatter radiation has a better chance of reaching the IR.
More kV, more scatter
Density (composition) of the object
the more dense the object is, the more scatter is produced.
More density, more scatter
All increased given factors ALSO increase scatter reaching IR
Field Size
Thickness
Density (composition)
Tube Potential (kV)
Beam Limitation
Reduce patient exposure
Increase image quality by decreasing scatter to the IR
Increases visibility of detail
Density on the radiograph is the result of how much scatter radiation?
50-90%
Penumbra greater at the…
edges of the beam
Types of Beam Limiting Devices
1.Aperture Diaphragm
2.Cones
3.Variable Aperture
constructed of lead or lead-lined because of its characteristic to attenuate
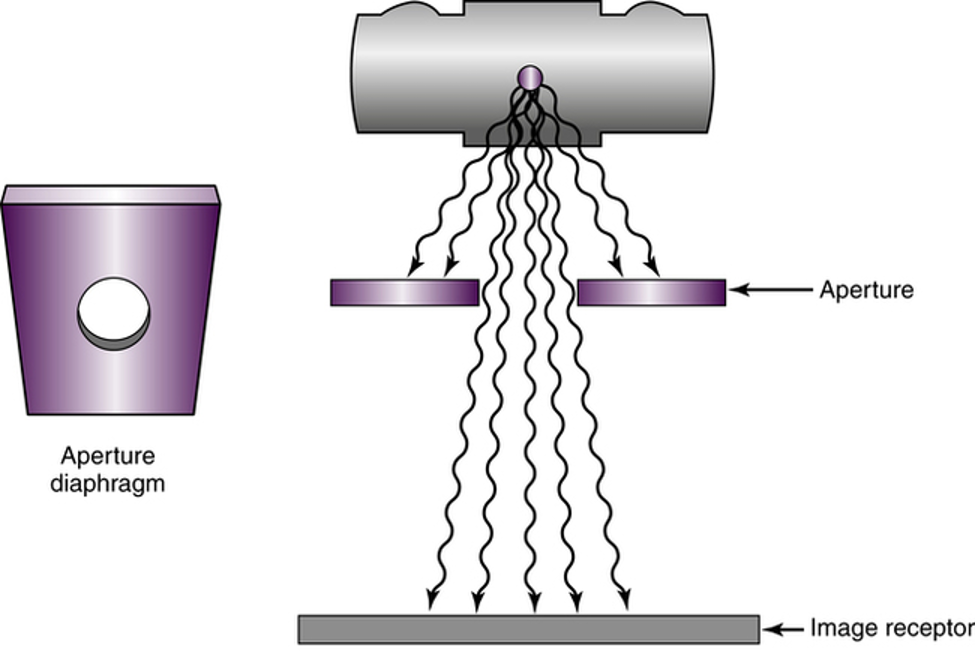
Aperture Diaphragms
Simplest, least expensive
Change for each size
Large amount of blur
Dedicated units
2 types of cones
1.Flared
2.Cylinder
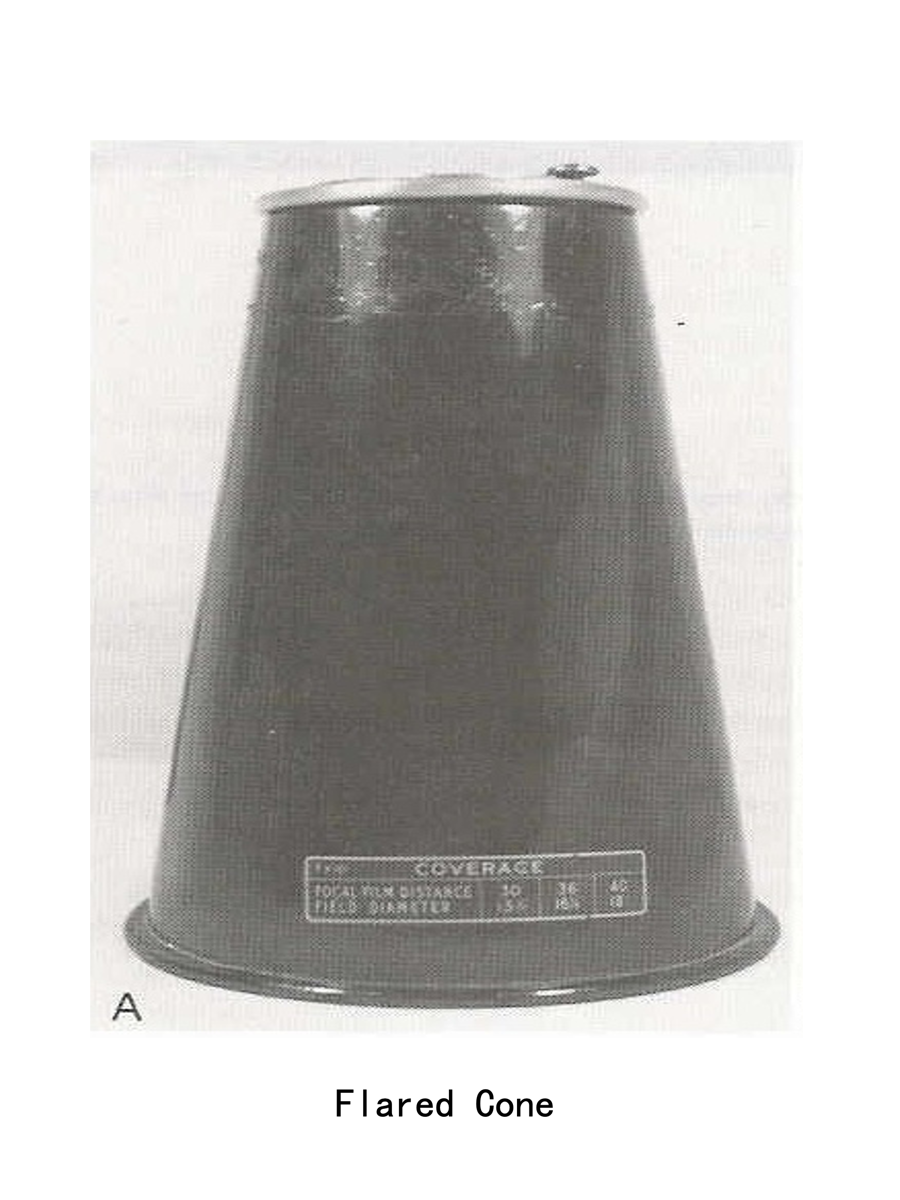

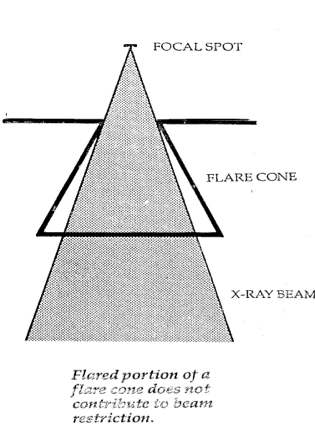
flared cone
Flared Cone
Matches the divergence of beam
Flare is usually larger than beam
Cylinder Cone
Blur is reduced because it truly limits the field size
Circular field
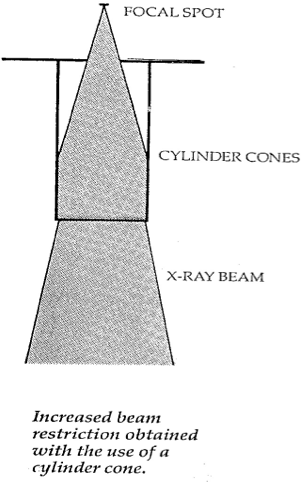

cylinder cone
Disadvantages of Cones
Excessive radiation for larger body parts, unneeded patient exposure
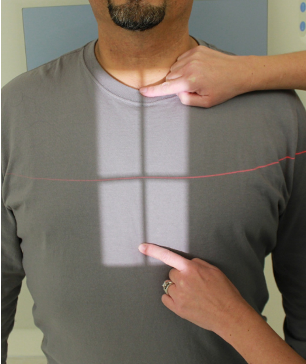
VARIABLE APERTURES
•Collimator
•Automatic Collimator
•Positive Beam Limiting Device (PBL) – assures the size of field does not exceed the size of the I
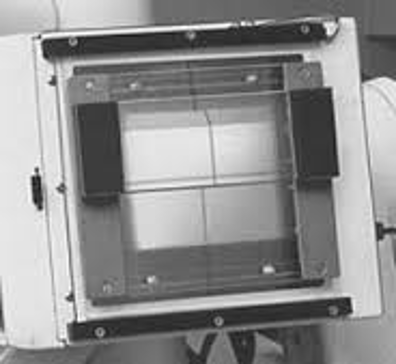
Automatic Collimator Housing
•Two sets of horizontal lead shutters
•Adjustable. Allows for infinite number of field sizes
•Adds to “added” filtration
•Provides a light field
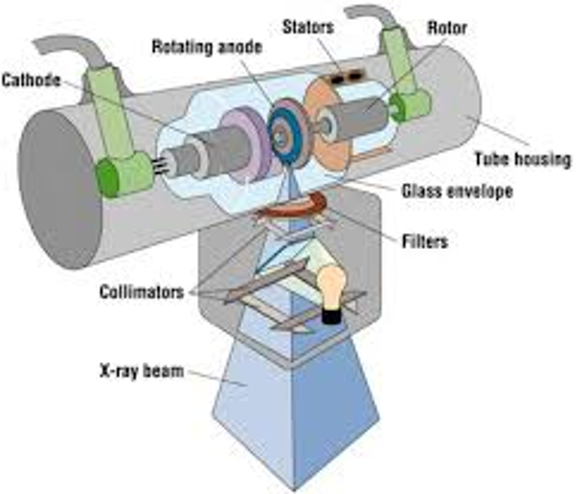
2 types of shutter
–Upper shutters control stem radiation (off-focus)
–Lower shutters reduce blur
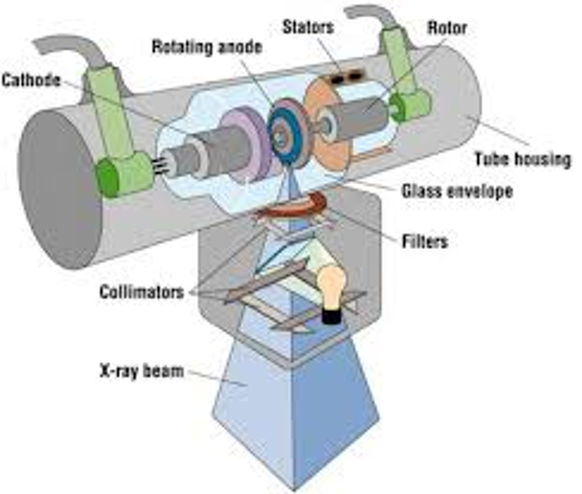
Stem Radiation refers to…
Off-focus, Extra-focal
Off-focus, Extra-focal means…
–Refers to photons not produced at the focal spot of the anode
•tube housing
evaporate tungsten on envelope
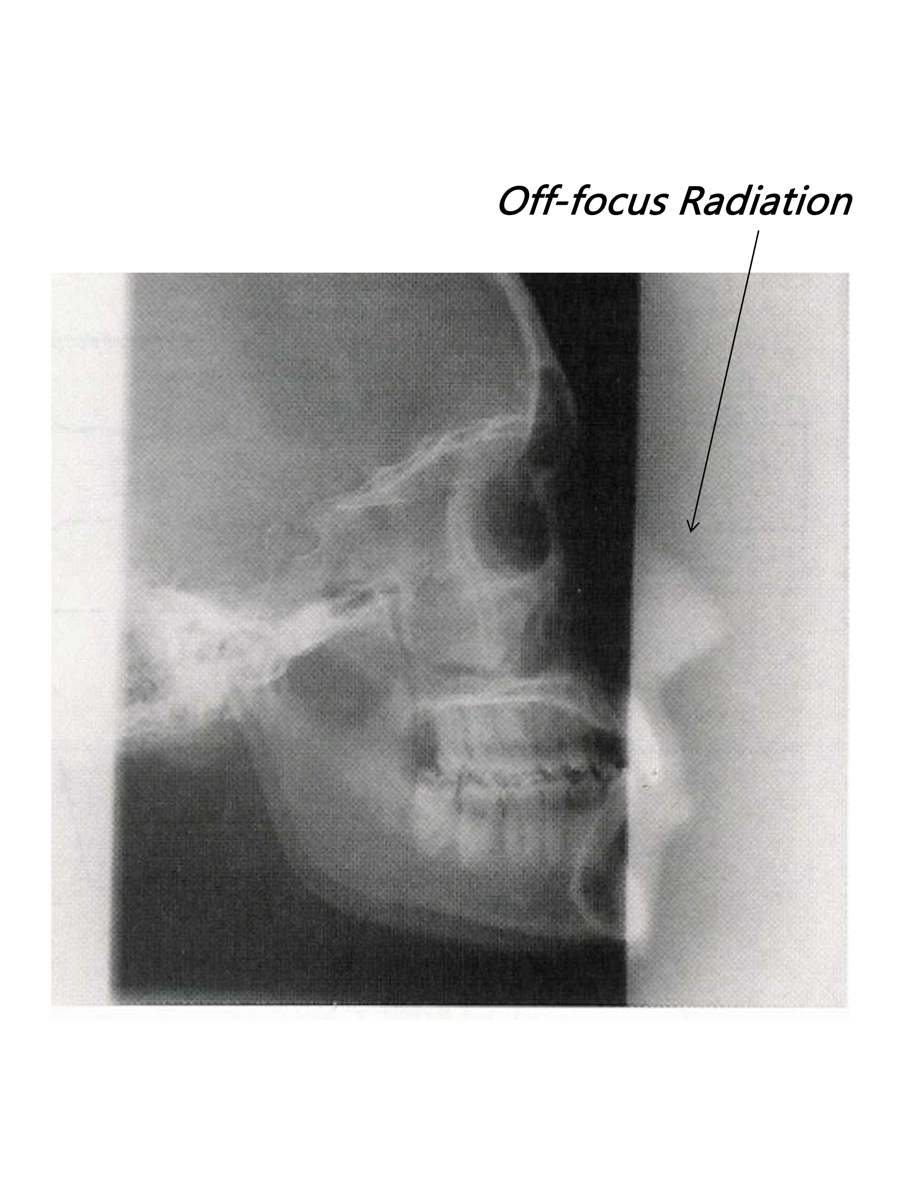
Off-focus Radiation
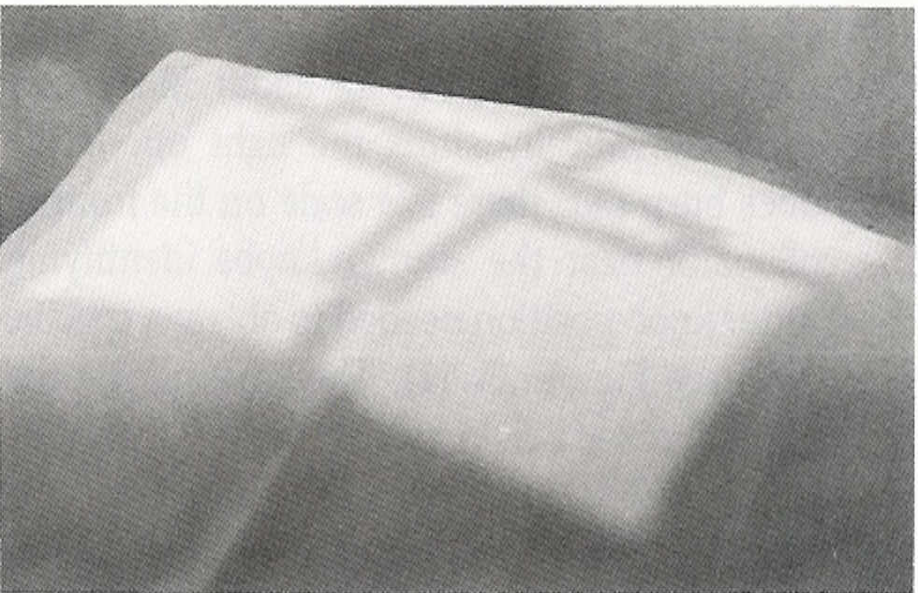
Field Light Congruency
Light field (light bulb and mirror) represents the X-ray field
Cross-hairs represent the CR
Poor field-to-light congruency may lead to
parts of the anatomy being cut off