Anesthesia - All Quizzes
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
What is not a reason a patient is intubated?
So the patient’s respiratory rate doesn’t have to be monitored
What is the safe PSI of oxygen to be delivered to a patient?
15 PSI
What part of the anesthesia machine prevents excess buildup of pressure?
Pop-off valve
When administering a breath to an anesthetized small patient, the pressure monometer should not exceed ______ cm H2O.
20 cm H2O
This scavenging system requires a vacuum and duct system, and typically includes a scavenger interface to regulate the vacuum.
Active Scavenge
The absorbent granules in the CO2 absorbing canister typically have an _____ hour duration of use before needing to be replaced.
8-10 hours
Mechanical dead space is the area where inhaled and exhaled gases mix, which can ultimately lead to increased end-tidal CO2 levels. What are some effects of increased end-tidal CO2?
Respiratory acidosis, Peripheral Vasoconstriction/vasodilation, Increased intracranial pressures
T/F: The selection of a breathing circuit is based on the patient’s weight. A non-rebreathing system is used for patients weighing more than 5 kg, while a rebreathing system is appropriate for patients weighing less than 5 kg.
False
The Murphy eye, located on an endotracheal tube, is a small hole situated just below the cuff. What is the primary function of the Murphy eye?
Minimizes the risk of asphyxiation in the event the end of the tube is blocked
You are evaluating a patient's level of consciousness (LOC) and find the patient in a sleeplike state, nonresponsive to verbal stimulus but arousable by painful stimulus. The patient is:
Stuporous
You are evaluating a patient and notice the patient has a mildly decreased level of consciousness (LOC) and can be aroused with minimal difficulty. The patient is:
Lethargic
Using the ASA physical status classification system, a patient who is anemic or moderately dehydrated would be classified as:
Class P3
What is not a sign of fluid overload?
Hypotension
What is not an example of a crystalloid solution?
Dextran
The fluid type most appropriate for replacing moderate losses due to dehydration would be:
Isotonic Crystalloids
Which of the following general guidelines about body fluids in a normal adult animal is INCORRECT?
About 40% of the body weight is water
What is a common equipment-related error that puts patients at risk for barotrauma?
Closure of the pop-off valve
Mucous membranes are an indication of blood flow to peripheral tissues. A patient presents to the clinic with yellow-colored mucous membranes. This is an indication of what?
Bilirubin accumulation
How much of the synthetic colloid will remain in the plasma 24 hours after administration?
30-60%
Which diagnostics are included in a big four?
Bun, TP, PCV, Glucose
Brown mucous membrane is caused by:
Acetaminophen toxicity in cats; intravascular hemolysis
Pale/white mucous membrane caused by:
Blood loss, shock, decrease in peripheral vessel blood flow
Yellow (icteric) mucous membrane caused by:
Hepatic or biliary disorder and/or hemolysis
Blue (cyanotic) mucous membrane caused by:
Hypoxemia
Sassy is a 32 lb mixed-breed dog presenting to the clinic for a routine dental prophylaxis. Dr. Daniels has asked you to calculate her fluid rate at 5mls/kg/hr for the procedure. How many mL/hr of LRS (Lactated Ringer's Solution) will Sassy receive? Round to the nearest tenth if applicable!
72.5 mls/hr
Sassy is a 32 lb mixed-breed dog presenting to the clinic for a routine dental prophylaxis. Following the procedure, Dr. Daniels would like Sassy to be on a 2ml/kg/hr fluid rate for 4 hours in effort to improve her hydration status. How much fluid in total following the procedure will Sassy receive? Round to the nearest tenth if applicable!
116 mls
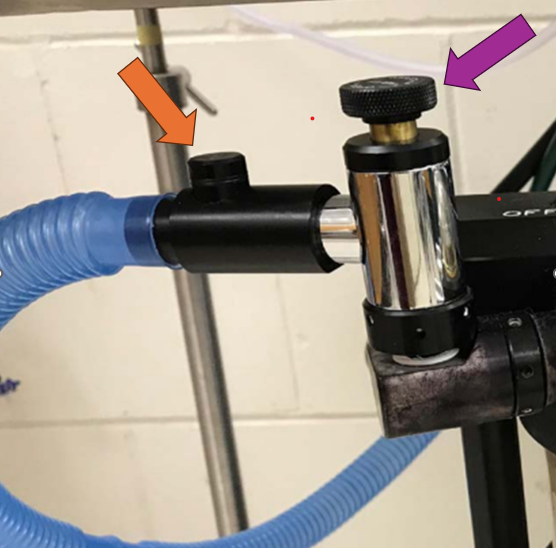

What is the purple arrow pointing to?
Pop-off Valve

What is the orange arrow pointing to?
Occlusion Valve
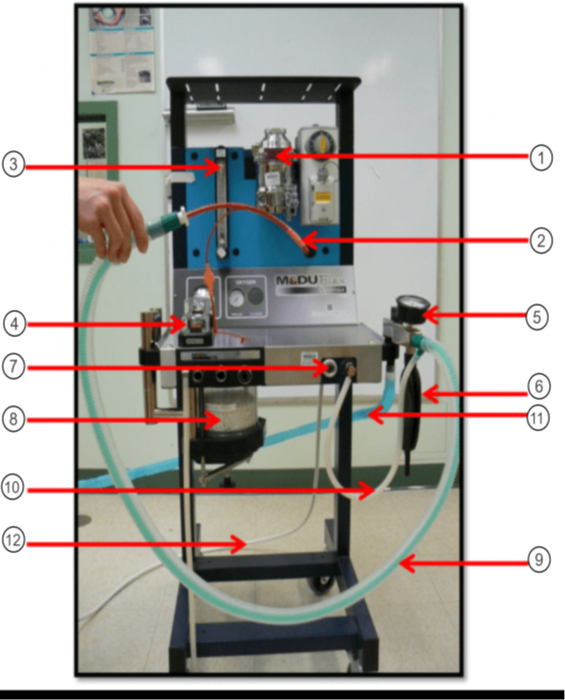
In the image what is #1?
Vaporizer
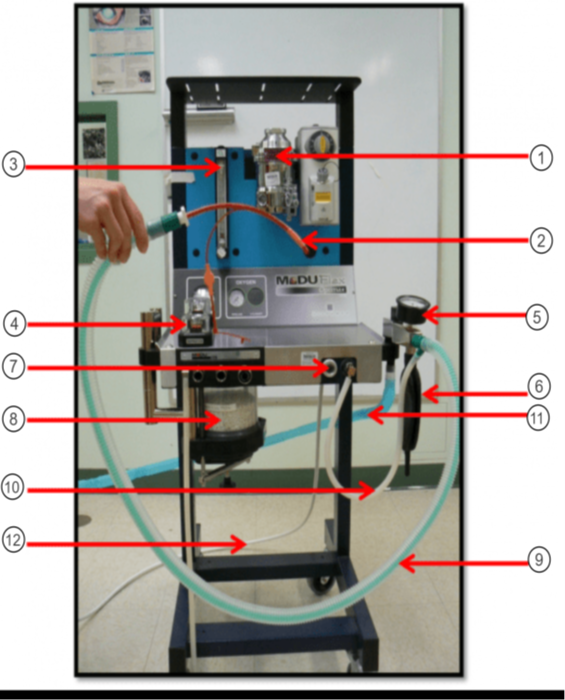
In the image what is #2?
ET tube
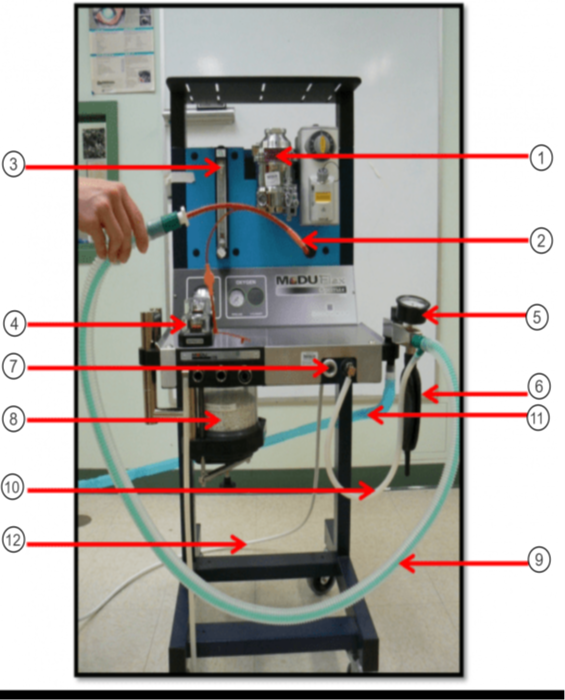
In the image what is #3?
Flow Meter
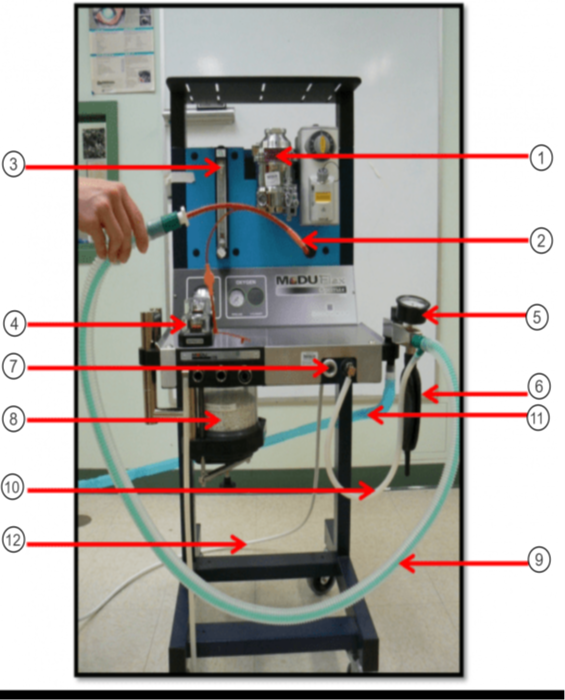
In the image what is #4?
Unidirectional Valves (One-Way Valves)
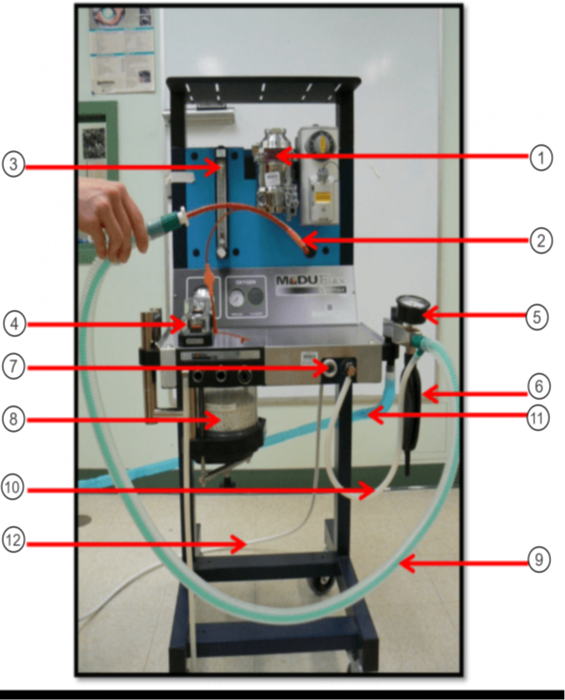
In the image what is #5?
Pressure Valve (Monometer)
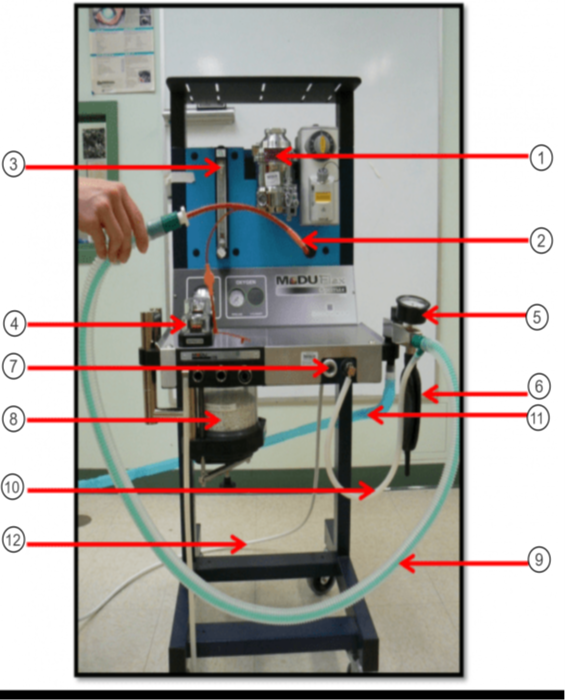
In the image what is #6?
Reservior Bag
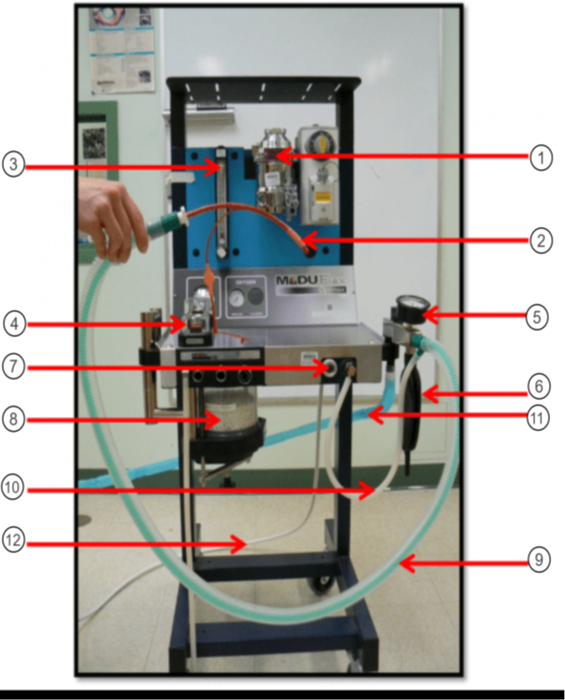
In the image what is #7?
O2 Flush
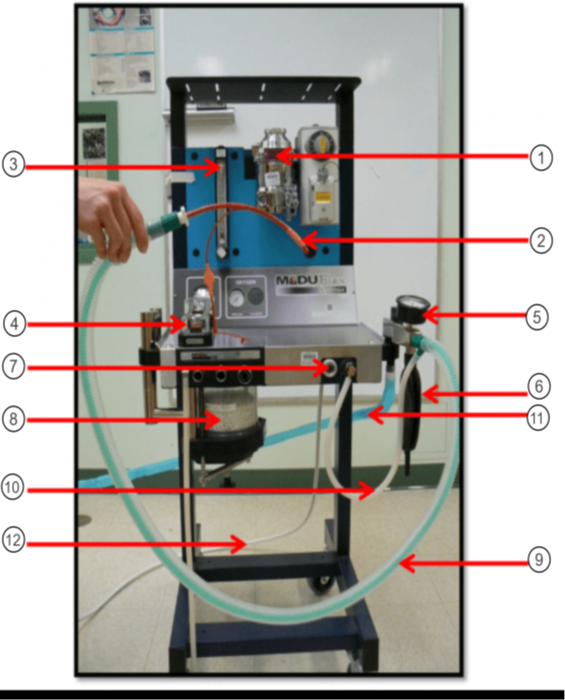
In the image what is #8?
Sodasorb/Sodalime
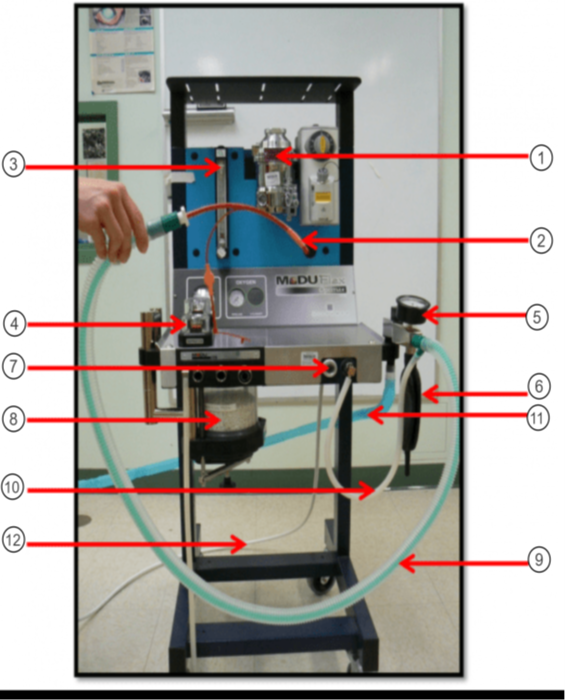
In the image what is #9?
Non-rebreathing/Bain Circuit
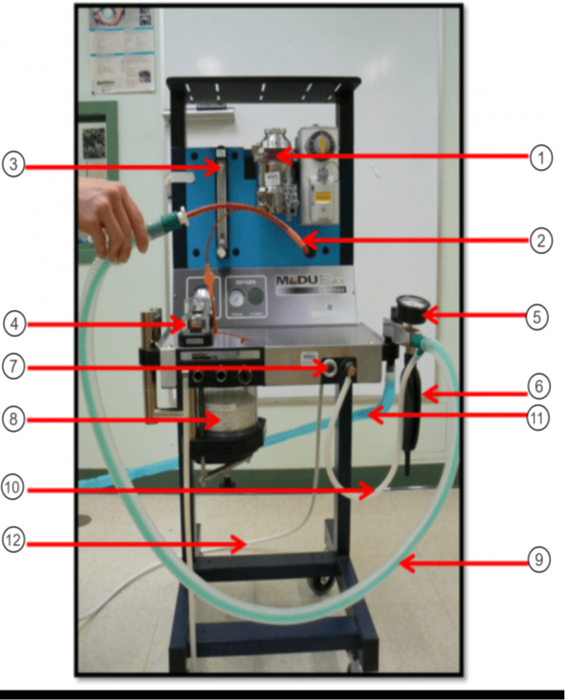
In the image what is #10?
Fresh gas inlet
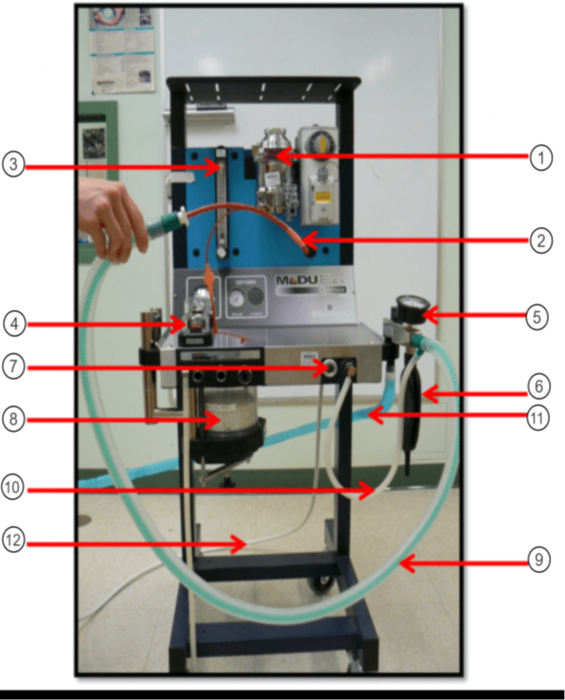
In the image what is #11?
Scavenge Hose
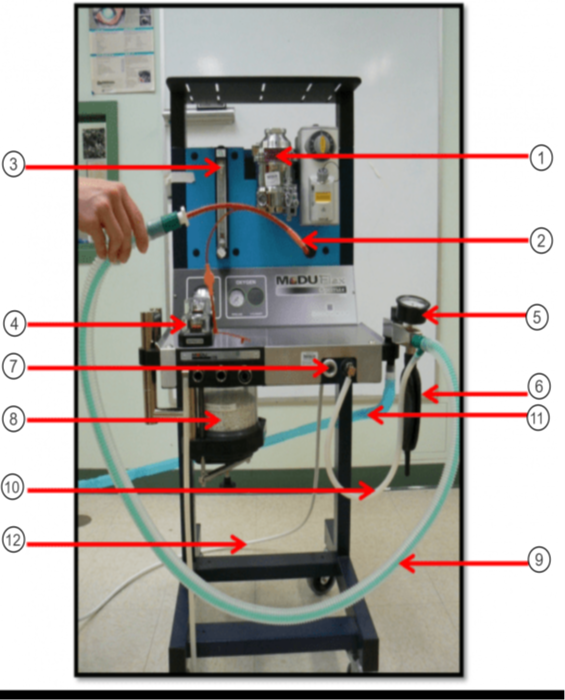
In the image what is #12?
Oxygen Supply
Which class of tranquilizer can cause penile prolapse in equine?
Pehnothiazines
What type of drug is Atropine?
Anticholinergic
Please list the most common routes for medication administration in anesthesia.
SQ (slowest), IM (medium), IV (fastest)
After IV administration, this class of drug may induce significant peripheral vasoconstriction and reflex bradycardia.
Alpha 2 adrenergic agonist
What are the drugs classified as tranquilizers?
Alpha 2 adrenergic agonist, Phenothiazines, & Benzodiazepines
T/F: Drugs such as Diazepam, Zolazepam, and Midazolam are classified as minor tranquilizers?
True
Which of the following drugs is an Alpha 2 Adrenergic Agonist?
Detomidine
T/F: Anticholinergics are used to treat tachycardia and increase salivary secretions.
False
T/F: Alpha 2 Adrenergic Agonists are metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine.
True
___________ is used to reverse the effects of dexmedetomidine in dogs, cats, and exotic species.
Atipamezole
What are the commonly used opioids?
Morphine, Hydromorphone, Oxymorphone (not used at MSU-CVM), & Fentanyl
Most opioids have a relatively short duration of action except _______________ and ________________.
Buprenorphine & Morphine
T/F: Opioids cause mydriasis (dilation) in dogs and miosis (constriction) in cats.
False
What are the TWO most commonly used halogenated compounds in veterinary medicine?
Sevoflurane & Isoflurane
The MAC of Sevoflurane in dogs is ____________.
2.4%
What are the side effects of inhalant anesthetics?
CNS depression, Hypoventilation, & Hypertension
The MAC of Isoflurane in dogs is _________.
1.3%
What type of opioid is Fentanyl?
Mu Agonist
Dolly weighs 10kgs and would need a 10mcg/kg/hr CRI of Fentanyl (50mcg/ml) and a 10mcg/kg/min CRI of 2% Lidocaine during surgery. How many mls/hr of each drug would Dolly receive?
2ml/hr of fentanyl; 0.3ml/hr of lidocaine
Post surgery, Dr. Davis would like to continue the Fentanyl (50mcg/ml) for Dolly at 2mcg/kg/hr for 5 hours. How many mls/hr will Dolly receive? How many mls total will Dolly receive over 5 hours?
0.4 ml/hr; 2 mls
Princess, a 20kg boxer, was given 12mls of Propofol (10mg/ml) for induction. What was she given in mgs? What was her mg/kg dose?
120 mgs; 6 mg/kg
How many mls of Acepromazine (10mg/ml) will a 1000lb equine patient require at a dose of 0.04mg/kg?
1.8 mls
A 5 year old male neutered schnauzer named Biscuit has presented to the CVM for a routine dental extraction with a grade 3 periodontal disease. What is the ASA status of this patient?
3
This stage of anesthesia is subdivided into 4 different planes of anesthesia based on eye movement, pupil size, and eyelid movement.
Stage III
This stage of anesthesia is known as the period of involuntary movement. Within this stage of anesthesia, the patient can go through an excitement stage and have involuntary reactions such as vocalizing, struggling, or paddling.
Stage II
This stage of anesthesia is known as the anesthetic overdose stage. Within this stage, the patient may experience a dramatic drop in heart rate and blood pressure.
Stage IV
This stage of anesthesia is known as the period of voluntary movement. Within this stage of anesthesia, the patient begins to lose consciousness and be difficult to handle that is characterized by fear, excitement, disorientation, and struggling.
Stage I
Subjective monitoring consists of physical assessment. All are included in subjective monitoring EXCEPT......
Blood Pressure
__________ is produced by the contraction of the left ventricle as it propels blood.
Systolic
________ measures the percentage of oxygen bound to hemoglobin.
Pulse Oximetry
A ______ in CO2 can indicate hyperventilation (alkalosis) in a patient under anesthesia.
Decrease
Monitoring patient under anesthesia help maintain legal records, record all drugs administered to the patient, and enhance recognition of trends or unusual values for physiological parameters. A minimum of what should be recorded?
Blood pressure, Heart rate, Oxygenation
This type of blood pressure monitoring gives a continuous reading of the blood pressure throughout the procedure and is more accurate.
Direct blood pressure
Blood gases are used to measure the blood pH, and the dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide gas in the arterial blood. Which value is use as a invasive method of monitoring the CO2?
PACO2
Pain is recognized as a complex phenomenon comprising several distinct types. This type of pain is characterized by an immediate onset of pain. Please match the term to the definition.
Acute pain
Pain is recognized as a complex phenomenon comprising several distinct types. This type of pain is characterized by the pain originating from organs. Please match the term to the definition.
Visceral pain
Pain is recognized as a complex phenomenon comprising several distinct types. This type of pain is characterized by having a long duration of pain. Please match the term to the definition.
Chronic pain
Pain is recognized as a complex phenomenon comprising several distinct types. This type of pain is characterized by pain occurring at the site of the tissue injury due to the release of chemical mediators. Please match the term to the definition.
Inflammatory pain
What drug is ideal for treating windup pain?
Ketamine
The pathway of pain in the body is referred to as nociception with four main steps. During this step, signals are transmitted to the brain, where they are processed and recognized. Please select the correct term.
Perception
The pathway of pain in the body is referred to as nociception with four main steps. During this step, signals are conducted to the spinal cord via the peripheral nerves. Please select the correct term.
Transmission
All are physiologic signs of pain under anesthesia EXCEPT:
Hypotension
Constant release of pain mediators can lead to other known conditions. One condition seen is when there is an increase in sensitivity to a painful stimulus, usually seen clinically as an exaggerated response to stimuli. Please select the correct term.
Peripheral hypersensitivity
T/F: Vocalization is a common sign of pain in all species of animals.
True
Regional/Local anesthetic blocks are important because they reduce the MAC of inhalant being used, lower the recovery time, and help avoid using general anesthesia in large animal patients such as equine and bovine. The retrobulbar block will block the orbit and optic nerve. When done correctly, the eye should look exophthalmic. True or False. This block can be used in most ophthalmology cases?
False
Regional/Local anesthetic blocks are important because they reduce the MAC of inhalant being used, lower the recovery time, and help avoid using general anesthesia in large animal patients such as equine and bovine. What block is used to block the half of the maxilla on which the block is performed?
Maxillary block
Regional/Local anesthetic blocks are important because they reduce the MAC of inhalant being used, lower the recovery time, and help avoid using general anesthesia in large animal patients such as equine and bovine. What block is used to block the maxilla rostral to the first premolar and can be used in procedures such as a rhinoscopy?
Infraorbital block
Regional/Local anesthetic blocks are important because they reduce the MAC of inhalant being used, lower the recovery time, and help avoid using general anesthesia in large animal patients such as equine and bovine. This block is used to block the forelimb from the distal half of the humerus to the toes and can be used in procedures such as elbow scopes or forelimb fractures.
Brachial plexus block
Regional/Local anesthetic blocks are important because they reduce the MAC of inhalant being used, lower the recovery time, and help avoid using general anesthesia in large animal patients such as equine and bovine. This block is used to block the perineum, rectum, and tail. It is the regional technique of choice with cats who are blocked.
Sacrococcygeal epidural
When performing a semimembranosus/semitendinosus IM injection, which nerve are you wanting to avoid?
Sciatic
During intubation, a cat trachea is much more sensitive than a dog trachea and more prone to trachea injuries. When intubating a cat, what is the max amount of air to use when inflating the cuff on the endotracheal tube?
3 mls
All are classified as agents that could be use for induction EXCEPT:
Acepromazine
There are many complications of intubation. One common complication is aspiration during the recovery period of anesthesia. Which complication is aspiration associated with?
Underinflation
There are many complications of intubation. One common complication is the diameter of the tube being too large. All are signs of the tube diameter being too large EXCEPT:
Reduces or block the flow of oxygen to the patient
T/F: Placement of the ECG electrodes does not matter as long as they cross the heart.
True
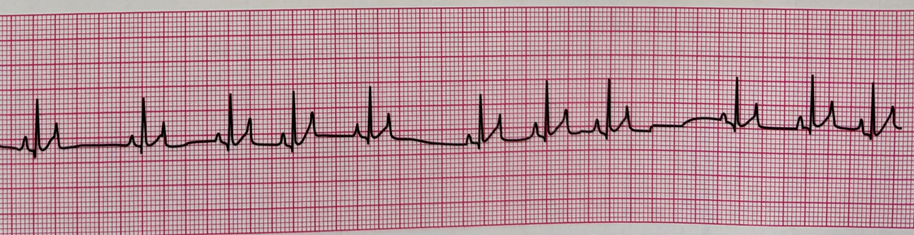
The _______ arrhythmia is common under anesthesia for dogs. It is characterized by longer than normal spaces between QRS complexes and corresponds with breathing. Please name the arrhythmia shown below.
Sinus
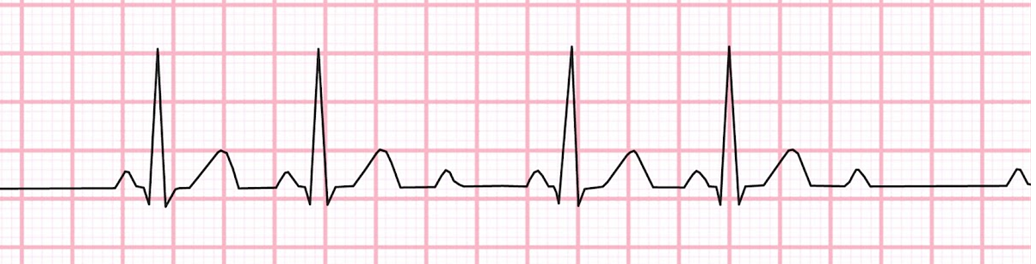
The _____ arrhythmia has no lengthening in the P-R intervals. It is characterized by a "lonely p wave" with no corresponding QRS complex. Please name the arrythmia shown below.
2nd degree AV block type II
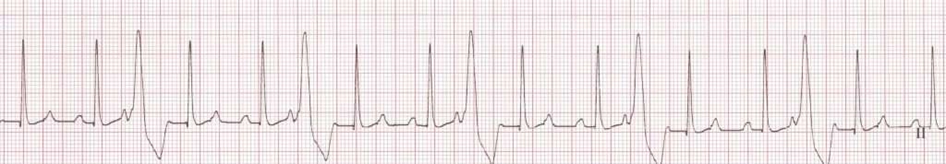
The ______ arrhythmia is characterized by wide and bizarre QRS complexes without a P wave. There are different types of this arrhythmia which include unifocal, multifocal, and runs. Please name the arrhythmia.
VPC or PVC
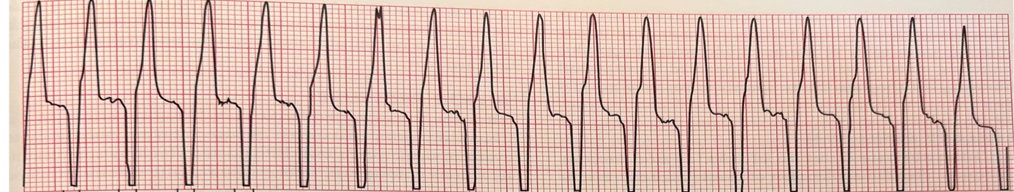
The _______ arrhythmia is fast and characterized by bizarre looking QRS complexes with no P or T wave. This arrhythmia can be treated with Lidocaine or beta blockers if the arrhythmia is stable. Please name the arrhythmia shown below.
V-Tach

The _______ arrhythmia is characterized by no palpable pulse or electrical activity. Compressions are required for this arrhythmia. Please name the arrhythmia shown below.
Asystole