Behavioural Ecology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
behavioural ecology
interactions between organisms and their environment which are mediated by behaviour
focuses on animals but has expanded to plants/microbes
behaviour
the internally coordinated responses of whole living organisms to external or internal stimuli
what causes adaptive behaviours
can vary between species (interspecific) or within (intraspecific)
when certain behaviours may increase the survival and reproductive output of an organism, as well as being related to genotype (genetic basis) - it can be selected for/shaped by natural selection
adaptive behaviours
a behaviour which increases the fitness of an organism and will be selected for over multiple generations
operate in a range of conditions and depend on genes and the environment
as well as cognitive ability to learn
behaviours and genetic basis ex
distribution of work based on age in bees - younger bees inside as brood care, older bees forage outside
foraging behaviour coded by single gene which produces a specific protein (PKG)
so change in expression of one gene can alter behaviour
hamiltons classes of social interaction
based on fitness consequences:
cooperation, altruism, selfishness, spite
cooperation
both the donor and recipient have fitness benefits, generally within a species/related animals, exchange of resources
ex wolf pack, ants, bees, clownfish
hamiltons class of social interaction
altruism
recipient gets benefits, donor will not
ex ground squirrels will alarm call when risk of predation, red squirrels can adopt offspring
due to group selection, manipulation, reciprocal altruism, or kin selection
hamiltons class of social interaction
selfishness
donor benefits, recipient does not
ex male lions killing cubs from other males, cowbirds and their brood parasitism
in herds they stick close together as a way to get away from predators - better them vs you (not cooperative)
hamiltons class of social interaction
spite
neither donor or recipient will benefit
ex european badger infected with tuberculosis will often leave kin (fitness disadvantage) and also spread pathogen to non-kin
hamiltons class of social interaction
fitness
the number of offspring contributed by an individual relative to the number of offspring produced by other population members
inclusive fitness
an individuals overall fitness is determined by its survival and reproduction, and the survival and reproduction of its relatives
natural selection favours behaviours which increase this
cooperation and selfishness
should be selected for by natural selection because they increase donor fitness
altruism and spite
should be selected against by natural selection because they decrease donor fitness
group selection and altruism
individuals neglect their own needs in favour of the needs of the group
manipulation and altruism
donor does not recognize it is being parasitized
reciprocal altruism and altruism
recipient will pay back at one point in the future
kin selection and altruism
individuals increase their inclusive fitness by helping increase the survival and reproduction of relatives
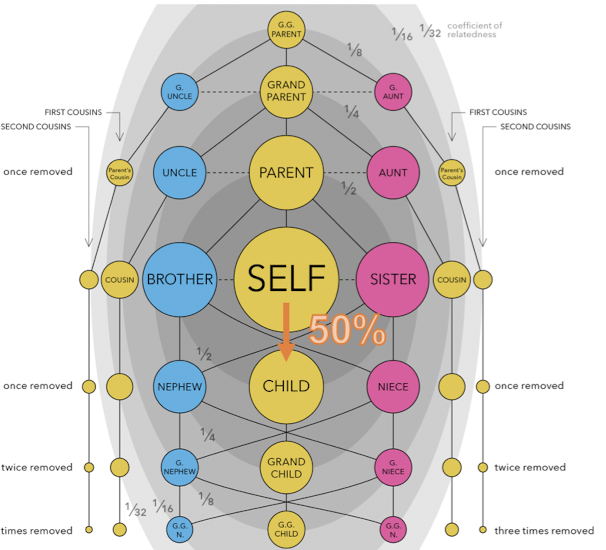
coefficient of the relationship (Rg)
coefficient of the relationship (Rg)
the probability that the alleles at a given locus will be identical by descent among two individuals in the population
50% reduction between each additional connection
ex parent 50%, grandparent to child - 25%
coefficient of the relationship and altruism
Rg x B > C, Rg X B - C >0
the more distant the relationship (Rg) the larger the benefits must be to the recipient to outweigh the cost (to the donor)
but when the relationship is closer, the benefits dont have the be as large to outweigh costs
obligate brood parasite
species must lay eggs in the nests of other birds
can be intra or interspecific
cowbirds and phoebe birds
selfish from the pov of the cowbird
but altrustic from the pov of the phoebe who raises another one’s young
considered manipulation because she has no means to prevent or recognize the act
sociality
consists of a group of individuals living together
evolution is supported by cooperative feeding, defense of social group, restricted reproductive opps
strong kin selection
ex mutual grooing, protection of young, alloparenting/allonursing, highly complex societies
wolf packs and sociality
alpha male and female are the only ones reproducing, this restricts the opportunities of other wolves and so they care for the young
cooperative breeders
live in groups, several adults help with offspring
defense, prepare/maintain living area, feed young
works because of inclusive fitness - most likely relatives, reciprocal altruism - u help me i help u
but can develop inbreeding
eusocial animals
highly complex social behaviour which evolved independently
individuals of more than 1 generation live together, cooperative care of young, division of individuals into sterile/non-reproductive and reproductive castes
ex leafcutter ants (7 castes), naked mole rats (3)
castes
generally likely to have larger workers specializing in defense (sterile), then there are smaller ones in foraging and maintenance - convergent evolution
queen on top
why has eusociality evolved?
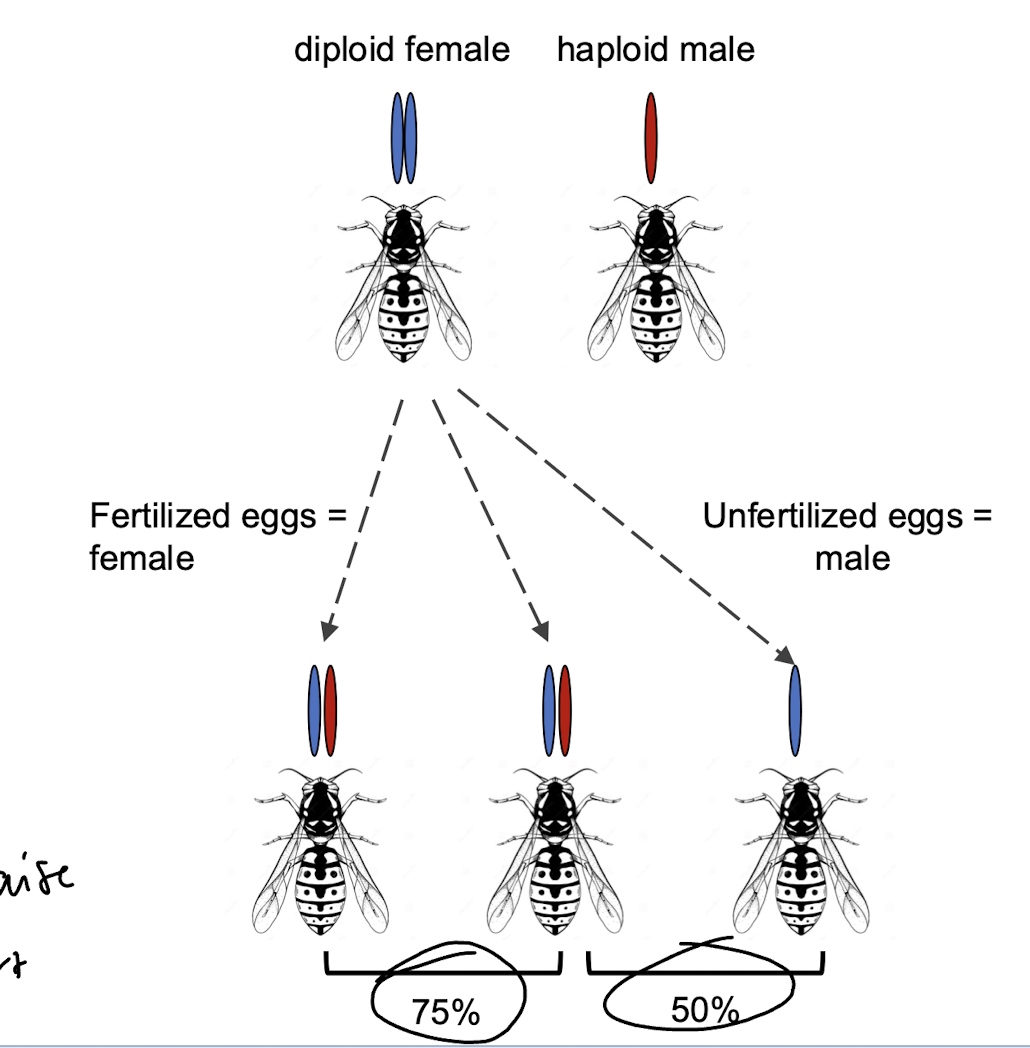
kin selection due to very high degree of relatedness - haplodiploidy
ecological restraints
haplodiploidy
sisters are more related to eachother (75%) than they are to their brothers (50%)
also then they would be to their own offspring (50%)
this means makes more sense to raise a sister than to raise a new