Unit 2: Population and Migration Patterns and Processes
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Population Distribution
Pattern of humans spreading
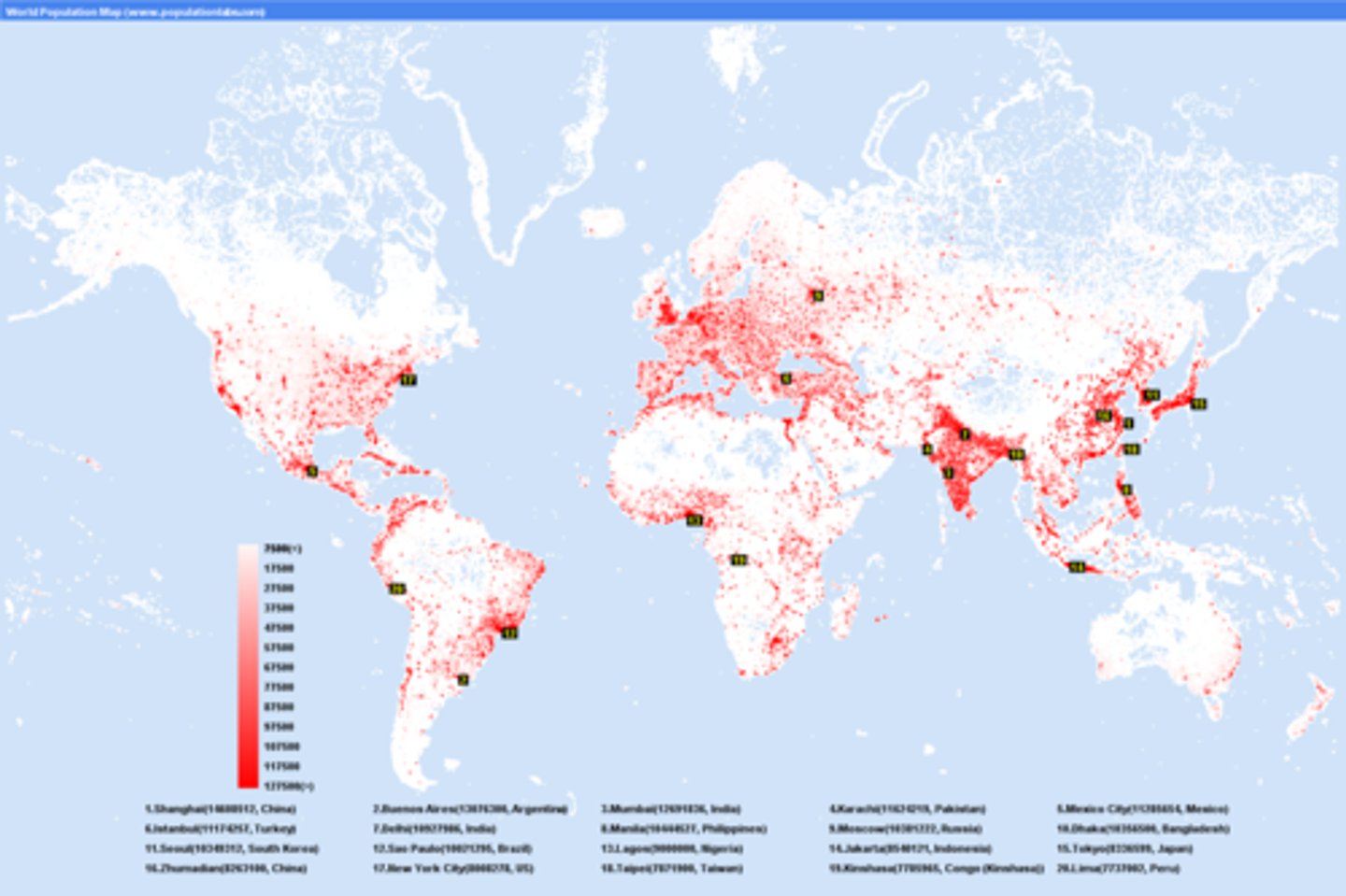
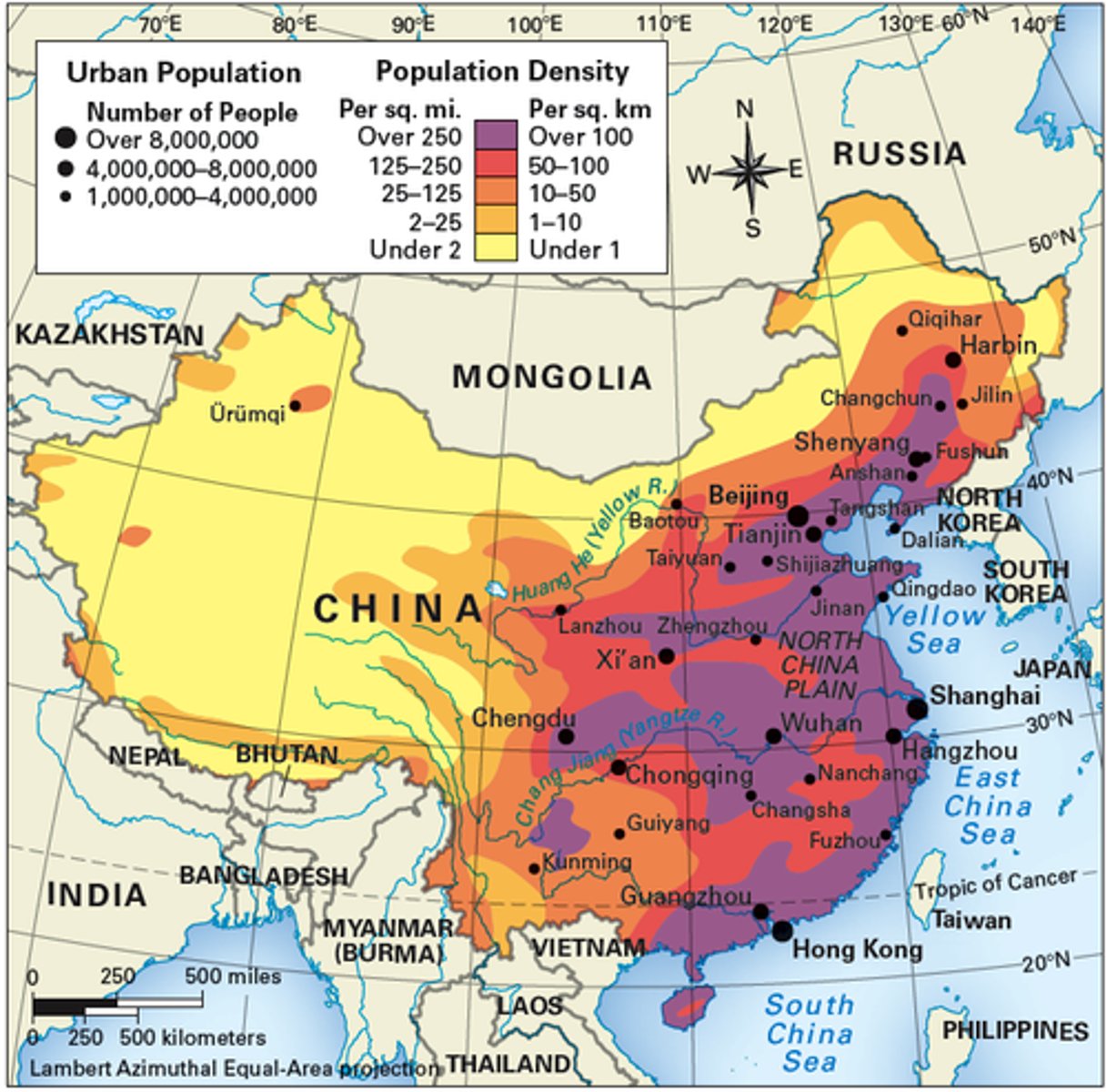
Population Density
People per square mile/kilometer
Megacities
10 million+ city population
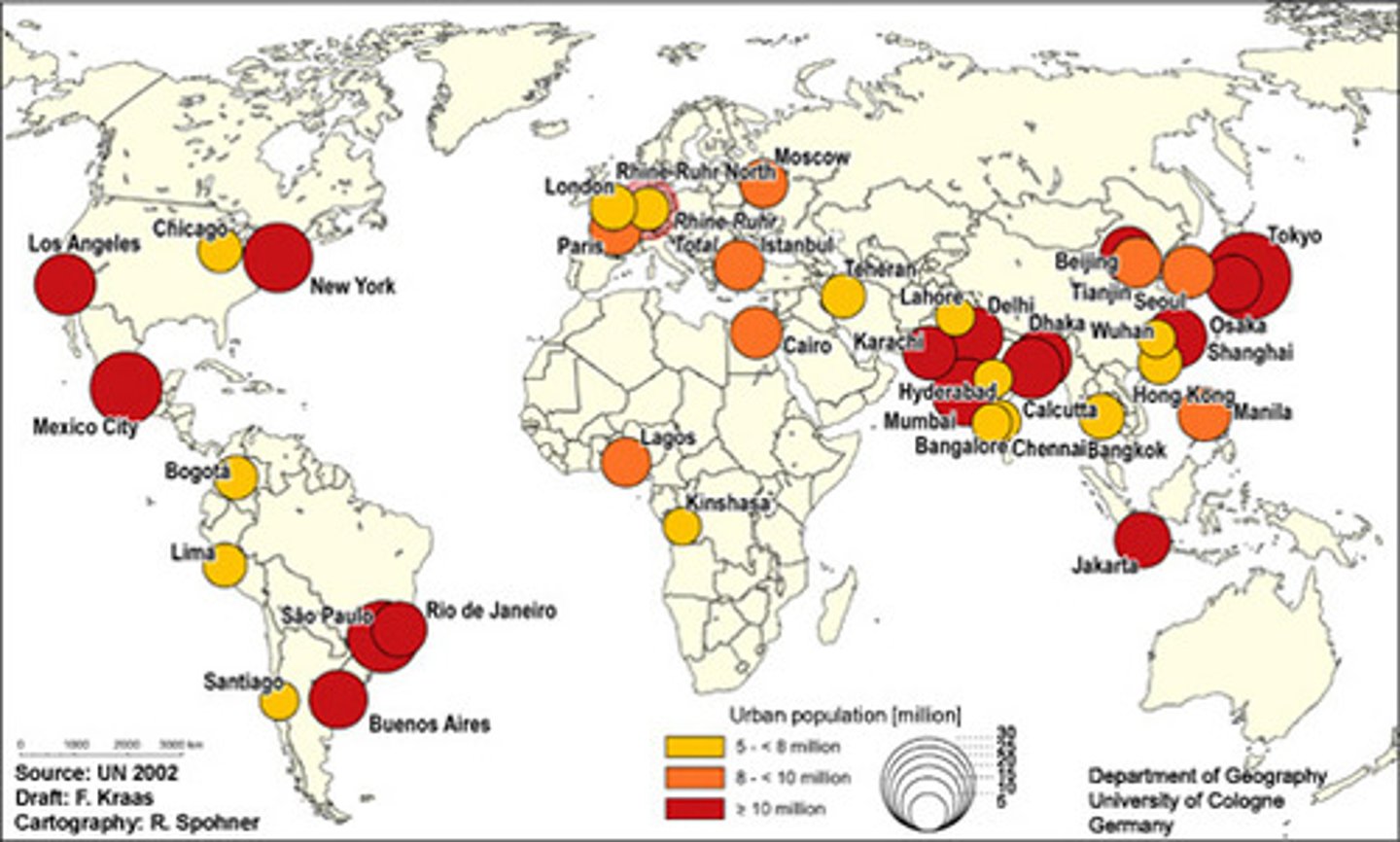
Metacitites
20 million+ city population

MDC
Countries with highly developed economies, industrialization, urbanization, advanced technological infrastructure, and high standards of living. Stages 4/5 DTM
NIC
LDCs with expanding industrial economies and a developing trade status in the global marketplace. Stage 3 DTM
LDC
A country at an early expanding stage in the process of economic development. Stage 2 DTM
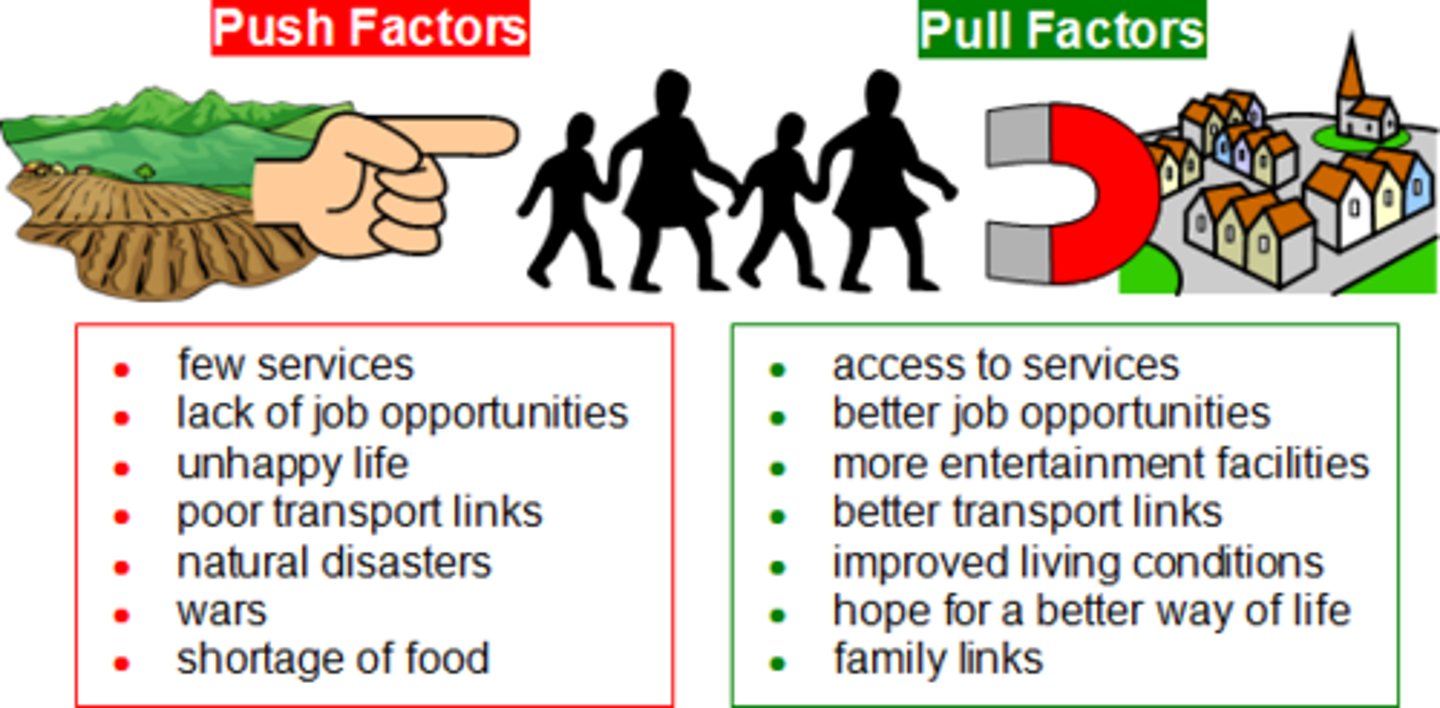
Push Factors
Reasons to emigrate (economic troubles, overcrowding, poverty)

Pull Factors
Reasons to migrate (economic opportunity, jobs, land, cost of living, stability, freedom)
Forced Migration
Movers have no choice but to relocate (political instability, ethnic cleansing, natural disasters, slavery, trafficking)

Arithmetic Population Density
Total people / total land
Physiological Population Density
Total people / arable land
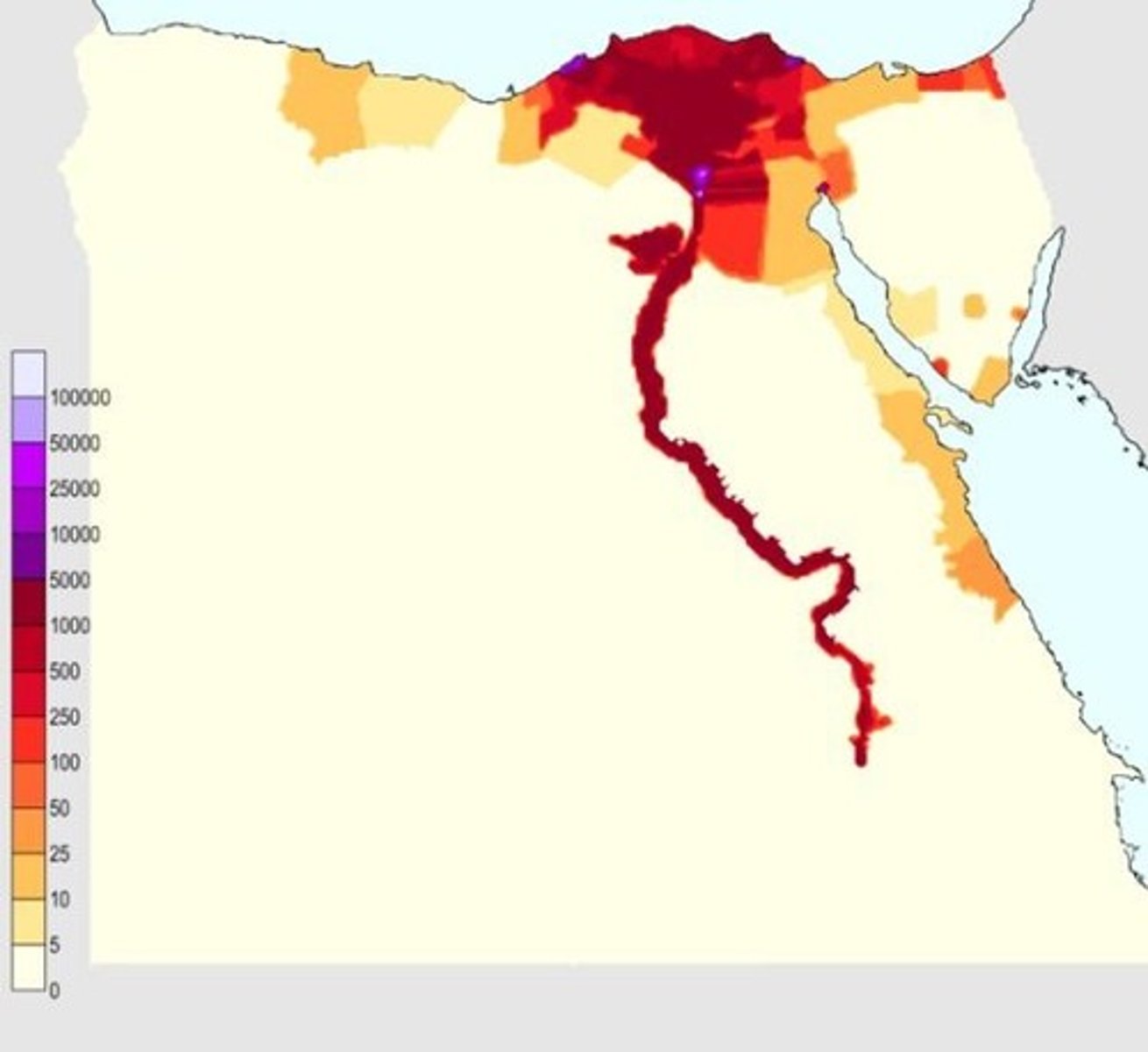
Carrying Capacity
Largest number of people an environment can support (increased due to technology and sustainability)

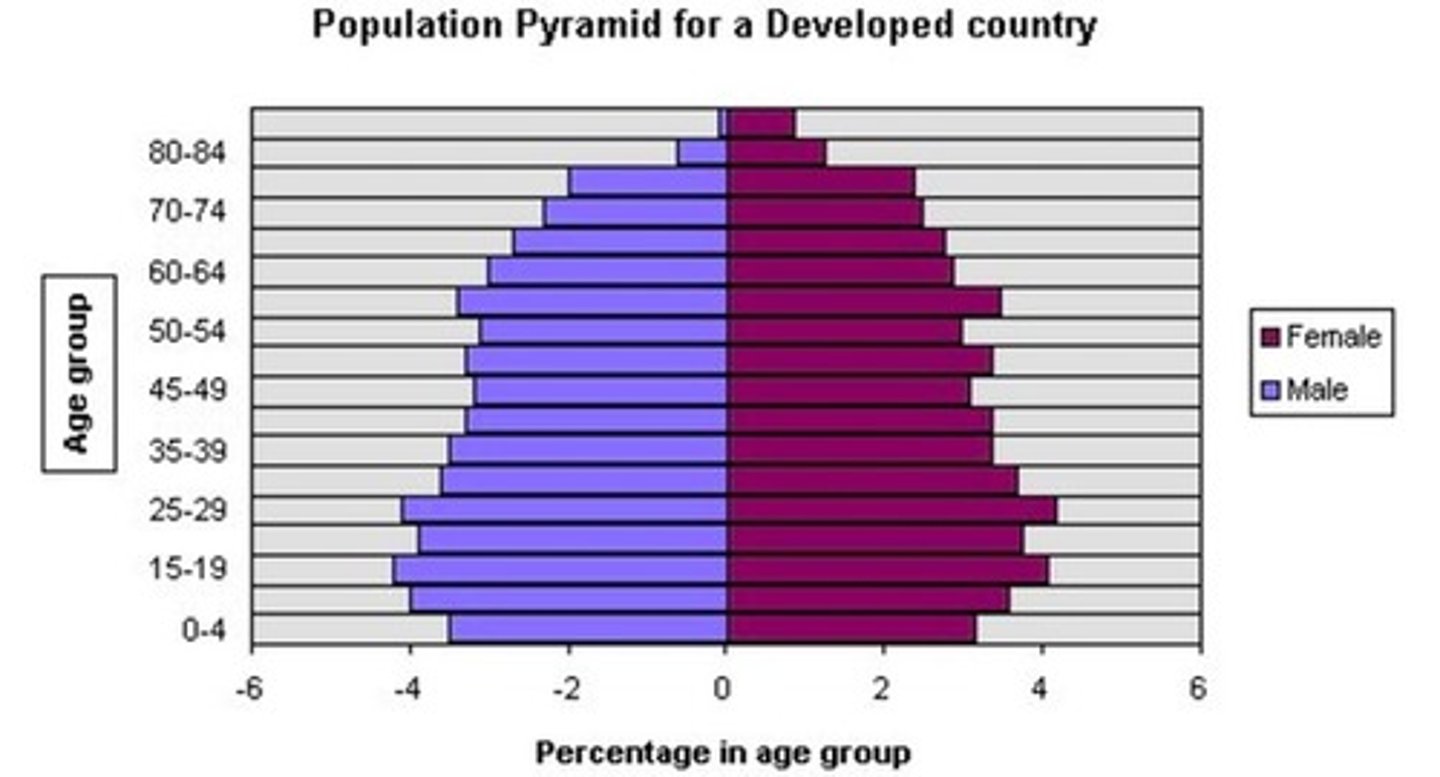
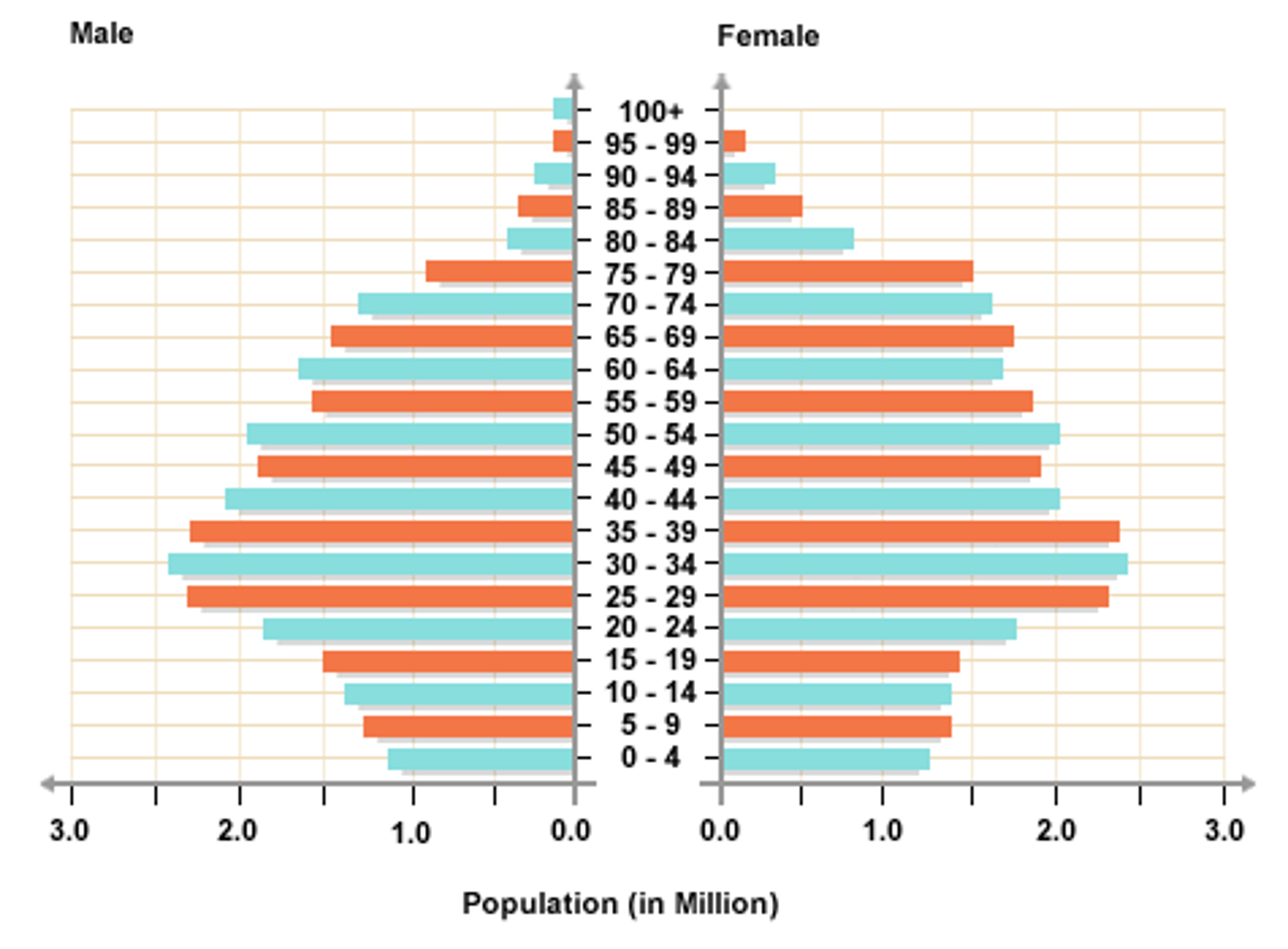
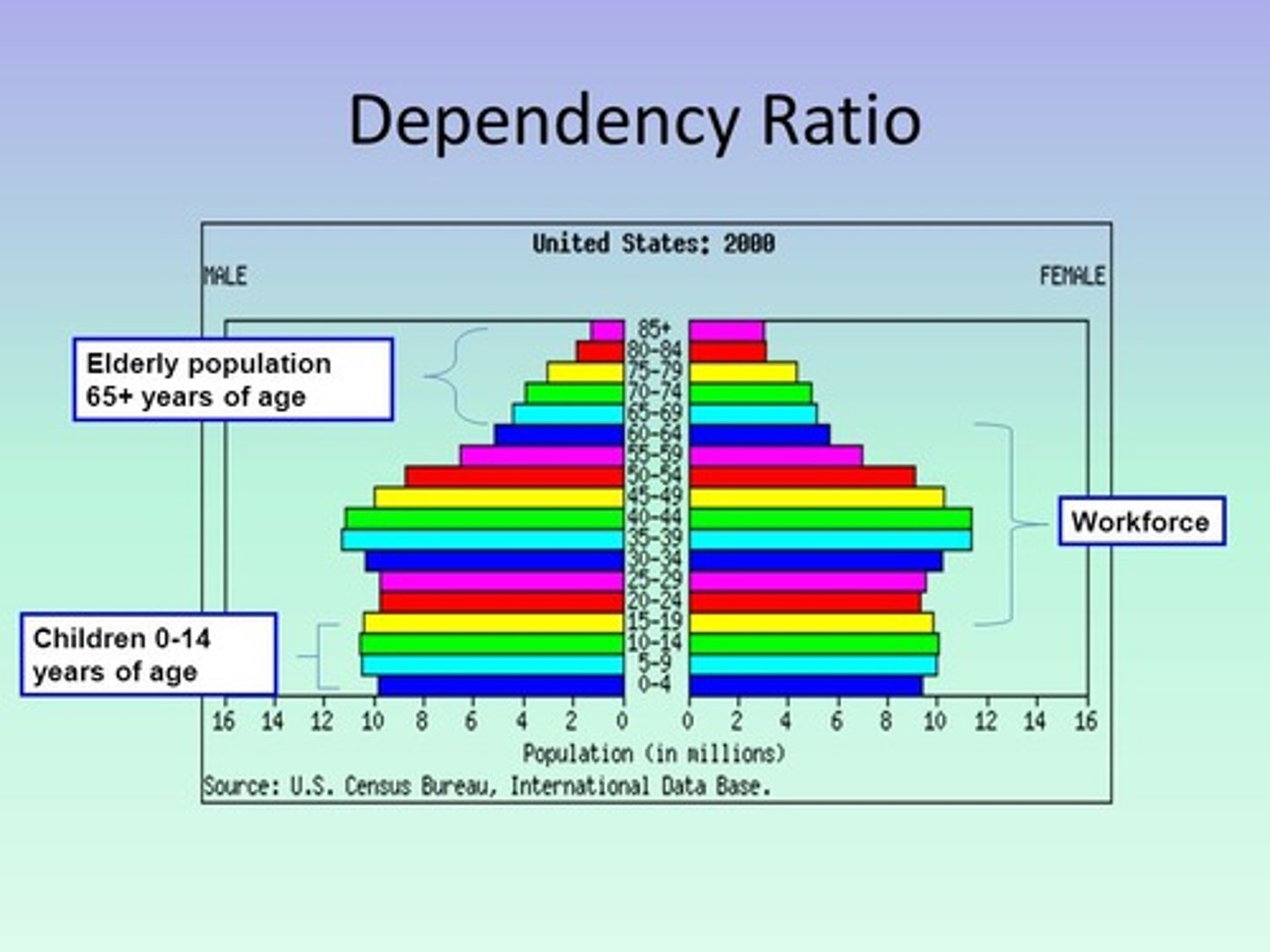
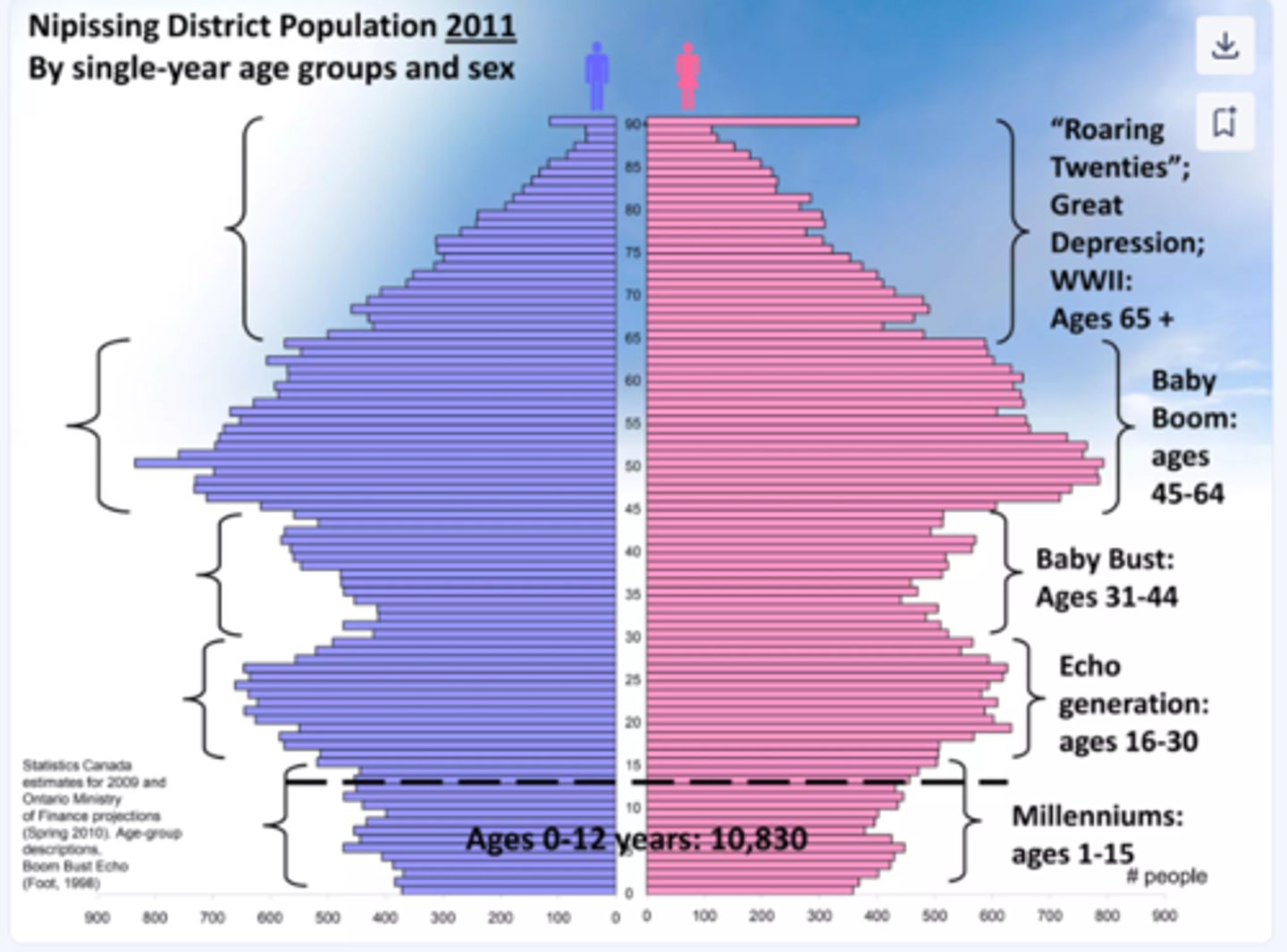
Population Pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
Aging Population
% of 65+ is increasing. Governments need to find ways to look after the elderly. Stage 5 DTM
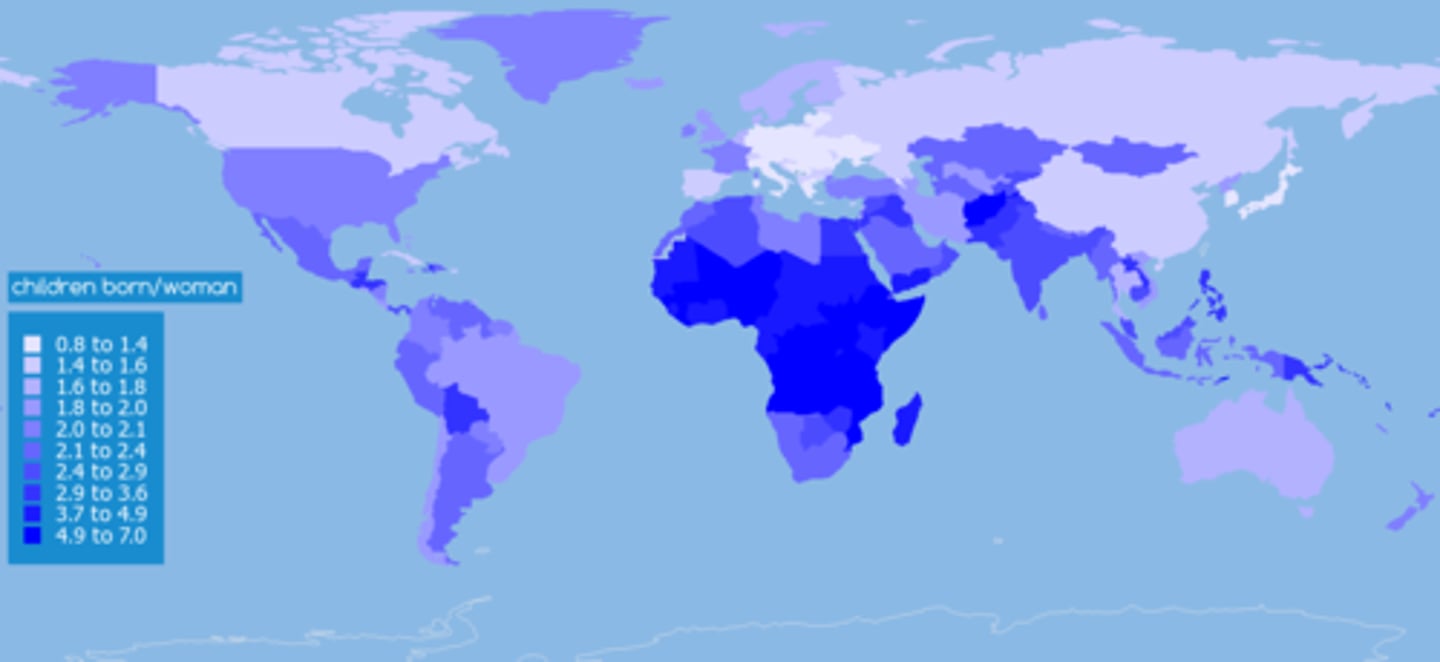
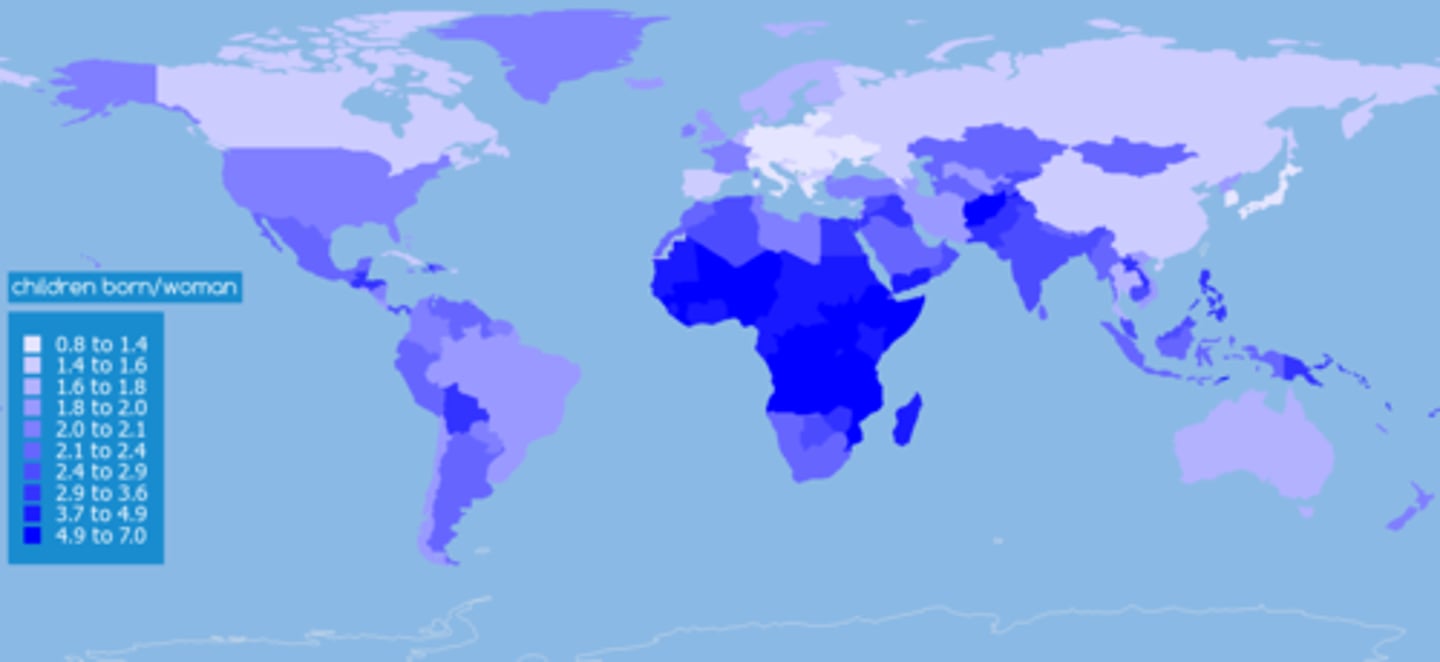
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
# of children a woman will have in her childbearing years. High in Stage 2 DTM due to lack of women education and rural
Dependency Ratio
# people who are too young/old to work, compared to # people in productive years (15-64)

2.1 Replacement Level
# children a woman must have to replace herself and her partner (.1 accounts for infant mortality). Found in Stage 4 DTM
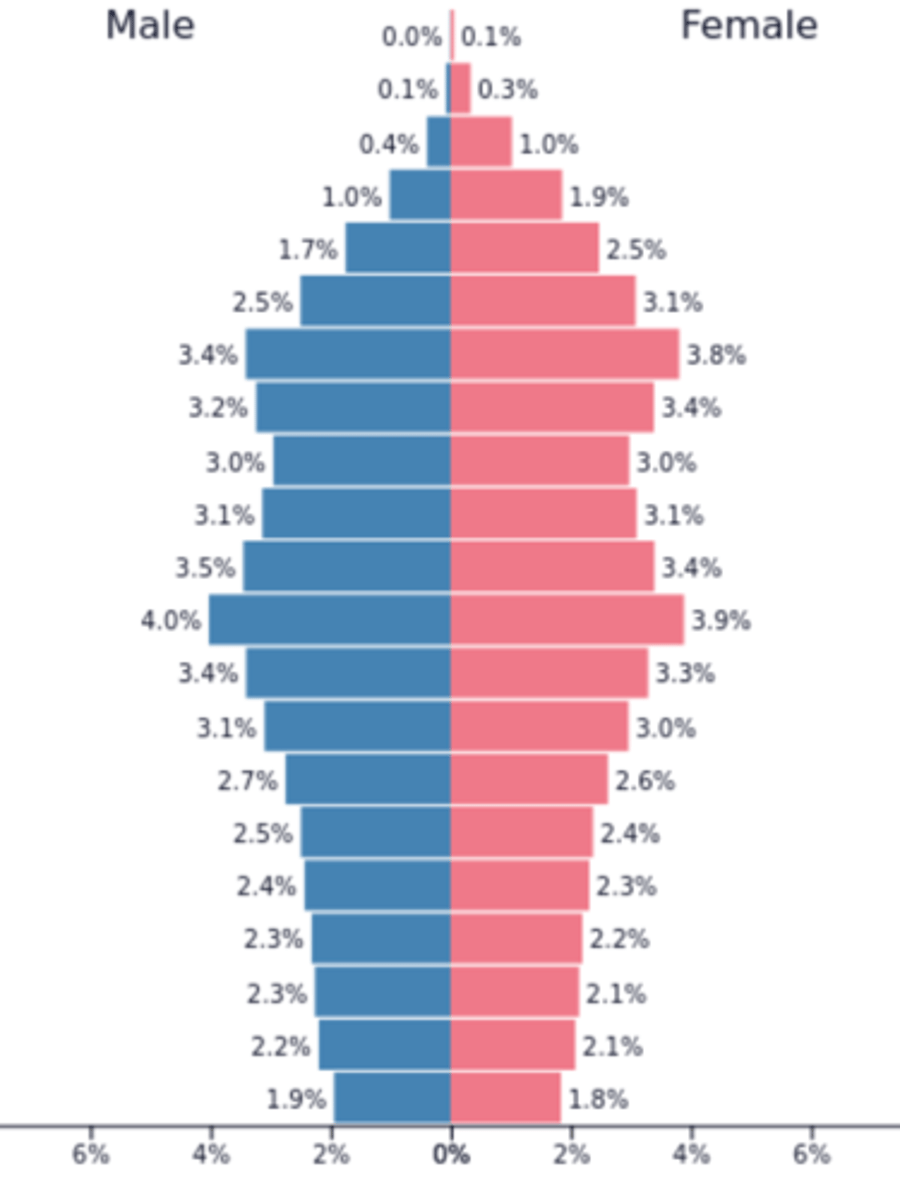
J-curve
For 10,000 years CDR and CBR were high and equal and population was limited. Industrial revolution - population grew exponentially, CDR and CBR was reduced allowing for substantial population growth.
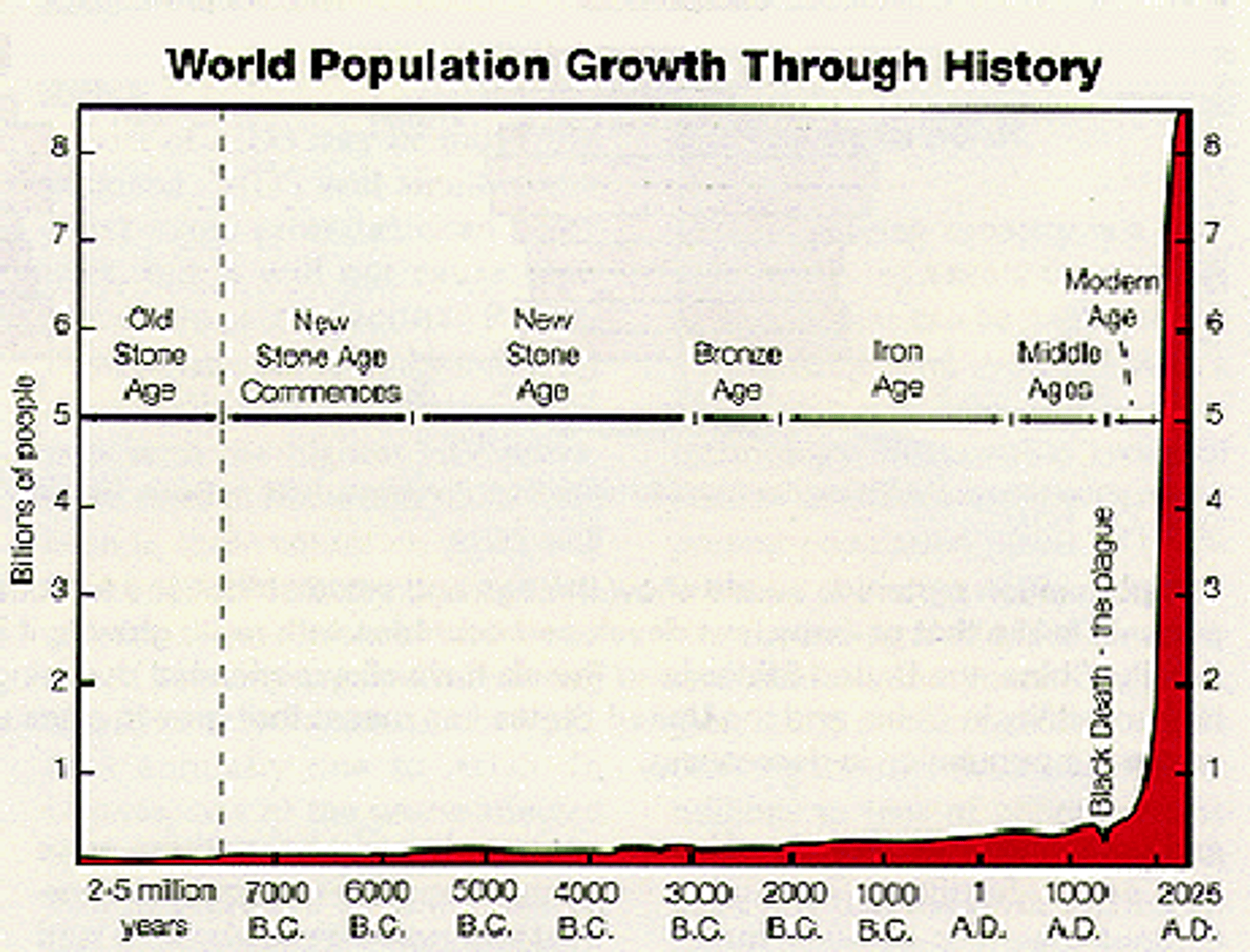
Potential Workforce
people ages 15-64 that are expected to be the society's labor force.
Baby Boom
Cohort of individuals born in US (1946-1964) after WWII in peace and prosperity. Better education and job opportunities caused high rates of marriage and fertility.
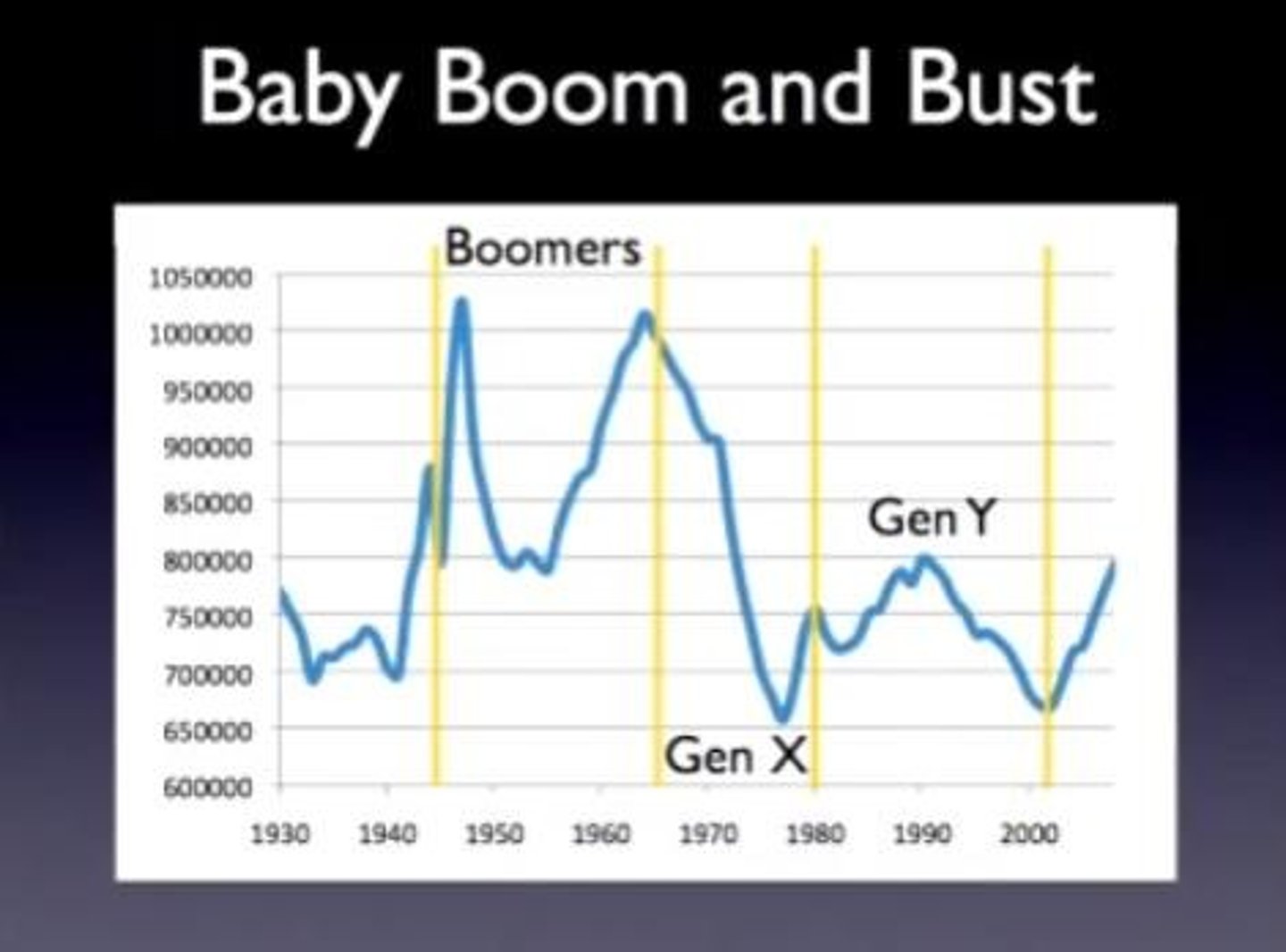
Baby Busters: "Generation X"
After the baby boom birth rates decrease until the children of baby boomers reach childbearing age.
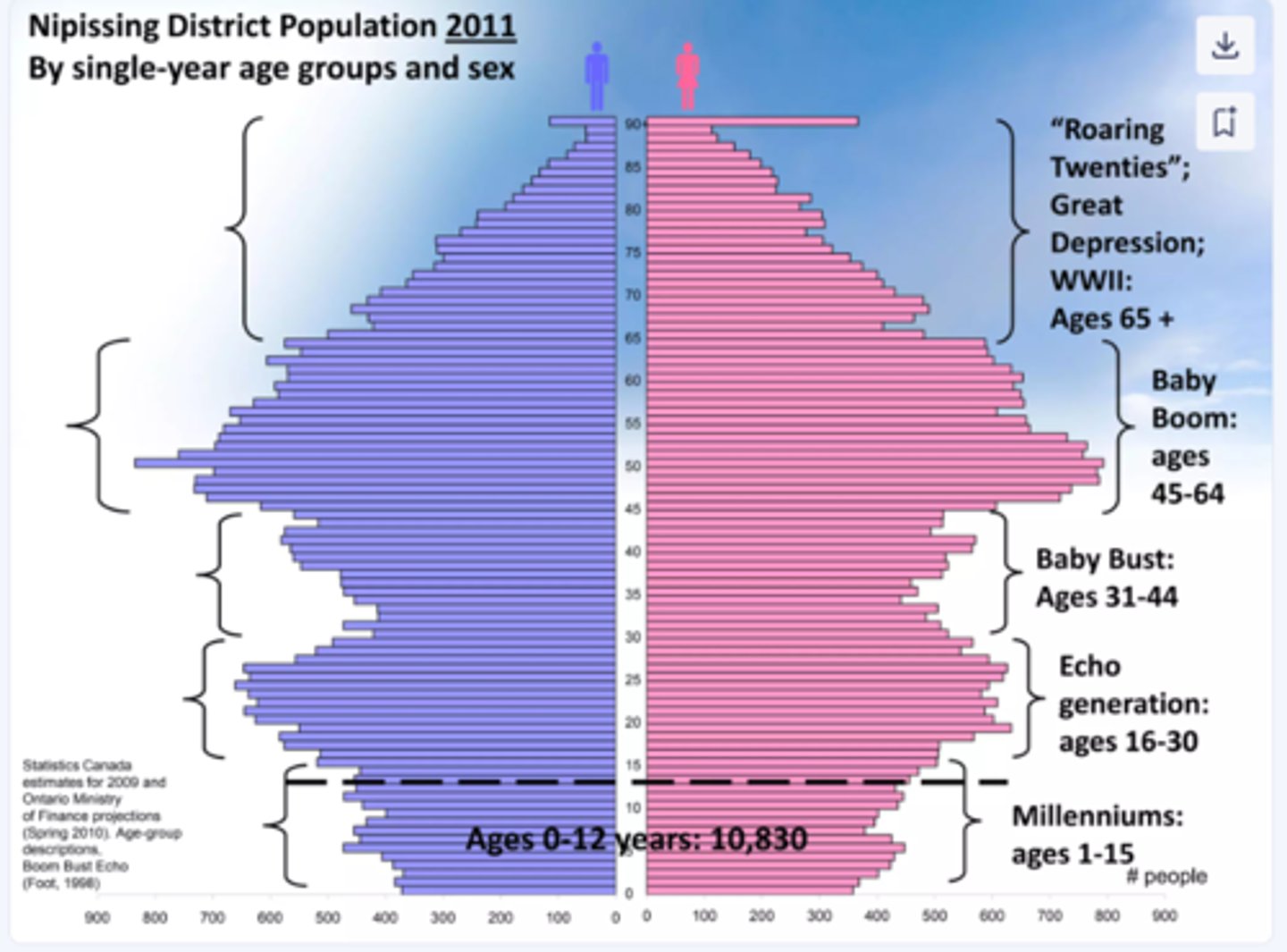
echo
Bulge indicating high childbearing
CBR
The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society. Crude Birth Rate
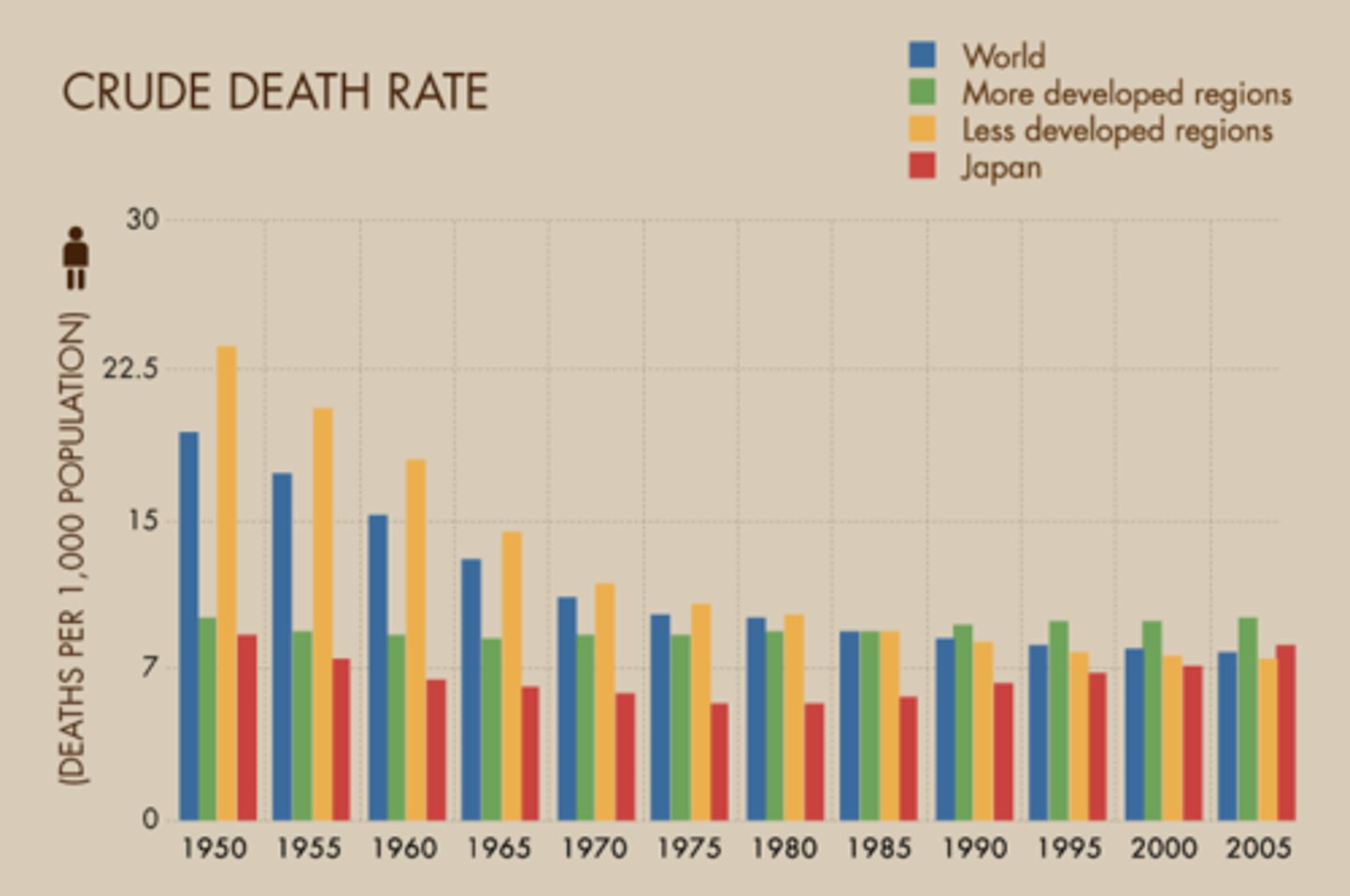
CDR
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society. Crude Death Rate
TFR
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
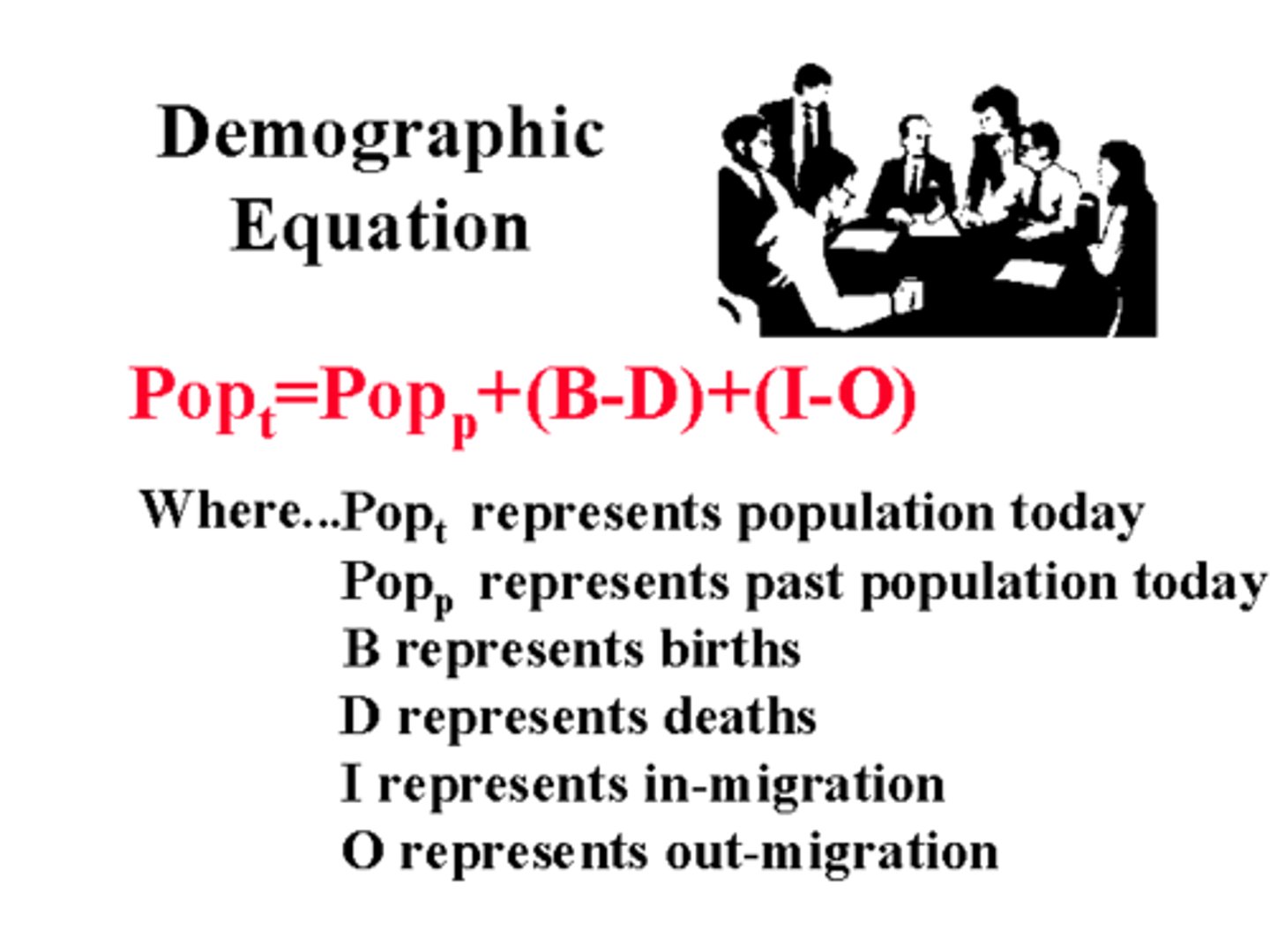
Demographic Balancing Equation
The future population = current population + (number of births - number of deaths) + (number of immigrants - number of emigrants).
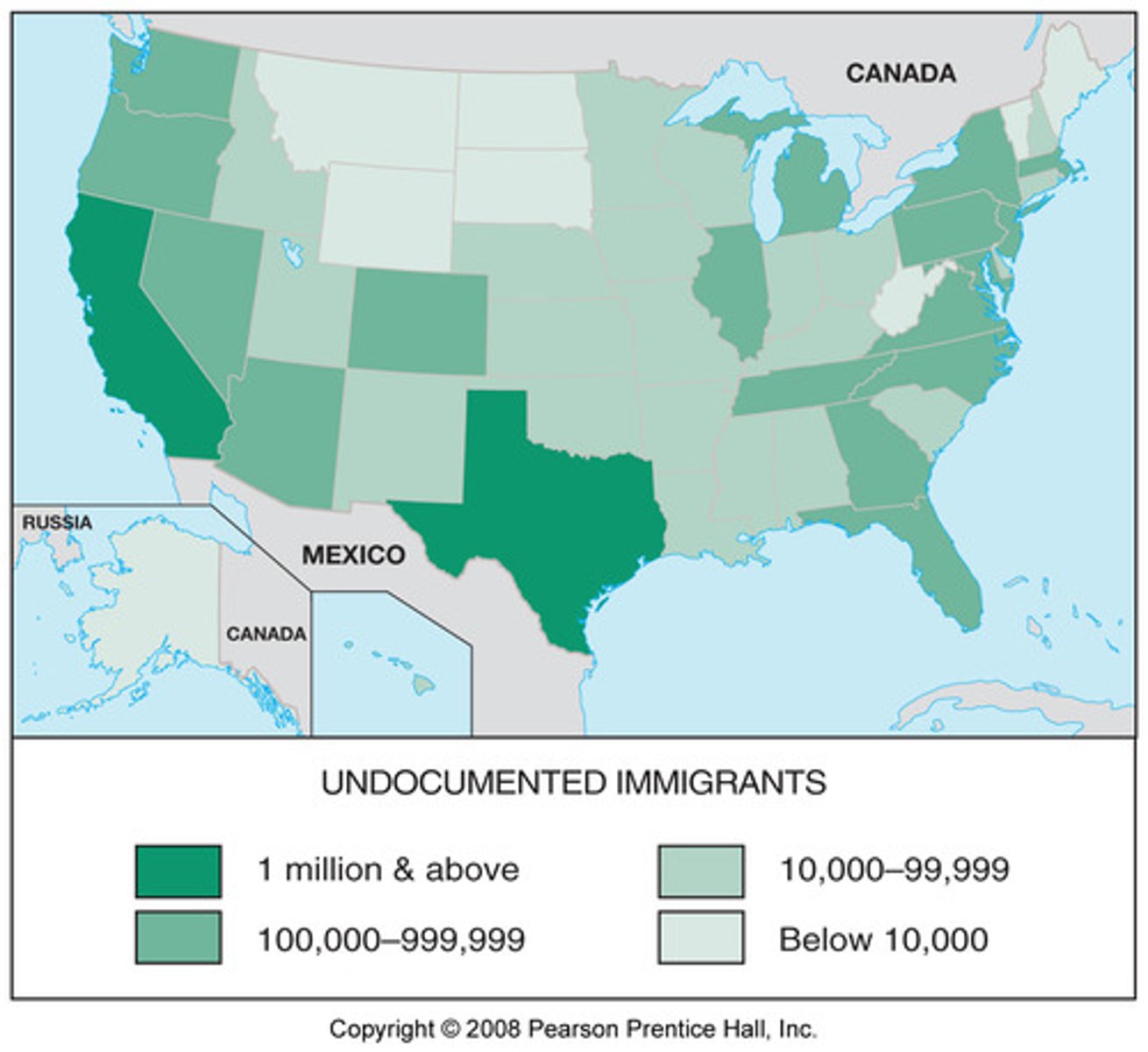
Immigrants
People who have left the country of their birth to live in another country.
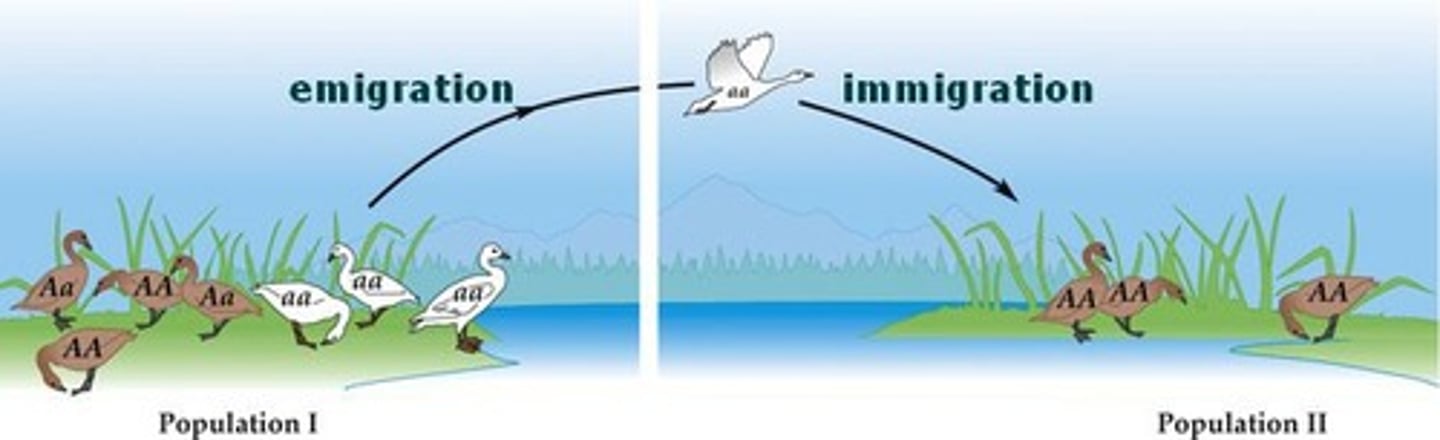
Emigrants
People who leave a country to live somewhere else.
life Expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live.
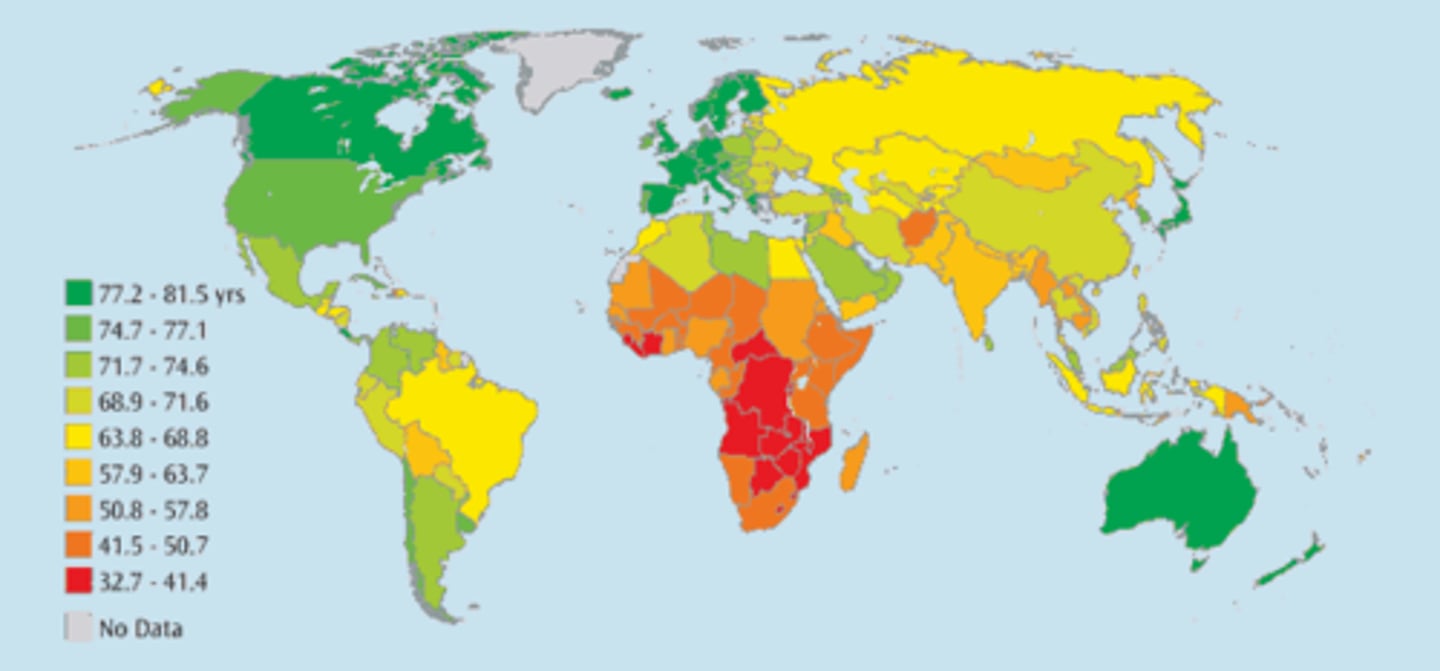
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under 1 year old for every 1,000 live births in a society.
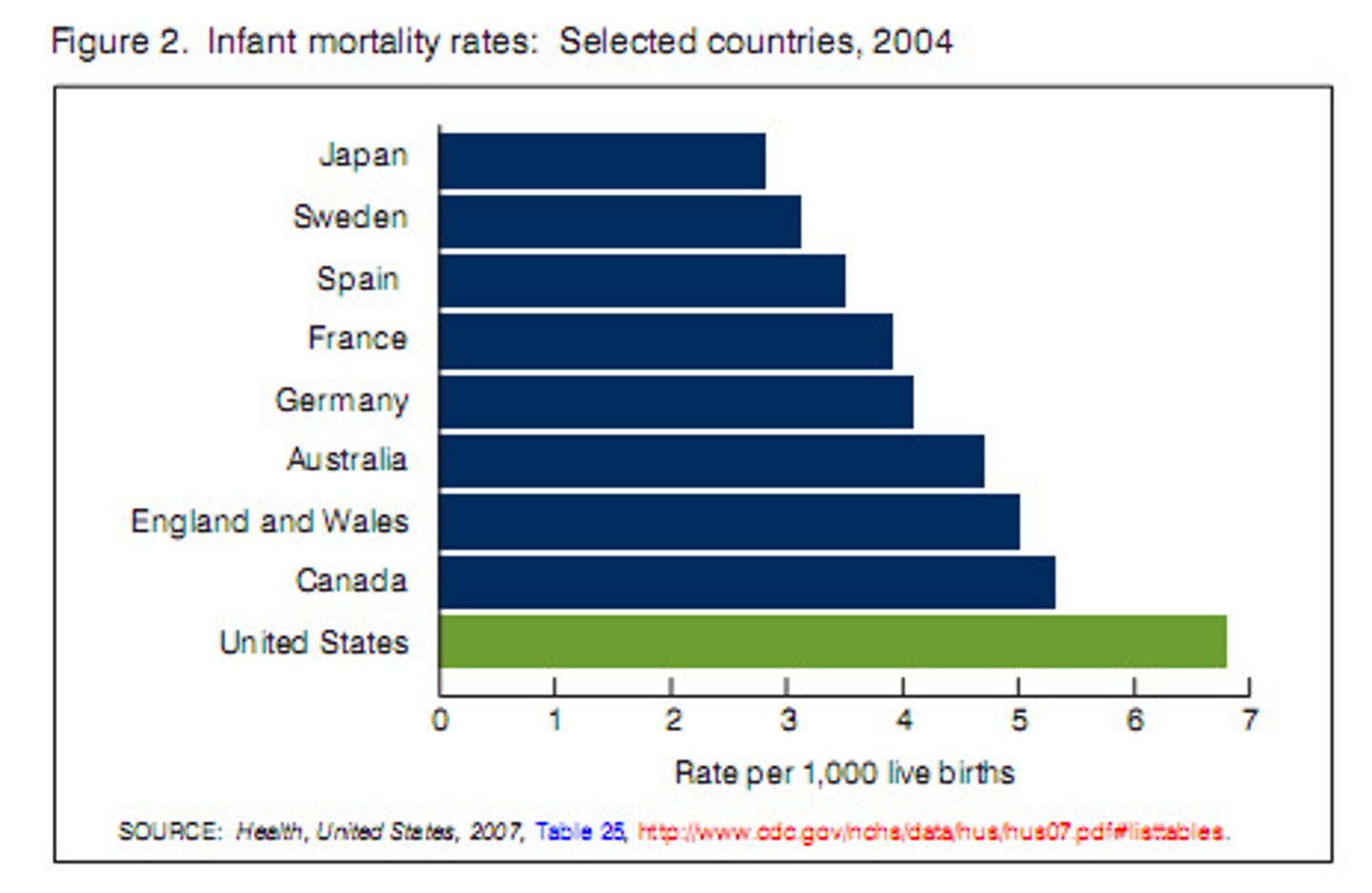
Factors that increase life expectancy.
Mechanized food production, improved seeds, fertilizers, food security, sewer systems, fresh water and water waste systems, vaccines and access to medical care.
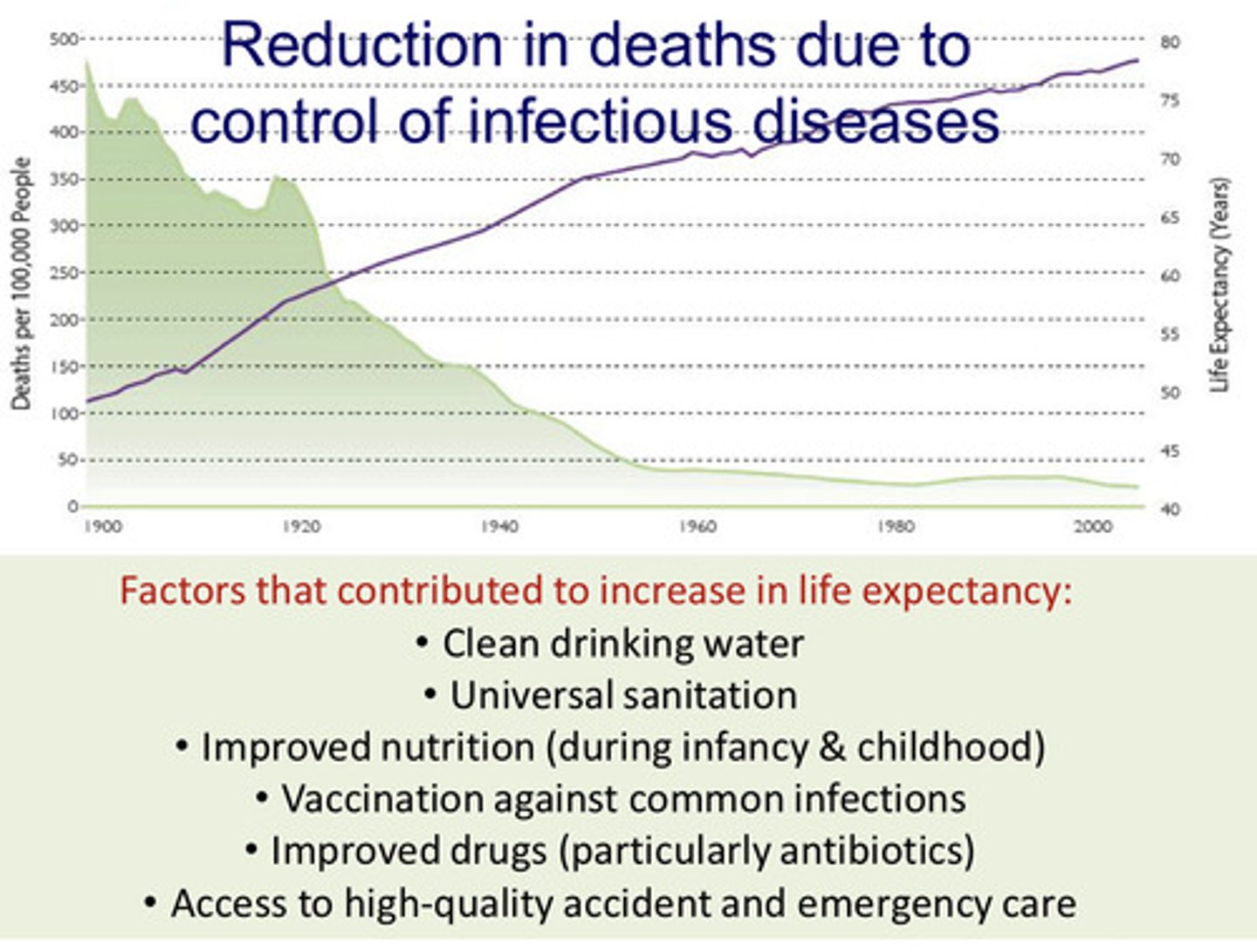
RNI
Rate of Natural Increase; (crude birth rate) - (crude death rate)
does not factor in emigration and/or immigration.
RNI= (CBR-CDR) / 10 add a percent sign. Currently CBR=~20, CDR=~8. Hence positive global population growth.
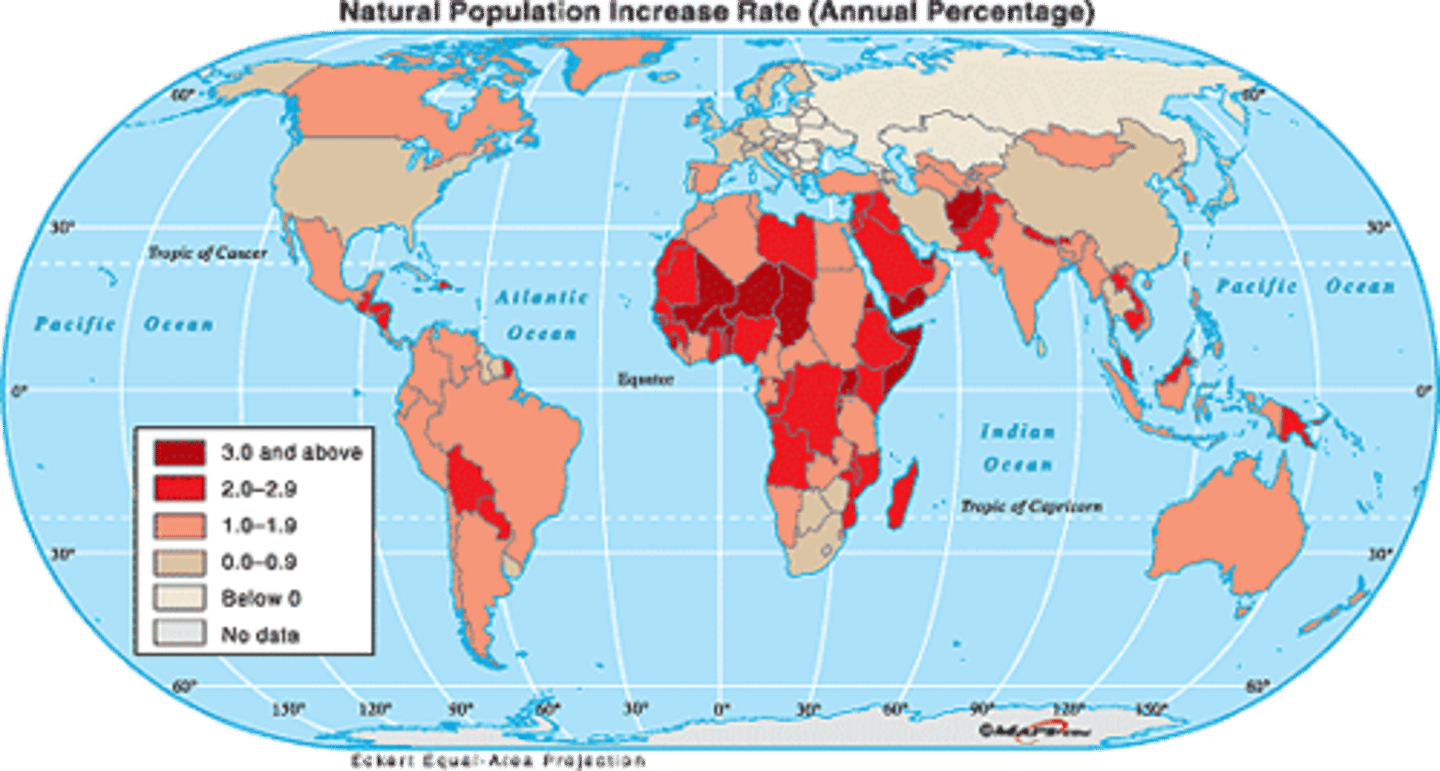
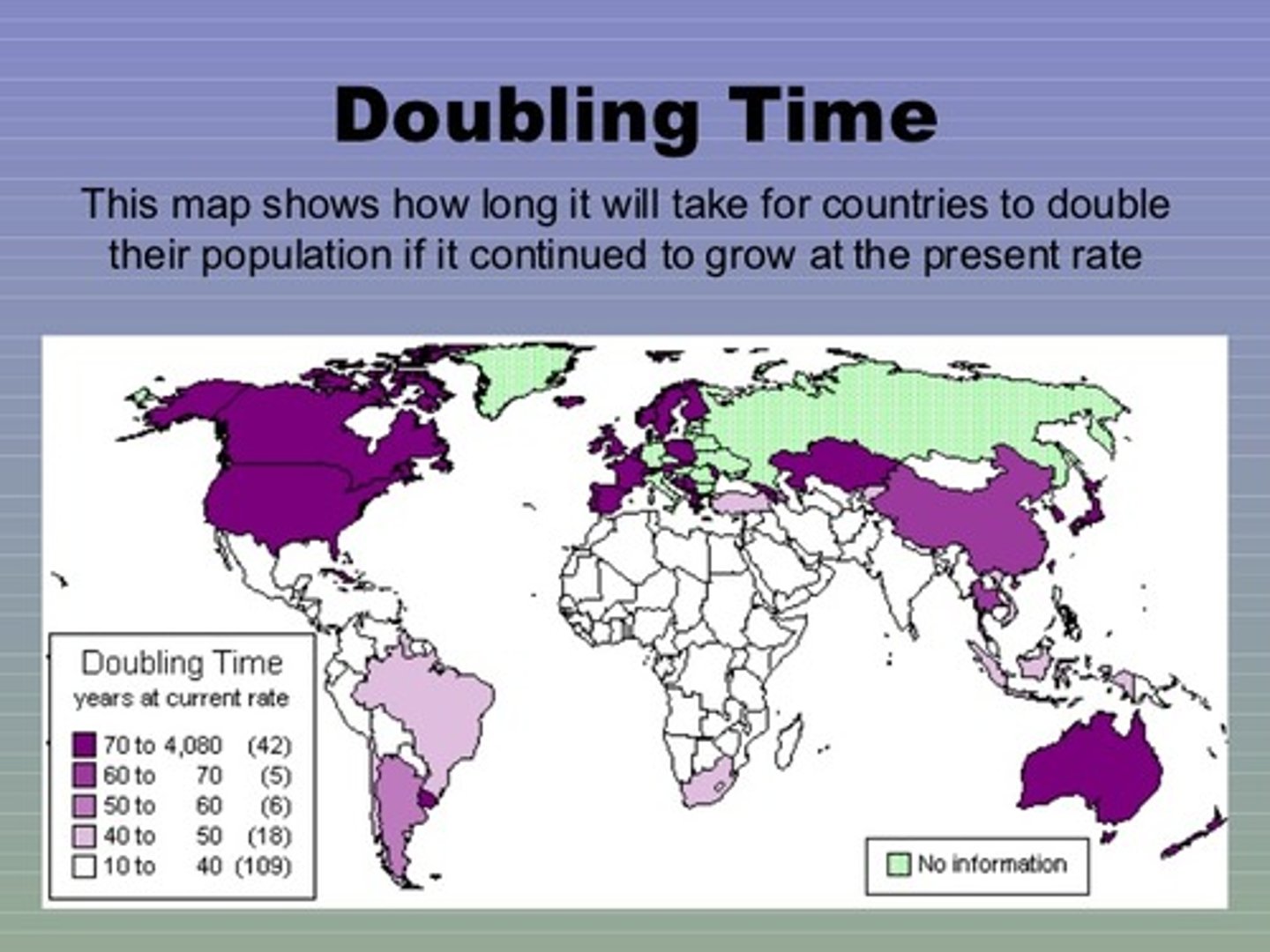
Population Doubling Time
The number of years it takes a population to double; calculated by dividing the number 72 by the rate of natural increase.
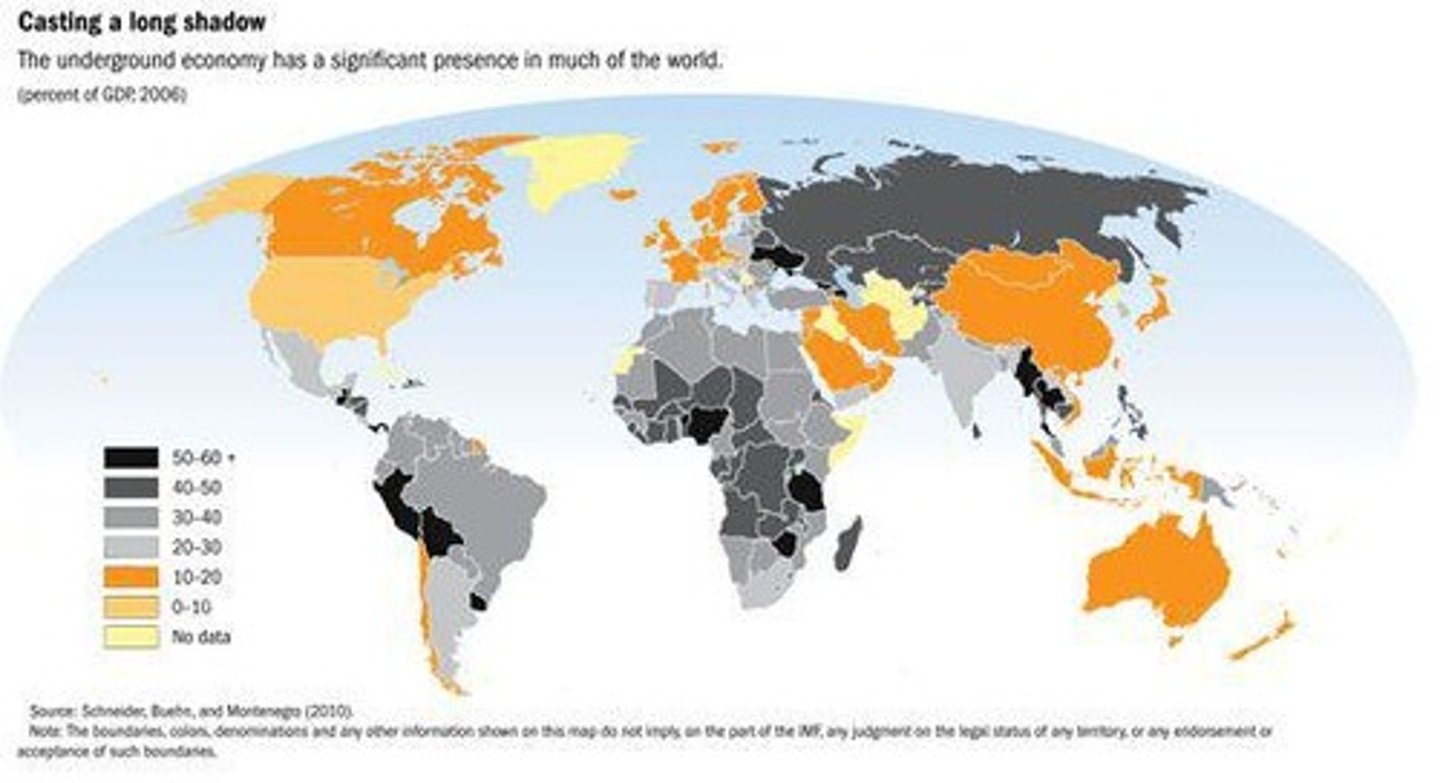
Shadow Economy
An informal economy in more developed countries that is not regulated by local government. Cash transaction, trading of services, because it is not regulated it cannot be directly taxed and typically this hiders and NIC from developing infrastructure at a faster rate.
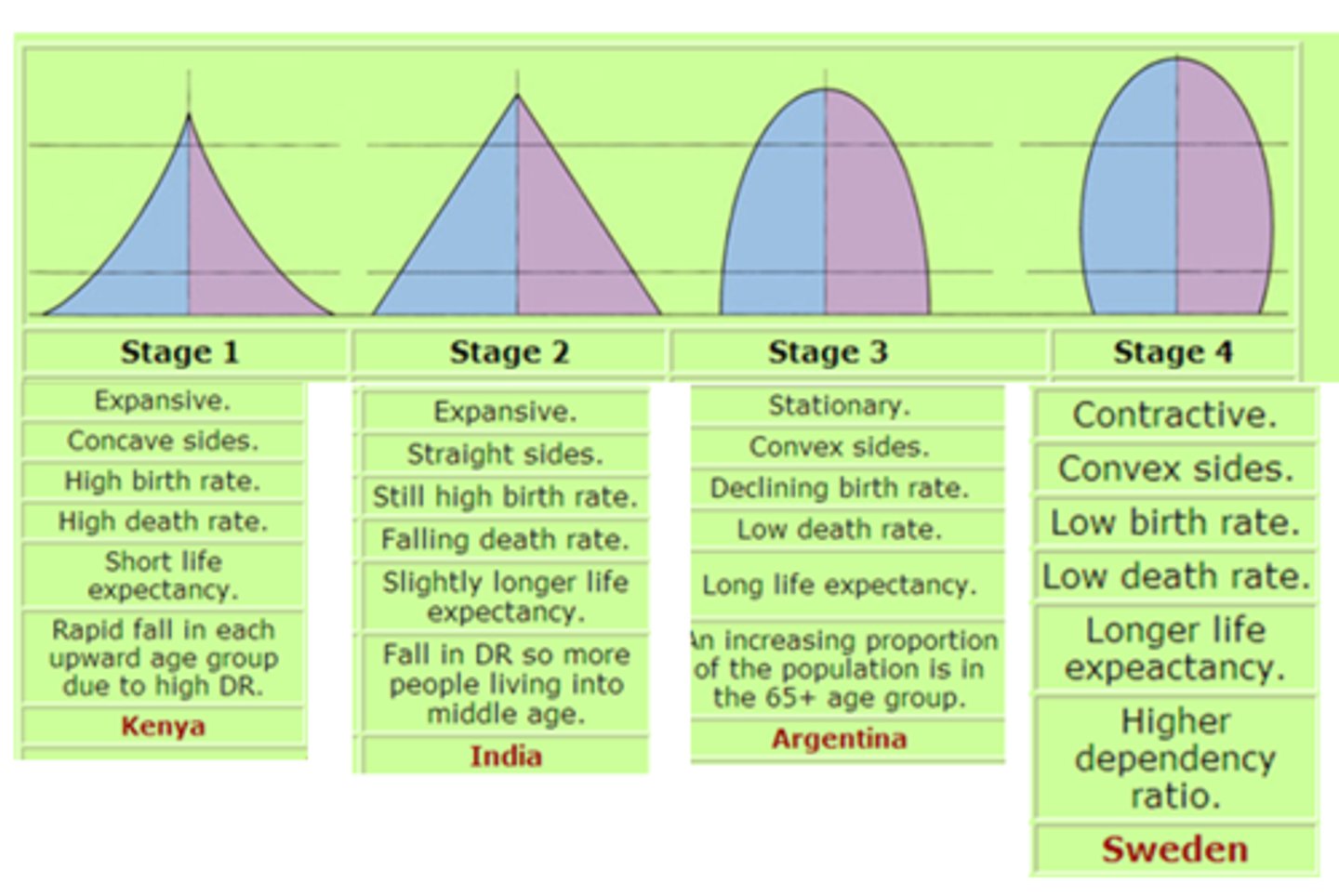
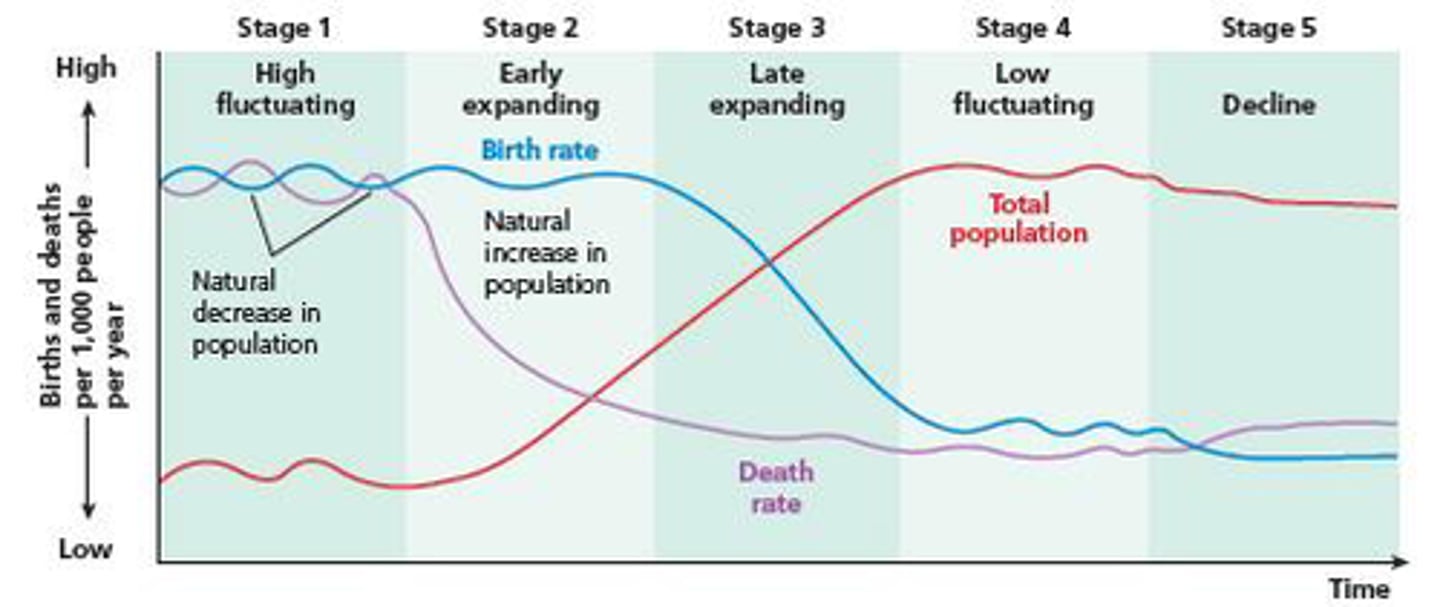
Demographic Transition Model
A sequence of demographic changes in which a country moves from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates through time. Stages 1-5. LDC=>NIC=>MDC.
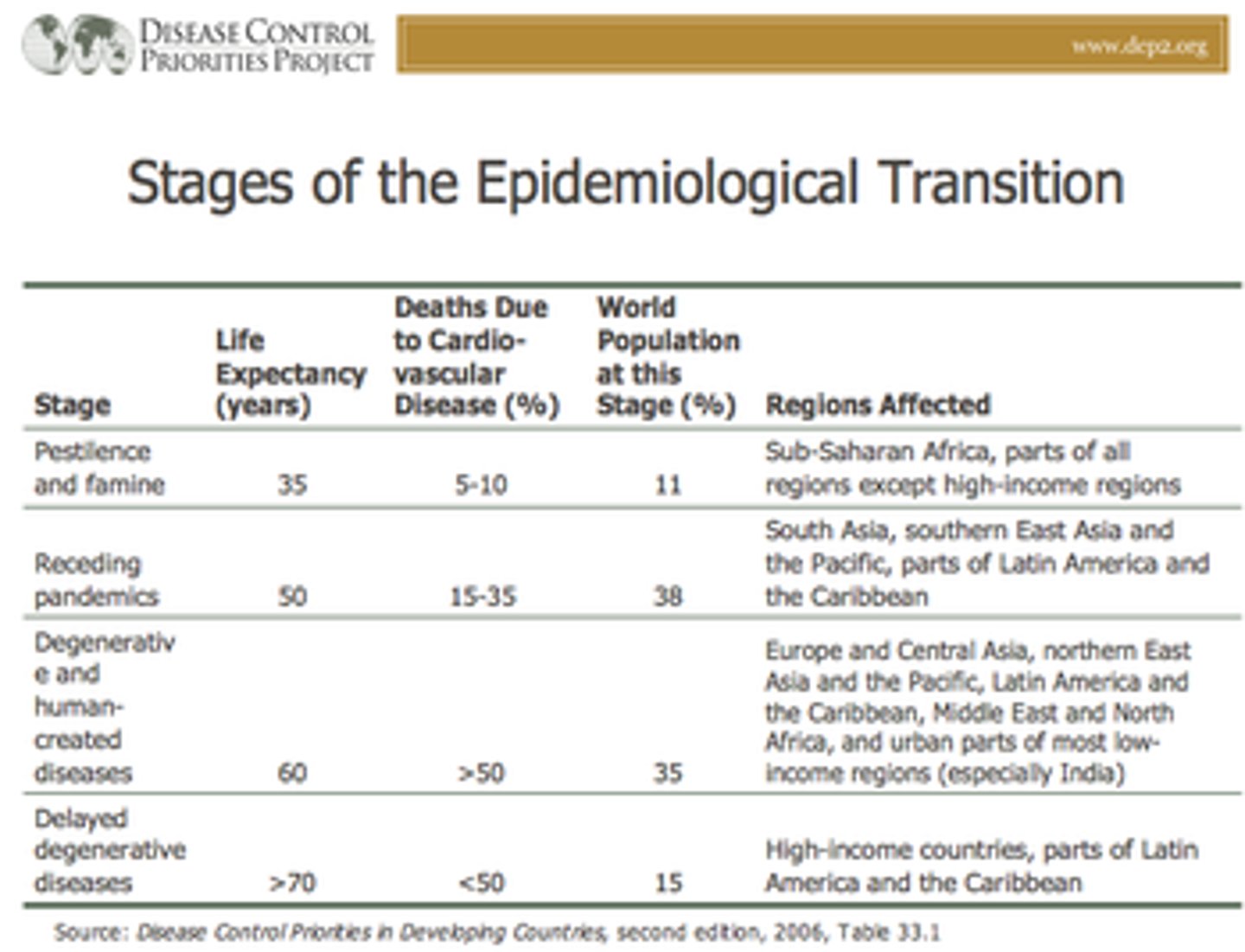
Epidemiological Transition Model
The theory that says that there is a distinct cause of death in each stage of the demographic transition model. It can help explain how a country's population changes so dramatically.
Stage 5 is potential epidemic and pandemic due to globalization.
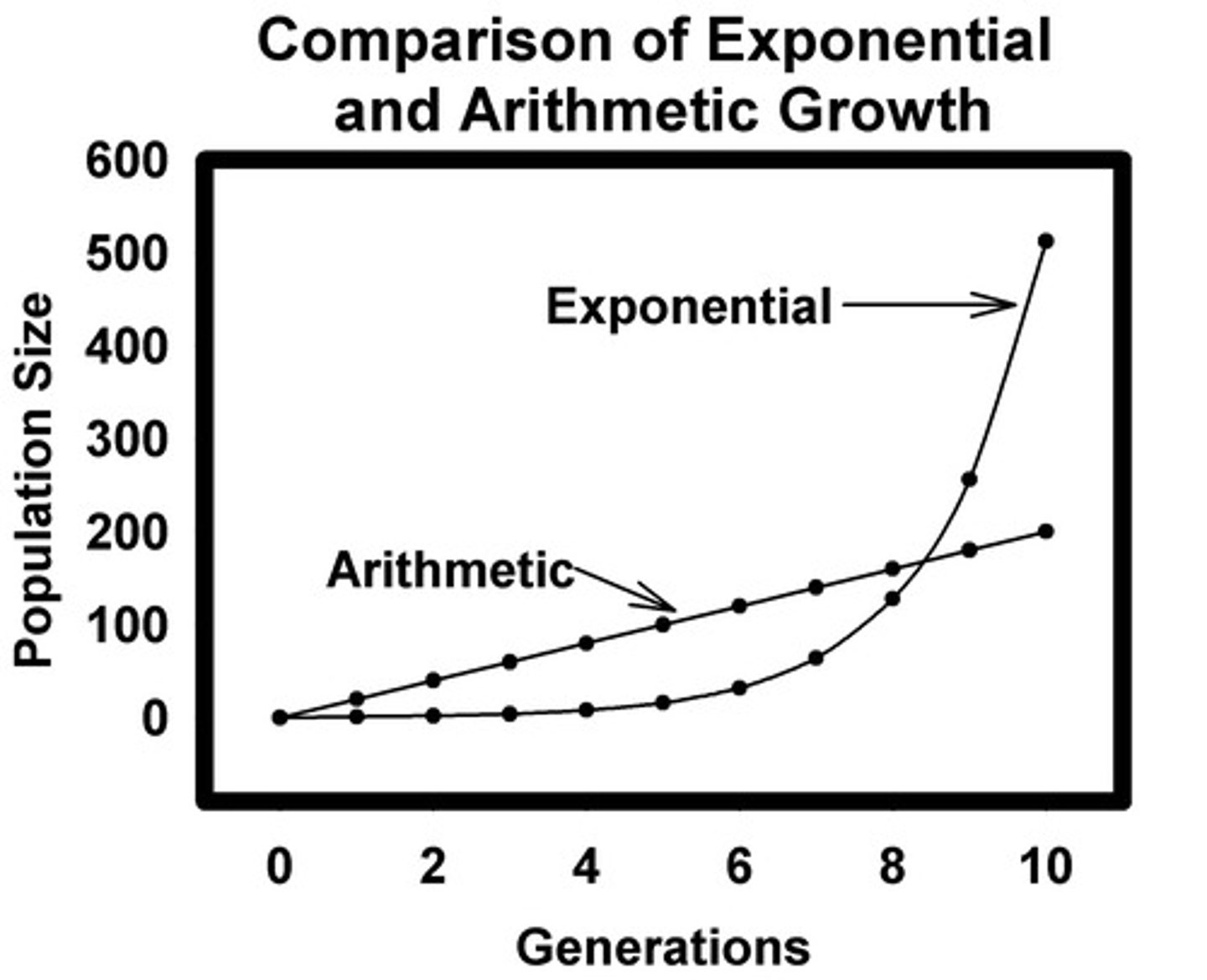
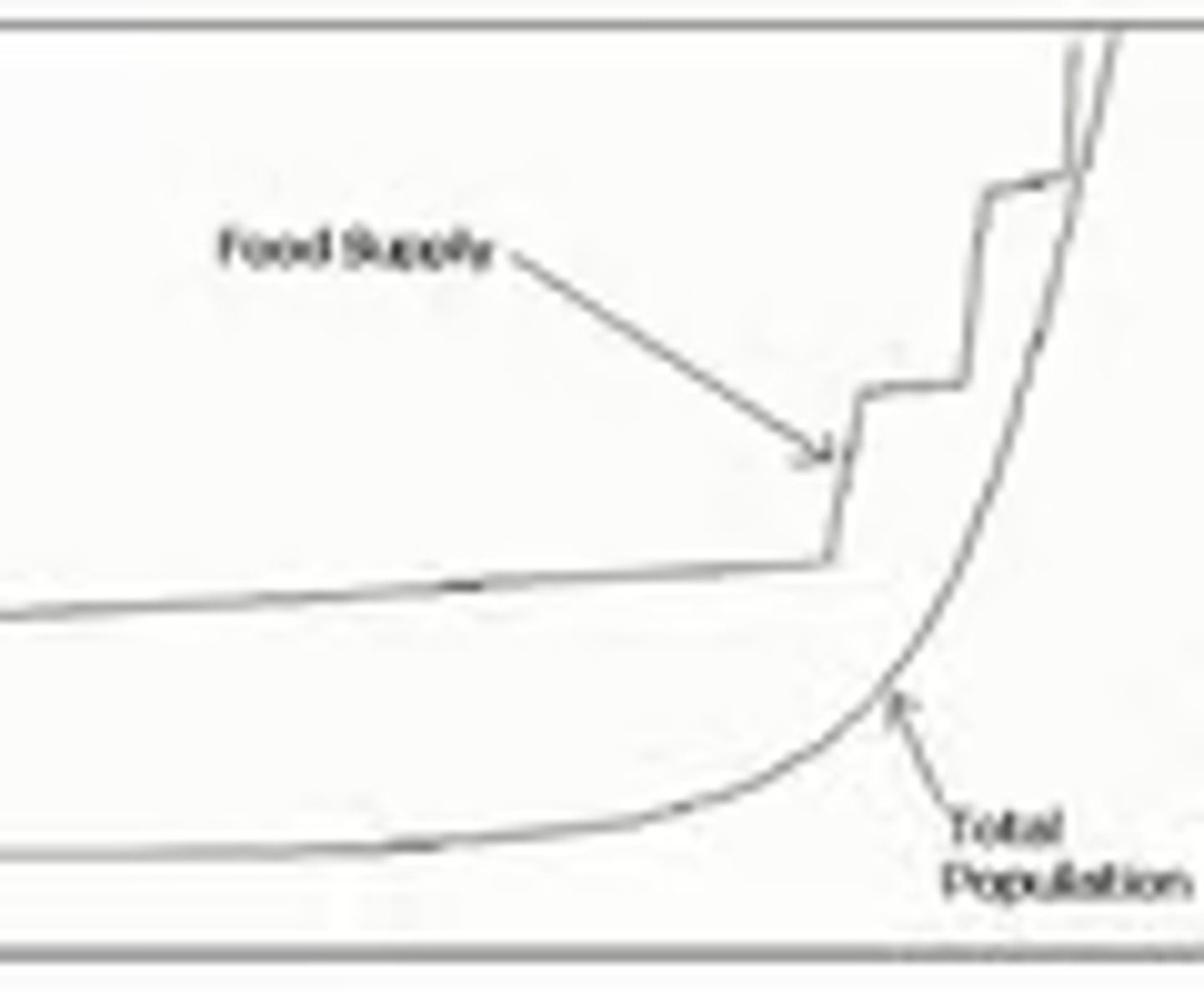
Malthusian Theory
The theory that population grows faster than food supply. Exponential Growth vs. Arithmetic Growth. Where the two lines cross is potential point of crisis.
Neo-Malthusian Theory
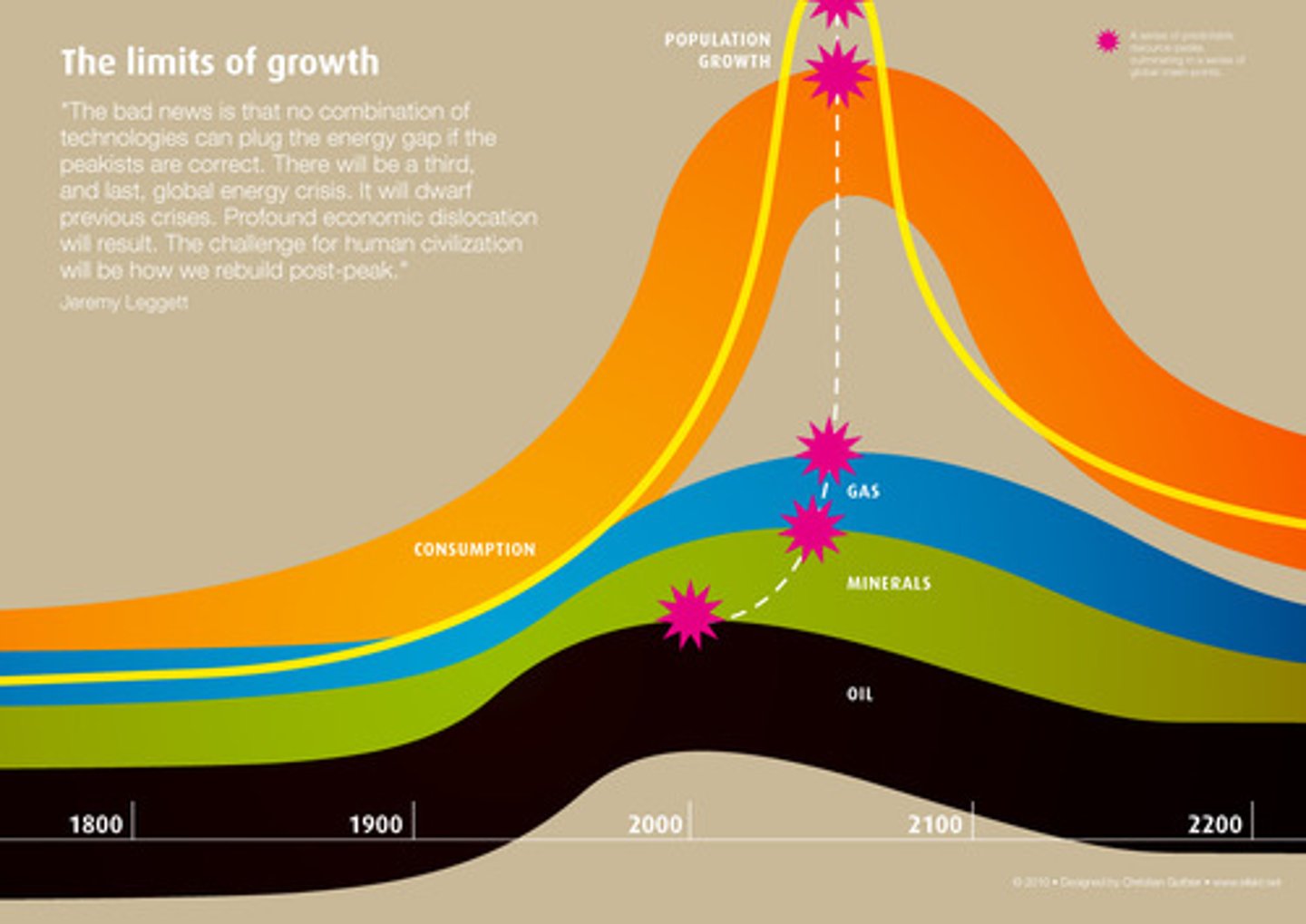
Revisions of Malthusian theory about food production and population growth that include more information, such as taking into account the effects of technology. However, population compromised due to environmental predicaments like drought, political predicaments like war and the exhaustion of non-renewable resources can all lead to point of crisis.
Boserup Theory (Esther Boserup)
When greater food production is needed, humans will find a way either through intensifying land use or developing new technology. Subsistence farmers want the most leisure time they can have, so they farm in ways that will allow them both to feed their families and to maximize free time.
Anti-Natalist Policy
A population policy designed to limit fertility through the use both of incentives and deterrents. China's former one-child policy and Kenya's 5 children to 3 children by 2030 are examples. +2.1 replacement, typically 4-5.

Pro-Natalist Policy
A population policy that aims to encourage more births through the use of incentives, sense of duty and nationalism. Countries in stage 5 employ these policies like that of Japan, France and Norway. China is projecting stage 5 and has implemented the 3-Child Policy. -2.1 replacement.

Aging Population Impact/Problems
Increased elderly care needs in healthcare.
Not enough young to look after them or to be party of the future workforce.
Migration Transition Model
Countries in stages 2 and 3 of the demographic transition model experience rapid population growth and overcrowding. This overcrowding then is a push factor forcing migration to 4s and 5s. limits
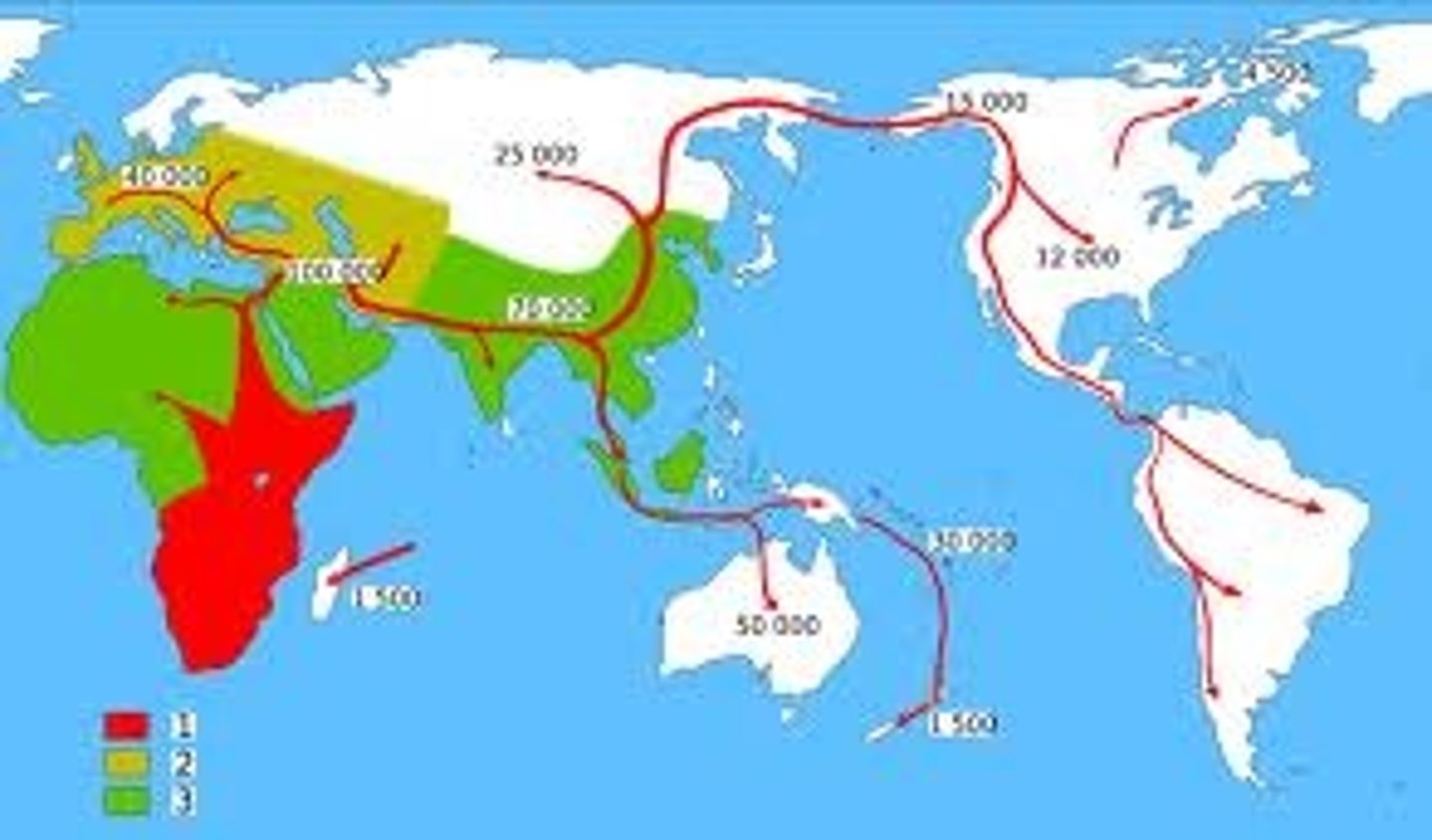
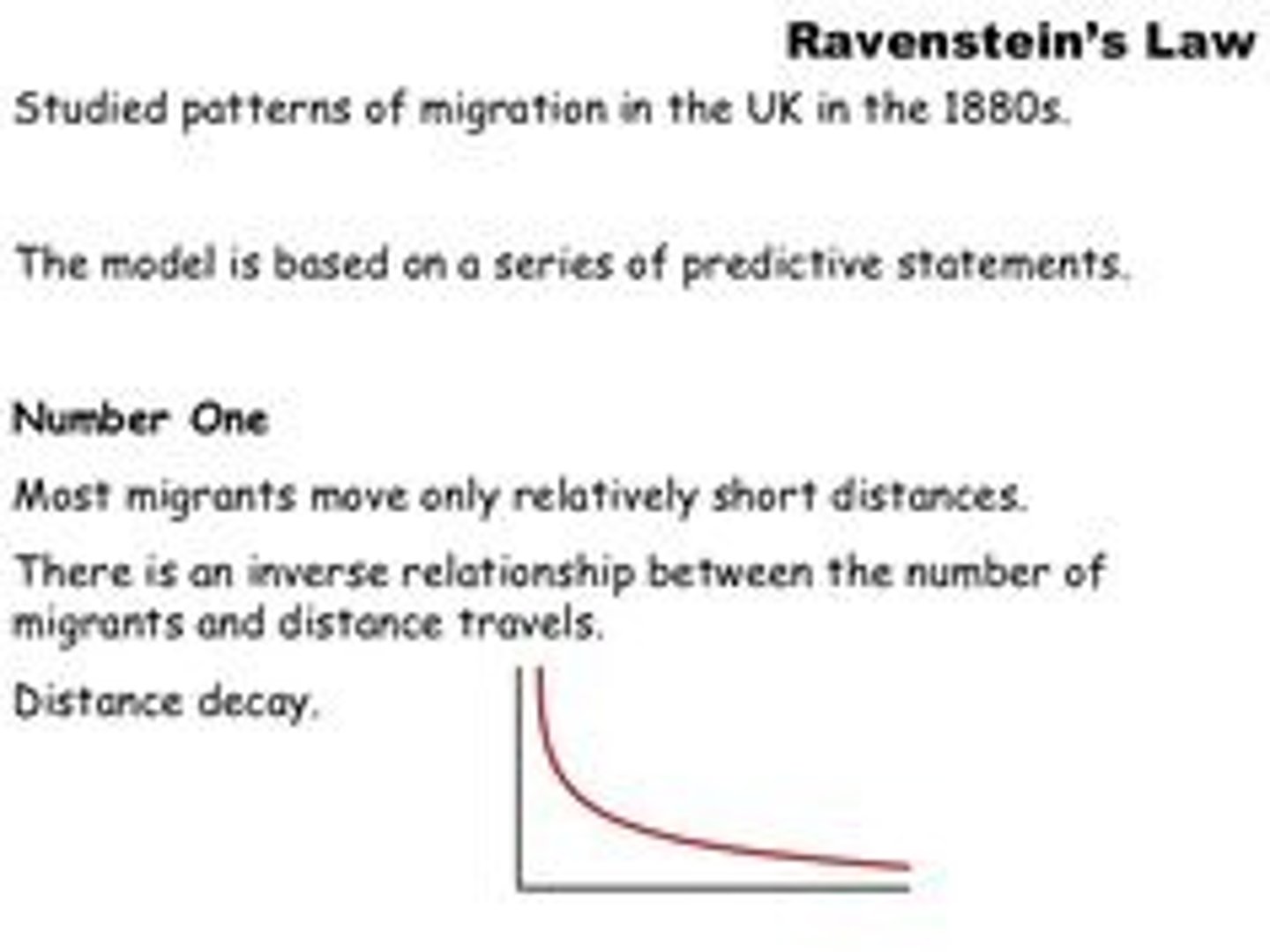
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
1. Most migration is over a short distance. 2. Migration occurs in steps. 3. Long-range migrants usually move to urban areas. 4. Each migration produces a movement in the opposite direction (although not necessarily of the same volume). 5. Rural dwellers are more migratory than urban dwellers. 6. Within their own country females are more migratory than males, but males are more migratory over long distances. 7. Most migrants are adults. 8. Large towns grow more by migration than by natural increase. 9. Migration increases with economic development. 2. Migration is mostly due to economic causes.
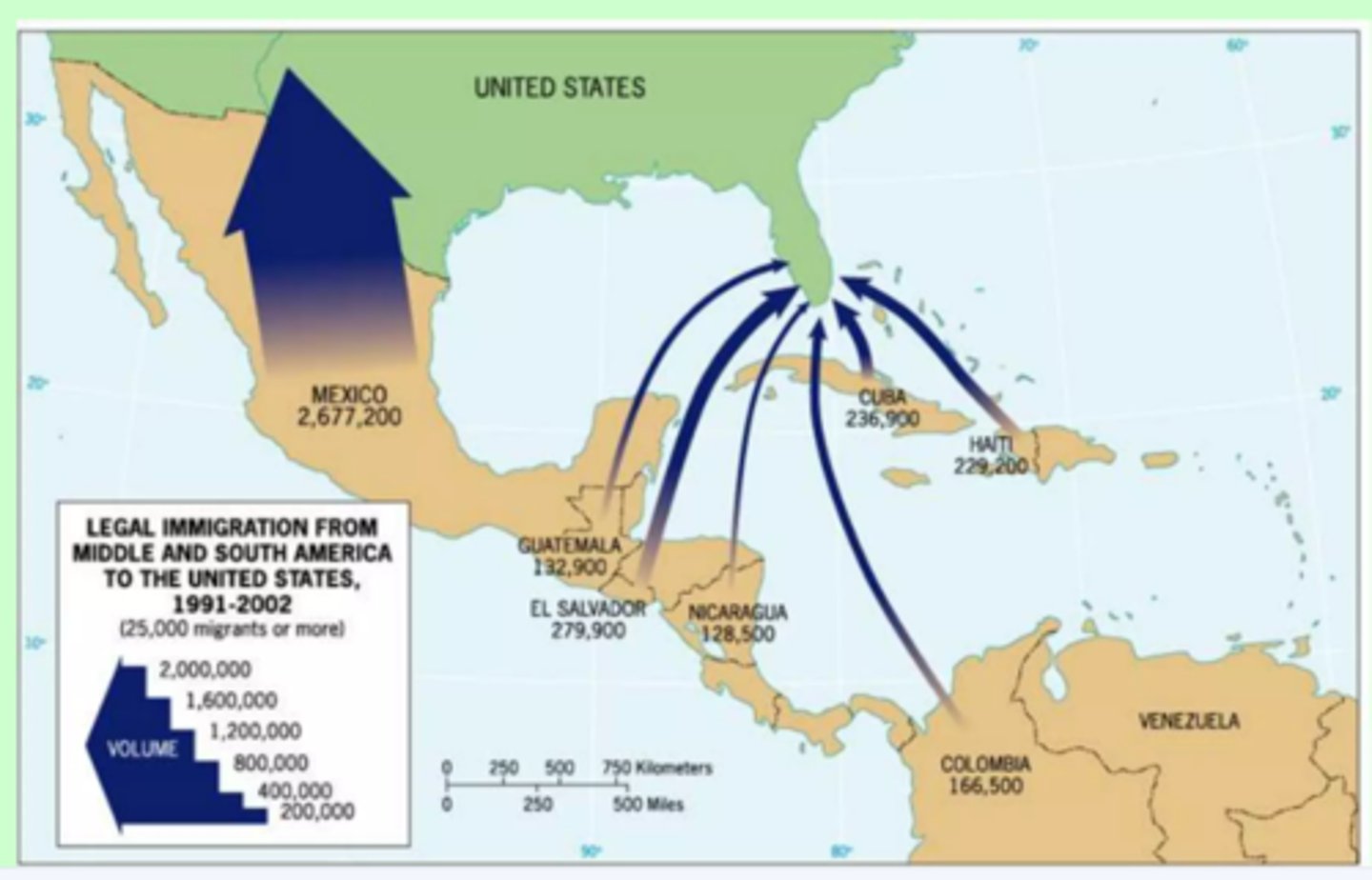
Step Migration
Migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages, for example, from farm to nearby village and later to a town and city. Potentially from country to country too. Libya is a step to destinations in Europe.
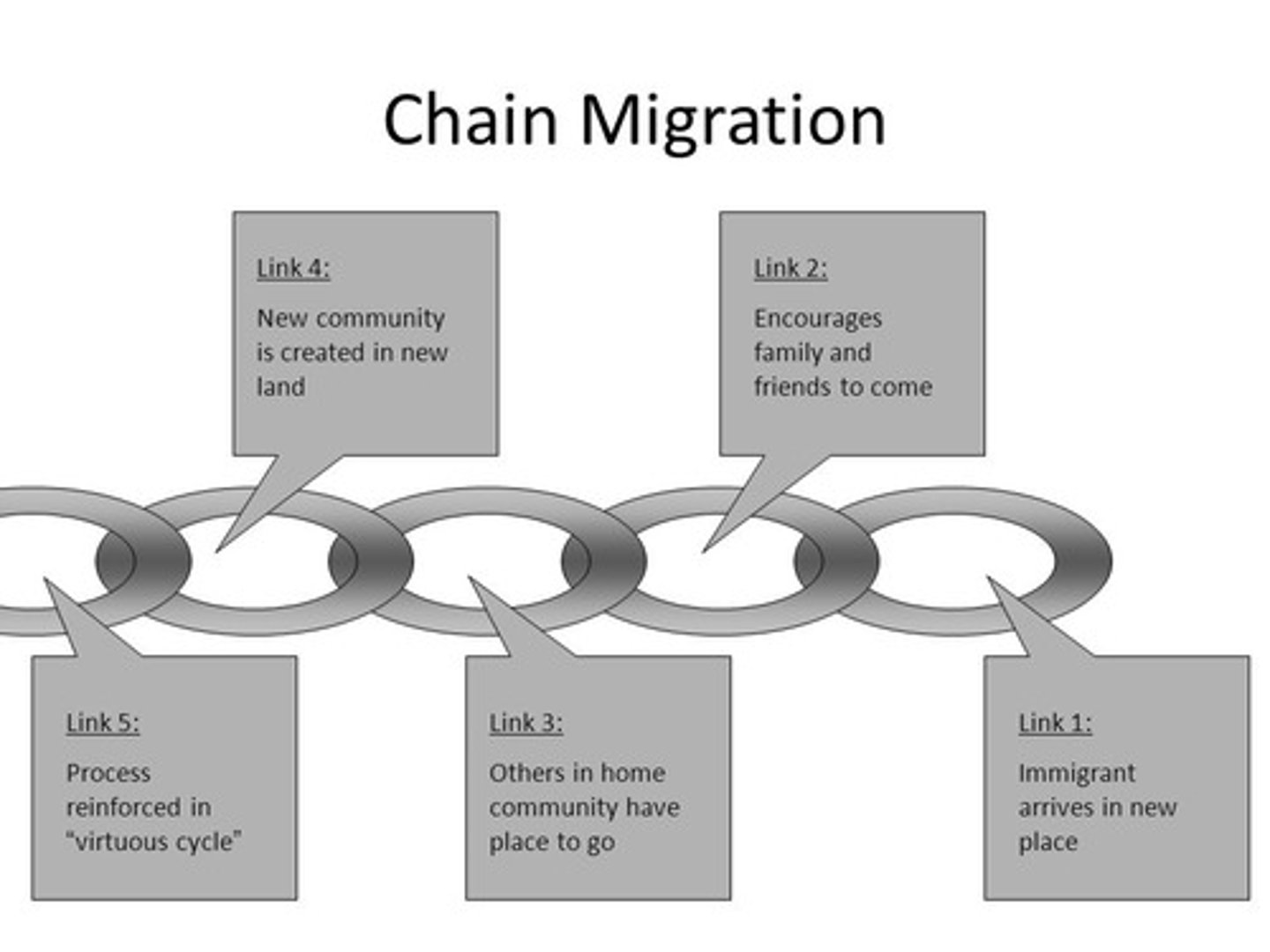
Chain Migration
The migration event in which individuals follow the migratory path of preceding friends or family members to an existing community.
Return Migration
The likelihood that as many as 25% of all migrants will return to their place of origin (counter migration).
Rural to Urban Migration
Permanent movement from suburbs and rural area to the urban city area. It is predicted that 80% of a country's population will be living in urban centers by 2050.

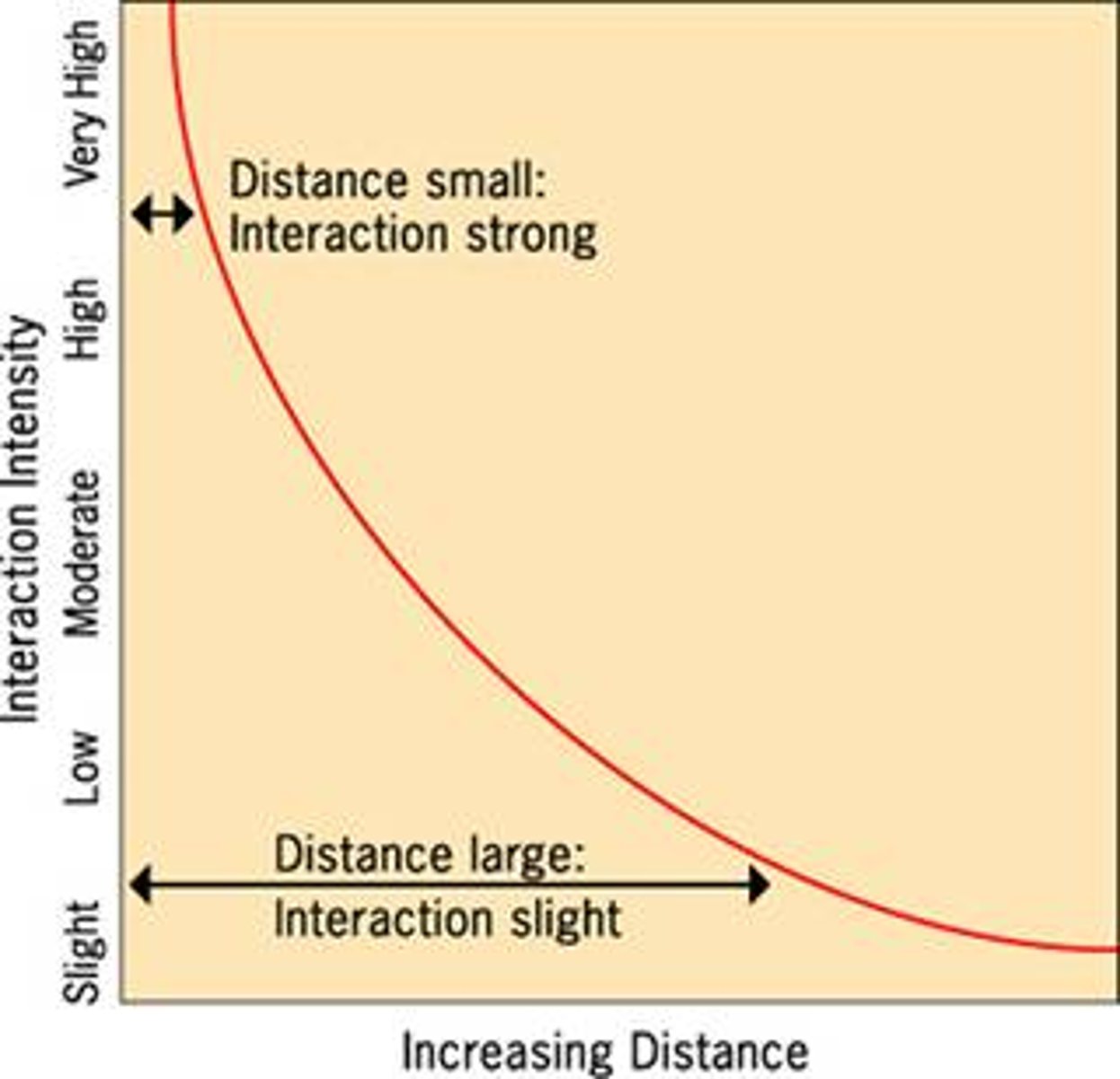
Time-Distance Decay and Migration
Most people only travel short distances. Few people have the means to migrate long distances. Women typically do not migrate far away.
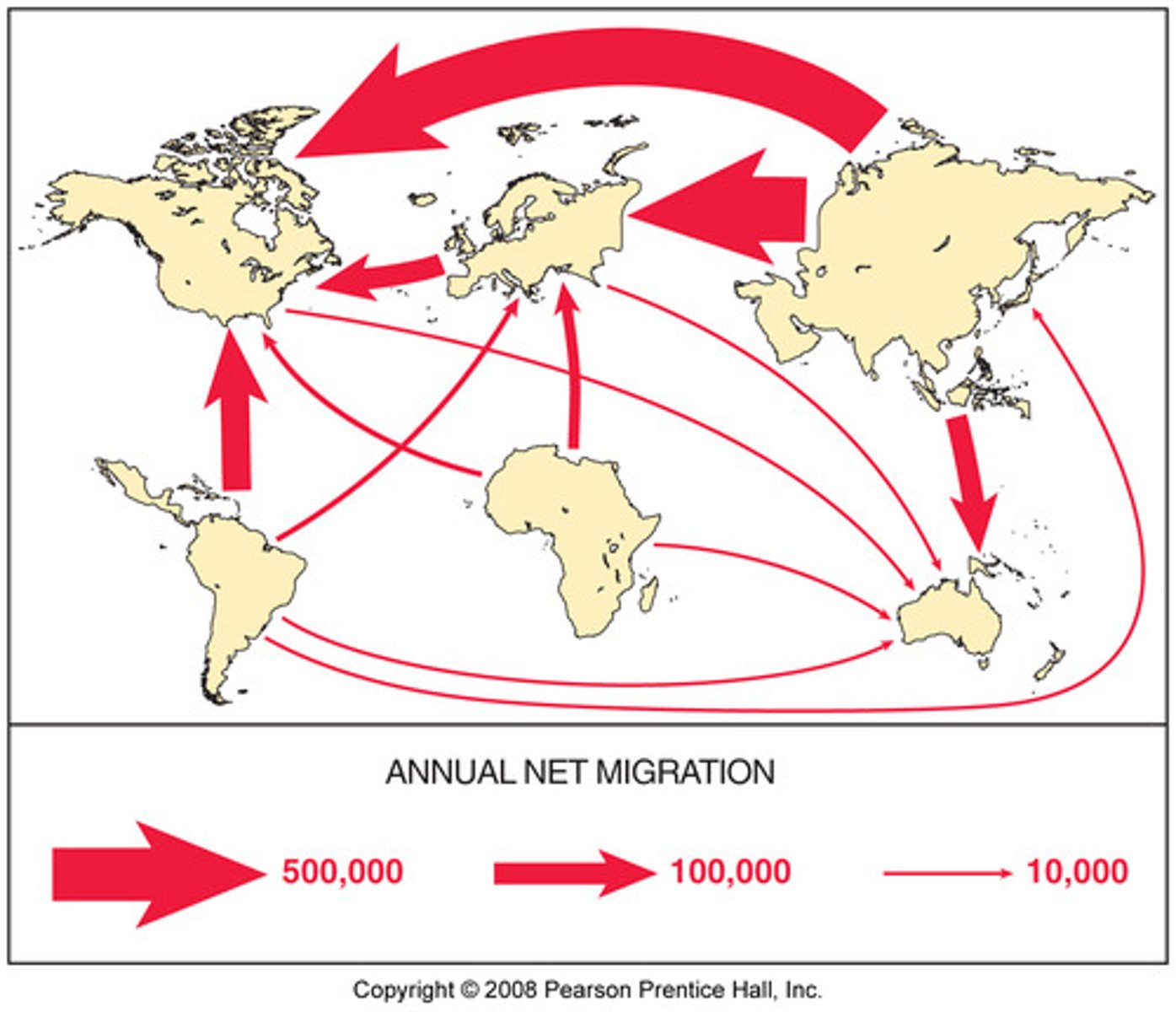
Counter Migration
Each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction. Typically overpopulation can produce a counter migration. Overpopulation for those can be push factor.

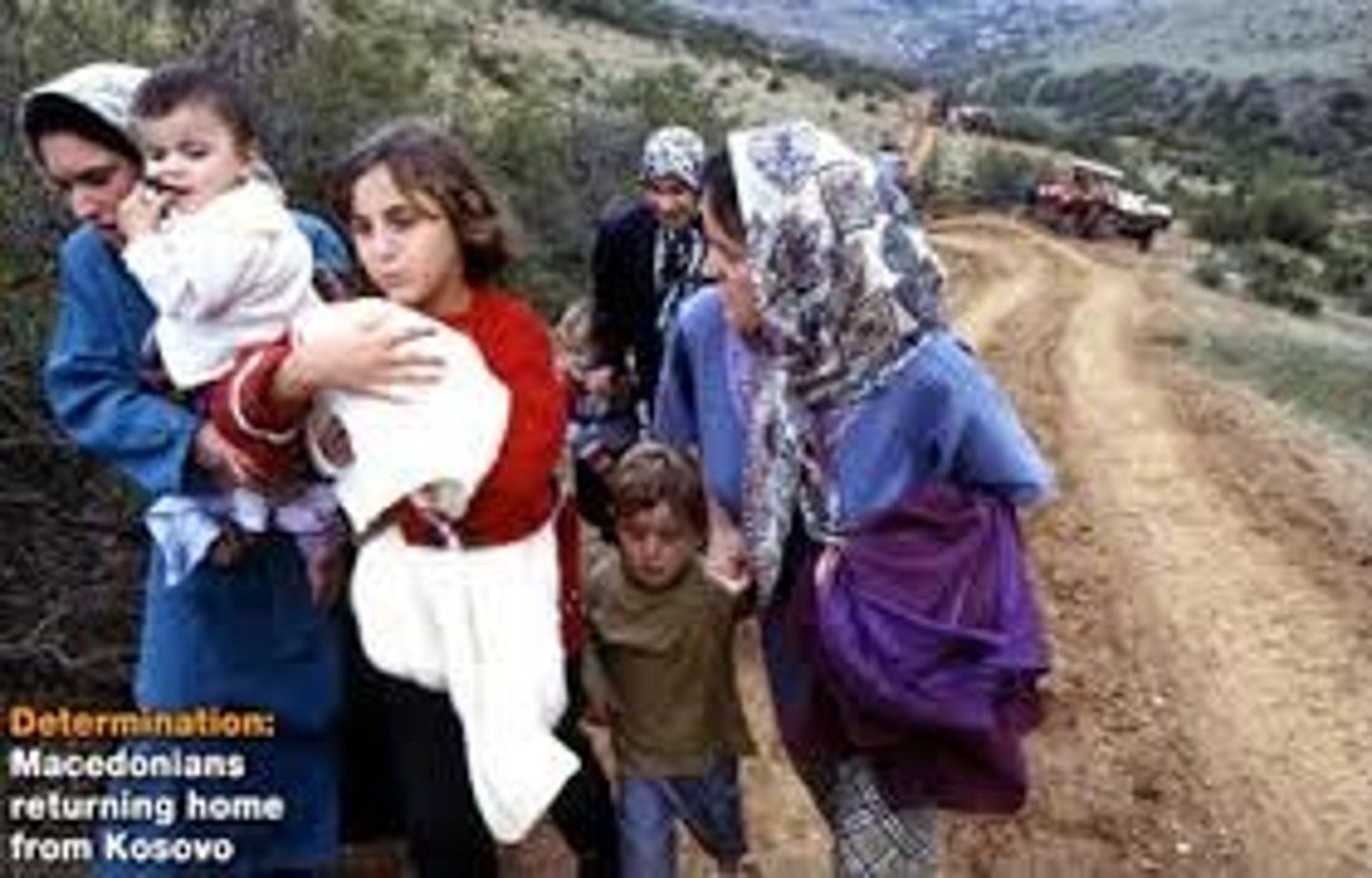
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the movers have no choice but to relocate, political instability, ethnic cleansing, human trafficking are examples.

IDP
Internally displaced person, typically more vulnerable as they are unable to migrate further away from a conflict zone or a zone of which a natural disaster has occurred.
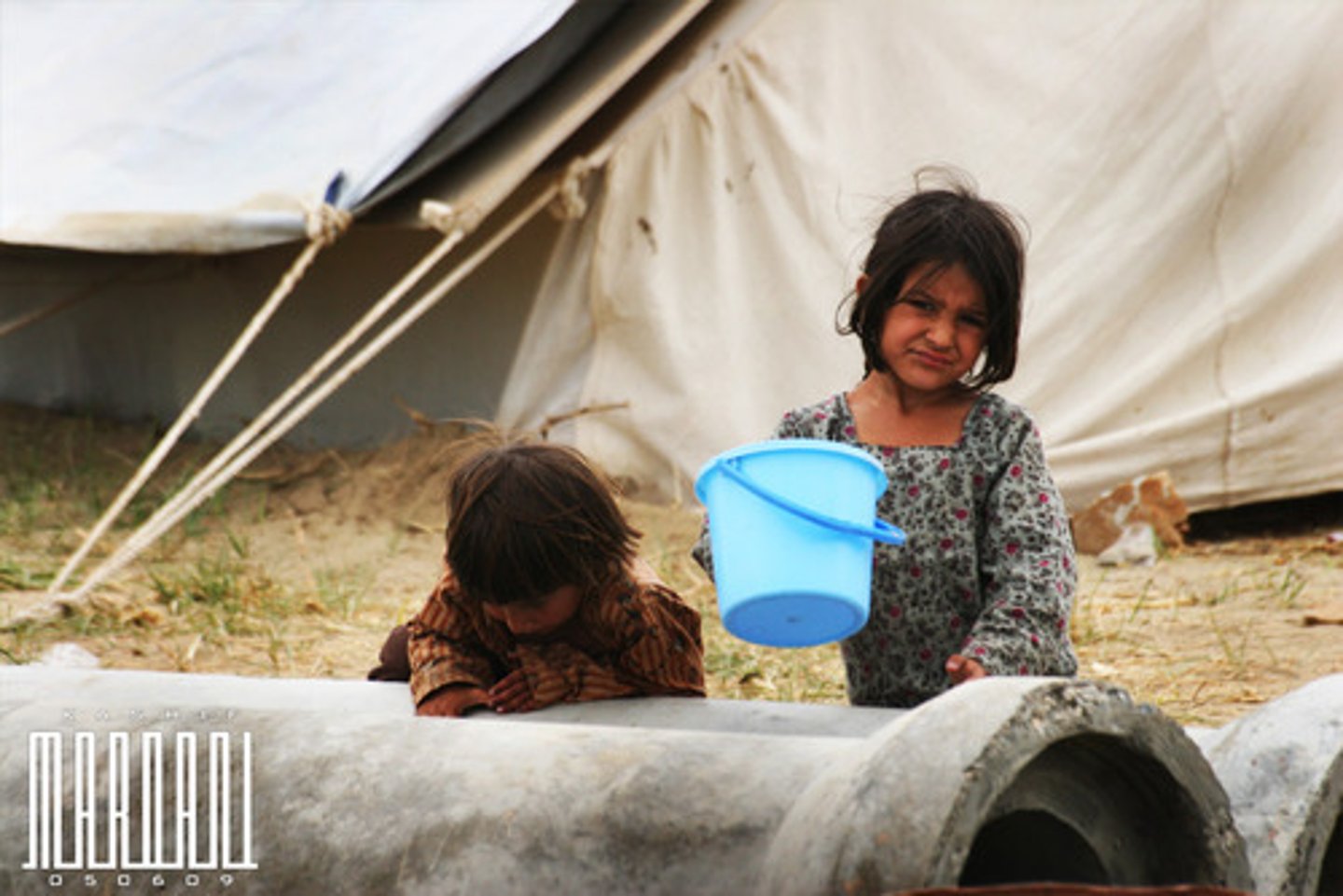

Refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster.

Transnational Migration
A form of population movement in which a person regularly moves between two or more countries and forms a new cultural identity transcending a single geopolitical unit. Culturall syncretism can occur.
Guest Workers
Workers who migrate to the more developed countries of Northern and Western Europe, usually from Southern of Eastern Europe or from North Africa, in search of higher-paying jobs.

Xenophobia
A fear or hatred of foreigners or strangers.

Brain Drain
Large-scale emigration by talented people. The educated leave their country for another.

Brain Gain
A phenomenon where a country or a place gains young, more educated, and skilled people through migration.

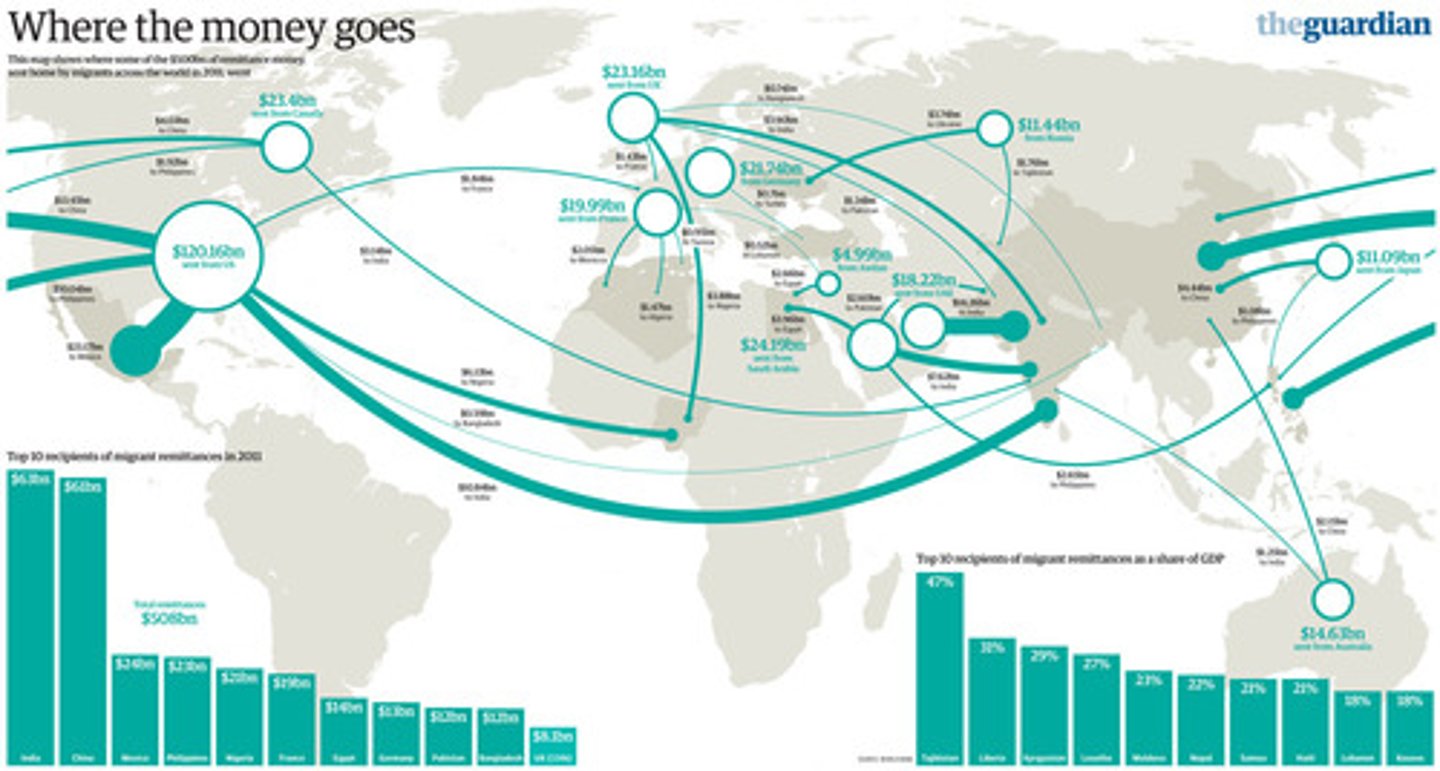
Remittances
Money migrants send back to family and friends in their home countries, often in cash, forming an important part of the economy in many poorer countries.
Ethnic Enclaves
Neighborhoods filled primarily with people of the same ethnic/cultural group. People are more likely to migrate to areas with lie cultures and ethnicities, China Town.

Demographic Momentum
This is the tendency for growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution. This is important because once this happens a country moves to a different stage in the demographic transition model.
Net Reproduction Rate (NRR)
Average # of daughters that would be born to a woman/group of women during her lifetime following age specific fertility rates and mortality rates of a given year.