AP BIO - Membranes
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Covers mostly vocabulary: Diffusion, permeability, etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Passive transport
the spontaneous movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, driven by a concentration gradient, and without the cell expending energy
Active transport
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, against a concentration gradient. This process requires energy,
Equilibrium
The state in which a substance is equally distributed throughout a space
Permeability
The quality of a membrane which allows substances to pass though it
Semipermeable
permeable to certain substances and not others (EX: some things can fit through a door, but not others)
Concentration Gradient
A region of space over which the concentration of a substance changes
Diffusion
The natural movement of particles from a high to low concentration to achieve equilibrium
Extracellular space
Space surrounding a cell
Extracellular Matrix (EMC)
Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space, creating a complex mesh work of proteins and carbohydrates.
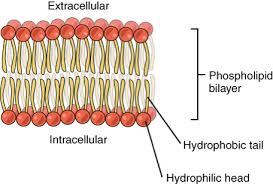
Plasma Membrane
a phospholipid bilayer with the consistency of salad oil, which protects the cell and allows it to interact with it’s surroundings in a controlled manner (excludes, takes in, and excretes)
Osmosis
is the net movement of a solvent, usually water, across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to an area of lower water concentration to equalize the solute concentrations on both sides |
Amphipathic
a type of molecule that has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions (like phospholipids)
Fluid Mosaic Model
A phospholipid bilayer, separating the inside of a cell from the outside, which contains a “mosaic” of proteins and other particles which serve specific purposes within the membrane
Integral proteins
completely submerged inside the membrane, very difficult to remove (channel proteins, carrier proteins, glycoproteins)
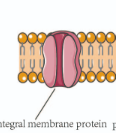
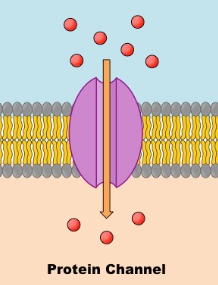
Channel Proteins
Integral proteins which allow items which cannot permeate the membrane to enter the cell. These can also pump out, and require no ATP.
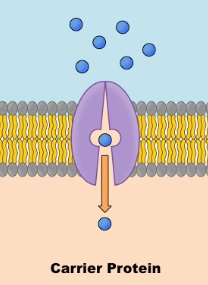
Carrier Proteins
A type of integral proteins which will see something a cell needs and allow it to enter the cell safely. These can go against the concentration gradient and DO require ATP
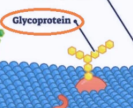
Glycoproteins
Technically an integral protein, which is made up of a chain of sugars (glyco-) attached to a protein which allows a cell to recognize another cell. (can be attached to any other the previous mentioned integral proteins)
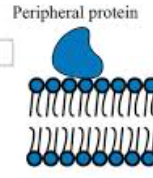
Peripheral Proteins
located on the periphery of the membrane/other proteins, can attach/detach themselves at will, generally there for cell functions such as hormones, etc.
Lipid-bound proteins
A very rare type of protein, located inside the lipid bilayer. Rare because membrane proteins are there to interact with the outside/inside of the cell, these guys can do neither and really serve no purpose.
Water Potential
The potential energy of water per unit area compared to pure water. Allows us to figure out if water is going to flow into the cell or not.
Pure water= 0 bars
ψs+Ψp=Ψ
Solute Potential
the effect of dissolved solutes on the water potential of a solution
Turgor pressure
the internal force within plant cells that pushes the plasma membrane against the rigid cell wall, a result of water uptake via osmosis
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things |
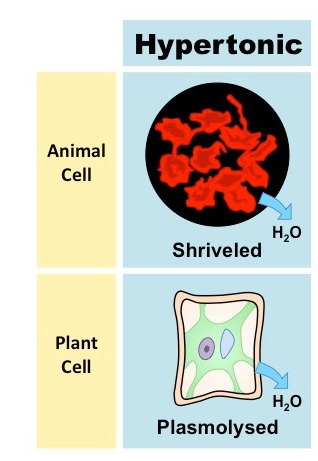
Plasmolysis
When a plant, fungi, or prokaryotic cell are placed in a hypertonic solution and their cytoplasm shrivels and breaks away from their cell wall.
Hypertonic Solution
a solution with more solutes in it then the inside of a cell. Will result in osmosis out of the cell and into the solution, shriveling the cell.
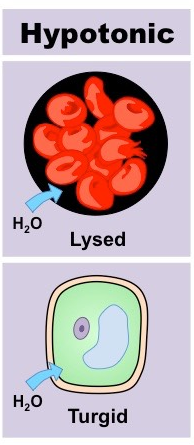
Hypotonic Solution
a solution with less solutes in it then the inside of a cell. Will result in osmosis into the cell from the solution, possibly lysing the cell in the process.
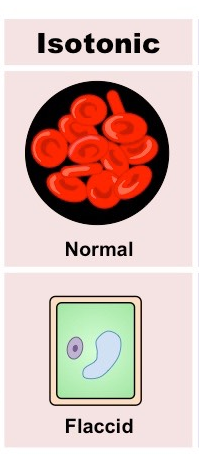
Isotonic
solutions that have the same solute concentration as another solution, typically inside a cell, leading to no net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane
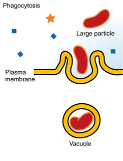
Endocytosis
The process by which cells internalize substances by engulfing them in a membrane-bound vesicle. Bonus: what are the two types of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis
a form of endocytosis where the cell engulfs large particles or microorganisms, forming a phagosome. (phago = eat, cytosis = cell)
Pinocytosis
a form of endocytosis in which the cell engulfs small amounts of liquid and solutes, forming a pinocytotic vesicle. (pino = drink, cytosis = cell)
Cholesterol as a temperature buffer
if the temperature is too high for the membrane, cholesterol decrease fluidity
if the temperature is too low for the membrane, cholesterol increases fluidity
The Plant Cell wall is what?
a structural boundary that protects and maintains the shape of the cell and a permeable barrier The cell wall is made of cellulose (a polysaccharide)
Fungi Cell wall
The fungi cell wall is made of chitin (a polysaccharide)
The prokaryotic cell wall
is made of peptidoglycan, which is a polymer of sugar and amino acids.
Plasmodesmata
small holes between the plant cells that allow the transfer of nutrients, waste, and ions
Osmolarity
the total solute concentration in a solution
lucasite
a white blood cell which rolls/velcros along the blood vessel (think a tennis ball on Velcro)