4.3 Consciousness
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Consciousness
One's level of awareness of both the world and one's existence within the world.
Alertness
State of consciousness in which we are awake and able to think. Higher cortisol levels.
Reticular Formation
A neural structure located in the brainstem that communicates with the prefrontal cortex to keep the cortex awake.
Beta Waves
Have a high frequency and occur when a person is alert or attending to a mental task. They occur when neurons are randomly firing.
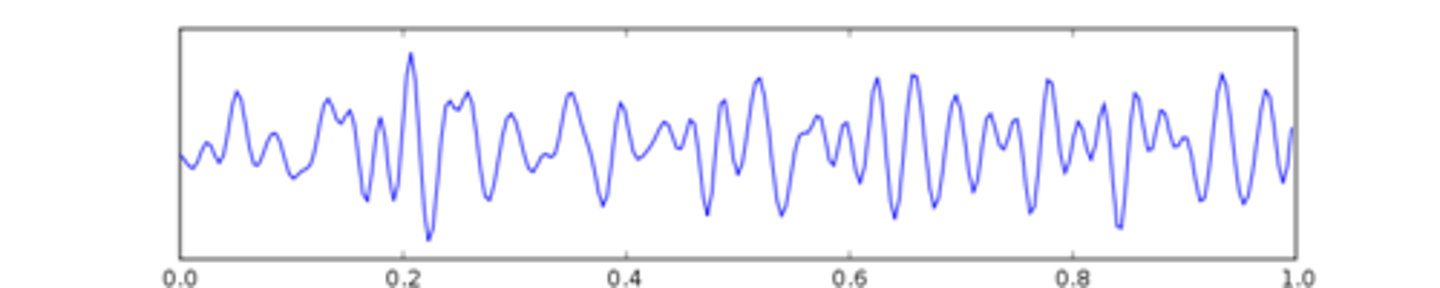
Alpha Waves
Occur when we are awake but relaxing with our eyes closed. They are somewhat slower than beta waves. They are more synchronized than beta waves.
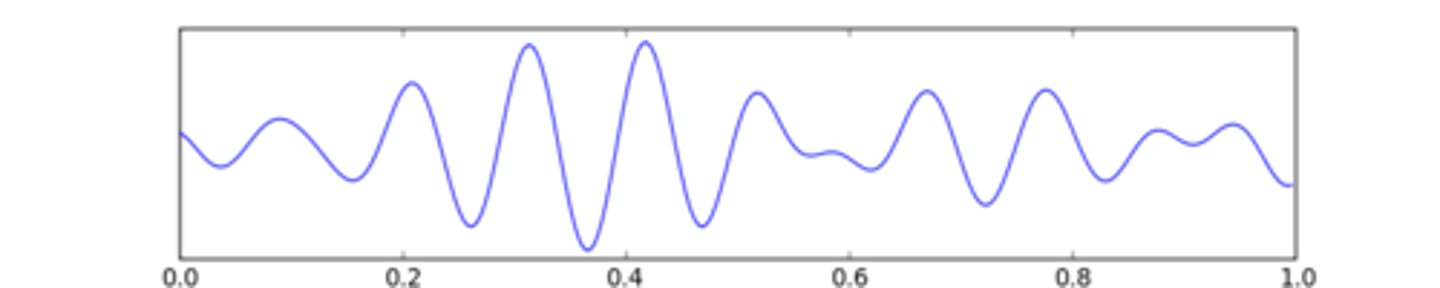
Theta Waves
Seen during stage 1 and stage 2 sleep.
Stage 1
Occurs as soon as you doze off and is characterized by theta waves.
Stage 2
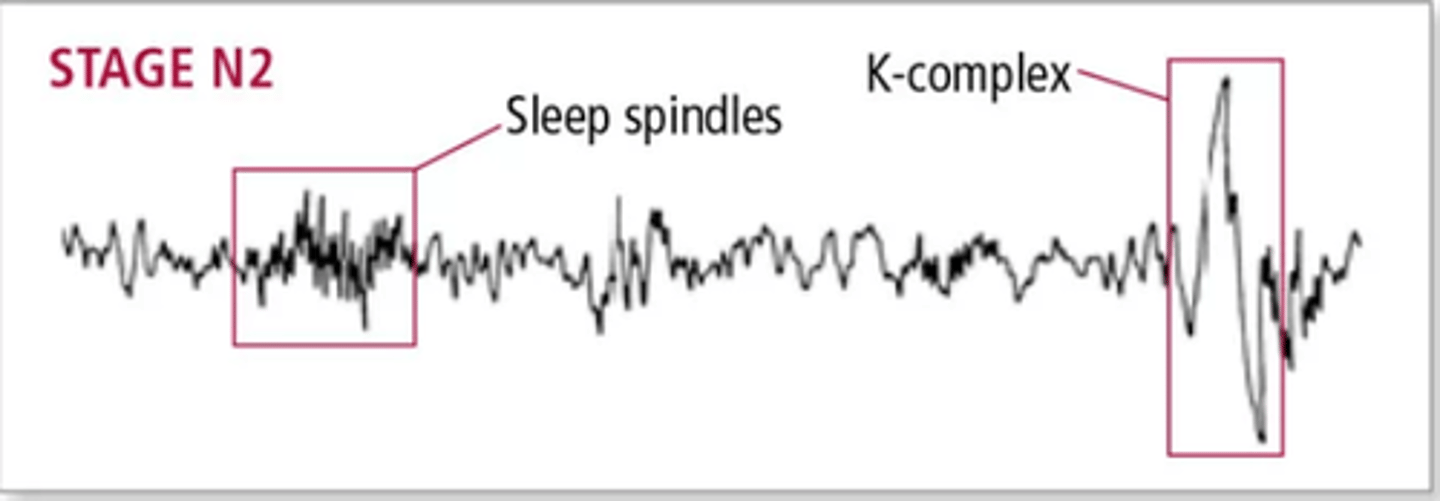
Occurs as you fall into a deeper sleep. EEG shows theta waves with sleep spindles and K-complexes.
Sleep Spindle and K-Complex
Seen in stage 2 sleep when the person is relatively difficult to awaken.
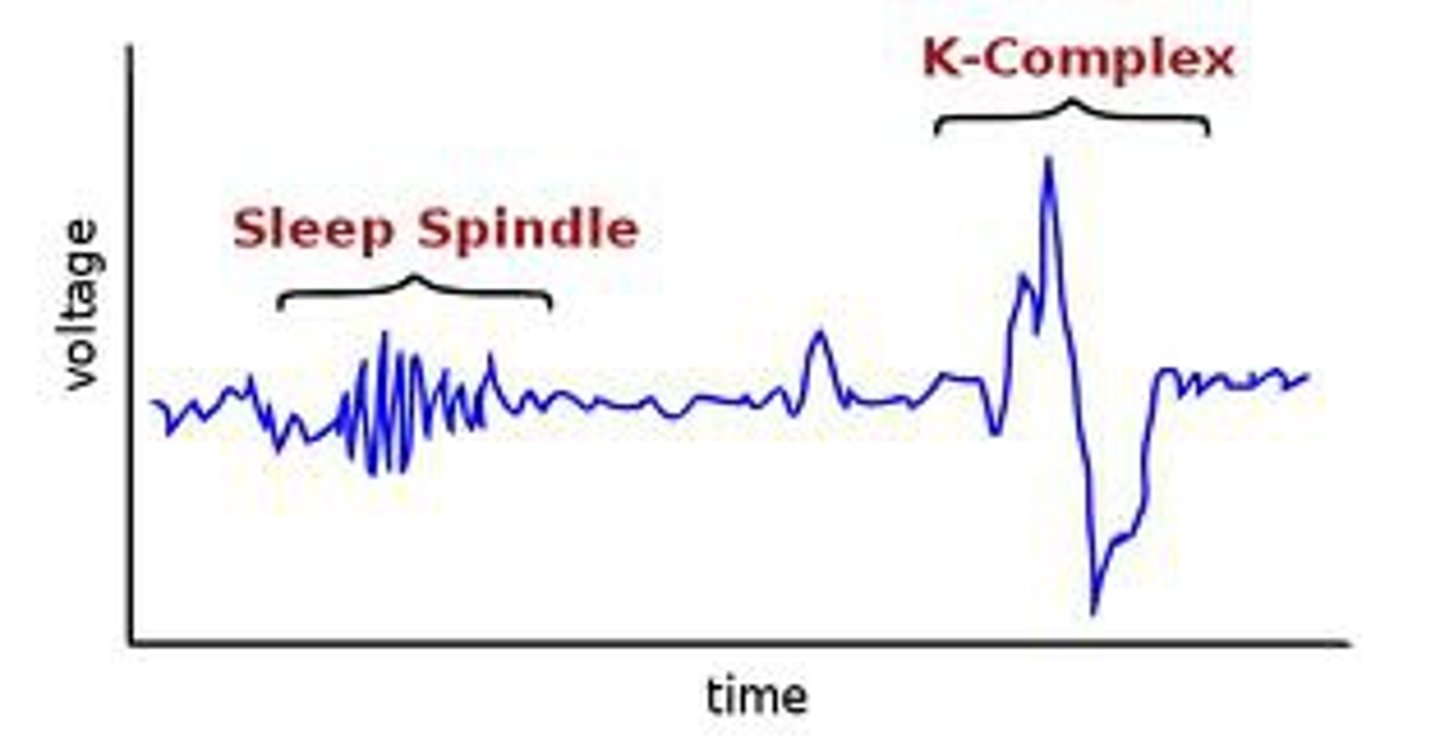
Sleep Spindle
Rapid bursts of high-frequency brain waves during stage 2 (N2) sleep that may help inhibit certain perceptions so we maintain a tranquil state during sleep. Sleep spindles in some parts of the brain are
associated with the ability to sleep through loud noises.
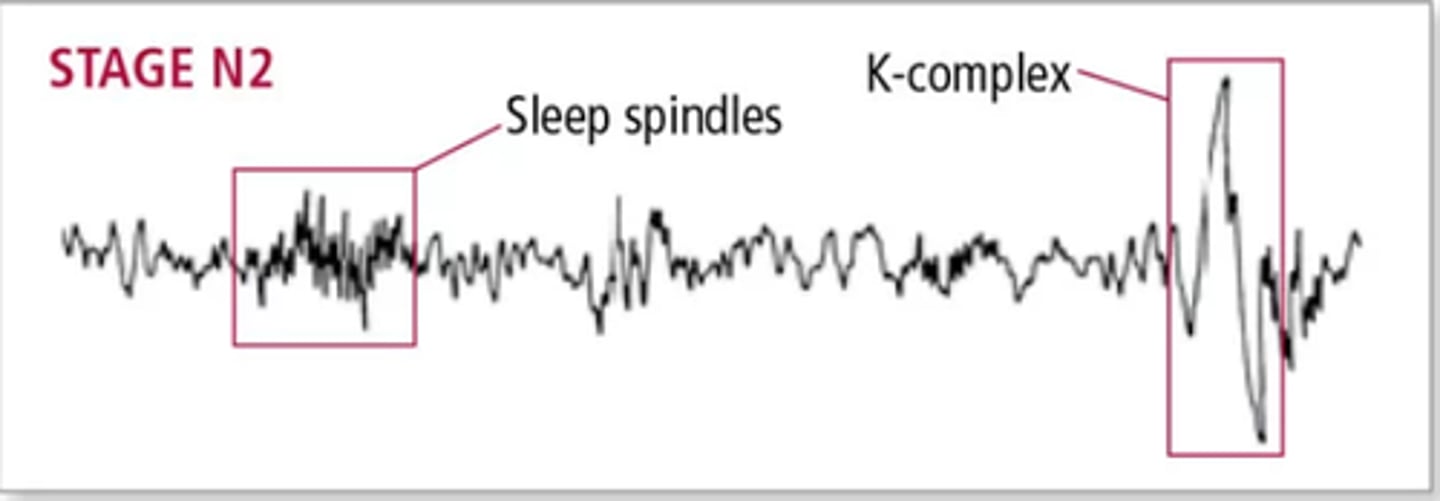
K-Complex
Seen in stage 2 (N2) to suppress cortical arousal and keep you asleep.
Also, help sleep-based memory consolidation. Even though they occur naturally, you can also make them occur by gently touching someone sleeping. "that touch was not threatening, stay asleep brain"
Sleep-Based Memory Consolidation
Some memories are transferred to long term memory during sleep, particularly declarative/explicit memories.
Declarative and Explicit
The types of memories that are stored in long-term memory during sleep.
Stages 3 and 4
Slow-wave sleep. EEG grows progressively slower until only a few sleep waves per second.
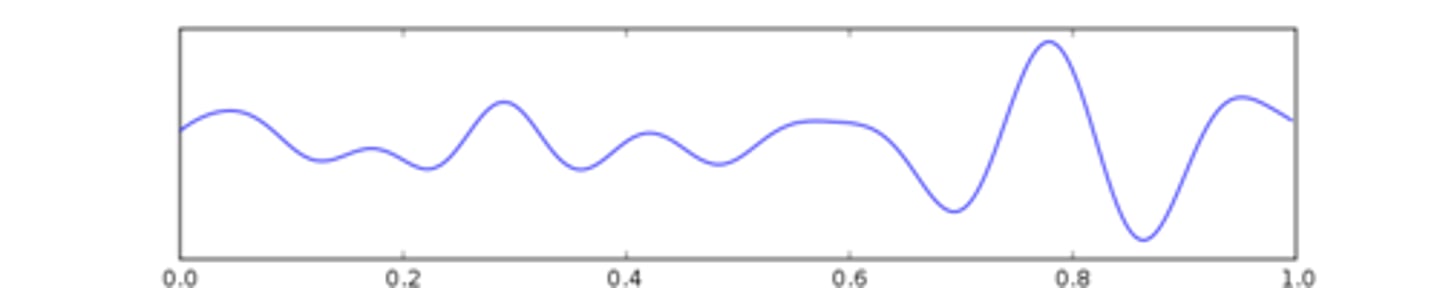
Delta Waves
Seen during slow-wave sleep in stages 3 and 4.
Non-Rapid Eye Movement
Stages 1 through 4.
Rapid Eye Movement
Interspersed between cycles of the NREM sleep stages. In this stage, arousal levels reach that of wakefulness, but the muscles are paralyzed.
Sleep Cycle
Refers to a single complete progression through the sleep stages.
Circadian Rhythm Hormones
Cortisol and melatonin.
Melatonin
Secreted by the pineal gland.
Cortisol
Steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex, related to the sleep-wake cycle. Contributes to wakefulness.
Corticotropin Releasing Factor
Secreted by the hypothalamus to trigger the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone
Secreted by the anterior pituitary in response to increased levels of CRF. Its secretion leads to the release of cortisol.
Dreaming
75% occurs during REM.
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Dreams are caused by widespread, random activation of neural circuitry. This activation can mimic incoming sensory information, and may also contain pieces of stored memory.
Problem-Solving Dream Theory
Dreams are a way to solve problems while you sleep.
Cognitive Process Dream Theory
Dreams contain random thoughts or sequences of thoughts during sleep.
Neurocognitive Models of Dreaming
Seek to unify biological and psychological perspectives on dreaming by correlating the subjective and cognitive experience of dreaming with measurable physiological changes.
Sleep Disorders
Disorders that disrupt the sleep cycle of a person. Frequently they occur during NREM sleep.
Dyssomnias
A group of sleep disorders that make it difficult to fall asleep, stay asleep or avoid sleep. Examples include insomnia, narcolepsy, and sleep apnea.
Parasomnias
A group of sleep disorders that include abnormal movements or behaviors during sleep. Examples include night terrors, and sleepwalking.
Insomnia
Difficulty falling asleep.
Narcolepsy
Uncontrolled falling asleep.
Cataplexy
A loss of muscle control and sudden intrusion of REM sleep during waking hours. Usually caused by an emotional trigger.
Sleep Paralysis
A sensation of being unable to move despite being awake.
Hypnagogic and Hypnopompic Hallucinations
Hallucinations when falling asleep or awakening.
Sleep Apnea
Inability to breathe while sleeping.
Night Terrors
Periods of intense anxiety that occur during slow-wave sleep.
Somnambulism
Sleepwalking. Usually occurs during slow-wave sleep in N3 and N4.
Sleep Deprivation
Results in irritability, mood disturbances, decreased performance and slowed reaction time.
REM Rebound
When people are recovering from sleep deprivation, they show a greater duration of REM sleep than normal.
Hypnosis
When a person appears to be conscious and in control, but they are in a highly suggestible state.
Hypnotic Induction
Beginning of hypnosis in which the hypnotist seeks to relax the subject and increase the subject's level of concentration.
Meditation
Involves the quieting of the mind and relaxing.