Human Bio Midterm 2024
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Cell
The smallest structural and functional unit of an organism.
Ex: Blood cells
Tissue
A group of cells that have similar structure and that function together as a unit.
Ex: Connective Tissue
Organ
A collection of tissues that structurally form a functional unit specialized to perform a particular function.
Ex: Heart
Organ System
A group of organs that work together in the body to perform a complex function.
Ex: Respiratory
Organism
Something having many related parts that function together as a whole.
Ex: Humans
Simple Squamous
Structure: Single layer of flat cells
Location: Gas exchange surfaces in lungs, blood permeability vessels, and portions of kidney tubes.
Function: Decreases friction and controls vessel permeability
Simple Columnar
Structure: Single layer of cells that are taller than wide
Location: Lining of stomach, intestine, gall bladder, fallopian tubes connecting ducts in kidney
Function: Protection, absorption, and secretion
Simple Cuboidal
Structure: Single layer of cube shaped cells.
Location: Glands and ducts
Function: Secretion
Pseudo-stratified Columnar
Structure: Appear stratified, nuclei of cells at different levels, and all cells contact the basement membrane.
Location: Lining of nasal passages, lining of bronchi, and lining of trachea
Function: Protection and Secretion
Stratified Squamous
Structure: Several layers of cells, cells at surface level are flat, but cells near basement are cuboidal.
Location: Lining of mouth, lining of throat, lining of anus, lining of rectum, lining of anus, and lining of vagina
Function: Provides physical protection against abrasion, pathogens, and chemical attacks
Stratified Columnar
Structure: Several layers of cells, cells are surface are column shaped, and cells that are closest to basement membrane are cuboidal
Location: Male uretha, vas deferens, and parts of pharyx
Function: Secretion and protection
Stratified Cuboidal
Structure: Several layers of cubiodial cells and the cells are the surface are cube-shaped.
Location: Lines the ducts of the mammary glands, salivary glands, and pancreas
Function: Secretion
Transitional
Structure: Seems to have many layers, layered appearance can result in overcrowding, and outermost cells appear rounded or cuboid.
Location: Urinary bladder
Function: Stretches and permits expansion and recoil after stretching.
Connective tissue general functions
Support and protection
Transportation of materials
Store energy
Defense against pathogens
Connective tissue general characteristics
Deep tissues
Never exposed to environment
3 basic components
Specialized cells
Fibers
Ground substance
Connective Tissue Proper
Many types of cells and fibers. Ground substance is syrupy.
Examples:
Loose (areolar)
Adipose (fat)
Dense
Fluid Connective Tissues
Distinctive population of cells. Ground substance is watery.
Examples:
Blood
Lymph
Supporting Connective Tissue
Less diverse population of cells
Ground substance:
Soft and rubbery
or
Solid and crystalline
Examples:
Cartilage
Bone
Big 4 - Epithelial Tissue
This tissue acts as a covering controlling the movement of materials across the surface.
Big 4 - Connective Tissue
This tissue integrates the various parts of the body and provides support and protection to organs.
Big 4 - Muscle Tissue
This tissue allows the body to move.
Big 4 - Nervous Tissue
This tissue is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities.
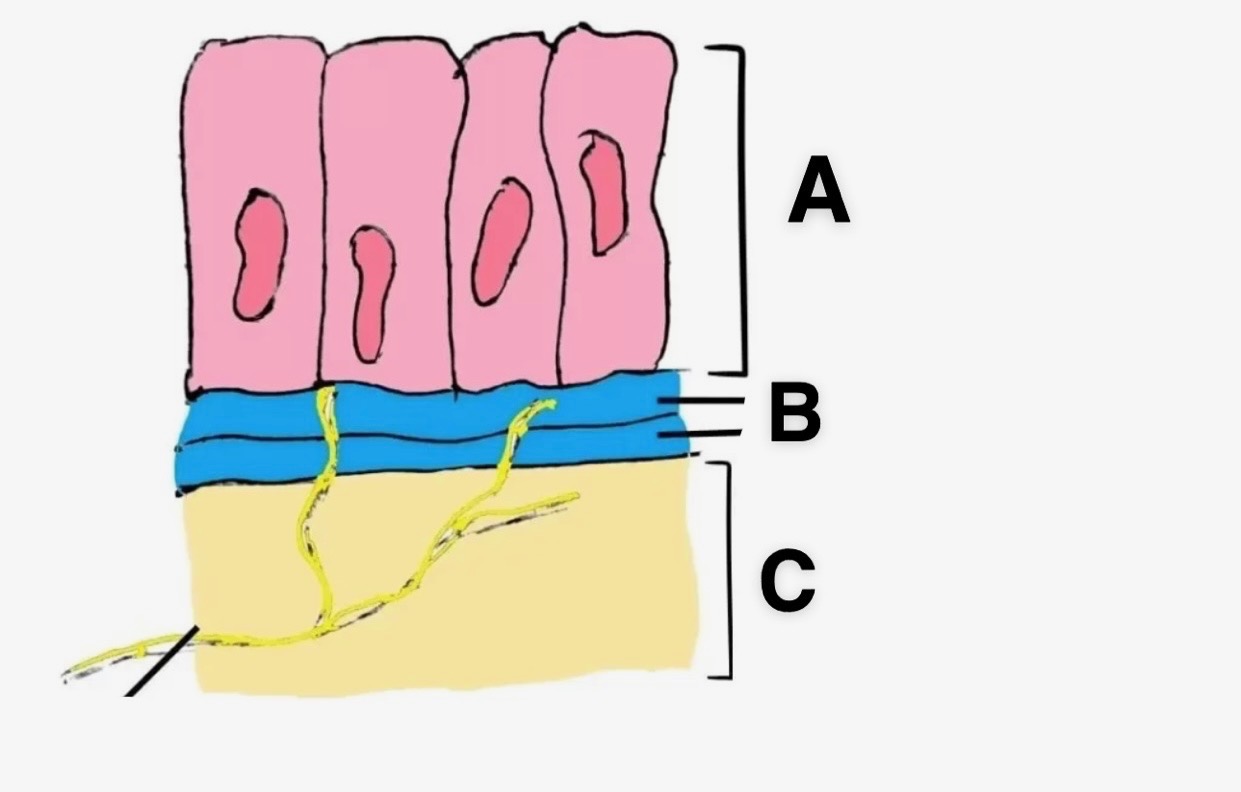
In this picture, what is A?
Epithelial Cells
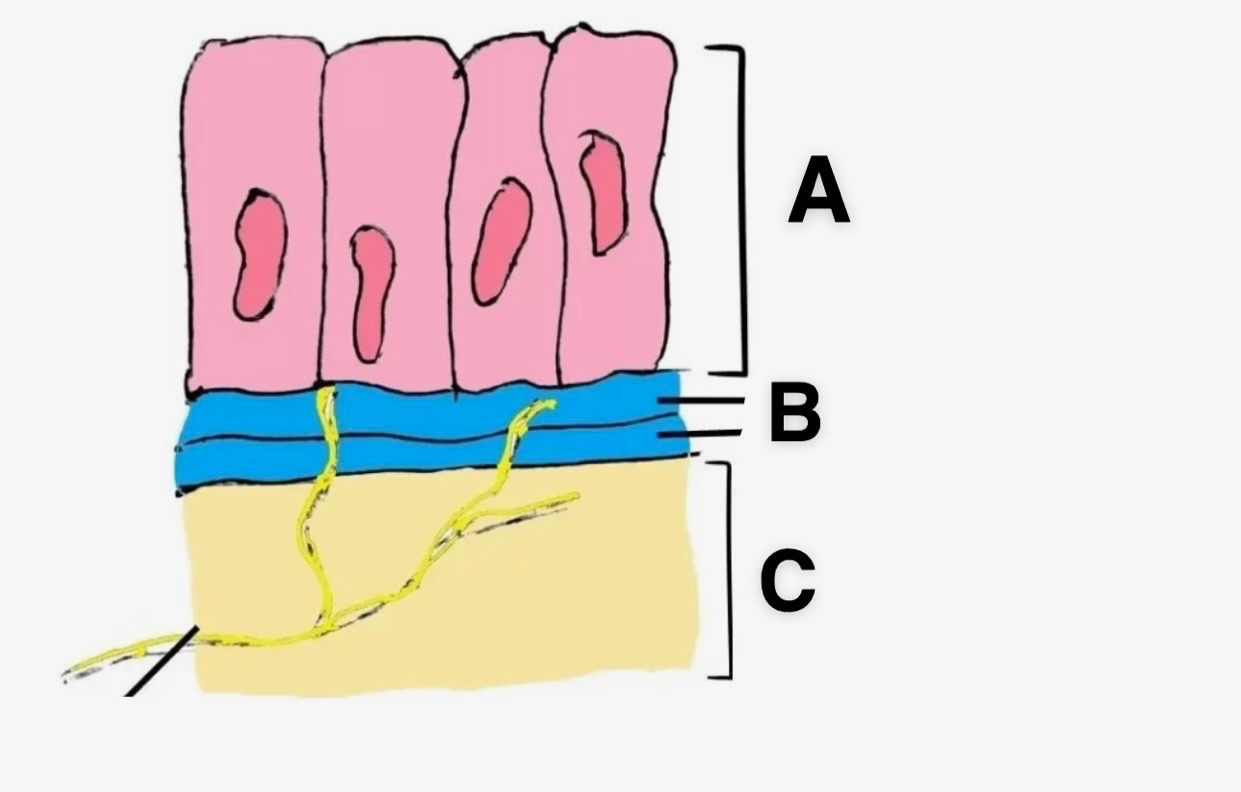
In this picture, what is B?
Basement Membrane
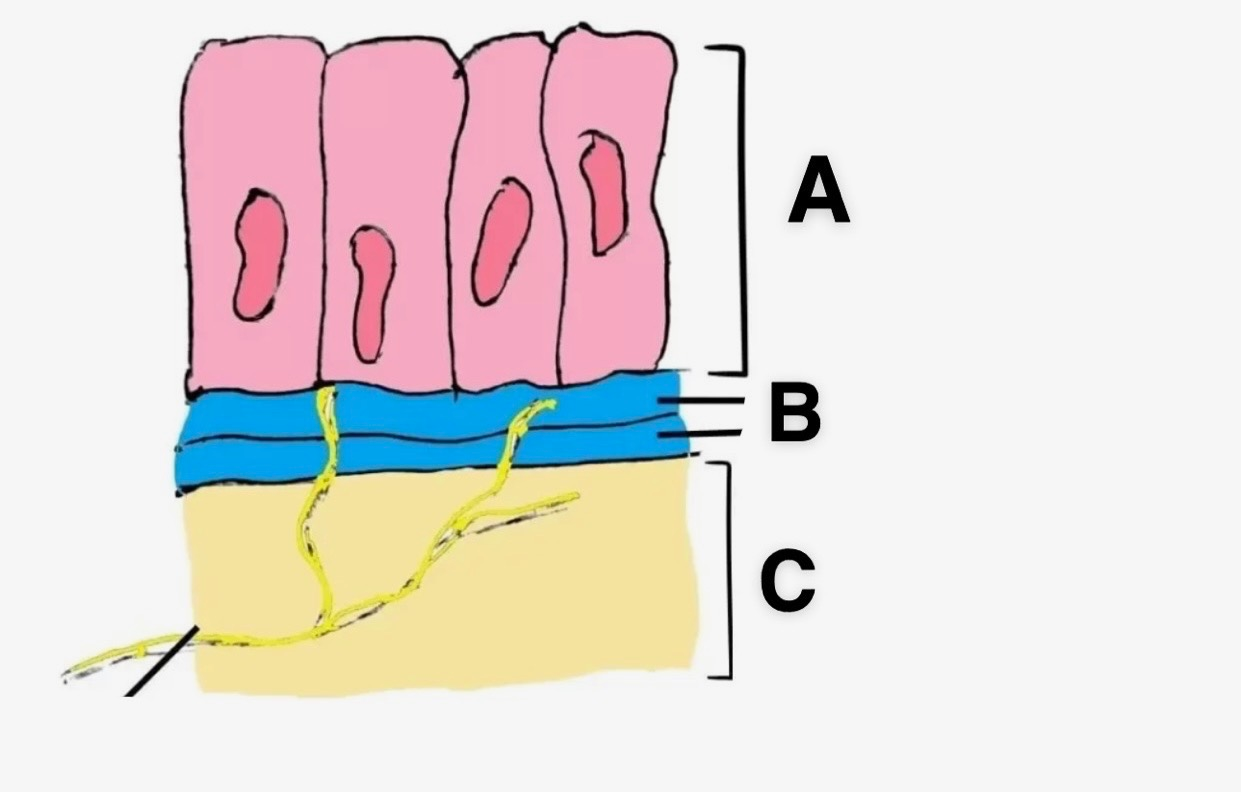
In this picture, what is C?
Connective Tissue
Epithelial Tissue Functions
Protection, permeability control, secretion protection (enzymes, mucus, and hormones), and absorption
Structure, Protection, Shape, and Movement (Functions of a Skeleton)
Muscle pulls on a bone and creates stress on a bone
Storage of Minerals (Functions of a Skeleton)
Calcium and Phosphorus
If the body can’t get enough calcium from nutrition, osteoclasts will break down the bone to obtain the minerals.
Bones produce __________ in bone marrow
Red and white blood cells
Anatomical Position
Facing frontwards
Palms up
Feet forward
Core Terms
Anterior, Posterior, Superior, and Interior
Limb Terms
Medial, Lateral, Distal, and Proximal
Anterior
Front portion
Ex: Clavicle to scapula
Posterior
Back of body
Ex: Scapula to clavicle
Superior
Above
Ex: Sacrum to coccyx
Inferior
Below
Ex: Coccyx to sacrum
Medial
Closer to the middle of the body (midline)
Ex: Torso to arms
Lateral
Further away from midline
Ex: Arms to torso
Distal
Furthest from trunk or core
Proximal
Closer to trunk or point of attachment
Osteology
The study of bones
Osteoporosis
Process is which bones become weak
Cleft Palate
The roof of the mouth doesn’t connect (a hole) forms a gap or cleft
Spina Bifida
Spinal cord end forms a ball on the outside of the skin.
Osteoma
Bone tumor attached to bone
Arthritis
Joint inflammation
Osteoarthritis
Most common form of arthritis, wear and tear after repetitive motions
Post-traumatic Arthritis
Occurs due to an injury of a joint, common after sports injuries
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune disease where the synovial joint gets thickened, leaving thick scales and deposits
Acromegaly
Bones are longer than usual, long fingers, long face, very tall, “Abe Lincoln disease”
Scoliosis
When back curves to one side or the other
Kyphosis
“Hunch back,” an increased curve from front to back
Lordosis
Increases curve from back to front, stomach sticks out
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cells
Osteoclasts
Resorb or break down bone
Axial Skeleton
Skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage

Appendiclar Skeleton
Shoulder girdle, arms, hands, pelvic girdle, legs, and feet
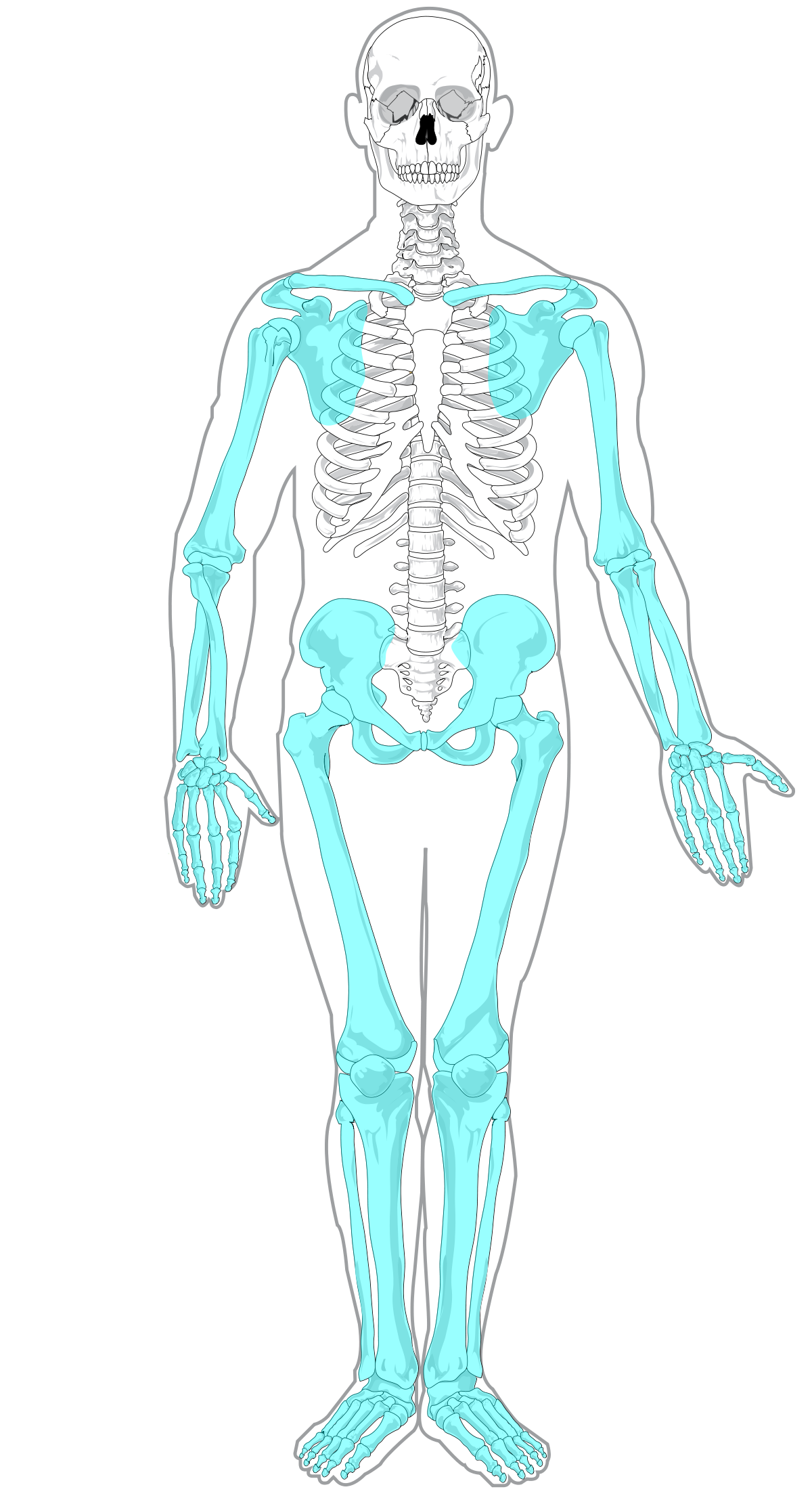
Flat bones
Thin, flat, and broad
Ex: Cranial bones
Short bones
Width and length of bone are about the same
Ex: Carpals and tarsals
Irregular bones
Irregular shape that doesn’t fit into another category
Ex: Vertebrae, all facial bones
Sesamoid bone
A bone that is found inside a tendon. This is where a tendon passes over the joint.
Long bones
Longer than wide
Ex: Humerus, phalanges
Shaft/Diaphysis (long bones)
Where red and white blood cells are made
Epiphysis (long bones)
Found at the two ends of the bone
Long Bone Components - Spongy
Contains holes, porous
Epiphysis
Long Bone Components - Compact
No space between the cells, solid
Shaft/Diaphysis
Bone Marrow Location
Middle of long bones
Joints
The meeting place between bones
Synarthrosis Joints
Movement: Non-moveable
Structural Category: Fibrous Joints
Ex: Sutures of skull
Amphiarthrosis Joints
Movement: Slightly moveable
Structural Category: Cartilaginous
Ex: Tibia and pubic bone
Dlathrosis Joints
Movement: Freely moveable
Structural Category: Synovial
Ex: Shoulders, hips, and knees
Flexion
Decreasing the angle at a joint.
Extension
Increasing the angle at a joint.
Hyperextension
Overly increasing the angle at a joint
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the body
Adduction
Movement of limb back to the body
Cirumduction
Movement of a limb in a circular motion
Hinge Joints
Movement in one plane only
Ex: Elbows and Phalanges
Pivot Joints
Allows for rotation
Ex: Radius rotates with ulna
Saddle Joints
Allows for sliding/gliding movements. Articulating surfaces have both convex and concave surfaces.
Ex: Allows you to twiddle your thumbs
Ball and Socket Joints
Head of one bone articulates with cavity of another. Movements in all planes and rotation. Allows bone to rotate on axis.