Exam 3- Pomarico LSU BIOL 1002
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
pollination
what bees (and others) are involved in.
microspore
first haploid male structure in angiosperms
filament
this holds the anther
sepals
used to protect the flower prior the blooming
coevolution
action that describes the growth from seed
ovule
part of ovary down where the megaspore mother cell is located
tube cell
structure that is part of pollen and contains the generative cell
incomplete flower
flower that is missing a part
microspore mother cell
diploid cell that gives rise to microspores
petal
the part of the flower that attracts the pollinators
zygote
what forms when the gametes unite
style
long neck-like part of the carpel
pollen
male gametophyte in seed plants
ovary
bottom of the carpel where the egg is located
stigma
top of the carpel designed to catch pollen
anther
this structure holds the pollen in the flower
endosperm
this is the stored food in the seed
integuments
these are parts of the ovule that becomes the seed coat
seedcoat
outermost part of the seed
fruit
in angiosperms this is used to disperse the seeds
generative cell
structure that directly gives rise to the sperm
carpel
female part of the flower
seed
has to do with the fruit and the seed coat
egg
female gamete
sporophyte
part of the life cycle that is dominant in angiosperms (and others)
megaspore
first haploid female structure in angiosperms
stamen
male part of the flower
double fertilization
the reason that there are 2 sperm
flower
one of the structures that is unique to angiosperms
spores
in the general alternation of generations cycle the things that the sporophyte produces
Which of the following is the best explanation of alternation of generations?
the plant life cycle alternates between two distinct, multicellular reproductive stages- one diploid and one haploid- that gives rise to each other.
the multicellular diploid form of the flowering plants is called the
sporophyte
What is the purpose of the ovary and anther in the flower?
to produce gametophytes and, ultimately, gametes
How does the sperm travel from one plant to another to get to the egg in the gymnosperms and angiosperms?
within a pollen grain
Which of the following is a conspicuous feature that distinguishes the angiosperms from gymnosperms?
angiosperms produce flowers
Where does the pollinating insect find pollen
weakly attached to the anther
The megaspore mother cell produces 4 haploid megaspores through meiosis. What happens to them?
3 degenerate, and one survives
What happens to the pollen grain once it pollinates a flower?
a pollen tube grows down through the style of the carpel to the ovary
Which of the following statements explains double fertilization?
Both sperm in the pollen grain fuse with cells of the female gametophyte
seed and fruit development
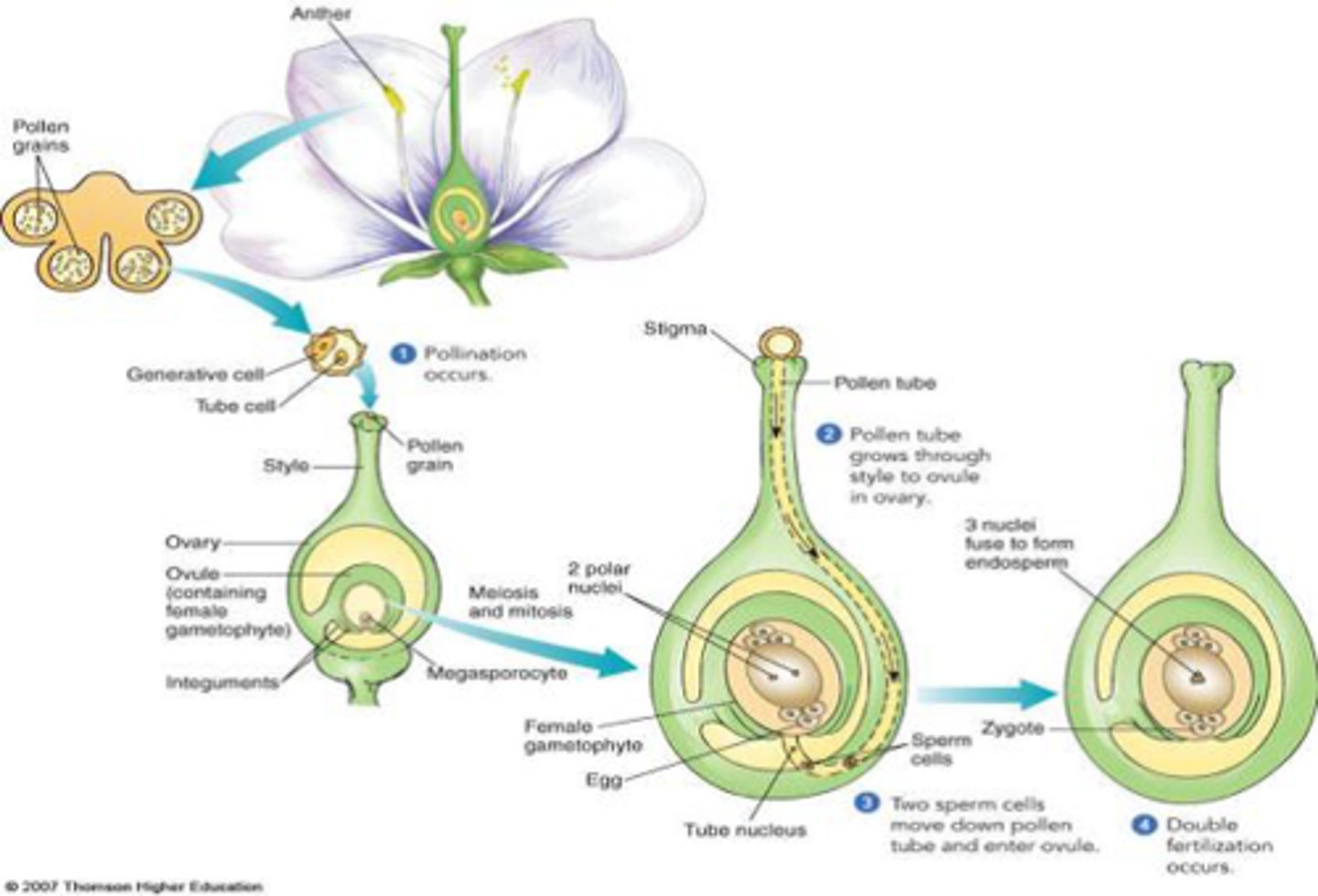
what is endosperm?
via cotyledons, a source of food for the embryo
a diploid cell that develops into the embryo
little dot at end of flower pocket
fruits evolved primarily as structures specialized to
disperse seeds
As a seed matures, the embryo begins to differentiate into the shoot and root. Where does the developing embryo get it's food?
endosperm
ovary
the structure inside a flower that houses female reproductive cells (eggs), and where fertilization and early development take place.
pollen grains
are tiny male gametophytes that carry sperm-producing cells. They are dispersed by wind or airborne insects.
fruit
after fertilization, the ovary will develop into a __, which surrounds and protects a flowering plant's seeds.
germination
occurs when the embryonic plant within a seed grows, breaks out of the seed, and forms a seedling.
In the life cycle of most plants, a diploid _ generation produces haploid spores through meiotic cell division. The spores develop into a haploid _ generation which produces sperm and eggs by mitosis. These fuse and produce a diploid zygote, and the life cycle begins again.
sporophyte; gametophyte
After a monocot seed germinates, a coleoptile develops and surrounds the shoot tip. Dicots, in contrast, develop either a(n) _ on the stem below the cotyledons, or a(n) _ on the stem above the cotyledons.
hypocotyl; epicotyl
endosperm
is a triploid food storage tissue found within the seeds of flowering plants.
Which characteristic would benefit a flower that relies on light-flying moths for pollination?
The flower's petals are white so they are more visible at night.
Asexual reproduction is rare in plants. True or false?
False.
Ferns and mosses live mainly in _ environments
moist
An oak tree is a _
sporophyte
The female gametophyte of angiosperms is made up of 8 diploid cells and one haploid egg cell. True or False?
FALSE
The male reproductive structure, the stamen, consists of
a filament that bears an anther
Meiosis produces a _, which eventually gives rise to an egg in an unfertilized seed.
megaspore
Which of the following undergoes meiosis during the development of pollen grains?
Microspore mother cell
Processes that occur during angiosperm reproduction
- the tube cell produces the pollen tube
-the microspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce 4 haploid microspores
-the megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to produce 4 haploid megaspores.
-the generative cell forms two sperm cells via mitosis
In flowering plants, the unfertilized ovule contains the
female gametophyte
Endosperm has allowed the angiosperms to become the most numerous and diverse plant group. What is the role of the endosperm?
It provides nutrition for the developing embryo, therefore increasing survival rates.
a fruit is a mature
ovary
In north-central Florida, the cars, homes, streets, and ponds are covered with an impressive coating of bright yellow dust every spring. Upon closer, microscopic examination, the yellow "dust" turns out to be pollen grains. This area of Florida has pine trees, showy daytime-flowering plants, and often-unnoticed nighttime-flowering plants, with sweet-scented flowers, releasing pollen at the same time of year.
Based on this information, which group of plants do you think is responsible for the yellow pollen? Why?
The pines are responsible, because conifers are pollinated by wind and must produce enormous amounts of pollen in order to ensure that some of it reaches the female cones.
Bilaterally symmetrical animals have three tissue layers that arise during embryonic development: an inner layer of _ , and outer layer of _, and a layer of _ that lies in between.
endoderm; ectoderm; mesoderm
pseudocoelom
is a body cavity that is NOT completely surrounded by mesoderm-derived tissue
cephalization
is the concentration of sensory organs and nervous tissue in a defined head region of the body.
during their development, insects undergo _, a radical change from juvenile body form to an adult body form.
metamorphosis
in organisms with an open circulatory system, blood empties into the _ where is bathes the internal organs directly
hemocoel
coelom
is a fluid-filled cavity completely lined with a thin layer of tissue that develops from the mesoderm. It separates the body wall from the inner organs.
Assume you are observing an animal embryo and find a layer of mesoderm. Which of the following are you studying?
an animal in bilateral symmetry
Which of the following best describes a pseudocoelom?
a body cavity that is not completely surrounded by mesoderm-derived tissue
Which is the term used to describe the concentration of sensory organs and a brain in a defined head region?
cephalization
Animal cells lack a cell was. True or False?
true.
In the animal kingdom, cephalization is
concentration of sensory structures in the head.
one trend in the evolution of animals is the increase in the number of tissue (germ) layers during embryonic development. Flatworms and more complex animals have _ layers.
three
Most animal phyla are radically symmetrical. True or false?
False.
The skin and nervous tissues develop from which germ layer?
Ectoderm
All animals with tissues have
symmetrical bodies
sea stars (starfish) are bilaterally symmetrical at one time in their life cycle. True or false?
true.
The currents of water (containing food) that pass through a sponge are maintained by
collar cells
Sponges have
spicules
A cnidarian that builds a calcium carbonate skeleton is a(n)
coral
The animal most like the ancestral protist colonies that likely gave rise to all animals are
sponges.
Which of the following phyla contains animals that reproduce asexually?
cnidaria
In the various cnidarian species
some live as polyps, some as medusae, and some as both in different stages.
An arthropod exoskeleton is composed of
chitin
The leeches used by doctors to prevent blood clotting and stimulate the growth of blood vessels in patients recovering from reconstructive surgery are members of the phylum
annelida
Which of the following is present in all chordates?
a notochord
The notochord persists into adulthood in all chordates. True or False?
False
In all chordates, the notochord
appears at least during early stages of development
Which of the following features is absent in lancelets?
Backbone