Unit 2: Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
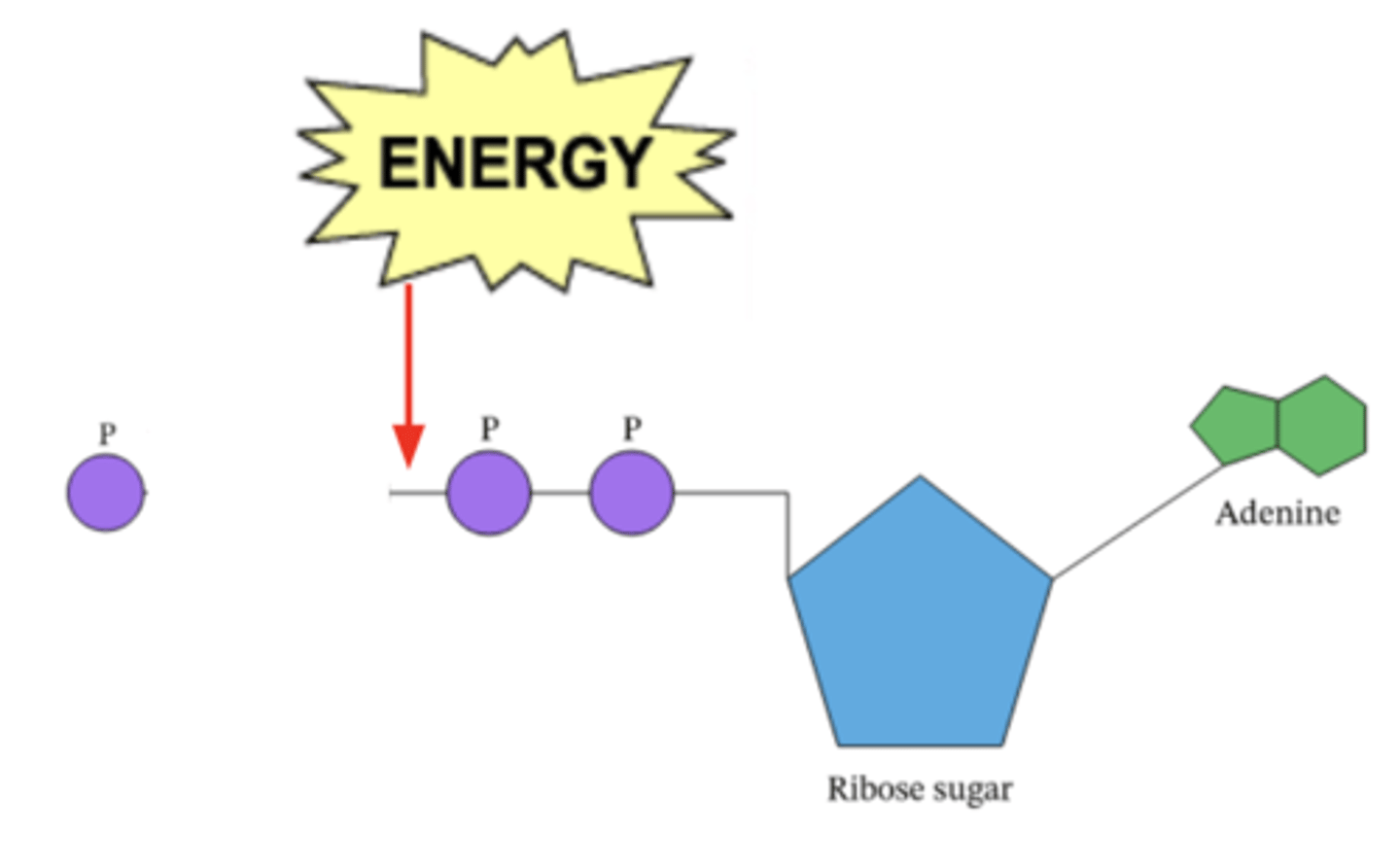
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate - an immediately available source of energy cells use to do work
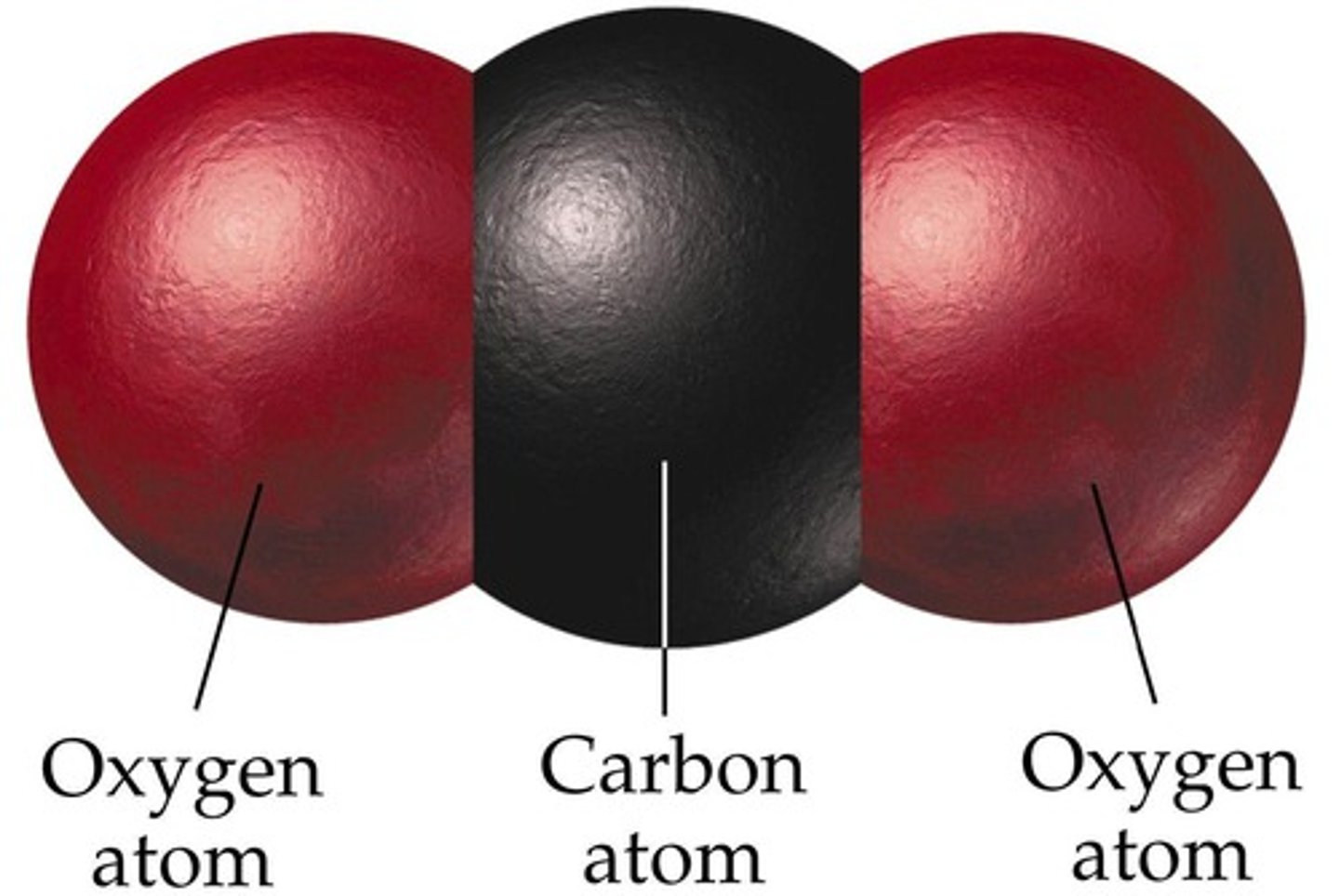
Carbon dioxide
CO2 - Plants use carbon dioxide to make glucose during photosynthesis.
cellular respiration
the process of breaking glucose to create ATP
Chemical energy
energy stored in chemical bonds
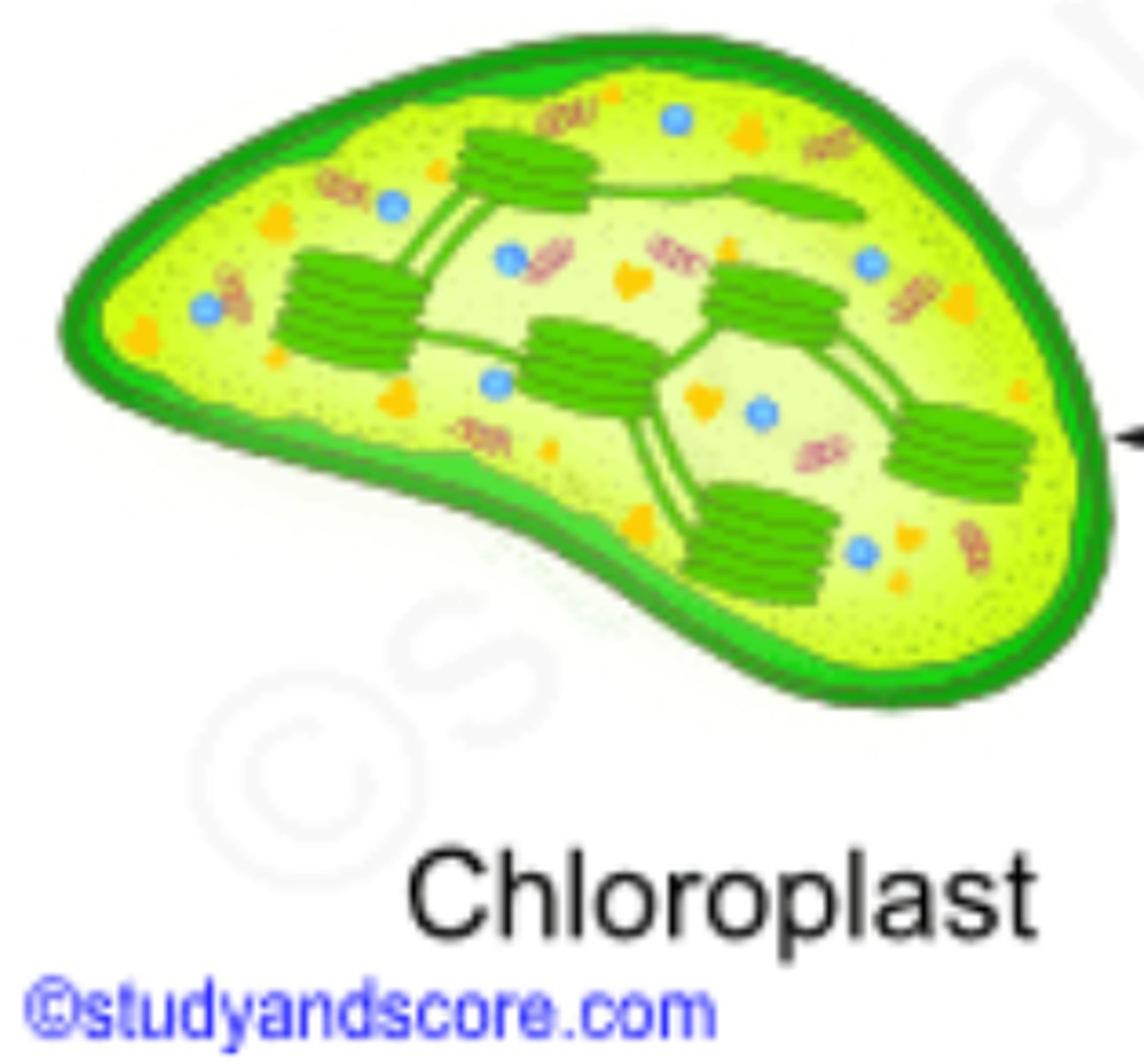
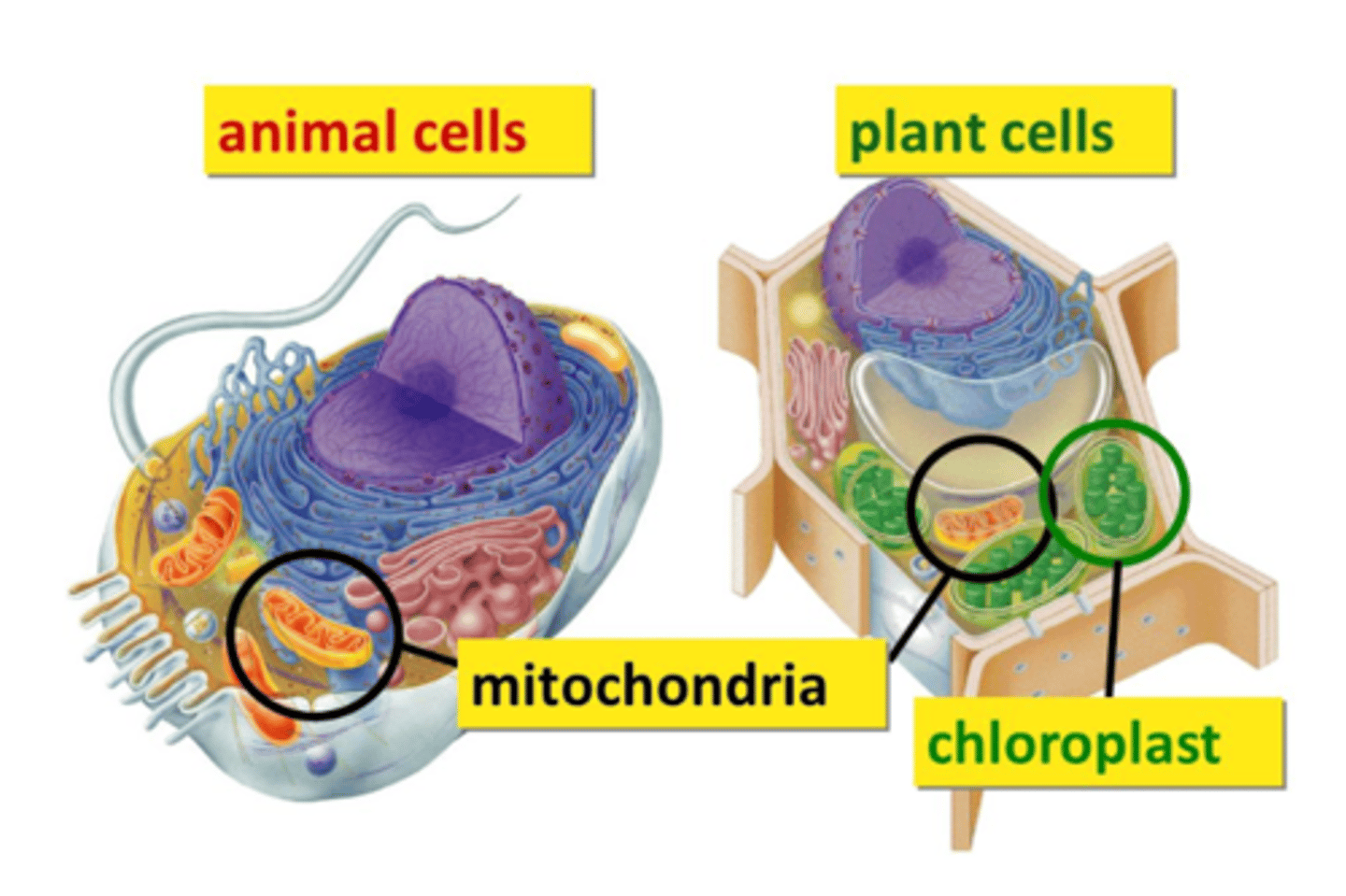
Chloroplast
an organelle in the plant cell that converts light energy into chemical energy via the photosynthetic process.
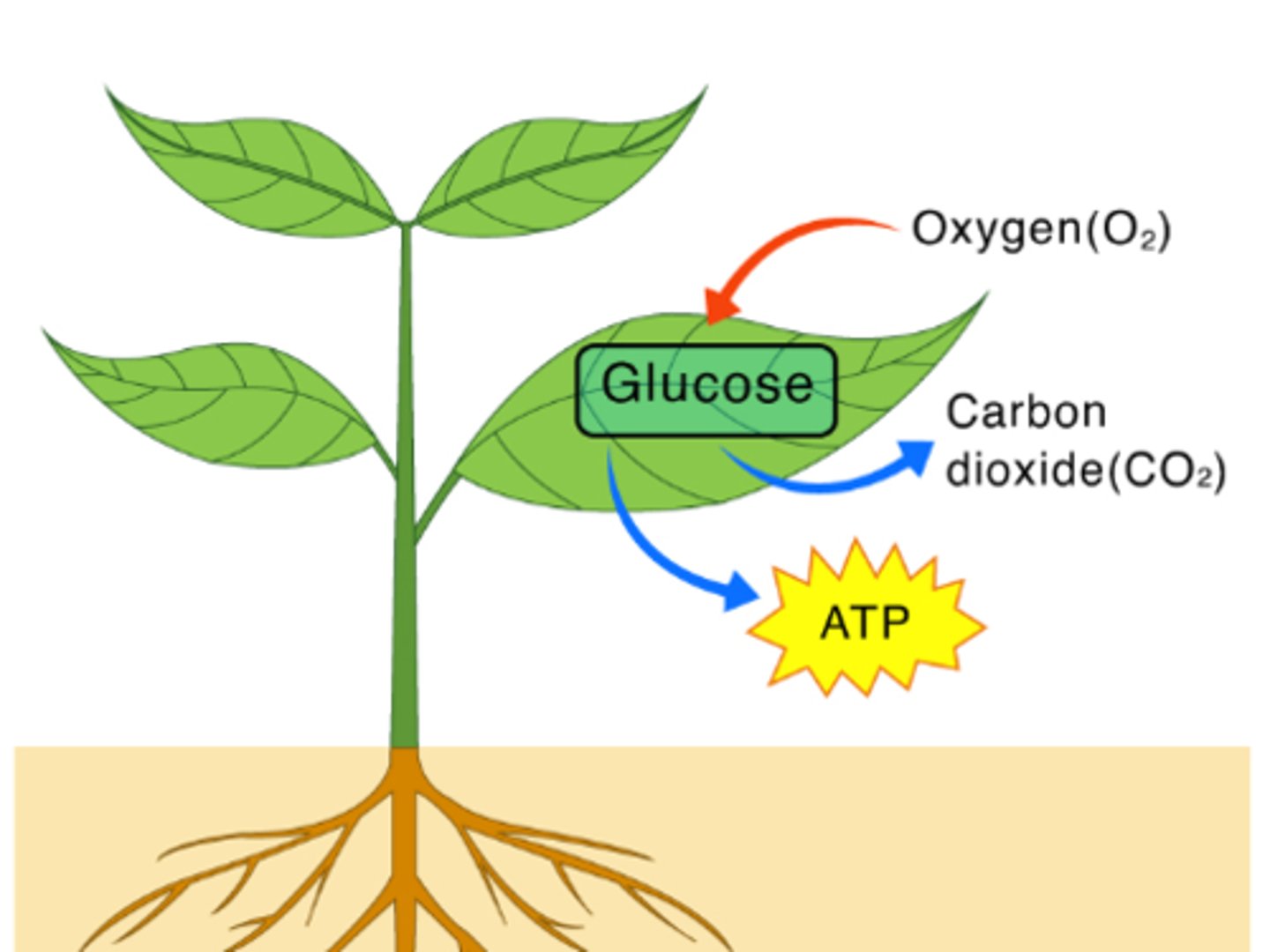
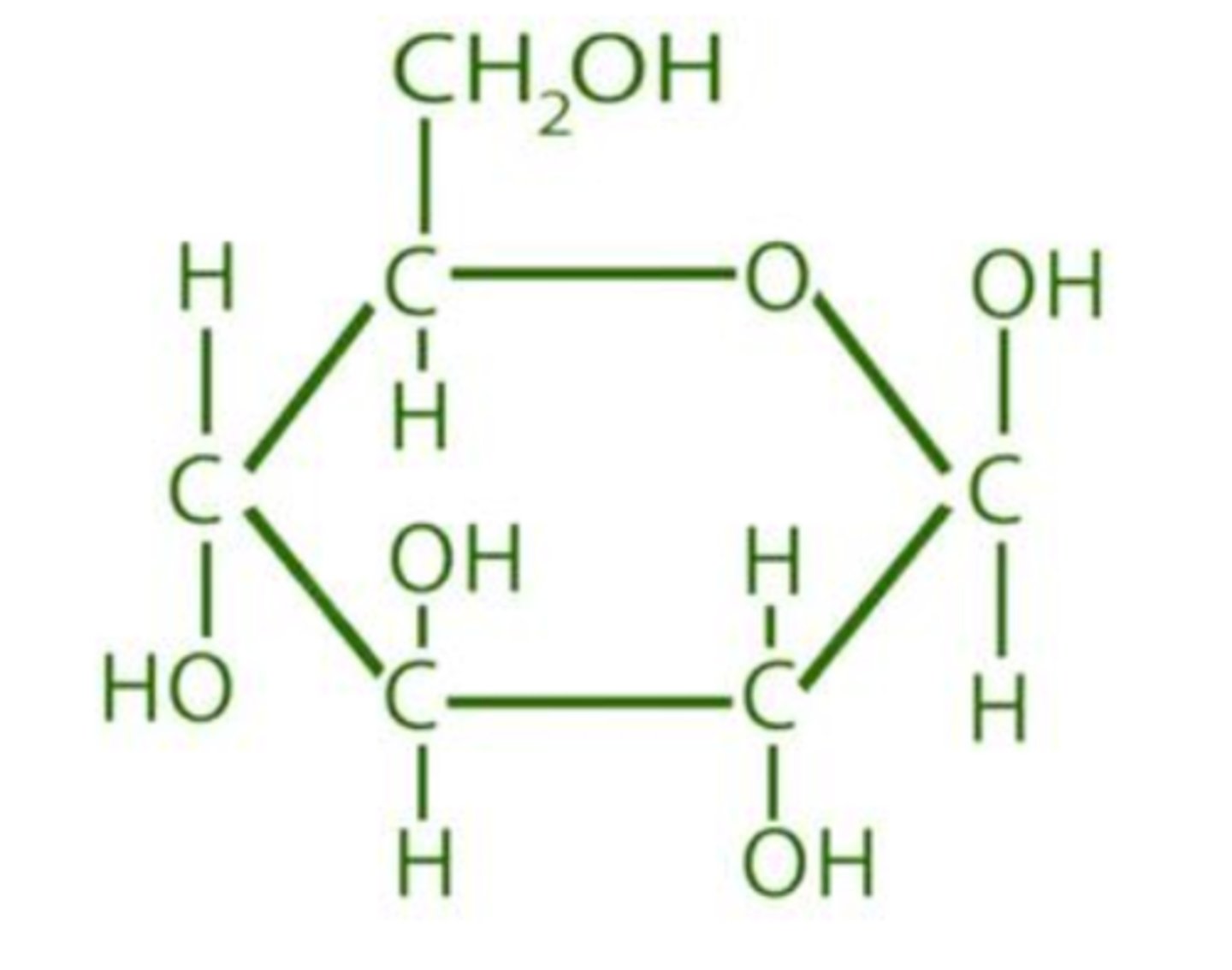
glucose
sugar molecule made of: 6 Carbons, 12 Hydrogens, and 6 Oxygens
Glucose = stored chemical energy
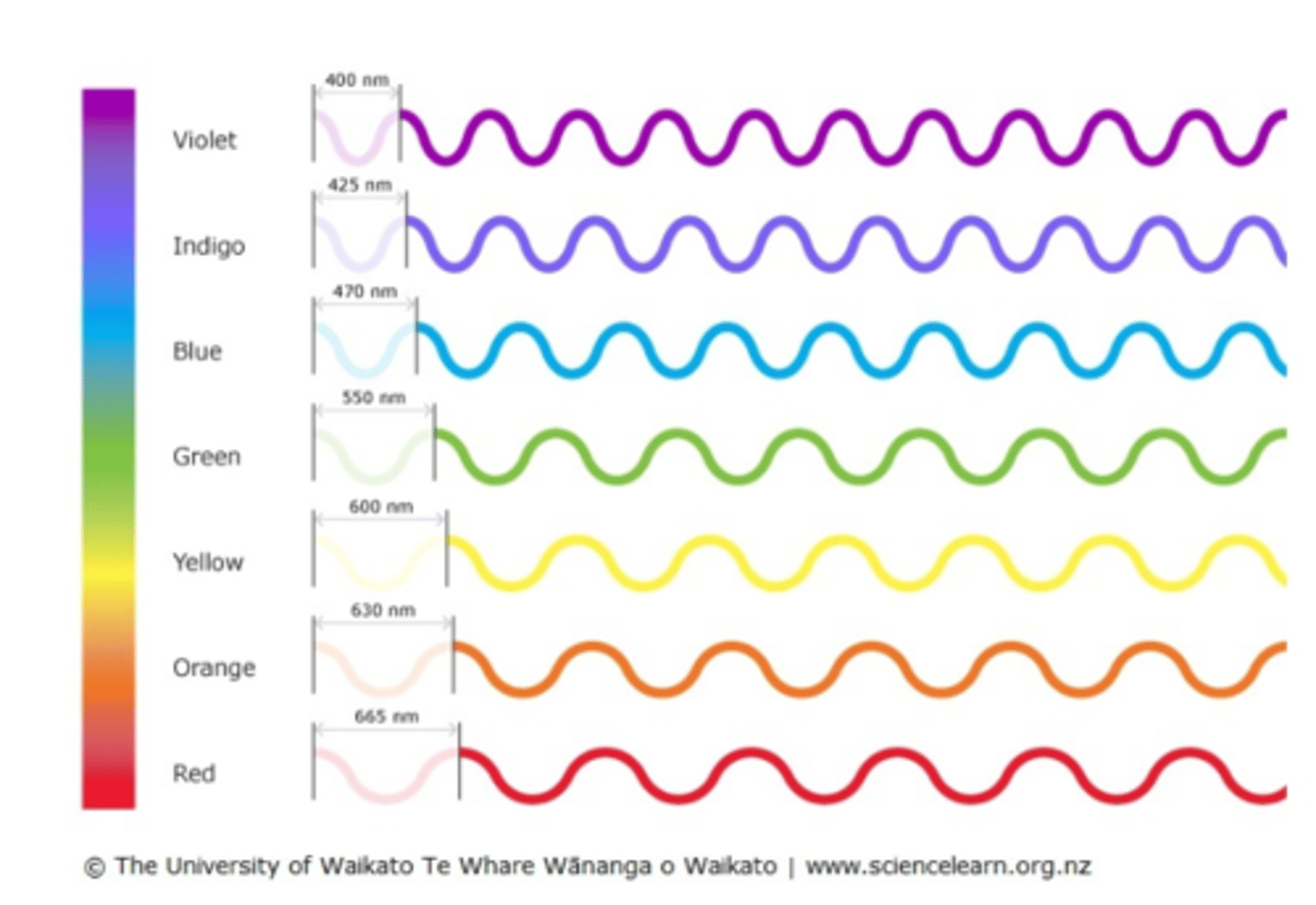
Light energy
A form of electromagnetic radiation that travels in waves and can be seen by the human eye. Light is made of many photons ("particles") moving in different waves of energy (seen as different colours)
mitochondria
an organelle in a cell that produces ATP. This is where cellular respiration takes place.
Oxygen
O2
Photosynthesis
the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy.
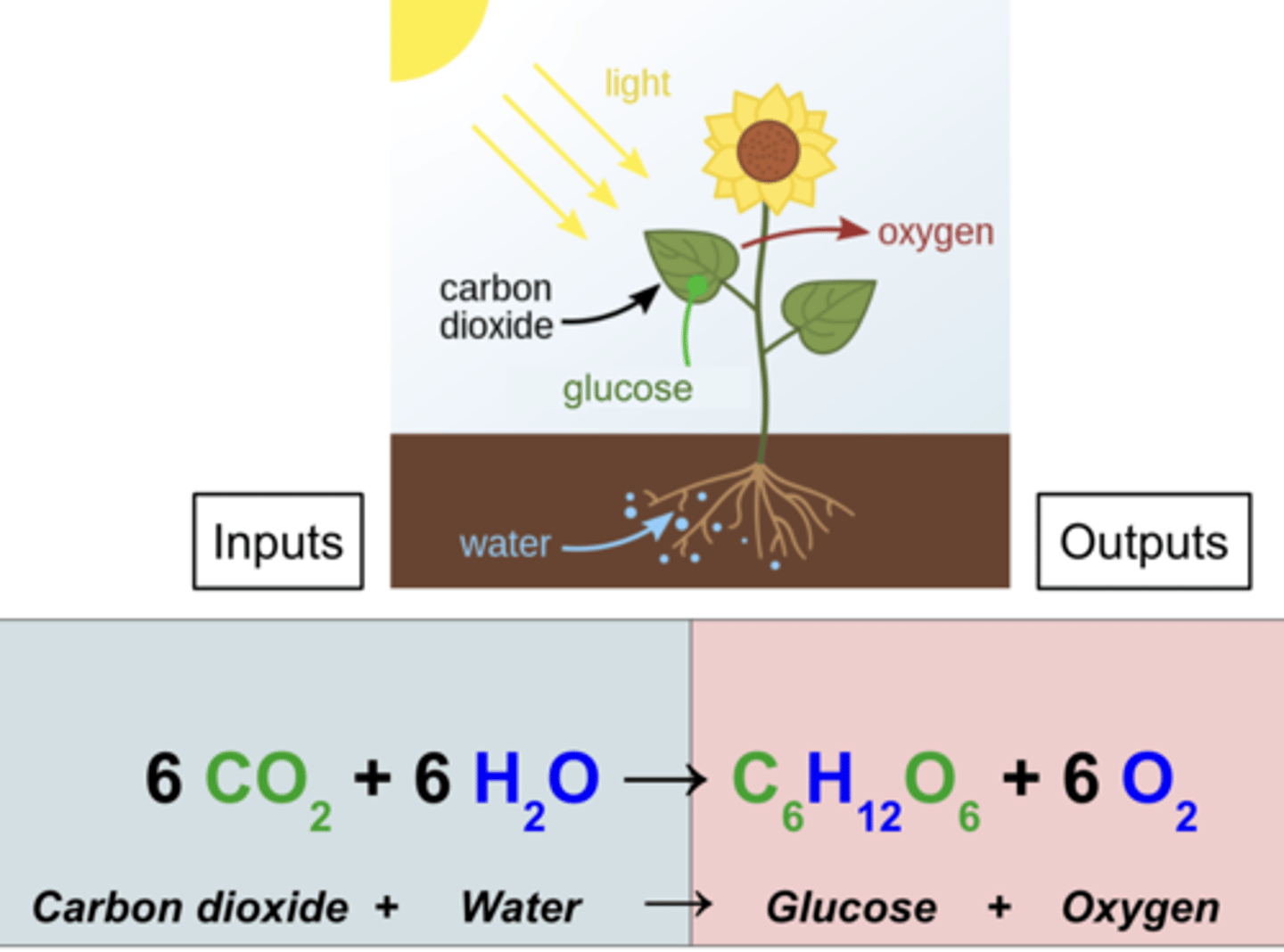
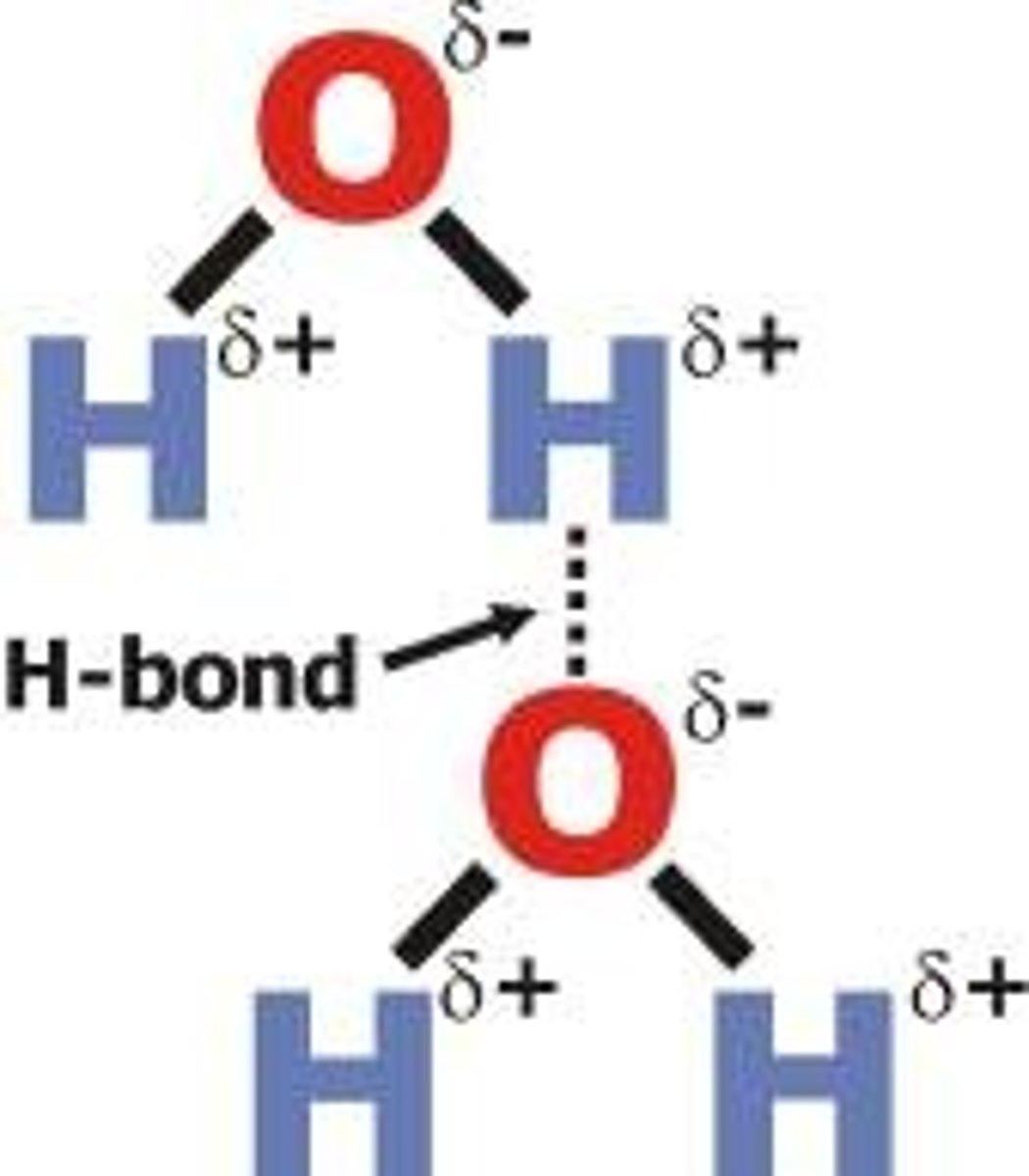
Water
H20
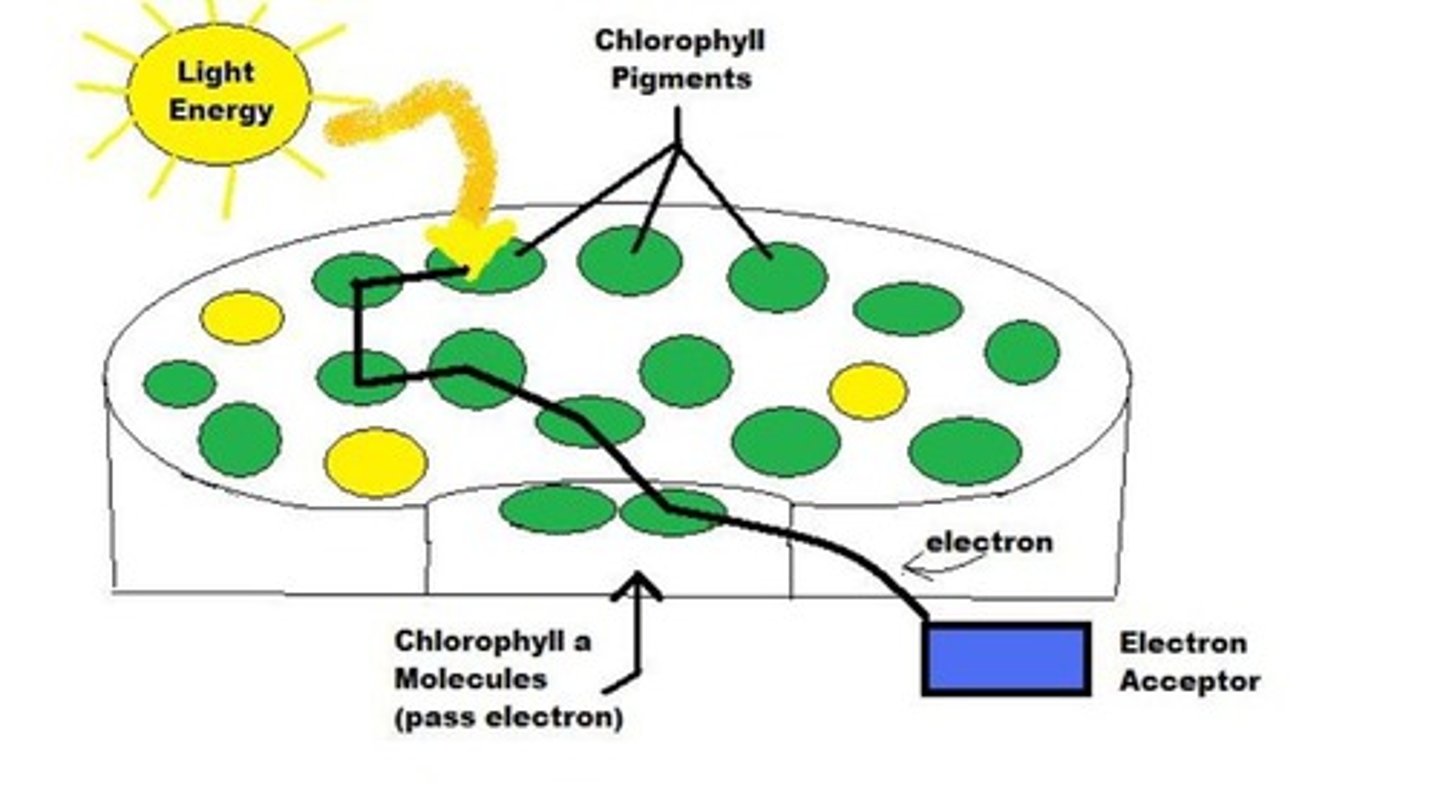
Chlorophyll
green pigment in a chloroplast that absorbs light energy during the light reactions of photosynthesis
Organic compound
a compound made by living organisms that contains carbon - hydrogen bonds
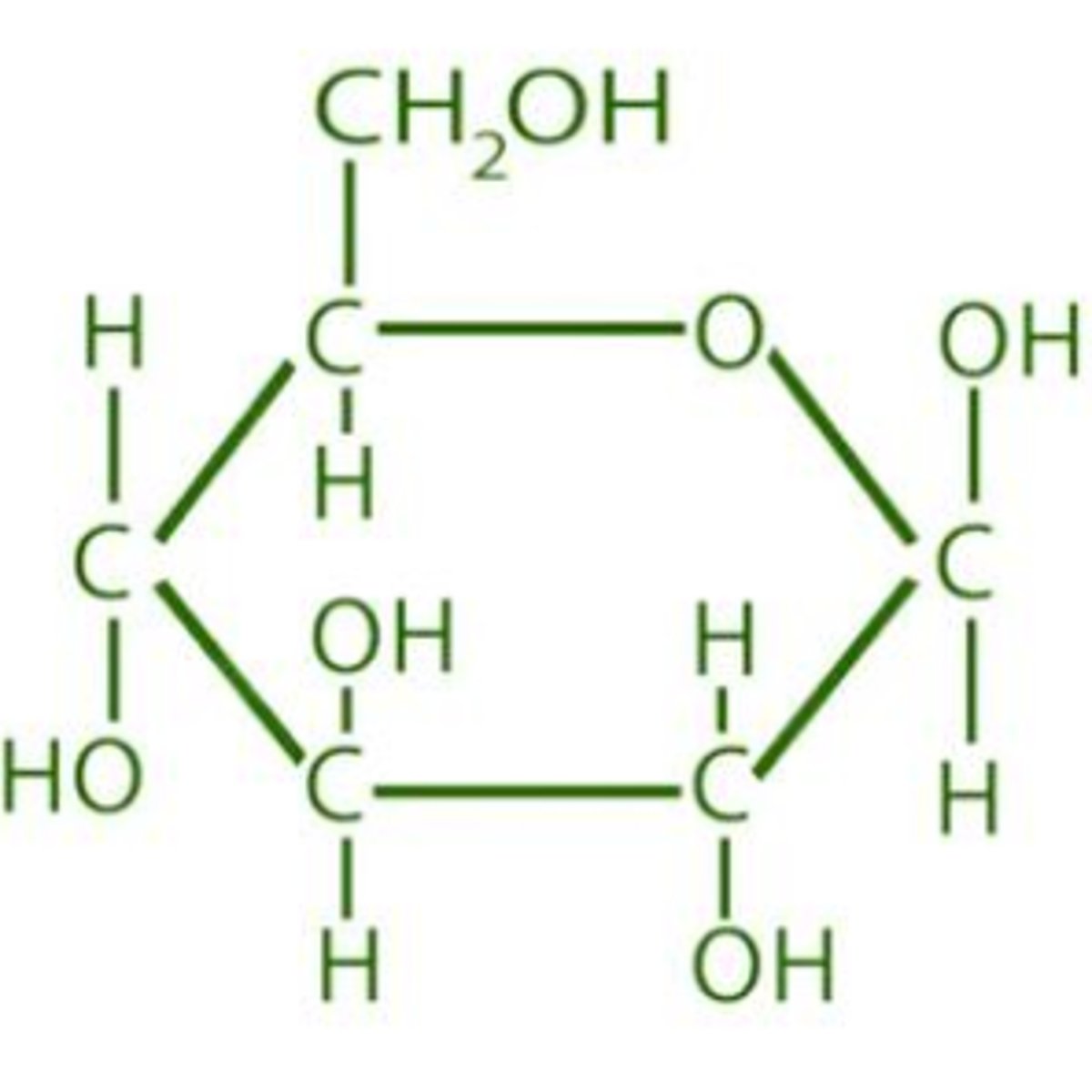
Inorganic compound
a compound that exists separately from living organisms and does not contain a carbon - hydrogen bond
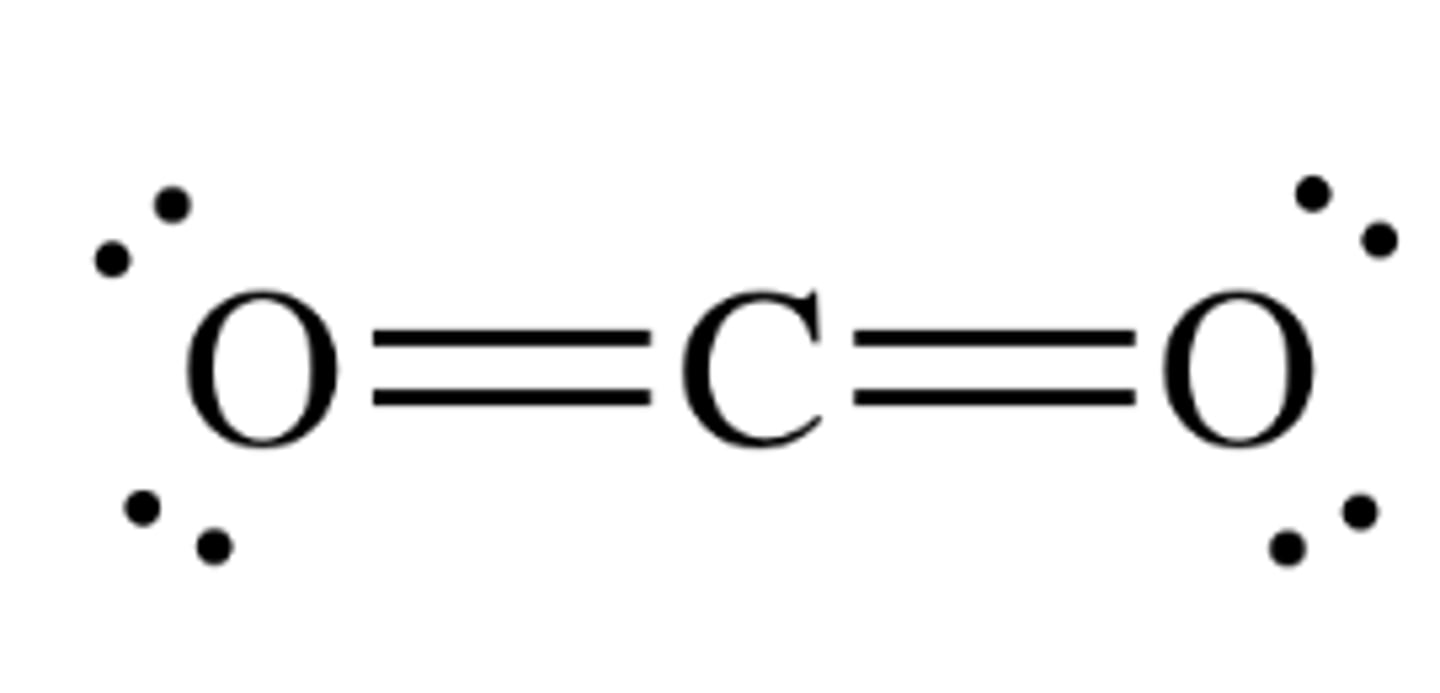
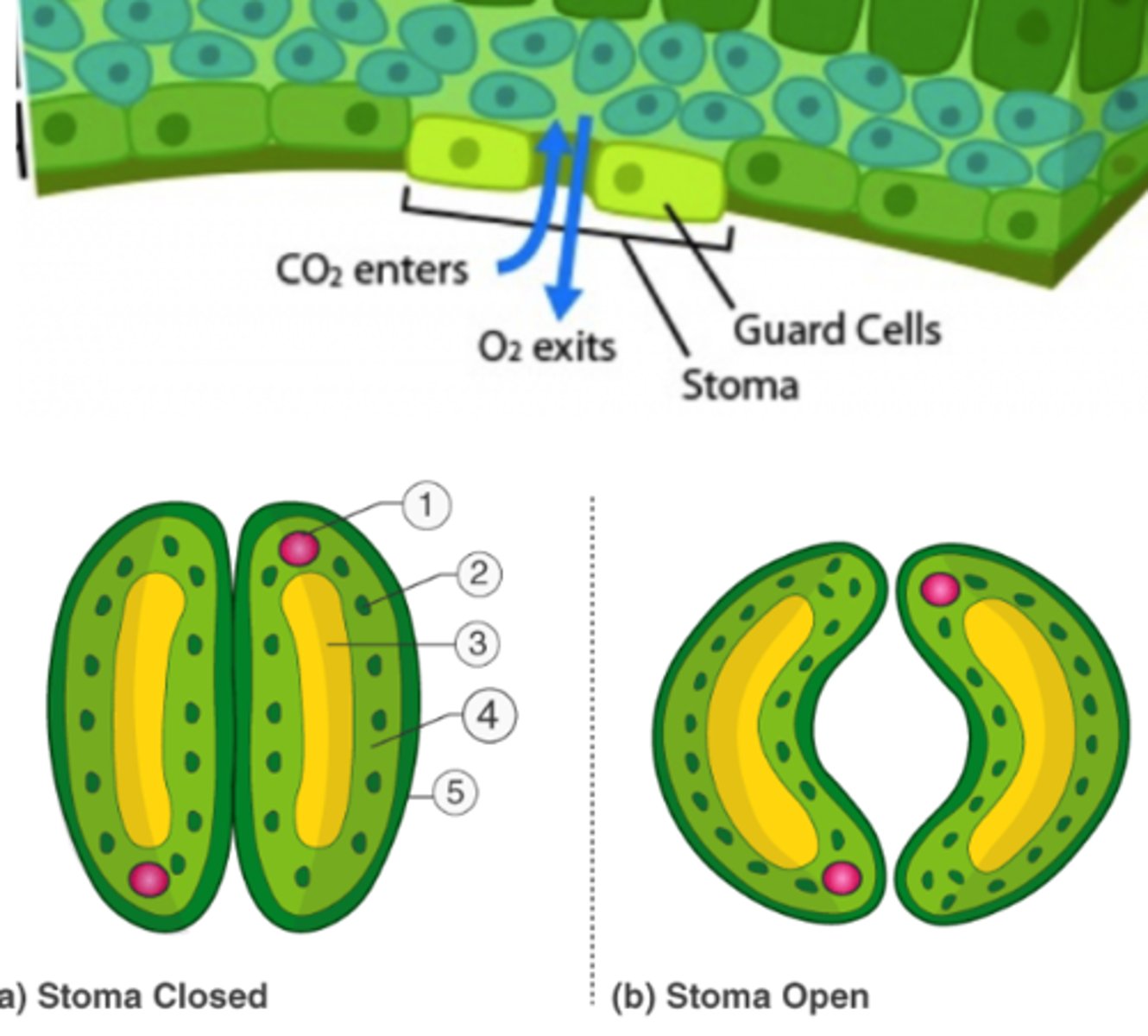
Stoma (stomata)
a hole-like structure found in leaves and stems of plants. Stomata control the rate of gas exchange between the plant and the atmosphere by opening and closing.
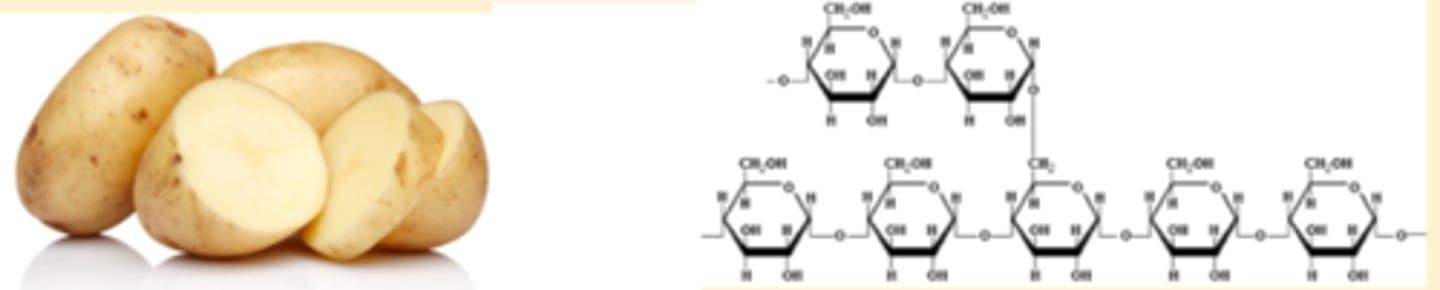
starch
a string (polymer) of glucose molecules
carbohydrate
a biomolecule (organic compound) made of simple or complex sugars. Carbohydrates supply energy to the body, such as sugar and starch.

biomolecule
a chemical compound found in living organisms