528 Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) and Intro to Epidemiology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
______ disease is most frequently studied in affluent countries
Chronic
Research tends to favor ____ drugs
NEW
- where the money is
- the QS being asked
- what gets published
Research agenda is set by _________ and ______ funding
federal funding - fairly small percentage
private sector pharmaceutical R&D companies
Why is Chronic disease is most frequently studied in affluent countries?
Biggest profit potential
• Incidence and prevalence
• Need to take medications indefinitely
• How many different statins are needed?
• How many different ACE inhibitors are needed?
Selection of study subjects for clinical trials who are:
• More likely to respond favorably to treatment
• Less likely to have side effects
• Do not have other diseases
Selection of study subjects for clinical trials: Exclude subjects who/who are
• Older
• Do not speak English
• More likely to be lost to follow-up
• Taking other chronic medications
• Have more conditions than the chronic disease of interest
• At high risk for outcome
Predictor variables
the previous exposure the subject has that can affect the outcome (ex:diabetes)
Outcome variables
dependent variables
outcome of the study
Quality elements of how a study is designed and conducted
Do investigators know who is receiving drug or placebo?
Do investigators control who receives which treatment?
Do investigators measure the effects the same way in all subjects?
What are the rules for stopping a study?
• How many comparisons are being made?
• Fraud
Type of outcome measured
• Clinical measure - MI
• Surrogate measure - Cholesterol measures
• Efficacy versus effectiveness
EVIDENCE ALONE IS NOT ENOUGH TO MAKE A CLINICAL DECISION: CLINICIANS MUST BALANCE THE
Benefits, costs, and nuisance of treatment/care options: balancing patient preferences and values with clinical decisions
Evidence-Based Medicine Philosophy is Based on Three Key Principles:
• Awareness of best clinical evidence
• Hierarchy of evidence exists, and it is used to guide clinical decision-making
• Evidence alone is not enough to make a clinical decision
Evidence alone is not enough to make a clinical decision
• Clinicians must balance risks, benefits, costs and the nuisance of treatment/care options
• Clinicians must factor in patient preferences and values to make clinical decisions
Hierarchy of Medical Evidence for Prevention and Treatment Decisions or Therapeutic Treatment Decisions:
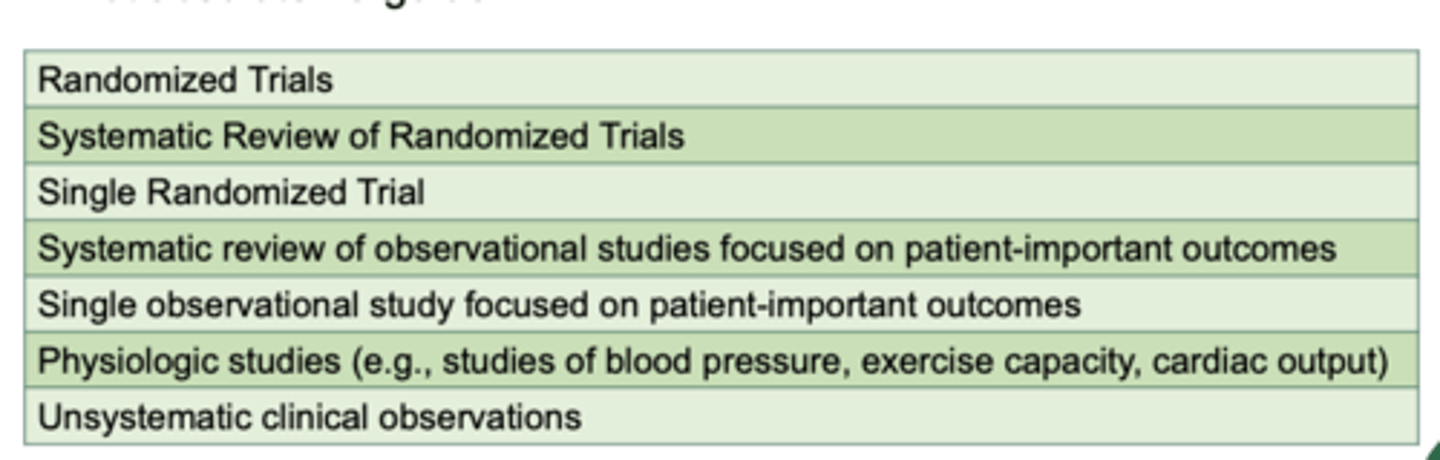
framing the clinical question invoves
patients
expourse
outcome
PICO
Clinical questions can be separated into _________ and _________
background questions and foreground questions
background questions
Typically answered using available tertiary literature (for example, textbooks) and are used to gain foundational knowledge
• Sometimes secondary literature is used
• Typically asked bya novice health professional
Foreground questions
usually require primary literature and are used for problem-solving
• Occasionally, secondary literature is used
• Typically asked by experienced health professionals
must be framed in a way they can beanswered given the large amount of existing information
PICO- P=
Patients or Population
• Which patients are relevant to the question?
PICO: I
Intervention (s) or Exposure(s)
• Which medications, risks, interventions, time period is/are of interest?
• What management or treatment strategies are of interest?
PICO: C
Comparator
• What are we comparing the medication, risk intervention or strategy of interest to?
PICO: O
Outcome
• What happens to the patient or population because of the exposure or intervention
5 Types of Clinical Questions
1) Therapy
2) Harm
3) Differential diagnosis
4) Diagnosis
5_ Prognosis
Therapy questions
used to determine the effect of exposures or interventions on patient outcomes
EX: Do patients with IBS experience fewer symptoms with medications than with dietary changes alone?
Harm questions
used to determine harmful effects of exposures or interventions on patient outcomes
• Can use these in conjunction with studies of therapy questions - what are the adverse effects of interventions
EX: Do CHF patients treated with amiodarone experience harmful side effects?
Differential diagnosis questions
are used to determine the frequency of various medical disorders in patients with particular clinical presentations
EX: In patients presenting with fever and chills, is it more likely they have influenza or malaria?
Diagnosis questions
are used to determine the ability of a test to separate or differentiate between individuals with and individuals without a disease or condition
EX: What is the sensitivity of a pregnancy test in determining women who are really pregnant?
Prognosis questions
used to assess or approximate a patient's future course
EX: How long will patients with hyperlipidemia who have already experienced one MI and are now being managed with statin therapy survive before a second MI?
Epidemic VS pandemic
epidemic is in a region or area
pandemic is a large area, often globally
Epidemiology
is the study of frequency and distribution of disease occurrence, as well as factors associated with disease occurrence or disease distribution in populations
concerned with distribution and determinants of health anddiseases, morbidity, injuries, disability, and mortality in populations*
Epidemiologic studies are applied to ....
control health problems in populations
Objectives of Epidemiology
1. . Identify etiology of disease and relevant risk factors
2. Determine disease burden in a community or communities
3. Study course or natural history of disease and its prognosis
4. Evaluate existing and emerging preventive routes and therapies, as wellas health care delivery methods
5. Provide supporting knowledge to develop public policy that relates to providing disease prevention and health promotion. Environmental.
Genetics
Other concerns affecting health
Determinants
factors or events that can cause a change in health/health status
Determinants Examples
• Infectious agents
• Chemical agents
• Environmental agents
• Personal habits or customs
Social determinants of health
Social determinants of health
are the circumstances in which people are born, grow up,live, work, and age, as well as the systems put in place to deal with illness
Frequency of disease
occurrence, mortality, morbidity or other measures vary from one population to another population
Distribution
reflects how disease or other measures occur in different groups or populations of people
Epidemiology focuses on _______ RATHER than ______
disease and mortality in populations rather than individuals
morbidity vs mortality
Morbidity: illness
Mortality: death
morbidity rate
Number of illness occurrences or number of disease cases in a specific population in a given time period
Mortality rates
Number of deaths in an area per time period (often per year)or in a specific population per time period
epidemiologic description includes
variations by age, gender, time, geography,as well as other terms
Clinical description
signs and symptoms
EBM
evidence based medicine