PFT, Chest X-Ray, and EKG exam
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
What are the four Volumes of the lungs? page. 166
Residual volume (RV)
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
tidal volume (Vt)
What are the four capacities of the lungs? page. 166
Total lung capacity (TLC)
Vital capacity (VC)
Functional residual capacity (FRC)
Inspiratory capacity (IC)
What is tidal volume (Vt)? page. 167
volume of air inhaled or exhaled during each normal breath
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)? page. 167
maximal volume of air that can be inhaled over and above the inspired tidal volume
What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV)? page. 167
maximal volume of air that can be exhaled after exhaling a normal tidal breath
What is residual volume (RV)? page. 167
volume of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal exhalation
What is total lung capacity (TLC)? page. 167
maximal volume of air in the lungs at the end of a maximal inhalation
What volumes is TLC a sum of? page. 167
RV + Vt + ERV + IRV
What is functional residual capacity (FRC)? page. 167
volume of air present in the lung at end-expiration during tidal breathing
What volumes is FRC a sum of? page. 167
RV + ERV
What is inspiratory capacity (IC)? page. 167
maximal volume of air that can be inhaled from the resting end-expiratory level
What volumes is IC a sum of? page. 167
Vt + IRV
What is vital capacity (VC)? page. 167
maximal volume of air that can be exhaled after a maximal inhalation
What volumes is VC a sum of? page. 167
IRV + Vt + ERV
STUDY THIS!!!
know all of the volumes and capacities as well as their normal values.
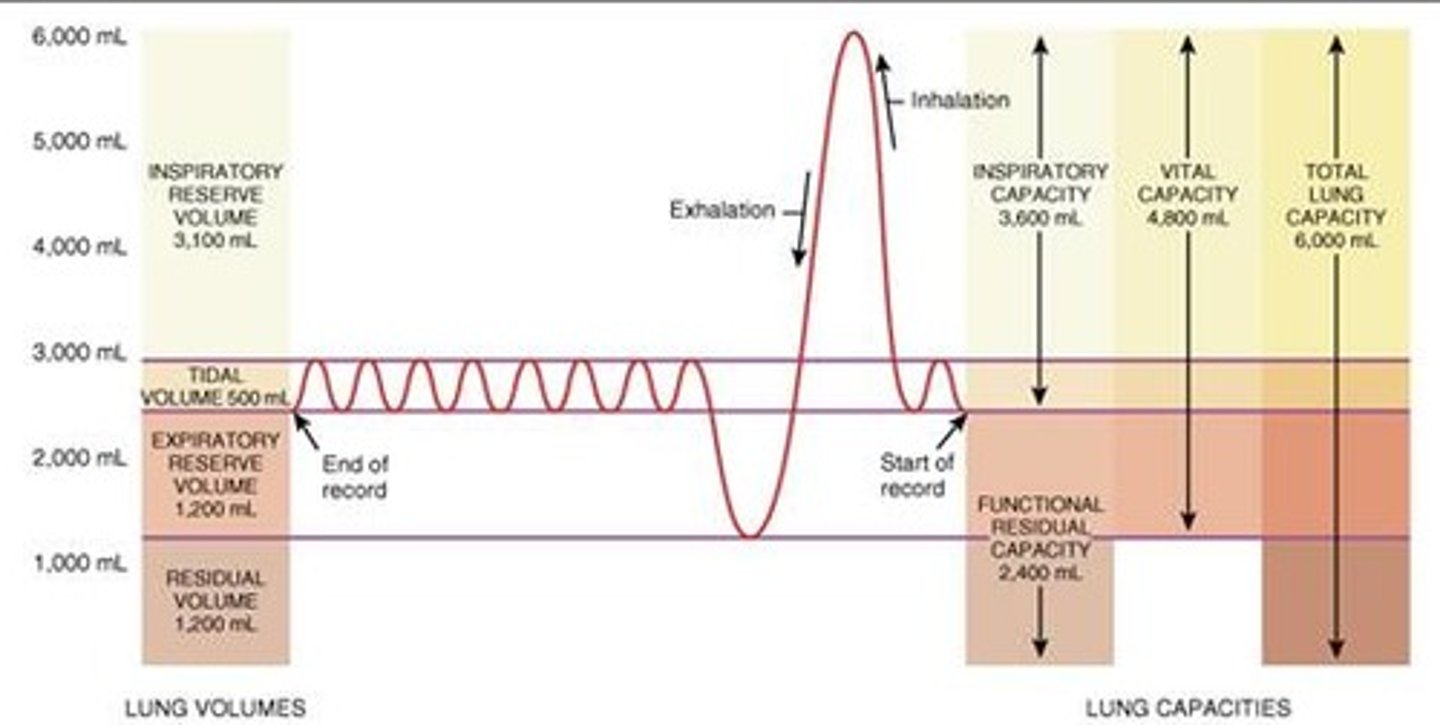
What are the normal values of the volumes of the lungs? page. 166
IRV- 3100 ml
Vt- 500 ml
ERV- 1200 ml
RV- 1200 ml
What are the normal values of the capacities of the lungs? page. 167
TLC- 6000 ml
VC- 4800 ml
IC- 3600 ml
FRC- 2400 ml
What is Forced vital capacity (FVC)? page. 168
total volume of air that can be exhaled during a maximal forced expiration effort
What is Forced expiratory volume (FEV1)? page. 168
volume of air exhaled in the first second after a maximal forced inhalation
What is FEV1/FVC? page. 168
proportion or percentage of the FVC expired during the first second of the maneuver
What is FEF25%-75%? page. 168
average flow occurring between 25% and 75% of the FVC
What does FEF25%-75% measure?
It measures the function of the small airways, which are crucial for airflow resistance in obstructive lung disease.
What does the X-axis on a flow volume loop show? page. 169
Volume
What does the Y-axis on a flow volume loop show? page. 169
Flow
What is true during an FVC vs. SVC measurement?
In an obstructive disease pattern, the SVC will be greater than the FVC
What are the normal values for a PFT?
Normal: 80-100%
Mild: 60-79%
Moderate: 40-59%
Severe: less than 40%
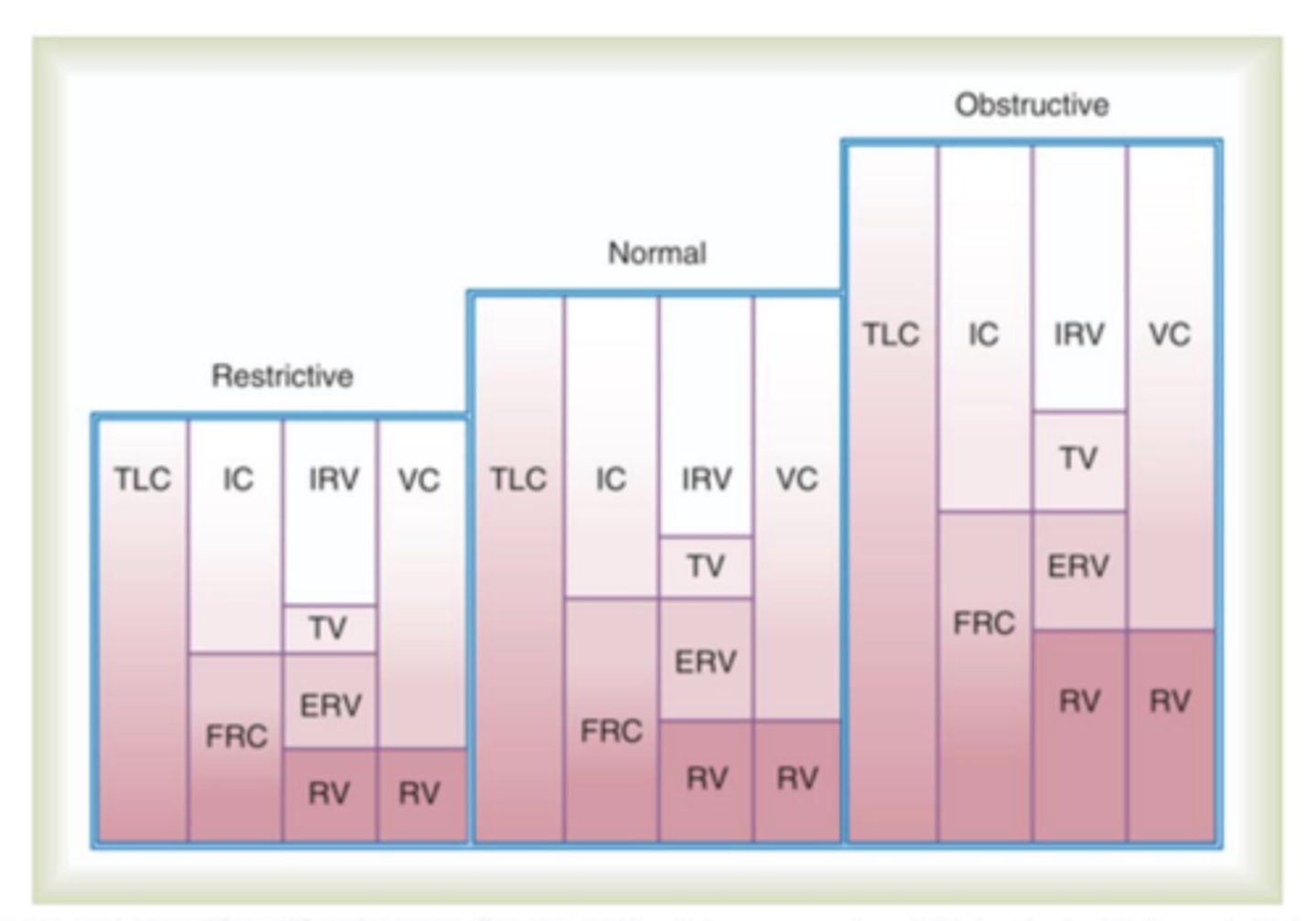
In restrictive lung patterns are volumes increased or decreased? page. 173
Decreased
In obstructive lung patterns is flow increased or decreased? page. 173
Decreased
Can FRC be directly measured? page. 174
No, they cannot be directly measured
What are the three ways that FRC can be measured? pages. 174-176
Closed-Circuit Helium Dilution
Open-Circuit Nitrogen Washout
Body Plethysmography
What is Boyles law?
at constant temperature, pressure and volume of a gas are inversely related
What is Charles law?
at constant pressure, the volume of a gas varies directly with its temperature
What is Gay-Lussac's law?
at constant volume, the pressure of a gas varies directly with its temperature
Changes in lung volumes and capacities
Understand how restrictive, normal and obstructive are impacted
What is the normal airway resistance in healthy adults?
0.5 to 2.5 cm H20/L/S
What is a normal DLCO?
80-120%
How do you calculate airway resistance? page. 179
PIP - Pplat/flow
What is the minimum compliance a patient can have in order to wean?
20 ml/cm H2O
What is bronchoprovocation test? page. 181
A test that uses a methacholine to try and trigger a bronchospasm that helps determine the level at which airway response occurs
What does bronchoprovocation testing help with? page. 181
rule out a diagnosis of asthma
assess the severity of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR)
evaluate for occupational asthma
assess response to airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) treatment
What is a common test done for asthma patients?
Peak flow
Which volumes can be directly measured?
Tidal volume
Expiratory reserve volume
Inspiratory reserve volume
Which capacities can be directly measured?
Inspiratory capacity
Vital capacity
Which volumes/capacities are indirectly measured?
Residual volume
Total lung capacity
Functional residual capacity
What quality control must be done for a Levey Jennings chart?
If there is an outlier outside of the lines, the machine must be recalabrated
What is the most important factor of PFT?
A well-trained energetic therapist
What are the factors that affect PFT results?
Age
Gender
Height
Weight
What are the four patterns for a PFT?
Normal
Obstructive
Restrictive
Mixed
What happens when doing a methacholine challenge test?
The therapist gives a dose then records FEV1, then gives a bigger dose then records FEV1 and continues to do so until the capacities drop 12%, if they drop 12% a bronchodilator is given to bring the patient back to their baseline.
How is a calibration test done for volume? page. 170
calibration check with a calibrated 3-L syringe
When looking at a chest X-Ray what are the five things we look at?
A: Airway
B: Bones
C: Cardiac
D: Diaphragm
E: Everything else (that's important)
What are the angles of the diaphragm called?
costophrenic angles
What is the notch above the heart called?
cardiac notch
What side does the trachea shift to if the patient has a pneumothorax?
The trachea shifts away from the affected side
What side does the trachea shift to if the patient has atelectasis?
The trachea shifts towards the affected side
How many ribs should be able to be counted on a chest X-ray?
8-10 Ribs
If a patient has a visible artificial airway on a chest X-Ray how far above the carina should it be?
3-5 cm
What is an enlarged heart on a chest X-Ray called?
cardiomegaly
How can we determine if the heart is enlarged on a chest X-Ray?
More than half the diameter of the chest
If the diaphragm on a chest X-Ray looks flattened what is that indicative of?
Air trapping, hyperinflated lungs
What are five findings on a chest X-Ray of someone who has COPD that someone else may not have if they don't have COPD
flattened diaphragm
less curved ribs
can count more than 8-10 ribs
hyperinflated lungs
Increased intercostal space
Heart becomes more narrow due to hyperactivity inflation
On a normal ECG rhythm, what are the events that occur for the P, QRS, and T waves?
P wave: atrial depolarization (contraction)
QRS: ventricular depolarization (contraction)
T: ventricular repolarization (relaxation)
What is happening between the PR intervals on a normal ECG?
period between atrial depolarization (contraction) and ventricular depolarization (contraction)
What is happening between the ST segment on a normal ECG?
period between ventricular depolarization (contraction) and ventricular repolarization (relaxation)
When should an ECG be obtained?
physicians order or protocol
known or suspected cardiac patient
known or suspected overdose on a tricyclic medication
electrical injuries
drop in blood pressure (Syncope)
What is PEA?
Pulseless electrical activity (looks normal on an ECG, but there is no heart activity going on)
What is septal infarct?
Tissue of the heart is dead and can't contract
What is angina pectores?
chest pain caused by decreased consistent low oxygenation to the heart (caused by ischemia)
What is Ischemia?
decreased oxygenation to the heart
What is infarction?
death of myocardial tissue. tissue is dead and cannot come back.
What happens first infarction or ischemia?
Ischemia will happen before infarction; can be long before infarction or just shortly before.
What are pacemaker cells?
specialized cells that can generate their own electrical activity
Where are pacemaker cells located?
They are mostly consolidated in the SA node but there are some in the AV node as well
What are conducting cells?
They are cells that conduct the electrical impulses throughout the heart
What is the pattern of electrical conduction of the heart?
SA node -> Internodal pathways -> AV node -> Bundle of His-> right and left bundle branches-> Purkinje fibers
What is the most important lead to respiratory therapists?
Lead II (2)
What is important of the ST segment?
very important in determining a STEMI
In terms of electrical impulse, what is important about the PR interval?
It is the time that it takes the SA node impulse to get to the AV node
How many seconds is each box on an ECG?
0.04 seconds
What are five important steps when interpreting an ECG?
looking at the rate
looking at the rhythm
looking at the shape of the QRS
looking at the PR interval
looking at the ST segment
What is a uni-focal PVC vs. a multi-focal PVC
uni=1 pvc
multi= multiple PVC's
What is cardioversion?
treatment that sends shock during R wave.
What is defibrillation?
shocking to stop fibrillation
Can asystole be shocked?
NO