Nueroanatomy Concepts
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Which structures are lateral to the pyramids on the medulla?
Olives
The substantia nigra supplies dopamine to the
Striatum
If you see the fourth ventricle, you are in the
Pons
Posterior cerebral artery stroke leads to
Macular sparing
Middle cerebral artery stroke and macular sparing
Macular sparing occurs
The caudate nucleus (C shaped structure) is in the
Lateral ventricle
The superior cerebellar peduncle has “lines” that run
Up
The lateral ventricles are separated by the
Septum pellucidum
the middle cerebral artery is in the
Sylvian fissure
The corticospinal tract is in the middle of the
Cerebral peduncle
The medial longitudinal fasciculus carries information from CNs
3, 4 and 6
Function of the fasciculus
Carries Touch and proprioreception from the spinal cord up
The cerebellum connects with the midbrain via the
Cerebella peduncle
Cingulate cortex function
Pain and anxiety
The cerebral peduncle with connects the
Brainstem to the cerebrum
Function of the denticulate ligament
Attach the dura mater to the rest of the spinal cord
End of the spinal cord…
Conus medullaris
The cervical slices have the most amount of
White tracts (those white specs)
The thoracic segments have the
Lateral horn (preganglion sympathetics)
The ventral horn in the lumbar segments are
Large and round (to supply the legs)
Which artery connects posterior to anterior circulation?
Posterior communicating artery
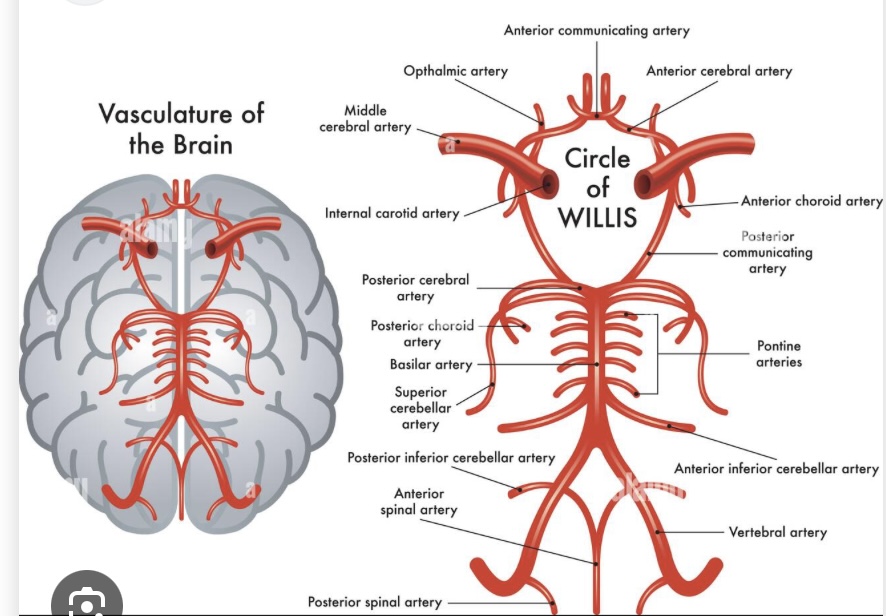
Which arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery
Anterior cerebral arteries
The vertebral arteries and the anterior spinal artery come together to make the
Basilar artery
The pontine arteries comes off of the basilar artery (look like little hairs) and supply the
Pons
The superior cerebellar artery comes off of the
Basilar artery
The posterior cerebral artery comes off of the
Basilar Artery
The posterior communicating artery connects to the anterior communicating artery where the _____ connects
Internal carotid artery
One branch of the internal carotid artery moves laterally and becomes the
Medial cerebral artery
One branch of the internal carotid artery moves anterior and becomes the
Anterior cerebral artery
Both anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the
Anterior communicating artery
CN1 comes off the
Olfactory bulb
The hypoglossal nerve comes out of the
olives
What structure forms when dorsal and ventral roots join?
Spinal nerve
Which spinal cord enlargement supplies the upper limbs?
Cervical enlargement
The precentral gyrus contains the
Primary motor cortex
The post central gyrus contains the
Primary somatosensory cortex
The occipital pole contains the
Primary visual cortex
The posterior cerebral artery supplies the
Occipital and inferior temporal lobes
Which enlargement supplies the lower limbs?
Lumbosacral enlargement
Which horn is present only in thoracic segments?
Lateral horn
What structure lies lateral to the pyramids?
Olive
Where does pyramidal decussation occur?
Caudal medulla
What structure connects the pituitary to the hypothalamus?
Infundibulum (tuber cinereum)
What paired round structures are posterior to the infundibulum?
Mammillary bodies
What connects left and right anterior cerebral arteries?
Anterior communicating artery
Which artery is excluded from the Circle of Willis?
Middle cerebral artery
What connects the internal carotid artery to the posterior cerebral artery?
Posterior communicating artery
What completes posterior circulation before the circle of Willis?
Basilar artery dividing into posterior cerebral arteries
The pons is supplied by
The basilar artery
The middle cerebral artery supplies the
Lateral brain
What midline cerebellar structure connects the hemispheres?
Vermis
What are the two layers of dura mater?
Periosteal layer and meningeal layer
Which dura layer contacts the skull?
Periosteal layer
Which Duran layer contacts the brain
Meningeal layer
What venous sinus forms between dural layers at the midline?
Superior sagittal sinus
What dural fold separates the cerebral hemispheres?
Falx cerebri
What dural fold separates cerebrum from cerebellum?
Tentorium cerebelli
Where is cerebrospinal fluid absorbed into venous blood?
Arachnoid granulations into superior sagittal sinus
Which insular gyri are shorter and more numerous?
Short gyri
Which spinal cord regions lack lateral horns
Cervical and lumbar regions
Which cerebellar structure is hidden by the pons?
Flocculonodular lobe
Which dura layer contacts the skull?
Periosteal layer
What dural fold separates cerebrum from cerebellum?
Tentorium cerebelli
Where is cerebrospinal fluid absorbed into venous blood?
Arachnoid granulations into superior sagittal sinus
Are dura and arachnoid attached everywhere?
No—except at arachnoid granulations
What sulcus separates frontal and parietal lobes?
Central sulcus
What sulcus forms the superior boundary of the temporal lobe?
Lateral (Sylvian) fissure
What sulcus forms the superior boundary of the temporal lobe?
Lateral (Sylvian) fissure
Which gyrus is anterior to the central sulcus?
Pre central gyrus
Which gyrus is important in face recognition?
Fusiform
Name the three frontal gyri (superior to inferior).
Superior frontal gyrus, middle frontal gyrus, inferior frontal gyrus
What sulci separate the frontal gyri
Superior frontal sulcus, inferior frontal sulcus
Where is the primary auditory cortex located?
Superior temporal gyrus
Where is Wernicke’s area located?
Posterior superior temporal gyrus
What parietal gyrus is involved in language and reading
Angular gyrus
What gyri project from the superior temporal gyrus into the insula?
Transverse temporal gyri
What are the two types of insular gyri?
Short and long gyri
Which insular gyri are shorter and more numerous
Short gyri
What is cranial nerve II composed of anatomically?
Axons connecting the retina to the optic chiasm and optic tract.
What structure marks the transition from optic nerve to optic tract?
Optic chiasm.
What makes cranial nerve 4 unique in its brain entry?
It enters from the posterior and superior aspect of the brain
Which cranial nerve lies adjacent to the facial nerve on the ventral surface?
Vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII)
Which structure anchors the spinal cord laterally to the dura mater?
Denticulate ligaments
What is the filum terminale?
An extension of the pia mater anchoring the spinal cord inferiorly.
At approximately what vertebral level does the spinal cord end?
Around the L2 vertebral level
Why does the lumbar spinal cord have an enlargement?
It contains lower motor neurons controlling the legs.
What grey matter feature is prominent in the lumbar spinal cord?
Large ventral horns
Which spinal cord region contains the most white matter?
Cervical region
Why does the cervical spinal cord have more white matter?
Ascending tracts from lower levels accumulate as they ascend.
What feature distinguishes thoracic spinal cord cross-sections?
Presence of lateral horns.
What do lateral horns contain?
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons.
Which structure anchors the spinal cord laterally to the dura mater?
Denticulate ligaments
Which cranial nerve is located just inferior to the glossopharyngeal nerve?
Vagus nerve (cranial nerve X).