Quiz 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Methyl red, citrate test, new bacteria, etc.
Last updated 4:31 PM on 1/24/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
Methyl red test
* +=convert glucose → pyruvate → mixed organic acids =red color
* indicator is methyl red, turns red at ph 4.5 or less
* IMViC media for MR/VP test
* Differential media
* indicator is methyl red, turns red at ph 4.5 or less
* IMViC media for MR/VP test
* Differential media
2
New cards
T/F organisms tested + in MR tested + in VP
F, anything negative in MR are positive in VP
3
New cards
VP test (Voges- Proskauer test)
* += pink, glucose→ Pyruvate→ acetoin (intermediate)→ butanediol pathway (2,3-butanediol)
* differential media
* Indicator: alpha-naphthol and potassium hydroxide
* differential media
* Indicator: alpha-naphthol and potassium hydroxide
4
New cards
IMViC stands for
I= Indole
M= Methyl red
V= Voges- Proskauer
C= citrate
M= Methyl red
V= Voges- Proskauer
C= citrate
5
New cards
Citrate test
* media contains: citrate (carbon source) and inorganic ammonium salts (nitrogen source)
* Tests for citrate permease: converts citrate to Pyruvate
* ammonia salt is broken down to ammonia it creates alkalinity
* Indicator: **bromthymol blue** **(**turns from green to blue for +)
* differential media, selective for citrate utilizers
* Tests for citrate permease: converts citrate to Pyruvate
* ammonia salt is broken down to ammonia it creates alkalinity
* Indicator: **bromthymol blue** **(**turns from green to blue for +)
* differential media, selective for citrate utilizers
6
New cards
HE agar
* selective and differential (isolation and differentiation of gram -)
* Differentia agents: lactose, sucrose, salicin
* Indicator: Bromothymol blue and acid fuchsin
* Colonies of Salmonella and Shigella spp. are green to bluish-green in color.
* H2S producers are black at the center of the colonies
* ph indicators turn yellow under acidic conditions
* selective agent: bile salt
* differential agent: sodium thiosulfate
* Indicator: ferric ammonium citrate
* Differentia agents: lactose, sucrose, salicin
* Indicator: Bromothymol blue and acid fuchsin
* Colonies of Salmonella and Shigella spp. are green to bluish-green in color.
* H2S producers are black at the center of the colonies
* ph indicators turn yellow under acidic conditions
* selective agent: bile salt
* differential agent: sodium thiosulfate
* Indicator: ferric ammonium citrate
7
New cards
Ferric ammonium citrate is added to HE agar why?
react with H2S and form a black precipitate
8
New cards
XLD agar
* Selective Agent: bilesalts Deoxycholate
* indicates lactose fermentation and H2S production
* Differential agent: lactose, sucrose, salicin
* Indicator: bromthymol blue,acid fuchsin –pH indicators that will turn yellow under acidic conditions
* Differential Agent: sodiumthiosulfate
* Indicator: ferric ammoniumcitrate
* Selective and differential
* indicates lactose fermentation and H2S production
* Differential agent: lactose, sucrose, salicin
* Indicator: bromthymol blue,acid fuchsin –pH indicators that will turn yellow under acidic conditions
* Differential Agent: sodiumthiosulfate
* Indicator: ferric ammoniumcitrate
* Selective and differential
9
New cards
In the XLD agar what is used to detect sulfer reduction
sodium thiosulfate and ferric ammonium citrate
10
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae
* all ferment glucose
* all are oxidase negative
* all reduce nitrates to nitrites
* Many are catalase positive
* all are oxidase negative
* all reduce nitrates to nitrites
* Many are catalase positive
11
New cards
Opprotunistic Enterobacteriaceae
* Often part of the humans normal intestinal flora
* Outside of normal habitat can cause serious infections
* ex. E.coli- can cause septicemia if its in the blood
* Outside of normal habitat can cause serious infections
* ex. E.coli- can cause septicemia if its in the blood
12
New cards
E. coli normal flora
* Normal GI tract flora
* female genital tract
* female genital tract
13
New cards
E. coli transmission
* for non-gastrointestinal- endogenous or direct contact for gastrointestinal (it varies with strain)
* fecal-oral spread
* contaminated food or water (uncooked beef or unpasteurized milk)
* fecal-oral spread
* contaminated food or water (uncooked beef or unpasteurized milk)
14
New cards
Edwardsiella tarda normal flora
* Gi tract of cold-blooded animals (reptiles)
15
New cards
Edwardsiella tarda transmission
* contaminated water
* Contact with animal carrier
* Contact with animal carrier
16
New cards
Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, Providencia, and Serratia Normal flora
Normal GI tract flora
17
New cards
Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, Providencia, and Serratia transmission
* Endogenous- direct contact
* Enterobacter-medical devices
* Serratia- healthcare associated
* Enterobacter-medical devices
* Serratia- healthcare associated
18
New cards
Ecoli extraintestinal infection
* Urinary tract infections
* Bacteremia
* Neonatal meningitis
* Most common G- causing nosocomial infections
* Bacteremia
* Neonatal meningitis
* Most common G- causing nosocomial infections
19
New cards
Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, Providencia, and Serratia pathogenesis
* Nosocomial infections of the respiratory tract
* urinary tract (==Proteus, Citrobacter==) infections
* blood infections
* ==Enterobacter==- top 10 in healthcare-related infections
* med. devices
* ==K. pneumoniae== CC23
* pyogenic liver abscess
* urinary tract (==Proteus, Citrobacter==) infections
* blood infections
* ==Enterobacter==- top 10 in healthcare-related infections
* med. devices
* ==K. pneumoniae== CC23
* pyogenic liver abscess
20
New cards
E.coli vireulence factors
* Adhesions Endotoxin
* Capsule production
* Pili- attachment
* Capsule production
* Pili- attachment
21
New cards
Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, Providencia, and Serratia virulence factors
* Endotoxins
* Capsules
* Adhesion proteins
* Resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents (panresistant strains of K. pneumoniae)
* Capsules
* Adhesion proteins
* Resistance to multiple antimicrobial agents (panresistant strains of K. pneumoniae)
22
New cards
Enterotoxigenic (ETEC) infection
Traveler’s and childhood diarrhea (food and water)
23
New cards
Enterotoxigenic (ETEC) virulence factor
* Pili
* GI colonization
* Heat-liable
* Heat-stable Enterotoxins
* (secretion of water and • electrolytes into bowel)
* GI colonization
* Heat-liable
* Heat-stable Enterotoxins
* (secretion of water and • electrolytes into bowel)
24
New cards
Enteroinvasive (EIEC) infection
* Dysentery (necrosis, ulceration,inflammation of the bowel)
25
New cards
Enteroinvasive (EIEC) virulence factor
* Invade enterocytes lining large intestine (Shigella-like)
26
New cards
Enteropathogenic (EPEC) infection
* Diarrhea in infants
* Can cause chronic diarrhea
* Can cause chronic diarrhea
27
New cards
Enteropathogenic (EPEC) virulence factors
* Bundle-forming pilus
* intimin
* other factors that mediate attachment to mucosal cells of the small bowel (loss of microvilli)
* intimin
* other factors that mediate attachment to mucosal cells of the small bowel (loss of microvilli)
28
New cards
Enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) (STEC) infection
* Inflammation
* bleeding of the mucosa of the large intestine.
* Hemolytic-uremic syndrome possible (toxin)
* bleeding of the mucosa of the large intestine.
* Hemolytic-uremic syndrome possible (toxin)
29
New cards
Enterohemorrhagic (EHEC) (STEC) virulence factors
* Similar to Shiga toxin of Shigella.
* E. coli O157:H7
* E. coli O157:H7
30
New cards
Enteroaggregative (EAEC) infection
* Watery diarrhea (can be prolonged)
31
New cards
Enteroaggregative (EAEC) virulence factors
* Binding by pili.
* Shiga-like toxin
* hemolysin- like toxins.
* Shiga-like toxin
* hemolysin- like toxins.
32
New cards
Salmonella enterica Occurance
Only in humans/mammals (not normal flora)
33
New cards
Salmonella bongori occurance
Widely spread in nature (animals)
34
New cards
Salmonella bongori transmission
* Contaminated food processed from animals
* Fecal-oral route in healthcare setting when handwashing guidelines not followed
* Fecal-oral route in healthcare setting when handwashing guidelines not followed
35
New cards
Salmonella enterica transmission
• Fecal-oral route (Contaminated food and water)
36
New cards
Shigella sp. occurance
Only in humans/primates (not normal flora)
37
New cards
Shigella sp transmission
* Person-to-person
* Contaminated food or water
* Contaminated food or water
38
New cards
Yersinia sp occurance
Rodents-(Y. pestis) (not normal flora)
39
New cards
Yersinia sp. transmission
* Bite of flea vectors
* Pneumonic by airborne droplets
* Other Yersinia sp. by undercooked meat or contact with infected animals
* Pneumonic by airborne droplets
* Other Yersinia sp. by undercooked meat or contact with infected animals
40
New cards
Salmonella sp. infection
* Gastroenteritis and diarrhea where infection is limited to mucosa and submucosa of GI tract
* Bacteremia and extra-intestinal infections
* Enteric fever (typhoid) prolonged fever and multisystem involvement blood, lymph nodes, liver, & spleen
* Bacteremia and extra-intestinal infections
* Enteric fever (typhoid) prolonged fever and multisystem involvement blood, lymph nodes, liver, & spleen
41
New cards
Salmonella sp. virulence factors
* allow survival in and destruction of phagocytes, and facilitate spread.
42
New cards
Shigella sp. infection
Dysentery- defined by acute inflammatory colitis and bloody diarrhea characterized by:
* cramps
* bloody and mucoid stools
* cramps
* bloody and mucoid stools
43
New cards
Shigella sp. virulence
* escape from phagocytic vesicles.
* Intercellular spread and inflammation.
* Shiga toxin.
* Intercellular spread and inflammation.
* Shiga toxin.
44
New cards
Yersinia pestis infection
* Bubonic plague
* High fever and buboes proceeding to rapid and severe bacteremia
* Pneumonic plague
* Involves the lungs and characterized by malaise and pneumonia symptoms.
* Both are rapidly fatal.
* High fever and buboes proceeding to rapid and severe bacteremia
* Pneumonic plague
* Involves the lungs and characterized by malaise and pneumonia symptoms.
* Both are rapidly fatal.
45
New cards
Yersinia pestis virulence factor
* Many - Adapt for intracellular survival.
* Produce antiphagocytic capsule
* exotoxins
* endotoxins
* coagulase
* fibrinolysin
* Produce antiphagocytic capsule
* exotoxins
* endotoxins
* coagulase
* fibrinolysin
46
New cards
Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis infection
* Enterocolitis is characterized by fever, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
* Can cause acute mesenteric lymphadenitis (presents as appendicitis).
* Can cause acute mesenteric lymphadenitis (presents as appendicitis).
47
New cards
Y. enterocolitica, Y. pseudotuberculosis virulence factors
Encoded on a virulence plasmid which allows attachment and invasion of intestinal mucosa and spread to lymphatic tissue.
48
New cards
Microbiome:
\
the community of microorganisms (such as fungi, bacteria and viruses) that exists in a particular environment” (NHGRI – genome.gov)
the community of microorganisms (such as fungi, bacteria and viruses) that exists in a particular environment” (NHGRI – genome.gov)
49
New cards
Gut Microbiome roles
* Gut microbes known to convert bile salt and bile acids to unconjugated bile acids and secondary bile acids.
* Gut microbes ferment starch and other polysaccharides the host cannot process.
* Gut microbes produce short chain fatty acids and vitamins for the host.
* Help development of the naïve immune system.
* Can work with host functions and alter regulation of host responses
* Gut microbes ferment starch and other polysaccharides the host cannot process.
* Gut microbes produce short chain fatty acids and vitamins for the host.
* Help development of the naïve immune system.
* Can work with host functions and alter regulation of host responses
50
New cards
IBD
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis no identified pathogenic cause
51
New cards
Type I diabetes
\- flora affecting handling of nutrients in the intestine.
52
New cards
Antibiotics- (microbiome)
need to use more focused antibiotics (fidaxomicin- C. difficile). • Bacteriophage therapy
53
New cards
Probiotics-
* try to add back the “missing” important microbe.
* Often Lactobacillus and Bifiddobacterium.
* Yogurt and kefir- some effect on C. difficile infections
* Best results for acute gastroenteritis in children
* Often Lactobacillus and Bifiddobacterium.
* Yogurt and kefir- some effect on C. difficile infections
* Best results for acute gastroenteritis in children
54
New cards
Prebiotics and diet therapy-
* supply nutrients to favor growth of beneficial microbes.
* Generally non-digestable carbohydrates (microbe will digest)
* Best results seen with Crohn’s disease in children
* exclusive enteral nutritional (EEN) therapy
* Generally non-digestable carbohydrates (microbe will digest)
* Best results seen with Crohn’s disease in children
* exclusive enteral nutritional (EEN) therapy
55
New cards
Microbial restoration
* transplantation of an intact microbial community.
* FMT- fecal material transplant
* Shown very effective in C. difficile treatment.
* Not shown effective in treatment for IBD or obesity yet.
* FMT- fecal material transplant
* Shown very effective in C. difficile treatment.
* Not shown effective in treatment for IBD or obesity yet.
56
New cards
What organisms are + for MR test and VP?
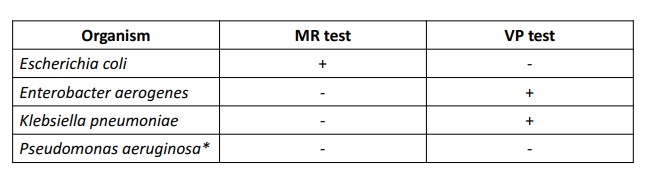
57
New cards
Lysine decarboxylase and ornithine decarboxylase test
* indicator is bromocresol purple and cresol red
* Works best when oxygen is excluded( hence mineral oil on top)
* enzyme removes a carboxyl group which leaves an alkaline end product
* Works best when oxygen is excluded( hence mineral oil on top)
* enzyme removes a carboxyl group which leaves an alkaline end product
58
New cards
Listeria monocytogenes found where
* Found in animals, birds, sewage, soil, milk, milk products, and vegetable matter.
* Found in the human GI tract and in the vagina of healthy humans
* Found in the human GI tract and in the vagina of healthy humans
59
New cards
Listeria disease is spread by:
In humans, the disease is spread by:
* Transmission- direct contact
* Ingestion of contaminated food (meat, vegetables, and diary)
* Transmission- direct contact
* Ingestion of contaminated food (meat, vegetables, and diary)
60
New cards
Listeria monocytogenes pathogenesis
* Bacteremia
* CNS infections- meningitis, encephalitis, spinal cord infections.
* Focal infections (endocarditis, arthritis, osteomyelitis, etc) is less common
* ==Neonatal==- Early- granulomatosis infantisepiticum (in utero infection disseminated systemically that causes stillbirth) -
* ==Late onset==- bacterial meningitis.
* CNS infections- meningitis, encephalitis, spinal cord infections.
* Focal infections (endocarditis, arthritis, osteomyelitis, etc) is less common
* ==Neonatal==- Early- granulomatosis infantisepiticum (in utero infection disseminated systemically that causes stillbirth) -
* ==Late onset==- bacterial meningitis.
61
New cards
Listeria virulence factors
* Listeriolysin O-hemolytic and cytotoxic toxin that allows survival within phagocytes
* Internalin- Cell surface protein that induces phagocytosis
* Act A- Induces actin polymerization on the surface of host cells
* Produces cellular extensions- facilitates cell-to-cell spread
* Siderophores- scavenges iron from human transferrin.
* Internalin- Cell surface protein that induces phagocytosis
* Act A- Induces actin polymerization on the surface of host cells
* Produces cellular extensions- facilitates cell-to-cell spread
* Siderophores- scavenges iron from human transferrin.
62
New cards
Vibrio species normal habitat
* Habitat- brackish or marine water
* Not part of the normal human flora
* Not part of the normal human flora
63
New cards
Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis
* profuse, watery diarrhea leading to dehydration, hypotension, and often death. (occurs in epidemics and pandemics)
* May cause nonepidemic diarrhea and occasionally extra-intestinal infections of wounds, septicemia, and eye and ear infections.
* May cause nonepidemic diarrhea and occasionally extra-intestinal infections of wounds, septicemia, and eye and ear infections.
64
New cards
Vibrio cholerae virulence factors
* Cholera toxin- causes mucosal cells to hyper-secrete water and electrolytes into the GI tract lumen Zot toxin
* accessory cholera toxin
* hemolysins/cytotoxins Motility and chemotaxis- mediate the distribution of the organisms
* Mucinase- allows penetration of the mucosal layer
* Toxin coregulated pili (TCP)- means by which the organism attaches to mucosal cells for cholera toxin release
* accessory cholera toxin
* hemolysins/cytotoxins Motility and chemotaxis- mediate the distribution of the organisms
* Mucinase- allows penetration of the mucosal layer
* Toxin coregulated pili (TCP)- means by which the organism attaches to mucosal cells for cholera toxin release
65
New cards
Acinetobacter sp occurance
* Widely distributed in nature (soil, water, food) including hospitals
* Can be found on skin
* UR tract in extended stay hospitalized patients
* Can be found on skin
* UR tract in extended stay hospitalized patients
66
New cards
Acinetobacter sp. transmission
* Medical instruments
* IV
* catheters
* IV
* catheters
67
New cards
Pseudomonas aeruginosa occurance
* Survives well in domestic and hospital environments
* Rarely found as normal flora
* Rarely found as normal flora
68
New cards
Pseudomonas aeruginosa occurance
* Survives well in domestic and hospital environments
* Rarely found as normal flora
* Rarely found as normal flora
69
New cards
Pseudomonas aeruginosa transmission
* Contaminated food and water
* Contaminated medical devices
* Introduced by penetrating wounds
* Contaminated medical devices
* Introduced by penetrating wounds
70
New cards
Pseudomonassp. occurance
* Environmental
* not normal flora
* not normal flora
71
New cards
Pseudomonas sp. transmission
Medical devices
72
New cards
Alcaligenessp occurance
* Soil and water
* Hospital environments
* Hospital environments
73
New cards
Alcaligenessp. transmission
* Contaminated medical devices
* solutions
* solutions
74
New cards
Acinetobacter sp disease
* Usually nosocomial
* During warm seasons
* Most commonly- genitourinary tract, respiratory tract, wounds, bacteremia
* During warm seasons
* Most commonly- genitourinary tract, respiratory tract, wounds, bacteremia
75
New cards
Pseudomonas aeruginosa disease
* Folliculitisotitis externa
* eye infections
* Following trauma
* osteomyelitis
* endocarditis
* Nosocomially RTI, UTI, wounds, bacteremia, and CNS infections
* eye infections
* Following trauma
* osteomyelitis
* endocarditis
* Nosocomially RTI, UTI, wounds, bacteremia, and CNS infections
76
New cards
Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors
* Exotoxin A
* endotoxins
* proteolytic enzymes
* alginate
* pilli
* Antimicrobial resistance
* endotoxins
* proteolytic enzymes
* alginate
* pilli
* Antimicrobial resistance
77
New cards
Pseudomonas sp. disease
Uncommon in UTI, RTI, wounds, and bacteremia
78
New cards
Alcaligenes sp. disease
* Usually immunocompromised patients
* Often a contaminant
* Found in blood, RT, and urine
* Often a contaminant
* Found in blood, RT, and urine
79
New cards
Oxidation-Fermentation Test
* Fermenters use pyruvate and NADH (from glycolysis) to produce acids that acidify medium (lowers pH)
* organisms that cannot use sugar may degrade amino acids alkalinizing medium (raises pH)
* Glucose oxidizers- in the absence of oxygen glucose cannot be utilized
* Fermentation generates more acid and will turn media more yellow than oxidation
* Contains bromthymol blue as pH indicator
\
* organisms that cannot use sugar may degrade amino acids alkalinizing medium (raises pH)
* Glucose oxidizers- in the absence of oxygen glucose cannot be utilized
* Fermentation generates more acid and will turn media more yellow than oxidation
* Contains bromthymol blue as pH indicator
\
80
New cards
The Enterotube II
* 15 biochemical tests
* (glucose, gas production, lysine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, H2S, indole, adonitol, lactose, arabinose, sorbitol, Voges-Proskauer, dulcitol, phenylalanine deaminase, urea and citrate)
* After 18 to 24 hours of incubation, interpret all reactions, with the exception of indole and VP.
* (glucose, gas production, lysine decarboxylase, ornithine decarboxylase, H2S, indole, adonitol, lactose, arabinose, sorbitol, Voges-Proskauer, dulcitol, phenylalanine deaminase, urea and citrate)
* After 18 to 24 hours of incubation, interpret all reactions, with the exception of indole and VP.
81
New cards
The API (Analytical Profile) 20E
* Biochemical panel for identification and differentiation of members of the family Enterobacteriaceae
* It holds 20 mini-test chambers containing dehydrated media having chemically-defined compositions for each test.
* They usually detect enzymatic activity, mostly related to fermentation of carbohydrate or catabolism of proteins or amino acids by the inoculated organisms.
* It holds 20 mini-test chambers containing dehydrated media having chemically-defined compositions for each test.
* They usually detect enzymatic activity, mostly related to fermentation of carbohydrate or catabolism of proteins or amino acids by the inoculated organisms.
82
New cards
Spores and toxins are killed using
bleach