BOTAONE Finals
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
170 Terms
Sexual reproduction
union of sperm and egg cell
progeny are genetically diverse
some are less adapted or more than parent
cannot colonize rapidly since not all are adapted for it
changes may affect some progeny but not all
isolated ones cannot reproduce
flowers
contain the organs and tissues angiosperms need for sexual reproduction
cones are equivalent structures in conifers
basically a stem with leaf-like structures
never become woody
secondary growth does not occur
asexual reproduction
producing progeny that are clones of themselves
progeny are as adapted as parent is
rapid colonization
all progeny may be adversely affected by change
even isolated can reproduce
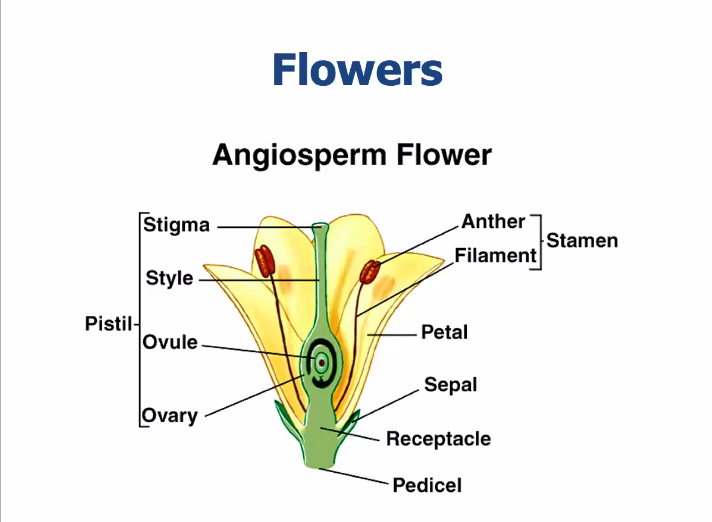
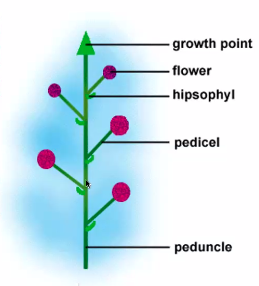
Flower parts
Pistil (stigma, style, ovule, ovary)
Stamen (anther, filament)
Petal
Sepal
Receptacle
Pedicel
pedicel
flower stalk
sepals
collectively, calyx
called reflect structure due to green color
lowermost and outermost of the four floral appendages
modified leaves that surround and enclose the other flower parts as they mature
typically the thickest, toughest, and waxiest of the flower parts
keeping bacterial and fungal spores away
maintaining a high humidity inside the bud
deterring insect feeding
colorful (petaloid) to help attract pollinators
petals
collectively, corolla
sepal or leaf like structures
Above the sepals on the receptacle
“leaf-like,” but they differ from leaves in that they contain pigments other than chlorophyll, have fewer or no fibers, and tend to be thinner and more delicately constructed
important in attracting correct pollinators
don’t develop in wind-pollinated species
seeds
produced within a fruit or a cone
have a means of long-distance dispersal (runners, rhizomes, plantlets)
pollen
complete plants
have less than a dozen cells, have no leaves, no roots, and no stems
carried by wind in many species and by water in a few
function of reproduction
producing offspring that have identical copies of the parental genes
generating new individuals that are genetically different from the parents
strawberries
have flowers and sexual reproduction involving genetically diverse embryos and seeds, but they also spread rapidly and asexually by runners
bamboos
perennial grasses that flower and set seed only occasionally (in some species, only once every 80 years), but their rhizomes grow vigorously and establish many new plants asexually.
Kalanchoes
produce large numbers of seeds each year, but they also produce such large numbers of plantlets along their leaf margins that they can be weeds in both nature and in greenhouses
fragmentation
large spreading or vining plant grows to several meters in length, and individual parts become self-sufficient by establishing adventitious roots.
bulbils
in some members of the saxifrage, grass, and pineapple families, plantlets are formed where flowers would be expected
these look like small bulbs
Adventitious buds
may grow out even while the parent plant is still alive, and a small cluster of trees may in fact consist of just a single individual
gametes
sex cells: egg and sperm cells
formed by the haploid plants by mitosis, not meiosis
zygote
fertilized egg
diploid
inherits mitochondria and a nucleus from the egg, a nucleus and plastids from the sperm cell
sporophytes
trees, shrubs, herbs
always diploid
have organs with cells capable of undergoing meiosis
spores
meiosis product
haploid
syngamy or fertilization
spores fusing with gametes
involves plasmogamy and karyogamy
plant spores
cannot undergo syngamy
undergo mitosis and grows into gametophyte
gametophyte
entire new haploid plant
produces gametes
does not resemble diploid sporophyte
tiny mass of cells with no roots, stems, leaves, or vascular tissues
plant life cycle
diploid sporophyte > meiosis > haploid spores > mitosis > haploid gametophyte > gametes > syngamy > diploid sporophyte
oogamy
sperms are produced by one type of individual and eggs by a different one
microgametophytes
male gametes
microspores > mitosis > vegetative cell + generative cell > 2 sperm cells
very small and simple, consisting of at most three cells located within the original pollen cell wall
megagametophytes
female gametes
from megaspores
has seven cells, one of which is binucleate
alternation of generation
with two generations: sporophyte and gametophyte
alternation of heteromorphic generations
gametophytes do not resemble sporophytes at all
complex life cycle, with at least three distinct plants (one sporophyte and two gametophytes)
human life cycle
receptacle
end of the axis
where other parts are attached
floral appendages
sepals
petals
stamens
carpels
complete flowers
have three, four, five or more appendages of each type
have sepals, petals, stamen, pistil
lilies
incomplete flowers
incomplete appendages
begonia
perianth
Sepals and petals together
stamen
collectively, androecium
above the petals
male part of the flower because they produce pollen
comprised of filament and anther that produce pollen
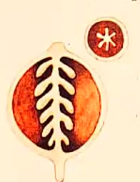
anther
composed of diploid cells
four columns of tissue become distinct as some cells enlarge and prepare for meiosis
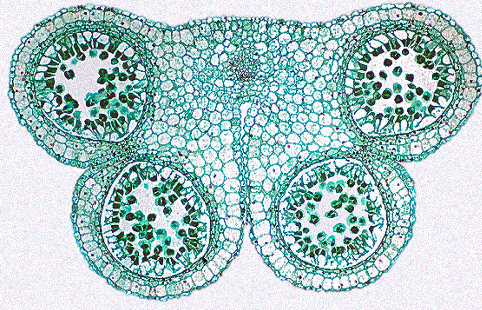
microsporocytes
microspore mother cells
anther cells that enlarge and undergo meiosis
tapetum
layer where neighboring anther cells act as nurse cells and contribute to microspore development and maturation
microspores
initially remain together in a tetrad, but later separate, expand to a characteristic shape, and form an especially resistant wall
becomes pollen
dehisce
opening of anther, releasing pollen
intine
inner layer of pollen grain wall
composed of cellulose
exine
outer layer of pollen grain wall
consists of polymer, sporopollenin
can have ridges, bumps, spines, and numerous other features so characteristic that
each species has its own particular pattern
germination pores
weak spots in pollen grain wall where pollen opens after it had been carried to stigma of another flower
Sporopollenin
remarkably waterproof and resistant to almost all chemicals;
it protects the pollen grain and keeps it from drying out as it is being carried by wind or animals
carpel
collectively, pistil
highest level on receptacle
stigma, style, ovary
stigma
catches pollen
style
elevates stigma to useful position
ovary
where megaspores are produced
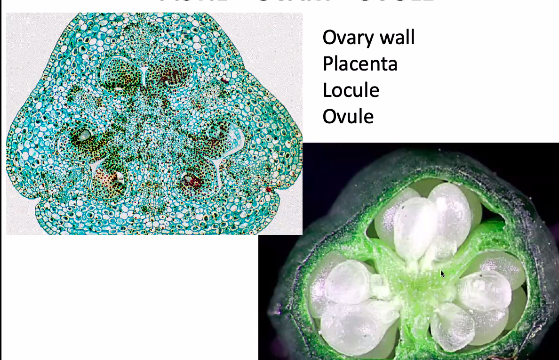
pistil
collectively, gynoecium
carpels fused together into single compound structure
placentae
regions of tissue inside ovary that bear small structures
ovules
small structures inside placentae
have a short stalk (funiculus) that carries water and nutrients from placenta to the ovule via vascular bundle
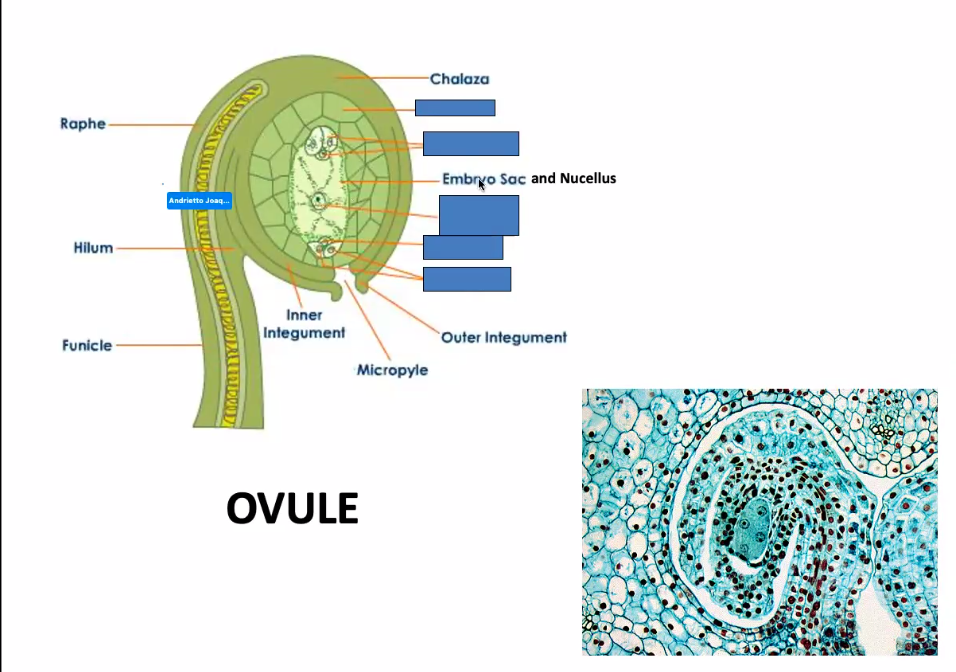
nucellus
ovule’s central mass of parenchyma
Around this are two thin sheets of cells (integuments) that cover almost its entire surface, leaving only a small hole (micropyle) at the top
megasporocytes
megaspore mother cells in nucellus
do not dehisce and megaspore remains inside the carpel
raceme
major inflorescence axis, and the flowers are borne on pedicels that are all approximately the same length

panicle
branched raceme with several flowers per branch.

corymb
Flowers in a flat or slightly rounded cluster with varying stem lengths.
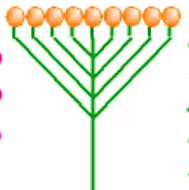
spike
similar to a raceme except that the flowers are sessile, lacking a pedicel

umbel
inflorescence stalk ends in a small rounded portion from which arise numerous flowers
Their pedicels are long and arranged so that all flowers sit at the same height, forming a flat disk.
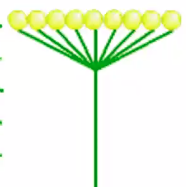
head
similar to an umbel except that the flowers are sessile and attached to a broad expansion of the inflorescence stalk

compound umbel
Umbel where each main stem ends in another smaller umbel
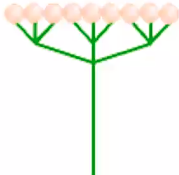
cyme
Flat or round cluster with central flowers blooming first
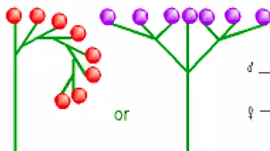
spadix
spikelike inflorescence with imperfect flowers, but both types occur in the same inflorescence, most often with staminate flowers located in the upper portion of the inflorescence and carpellate flowers in the lower portion, although they can intermingle.
The main inflorescence axis is thick and fleshy with minute flowers embedded in it
multiple flowers parts
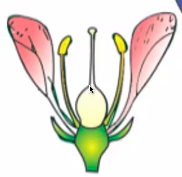
perfect flowers
have both male and female reproductive structures within the same flower
imperfect flowers
lack one of the reproductive structures, either male or female.
monoecious plants
have both male and female flowers on the same individual plant
dioecious plants
have separate male and female plants
polypetalous
multiple petals
apopetalous
separate petals
apetalous
no petals
gamopetalous
fused petals
bracts
modified leaf that protects flower
hypogynous or superior
perigynous or hemi-inferior
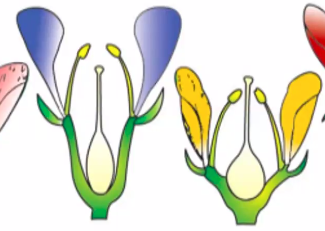
epigynous or inferior

actinomorphic or regular flower
has radial symmetry
zygomorphic or irregular flower
has bilateral symmetry
bilabiate flower
two-lipped flower
has fused calyx and corolla tube
papilionaceous flower
for legumes
has banner, wings, keels
banner
outermost and largest part of flower
wings
lateral parts
aka alae
keels
two innermost and smallest petal
aka carinae
orchidaceous flower
has wings, and lip which helps identify species
composite flowers
cluster of small individual flowers grouped together to form a single, larger flower-like structure
ray flower
outermost flower in composite flowers
resemble petals
disc flowers
central tubular-shaped flowers within composite flower head
consists of a tubular corolla with five fused petals and reproductive structures
rachis
central axis of a flower cluster
central stalk of a compound leaf, from which the leaflets are attached
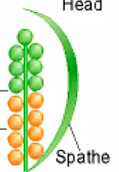
spathe
large, often leaf-like bract that surrounds or encloses a flower cluster or inflorescence
serves for protection, attraction, temperature regulation, and odor emission
pollination
transfer of pollen from male anther to female stigma
abiotic pollen vectors
anemophily
hydrophily
anemophily
wind pollination
reduced perianth
synchronous flowering
pollen storage - starch
hydrophily
water pollination
surface
submerged
entomophily
pollination via insects (bees, beetles, butterflies, flies)
chiropterophily
pollination via bats
ornithophily
pollination via birds
placentation
how ovules are attached to placenta
parietal
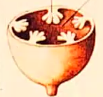
marginal
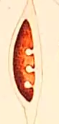
axile
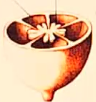
free central