Chapter 14: Trigonometry
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Trigonometric identities, basic rules, drawing graphs, etc.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Radians and Conversion between Radians/Degrees
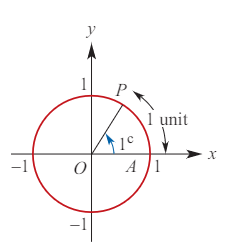
Angles are positive when measured anticlockwise and negative when measured clockwise. One radian (1c) is the angle subtended at the center of a unit circle by an arc of length 1 unit.
Conversions:
Degrees → Radians: Multiply by π/180.
Radians → Degrees: Multiply by 180/π.
Note: 1 radian ≈ 57.3. Arc length = radius x θ!
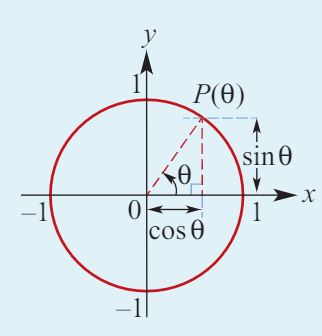
Defining Sin/Cos using Unit Circle
The coordinates of a point P(θ) on the unit circle are given by:
x = cos(θ)
y = sin(θ)
Thus, P(θ) = (cos(θ), sin(θ)).
Key Properties:
cos(2π + θ) = cos(θ), sin(2π + θ) = sin(θ) (periodicity).
At θ = π, P(π) = (-1,0) → cos(π) = -1, sin(π) = 0.
If θ is an odd multiple of π/2, sine is ±1 and cosine is 0.
If θ is an even multiple of π, cosine is ±1 and sine is 0.
Defining Tan using Unit Circle
The tangent of an angle θ is given by:
tan(θ) = sin(θ) / cos(θ)
Tan(θ) is undefined when cos(θ) = 0, i.e., at θ = ±π/2, ±3π/2, etc.
The domain of tan(θ) is R \ {θ : cos(θ) = 0}.
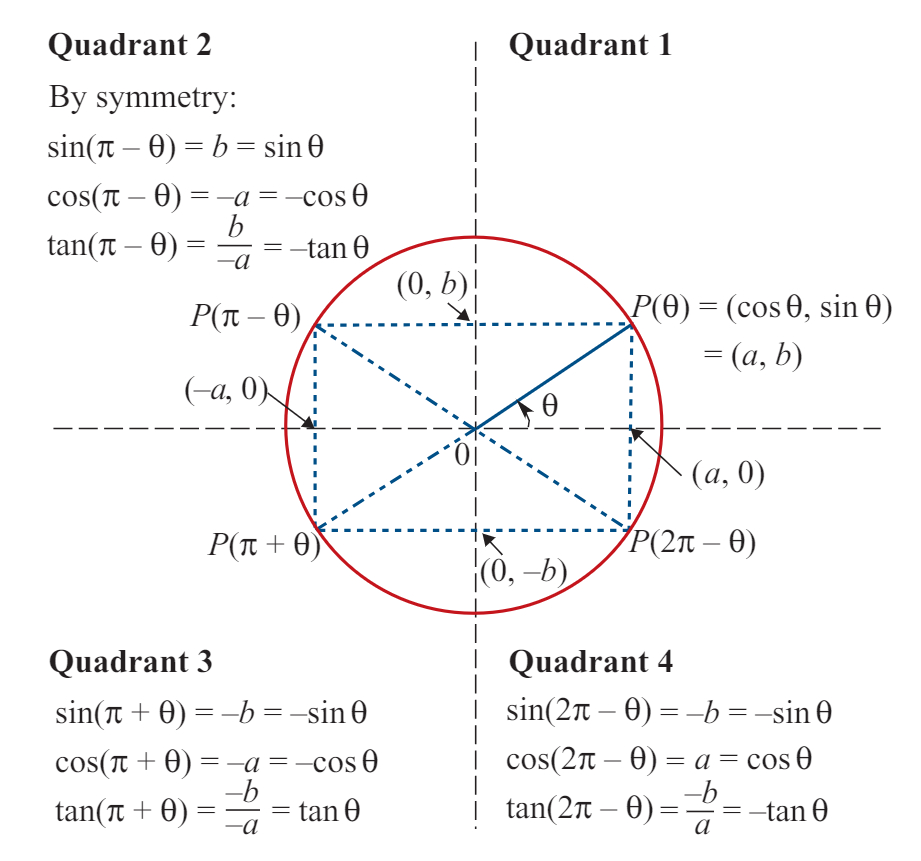
Key Symmetry Properties of Trigonometric Functions
Key Symmetry Properties
Second Quadrant (π - θ)
sin(π - θ) = sin(θ)
cos(π - θ) = -cos(θ)
tan(π - θ) = -tan(θ)
Third Quadrant (π + θ)
sin(π + θ) = -sin(θ)
cos(π + θ) = -cos(θ)
tan(π + θ) = tan(θ)
Fourth Quadrant (2π - θ)
sin(2π - θ) = -sin(θ)
cos(2π - θ) = cos(θ)
tan(2π - θ) = -tan(θ)
Negative Angles
sin(-θ) = -sin(θ)
cos(-θ) = cos(θ)
tan(-θ) = -tan(θ)
Signs of Circular Functions in Quadrants
1st Quadrant (0 to π/2): All functions are positive.
2nd Quadrant (π/2 to π): Only sin is positive.
3rd Quadrant (π to 3π/2): Only tan is positive.
4th Quadrant (3π/2 to 2π): Only cos is positive.
Mnemonic: "All Students Take Calculus"
(A = All, S = Sin, T = Tan, C = Cos)
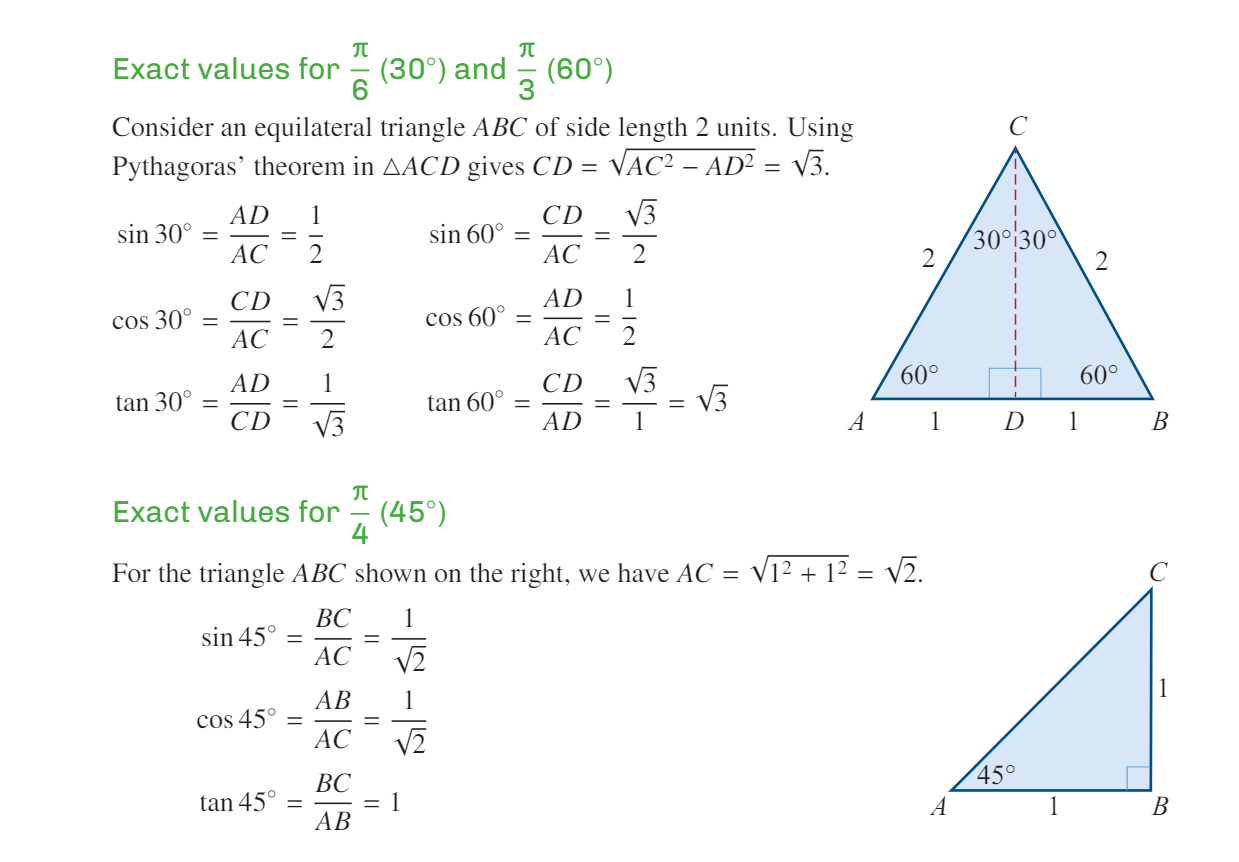
Exact values for Trig Functions
θ | sin(θ) | cos(θ) | tan(θ) |
|---|
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
π/6 (30°) | 1/2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 |
π/4 (45°) | √2/2 | √2/2 | 1 |
π/3 (60°) | √3/2 | 1/2 | √3 |
π/2 (90°) | 1 | 0 | undef |
Wavelength, Period and Amplitude
A function which repeats itself regularly is called a periodic function, and the interval between the repetitions is the period of the function (also called the wavelength).
The distance between the ‘mean position’ and the maximum position is the amplitude.
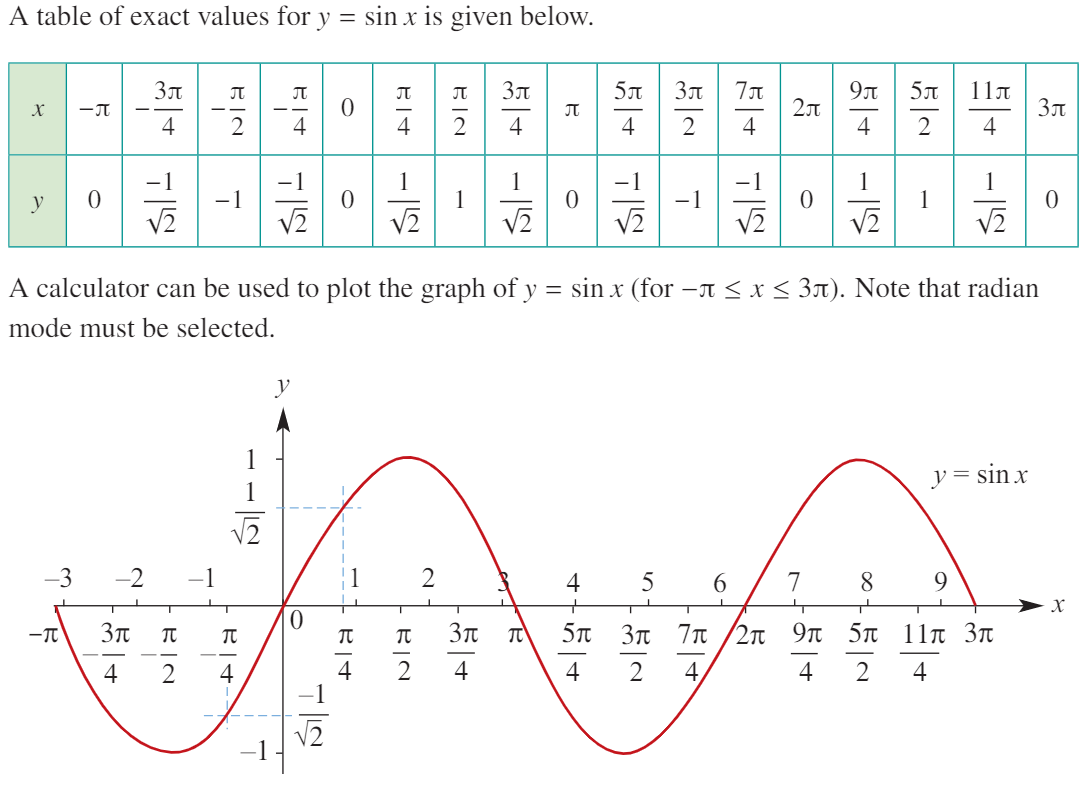
y = sin (x)
Period: 2π (the graph repeats every 2π units).
Amplitude: 1 (distance from the mean position to the maximum).
Maximum value: 1, Minimum value: -1.
Starts at: (0,0) (sin 0 = 0)
y = cos (x)
Period: 2π (the graph repeats every 2π units).
Amplitude: 1 (distance from the mean position to the maximum).
Maximum value: 1, Minimum value: -1.
Starts at: (0,1) (cos 0 = 1)
y = a sin (nt)
Obtained from y = sin (x)
Amplitude: a
Period: 2π / n
Transformation from y = sin t:
Dilation of factor a from the t-axis (affects amplitude).
Dilation of factor 1/n from the y-axis (affects period).
Maximal Domain: R
Range: [-a, a]
Starts at (0,0)
y = a cos (nt)
Obtained from y = cos (x)
Amplitude: a
Period: 2π / n
Transformation from y = sin t:
Dilation of factor a from the t-axis (affects amplitude).
Dilation of factor 1/n from the y-axis (affects period).
Maximal Domain: R
Range: [-a, a]
Starts at (0,1)
Special: Reflection of a sin or cos (nt)
Reflection in the y-axis:
y = cos x becomes y = -cos x (starts at (0,-1), from W to M)
y = sin x becomes y = -sin x (starts at (0,0) but go from ~ to reversed ~)
The point with coordinates (t, y) is mapped to the point with coordinates (t/n, ay).
Solving Trigonometric Equations Steps
Steps:
Isolate the Trig Function as needed;
Adjust domain as needed;
Use the inverse function to find the principal angle:
t = sin⁻¹(a), t = cos⁻¹(a), or t = tan⁻¹(a).
Adjust for the quadrant based on the sign of the trig function.
Reference angle:
1st Quadrant: θ
2nd Quadrant: π - θ
3rd Quadrant: π + θ
4th Quadrant: 2π - θ
General Solution:
sin(t) = b → t = θ + 2kπ or t = π - θ + 2kπ
cos(t) = b → t = ±θ + 2kπ
tan(t) = b → t = θ + kπ
Solve sin θ = 1/2 for 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π.
θ = π/6 (1st quadrant)
θ = π - π/6 = 5π/6 (2nd quadrant)
Solutions: θ = π/6, 5π/6
Solving Trigonometric Functions Example: tan(2x - π/4) + 1 = 0, where x ∈ [0, π]
Find the reference angle:
The reference angle for tan(θ) = -1 is:
θ = π/4.Set the domain for 2x - π/4:
The equation becomes:
-π/4 ≤ 2x - π/4 ≤ 7π/4.
Therefore,
2x ∈ [-π/4, 7π/4].Identify the quadrants where tan(θ) = -1:
Since the tangent is negative, the solutions lie in the 2nd and 4th quadrants.Possible angles:
The possible angles are:
-π/4 (4th quadrant),
3π/4 (2nd quadrant),
7π/4 (4th quadrant).Solve for x:
For 2x - π/4 = -π/4,
x = 0.For 2x - π/4 = 3π/4,
x = π/2.For 2x - π/4 = 7π/4,
x = π.
Solving Trigonometric Equations: Hints
If sin(x) = a cos(x), then get it to tan(x) = a by dividing both sides by cos(x).
If sin²(x) = a, then sin(x) = ±√a.
If a sin²(x) + b sin(x) + c = 0, use substitution (e.g., u = sin(x)) to transform it into a quadratic equation a u² + b u + c = 0.
Example:
Solve cos²(x) + cos(x) − 2 = 0, where x ∈ [0, 2π].
Let a = cos(x).
Then the equation becomes:
a² + a − 2 = 0
Factor: (a − 1)(a + 2) = 0
So, a = 1 or a = −2
Now back-substitute:
cos(x) = 1 or cos(x) = −2
cos(x) = 1 → x = 0 or 2π
cos(x) = −2 → reject, since cos(x) ∈ [−1, 1]
Final Answer:
x = 0, 2π
Solving a sin(nt) = b and a cos(nt) = b
First, substitute x = nt.
Work out the interval in which solutions for x are required.
Rewrite as sin(nt) = b/a or cos(nt) = b/a.
Solve for x first, then divide by n to get t.
Extend solutions using periodicity.
Example:
Solve 2sin(2θ) = -√3 for -π ≤ θ ≤ π.
Rewrite: sin(2θ) = -√3/2.
Substituting x = 2θ: Find solutions for x.
Principal solutions: x = 4π/3, 5π/3.
Divide by 2:
θ = 2π/3
θ = 5π/6
Graphs of y = a sin n(t ± ε) and y = a cos n(t ± ε)
Translations: The term ±ε shifts the graph horizontally along the t-axis. (They are translations of the graphs of
y = a sin(nt) and y = a cos(nt) respectively.)
(t - ε) shifts right by ε.
(t + ε) shifts left by ε.
Transformations:
Amplitude = |a| (vertical stretch/shrink).
Period = (2π/n) (horizontal stretch/shrink).
Phase Shift = ±ε (horizontal translation).
Graph Shape: The shape remains the same but is transformed accordingly.
Examples
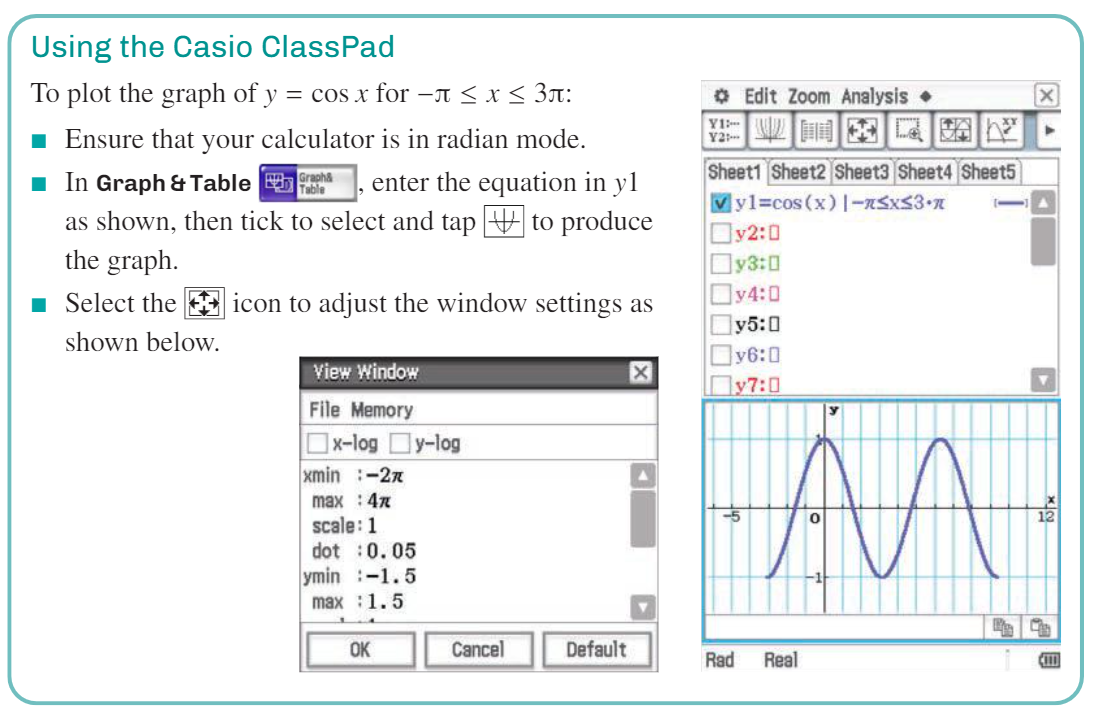
✅ Example 1: y = 3 sin(2t - π/4)
Amplitude = 3, Period = π
Phase shift: Right by π/4
Translations and Transformations for y = a sin(nt ± ε) ± b and y = a cos(nt ± ε) ± b
Translations:
±ε shifts the graph horizontally:
(t - ε) shifts right by ε.
(t + ε) shifts left by ε.
±b shifts the graph vertically:
+b shifts up by b.
-b shifts down by b.
Transformations:
Amplitude: [b-a,b+a] (vertical stretch/shrink)
Period: (2π/n) (horizontal stretch/shrink)
Phase Shift: ±ε (horizontal translation)
Vertical Shift: ±b (vertical translation)
Graph Shape: The shape remains the same but is transformed accordingly.
Example:
y = 3 sin(2t - π/4) + 2
Amplitude: 3, Period: π
Phase shift: Right by π/4
Vertical shift: Up by 2
![<p><strong>Translations:</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>±ε</strong> shifts the graph <strong>horizontally</strong>:</p><ul><li><p><strong>(t - ε)</strong> shifts <strong>right</strong> by ε.</p></li><li><p><strong>(t + ε)</strong> shifts <strong>left</strong> by ε.</p></li></ul></li><li><p><strong>±b</strong> shifts the graph <strong>vertically</strong>:</p><ul><li><p><strong>+b</strong> shifts <strong>up</strong> by b.</p></li><li><p><strong>-b</strong> shifts <strong>down</strong> by b.</p></li></ul></li></ul><p><strong>Transformations:</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>Amplitude:</strong> <strong>[b-a,b+a]</strong> (vertical stretch/shrink)</p></li><li><p><strong>Period:</strong> <strong>(2π/n)</strong> (horizontal stretch/shrink)</p></li><li><p><strong>Phase Shift:</strong> <strong>±ε</strong> (horizontal translation)</p></li><li><p><strong>Vertical Shift:</strong> <strong>±b</strong> (vertical translation)</p></li><li><p><strong>Graph Shape:</strong> The shape remains the same but is transformed accordingly.</p></li></ul><div data-type="horizontalRule"><hr></div><p><strong>Example:</strong><br><strong>y = 3 sin(2t - π/4) + 2</strong></p><ul><li><p><strong>Amplitude:</strong> 3, <strong>Period:</strong> π</p></li><li><p><strong>Phase shift:</strong> <strong>Right</strong> by π/4</p></li><li><p><strong>Vertical shift:</strong> <strong>Up</strong> by 2</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/779455cb-2145-4fec-ae43-51f0279f1e82.png)
Sketching y = a sin(n(x - h)) + k or y = a cos(n(x - h)) + k
Amplitude = [k-a, k+a], Period = 2π/n
Draw equilibrium line at y = k
Shift horizontally by h, endpoints adjusted by n
Divide one period into 4 equal sections (5 key points: 0, ±1)
Match domain if given
Plot & connect smoothly
Example: Sketch y = cos(2(x + π/3)), Domain: 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π
Period = π, Amplitude = 1, Line at y = 0
Endpoints of the first cycle:
From 0: -π/3, From π: 2π/3 (since one cycle spans from 0 to π, 0-π/3 = -π/3, π -π/3 = 2π/3)
Critical points:
-π/3, -π/12, π/6, 5π/12, 2π/3 (original points 0, π/2, π, 2π divided by 2, with each interval increasing by π/4 (+pi/2 divided by 2 = pi/4 increments) from the endpoints)
Domain is 0 ≤ x ≤ 2π, so ignore -π/3 and -π/12
Connect the points and adjust endpoints at x = 0 and x = 2π
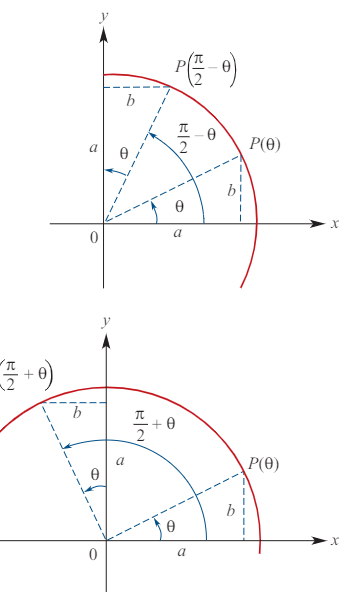
Complementary Relationships
From the diagram, we have the following complementary relationships:
sin(π/2 − θ) = cos(θ)
cos(π/2 − θ) = sin(θ)
Similarly:
sin(π/2 + θ) = cos(θ)
cos(π/2 + θ) = −sin(θ)
Example:
Given sin(θ) = 0.3 and cos(α) = 0.8, find:
cos(π/2 − α) = 0.8
sin(π/2 − α) = cos(α) = 0.8
Full table (inc. Tan):
Angle | cos(θ) | sin(θ) | tan(θ) |
|---|---|---|---|
π/2−θ | sin(θ) | cos(θ) | cot(θ) |
π/2+θ | -sin(θ) | cos(θ) | -cot(θ) |
3π/2−θ | -sin(θ) | -cos(θ) | cot(θ) |
3π/2+θ | sin(θ) | -cos(θ) | -cot(θ) |
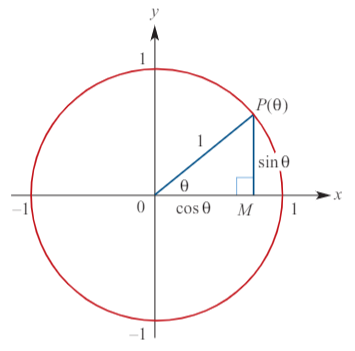
Pythagorean Identity
Consider a point P(θ) on the unit circle. By Pythagoras' theorem:
OP² = OM² + MP² → 1 = (cos(θ))² + (sin(θ))²
Thus, we have the Pythagorean identity:
cos²(θ) + sin²(θ) = 1
Pythagorean Identity Questions: Solving
Identify Quadrant
Draw triangle to identify unknown angles
Find values.
Example:
Given that cos(x) = -1/3 and π ≤ x ≤ 3π/2, we need to find sin(x) and tan(x).
Step 1: Use the Pythagorean Identity
The Pythagorean identity is:
sin²(x) + cos²(x) = 1
Substitute cos(x) = -1/3 into the identity:
sin²(x) + (-1/3)² = 1
sin²(x) + 1/9 = 1
Now, solve for sin²(x):
sin²(x) = 1 - 1/9
sin²(x) = 9/9 - 1/9 = 8/9
Take the square root of both sides:
sin(x) = ±√(8/9) = ±2√2/3
Since π ≤ x ≤ 3π/2 (third quadrant), sin(x) is negative, so:
sin(x) = -2√2/3
Step 2: Find tan(x)
We know that:
tan(x) = sin(x) / cos(x)
Substitute the values of sin(x) = -2√2/3 and cos(x) = -1/3:
tan(x) = (-2√2/3) / (-1/3) = 2√2
Final Answer:
sin(x) = -2√2/3
tan(x) = 2√2
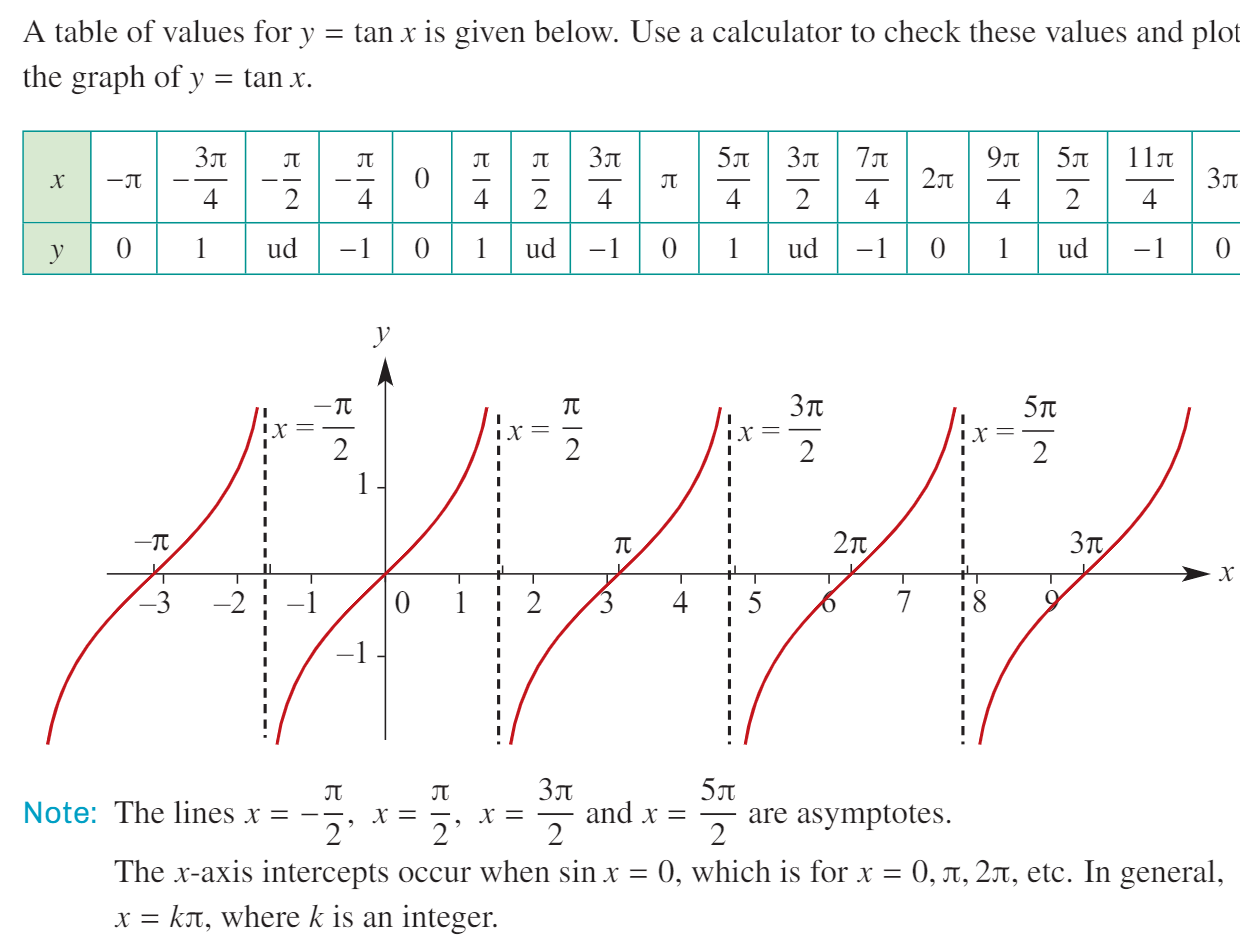
The tangent function
Transformation: y = a tan(nt)
Dilation by factor a from the t-axis (vertical scaling).
Dilation by factor 1/n from the x-axis (horizontal scaling).
Period: π/n.
Asymptotes: t = (2k + 1)π / (2n), where k is an integer.
Intercepts: The t-axis intercepts are t = kπ / n, where k is an integer.
Range is R.
Axis intercepts: find using solving tangent equation within a certain range.
Steps to sketch:
Find the Period:
→ Period = π / |n|Locate the First Asymptote:
→ Based on the shape (e.g. increasing for tan), start with the first vertical asymptoteFind All Asymptotes:
→ Each one is π / |n| apart, first at x = ±π / (2n) from y-axisFind First X-Intercept:
→ Add π / (2n) to the first asymptote
Solving Tangent Equations
Start with the equation:
tan(2x) = √3Solve for 2x:
The general solution for tan(θ) = √3 is:
θ = π/3 + kπ, where k is an integer.So, for tan(2x) = √3:
2x = π/3 + kπSolve for x:
Divide both sides by 2:
x = π/6 + kπ/2, where k is an integer.
Optional: General solutions for Trigonometric Functions (Recap from 9 SEAL Extension)
For a ∈ [−1, 1], the general solution of the equation cos x = a is:
x = 2nπ ± cos−1(a), where n ∈ Z
For a ∈ R, the general solution of the equation tan x = a is:
x = nπ + tan−1(a), where n ∈ Z
For a ∈ [−1, 1], the general solution of the equation sin x = a is:
x = 2nπ + sin−1(a) or x = (2n + 1)π − sin−1(a), where n ∈ Z