Biology 2024
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
DNA Replication
The process by which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA before cell division.
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds and separates the two strands of DNA during replication.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the exposed strands of DNA during replication.
Chromosome
A structure made of DNA coiled around proteins (histones) that carries genetic information.
Chromatid
One of the two identical halves of a duplicated chromosome.
Centromere
The region where two sister chromatids are joined together in a chromosome.
Daughter Cells
The new cells that are produced as a result of cell division, containing identical DNA to the parent cell.
Parent Cell
The original cell that divides to produce daughter cells.
Cell Cycle
The series of phases that a cell goes through to grow and divide.
Nucleotides
The building blocks of DNA, consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Template Strand
The original DNA strand that serves as a guide for the synthesis of a new complementary strand during replication.
Chromatin
The material that makes up chromosomes, consisting of DNA and proteins, in a less condensed form.
Non-Dividing Cell
A cell that is not currently undergoing division, typically containing a single chromatid per chromosome.
Why do cells divide?
In order for your body to grow, replace old, damaged and dead cells
Cell division
The amount of DNA in the new cells produced, called the daughter cells needs to be an exact copy of the DNA in the original cell, called the parent cell
Mitosis
The process of division of the nucleus of a cell in which the two daughter nuclei have the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent nucleus
Interphase
This is the phase of a cell in which normal functioning and growth occurs
The four stages of cell division
PMAT
Prophase (early)
Centrioles become visible and migrate to the poles of the cell and start to produce spindle fibres. Spindle fibers grow towards the chromosomes.
Prophase (late)
Nuclear membrane breaks down and the chromosomes become visible in the cytoplasm. Chromosomes move towards the equator (center) of the cell.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up on the equator. Spindle fibres attach to the centromere of each chromosome
Anaphase
Spindle fibres contract towards the centrioles. The chromosome are are separated at eh centromere and the chromatids are pulled towards the poles of the cell.
Telophase
The nuclear membrane reforms
Cytokinesis
The cell membrane and cytoplasm split into two new cells
Outcome of mitosis
Two new daughter cells are formed that are exact copies of the parent and have the same number of chromosomes as the parent.
A chromatid
One singular strand of a chromosome
Centromere
Where the chromosomes are joined
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic Acid, a chemical substance that carries the genetic information that determines the structure of the cell and the way it functions.
Where is DNA found?
Mitochondria and nucleus of a cell
Nucleotides
Make up DNA, a monomer
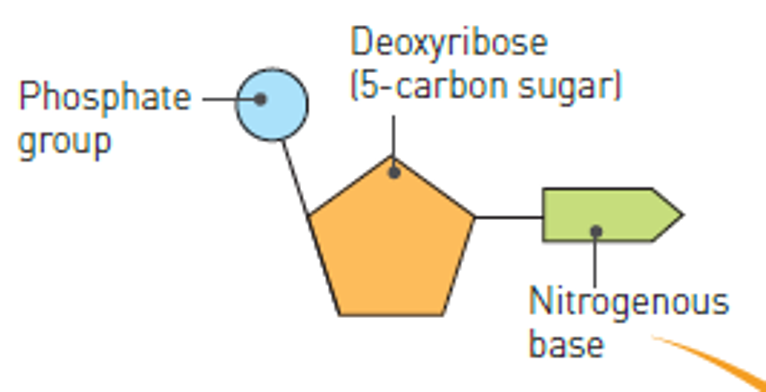
What are nucleotides made of?
A phosphate group, a sugar and a nitrogenous base.
The different nitrogenous bases
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Uracil (U; only in mRNA)
A
Adenine
T
Thymine
C
Cytosine
G
Guanine
U
Uracil
Complementary base bonding
A with T and C with G
Protein synthesis
The order of base pairings represent a code for making proteins.
Structure of DNA
Double helix
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model for DNA
Why do living things grow?
Because cells are dividing to produce more and more cells.
The first step of cell division
DNA replication, where the two linked chains of DNA molecules seperate or unzip controlled by the enzyme DNA helicase.
Allele
An allele is an alternative form/ variation of a gene. Each chromosome contains alleles, or different variations of the same gene.
How many chromosomes do you get from your mother and father respectively?
23 and 23
Chromosomes in homologous pairs:
Are the same shape and size and carry genes controlling the same traits
Gregor Mendel
First came up with this idea of offspring inheriting genes from their parents and concluded genes exist in pairs, (one from each parent) and they can separate and form pairs again in the next generation.
Dominant allele
A dominant allele will mask the trait of a recessive allele if it is present.
Recessive allele
A recessive allele will only be expressed if a dominant allele is not present
HH
Straight hair, homozygous. Offspring only have straight hair.
Hh
Straight hair, heterozygous. Offspring could have both straight or curly hair.
hh
Curly hair, homozygous. Not all offspring may have curly hair.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism; The gene (or allele) combination an organism has.
Phenotype
The physical characteristics of an organism.
Homozygous
Term used to refer to an organism that has two identical alleles for a particular trait.
Heterozygous
Term used to refer to an organism that has two different alleles for the same trait
Monohybrid cross
In a monohybrid cross two plants or animals, which differ at only one gene, are bred together. It is a simplified model that helps predict outcomes of breeding
Punnet Square
Diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross, used to calculate the probability of inheriting a particular trait
If two parents are homozygous for a genetically inherited recessive trait (that they have), what is the probability that they will have a child who does not have this trait in his or her phenotype. Use the letters “G” and “g” to represent the alleles for this gene.
0%
Black fur(B) in guinea pigs is dominant over white fur(b). Find the probability of a white offspring in a cross between two heterozygous guinea pigs.
25%
A brown eyed mother is heterozygous for eye colour. Her partner has blue eyes. If the couple have 6 children, how many of them are likely to have blue eyes?
3 of 6
Body cells
In a body cell, and one which has undergone mitosis, it has a diploid number of chromosomes, referred to as 2n where n is the the number of different chromosomes.
Gamete cells
In a gamete (sperm or egg cell) there is a haploid number of chromosomes, referred to as n.
Meiosis
Meiosis is the process of cell division that produces the gametes (sperm and ova).
Aim of meiosis
To produce haploid cells, from diploid body cells, so that they can go on to meet another haploid cell in fertilization and become a diploid cell.
Two major events in meiosis
First meiotic division and second meiotic division
Stages of meiosis 1 (first division)
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase