Part 2. Internal Regulation (Hunger and Thirst)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What percent of the mammalian body does water constitute?
70%
Vasopressin/anti-diuretic hormone
Raises blood pressure by constricting blood vessels
Helps to compensate for decreased water volume
Enables the kidneys to reabsorb water and excrete highly concentrated urine
What is vasopressin also known as?
Anti-diuretic hormone
Diuretic
Increasing the passing of urine
Osmotic thirst
Caused by eating salty foods
Hypovolemic thirst
A thirst resulting from loss of fluids due to bleeding or sweating
Why do salty foods makes one thirsty?
Because salty foods increase solute concentration outside the cell, so water leaves the cell to balance it out
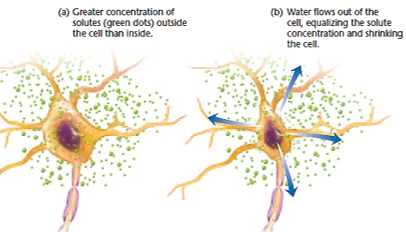
What is the set-point of solutes in mammals?
0.15 M (molar)
What receptors around the third ventricle detect osmotic pressure?
OVLT (organum vasculosum laminae terminalis)
Subfornical organ (SFO)
NOTE: Peripheral receptors, such as in the stomach and digestive track also exist.

What three areas of the hypothalamus do the OVLT, SFO, stomach and like organs send signals too?
Supraoptic nucleus
Paraventricular nucleus
Lateral preoptic area
What do the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei control?
The release of vasopressin
What does the lateral preoptic area control?
Drinking
What happens when blood volume is low?

Cause, reliever, and receptor location of osmotic thirst

Cause, reliever, and receptor location for hypovolemic thirst
Animals with hypovolemic thirst prefer slightly salty fluids, like Gatorade, as such fluids compensate for sodium, potassium, and carbohydrates lost in the blood

What amino acid is Turkey supposed to release that makes you sleepy?
Tryptophan
What smaller molecule is food broken down into for cells to use?
Glucose
Three key facts about glucose
Main product of digestion
Important source of energy for the body
Nearly the only fuel used by the brain
Where does excess glucose go?
The liver and fat cells
Insulin
Causes the body to store glucose
Glucagon
Stimulates the liver to convert some of its stored glycogen to glucose
What organ releases insulin and glucagon?
The pancreas
Two main body parts that tell us we’re full
The vagus nerve
The duodenum
The vagus nerve
Conveys information about the stretching of the stomach walls to the brain
Duodenum
Distention of the duodenum can produce feelings of satiety, and it also releases CCK, a satiety hormone
Leptin
A hormone released by fat cells in proportion to their volume which signals your brain about your fat reserves
What happens when your fat reserves decrease?
Leptin levels decrease, causing your appetite to increase
Does increase leptin automatically increase hunger?
Not necessarily, as obese people are often less sensitive to leptin
Hypothalamic transmitters of feeding
See paper flashcards

Three hypothalamic feeding areas (in order)
Arcuate nuclei — paraventricular nucleus — lateral nuclei
Orexin
(From lateral nuclei) a neurotransmitter that increases wakefulness and arousal
Ghrelin
(Acts on the stomach and arcuate nuclei) A neurotransmitter that promotes hunger and stimulates eating
Melanocortin
(Between arcuate nuclei and paraventricular nucleus)
A neurotransmitter that works to limit appetite