lab final review
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
What isnt a haedy winberg assumption
Small population
What method could you not use for concepts if your animal dies
Biological
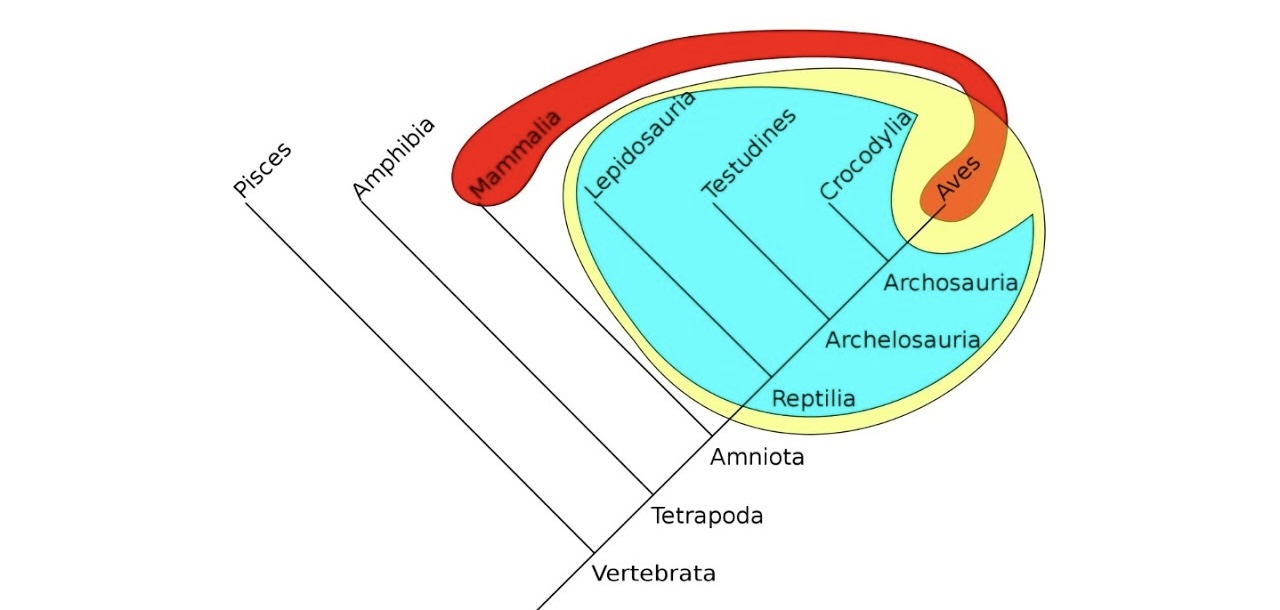
What does red show
Polyphyly
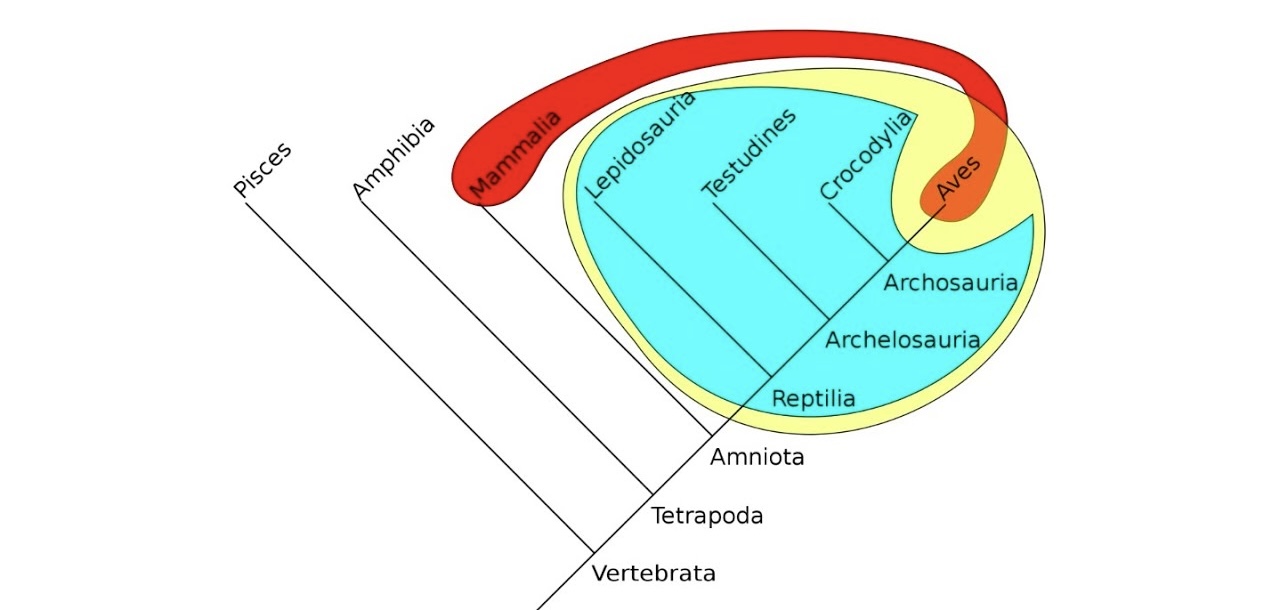
What does cyan show
Paraphyly
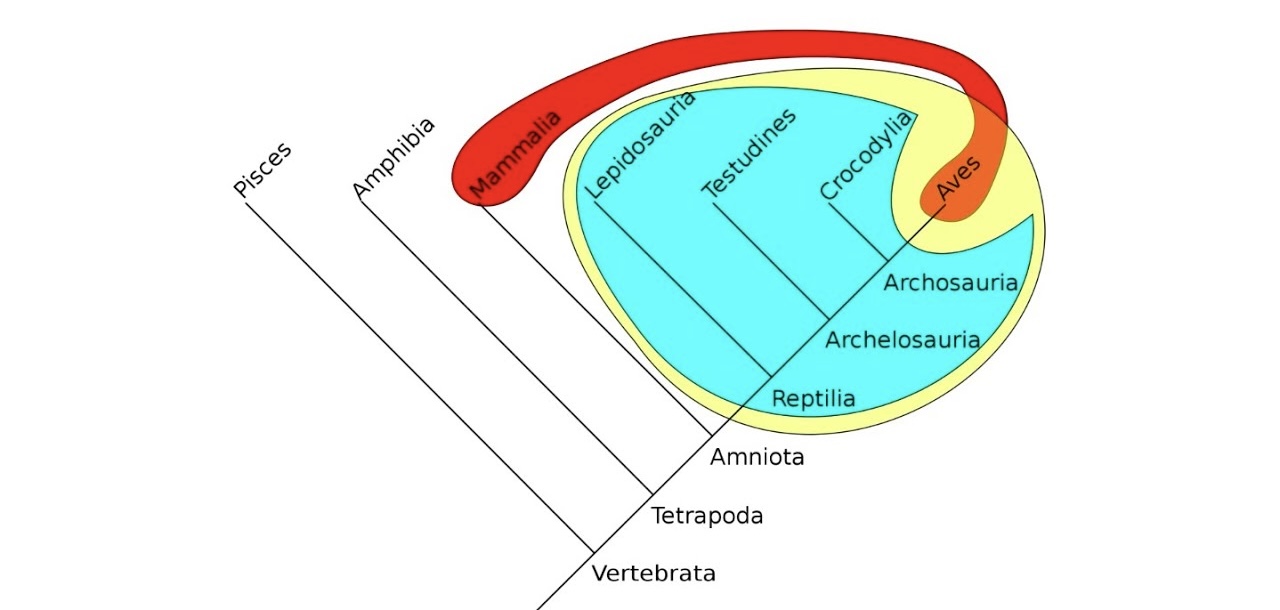
What does yellow show
Monophyly
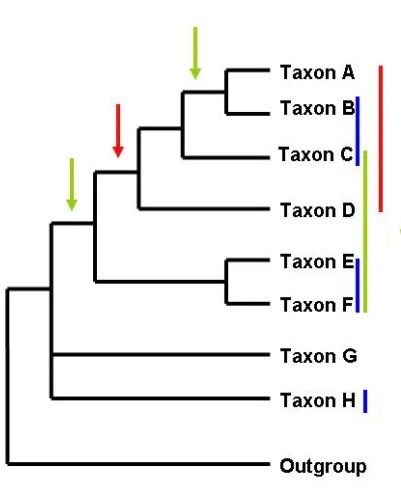
What does red show
Monophyly
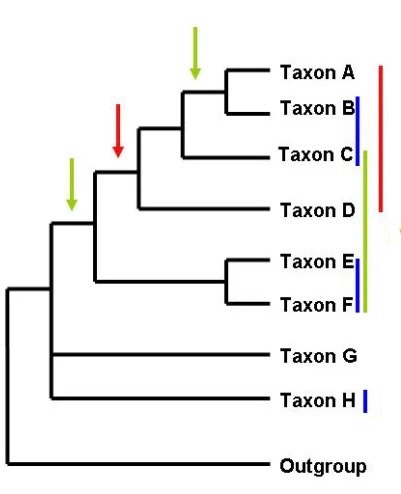
What does green show
Paraphyly
What does blue show
Polyphyly
polyphyletic definition
organisms from more than one ancestral lineage
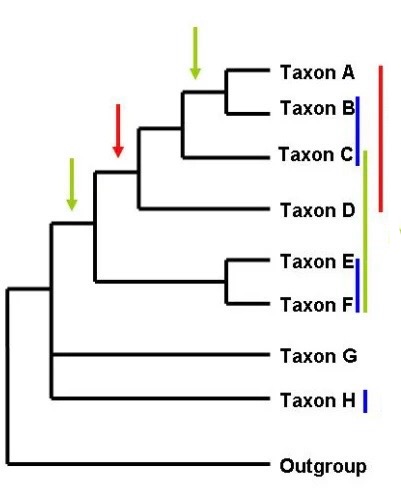
Red phylogenetic group
Polyphyly
Green phylogenetic group
Paraphyly
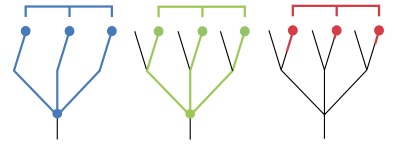
Blue phylogenetic group
Monophyly
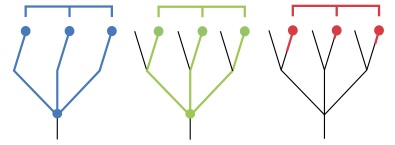
paraphyletic definition
an ancestor but only some of its descendants
Monophyletic definition
an ancestor and all of its descendants
whats a feature of monodicots
Parallel veins, petals of 3, scattered vascular bundles (stems), 1 cotyledon (Seed leaf within the embryo of a plant)
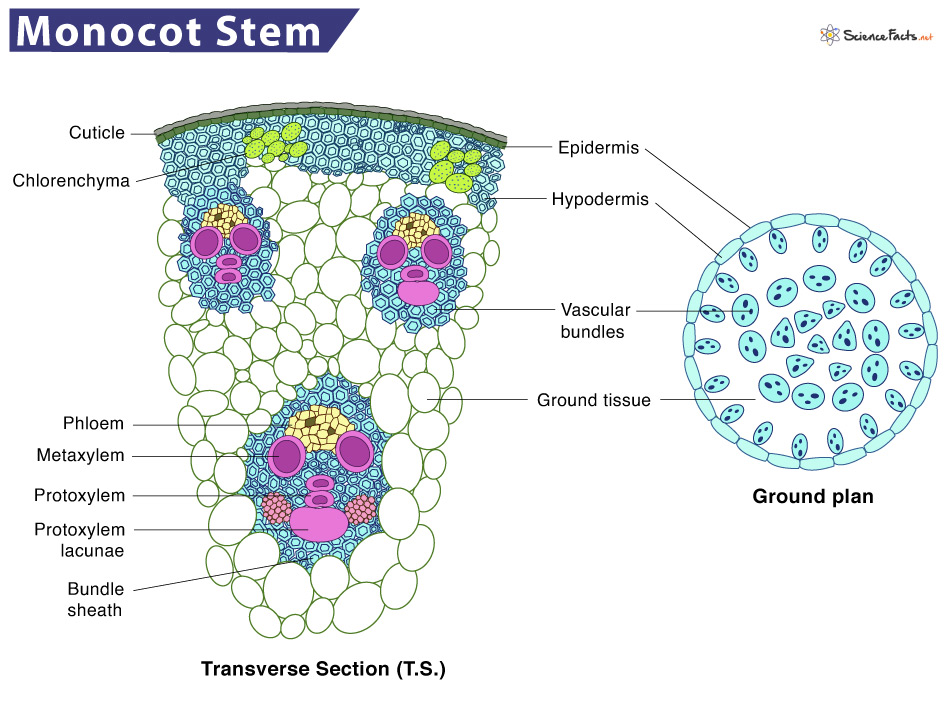
whats a feature of eudicots
Vascular bundles in a ring arrangement, flowers of 4/5, net like vein structure, 2 cotyledon (Seed leaf within the embryo of a plant), common to have wood, one main root
birds snakes sharks
Chordata
Starfish sea urchins
Echinoderms
Which phylum(s) include larval bilateral symmetry and adult radial symmetry
Echinoderms
Bottleneck effect
reduction in a population's size and genetic diversity, caused by a random event
Founder effect
Few members of a population break away from original population and are excluded in another area
Morphological species concept defined by
Observable appearance
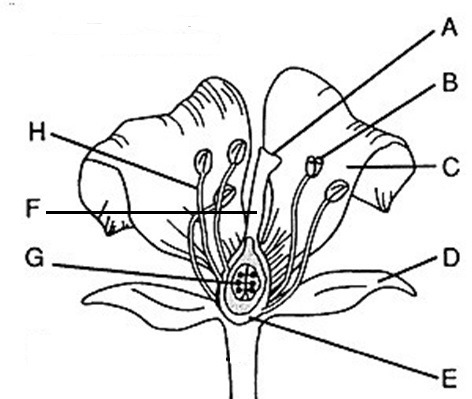
Flower part Anther
B, where pollen (male gametophytes), are produced
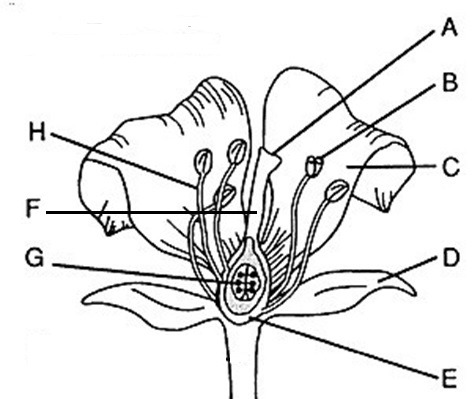
Flower part style
F, Connects stigma and ovaries
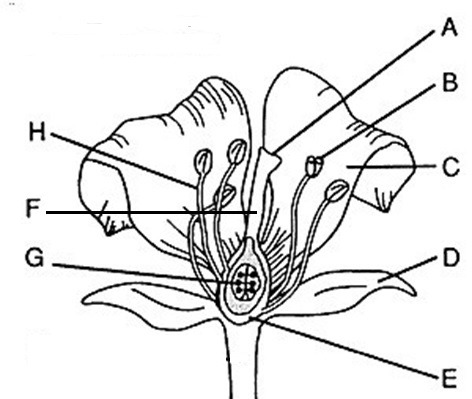
Flower part Stigma
A, sticky, feathery portion at top of style, captures pollen
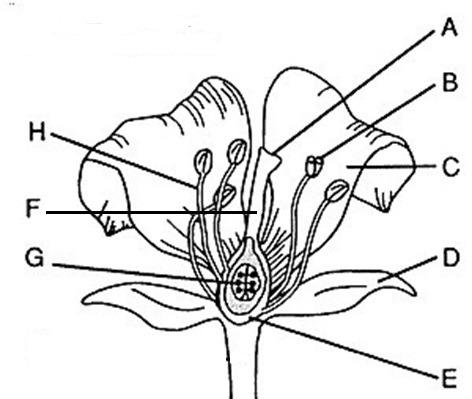
Flower part Filament
H, stalk that supports anthers
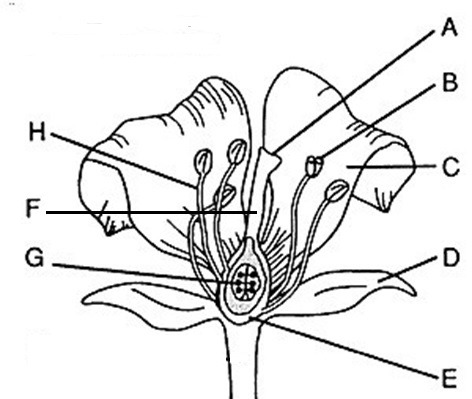
Flower part Ovary
E, produces eggs or ovules
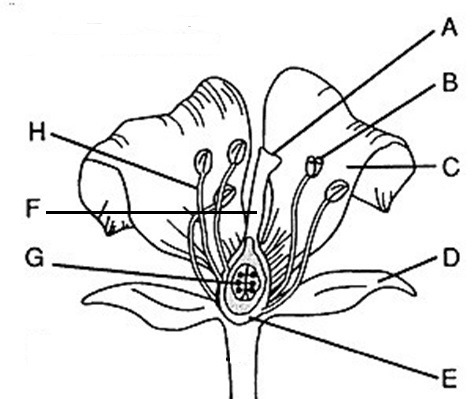
Male flower parts
H and B/stamen: Anther + filament
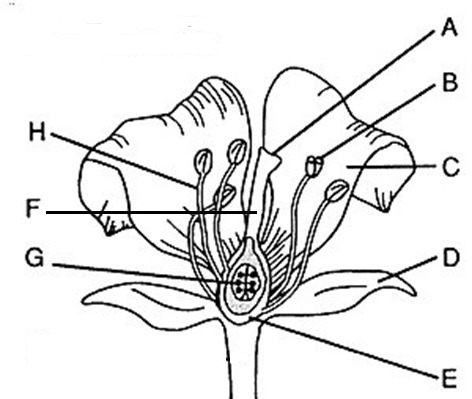
Female flower parts (carpel)
AFE, has stigma, style, ovary
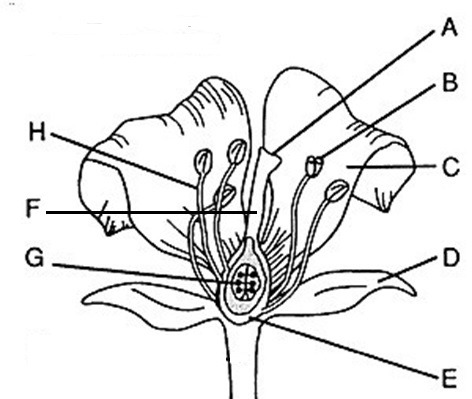
Flower part petals
C Attracts pollinators
Flower part stamen
B+H Male, has stalk (filament) with anther at tip
bilateral adult symmetry, deuterostome, triploblastic, endoskeleton
Chordata
Bilateral only young symmetry, adult radial symmetry, deuterosome, triploblastic, endoskeleton
Echinoderms
Squids are in what phyla
Mollusca
Triploblast tissue
Endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm (everything besides cnidaria and porifera)
diploblasts tissue (might have NONliving middle layer)
Endo and ectoderm, cnidaria
Protostome
blastopore=mouth, spiral cleavage
Deuterostome+examples
blastopore=ass, radial cleavage, (echinoderms, chordata)
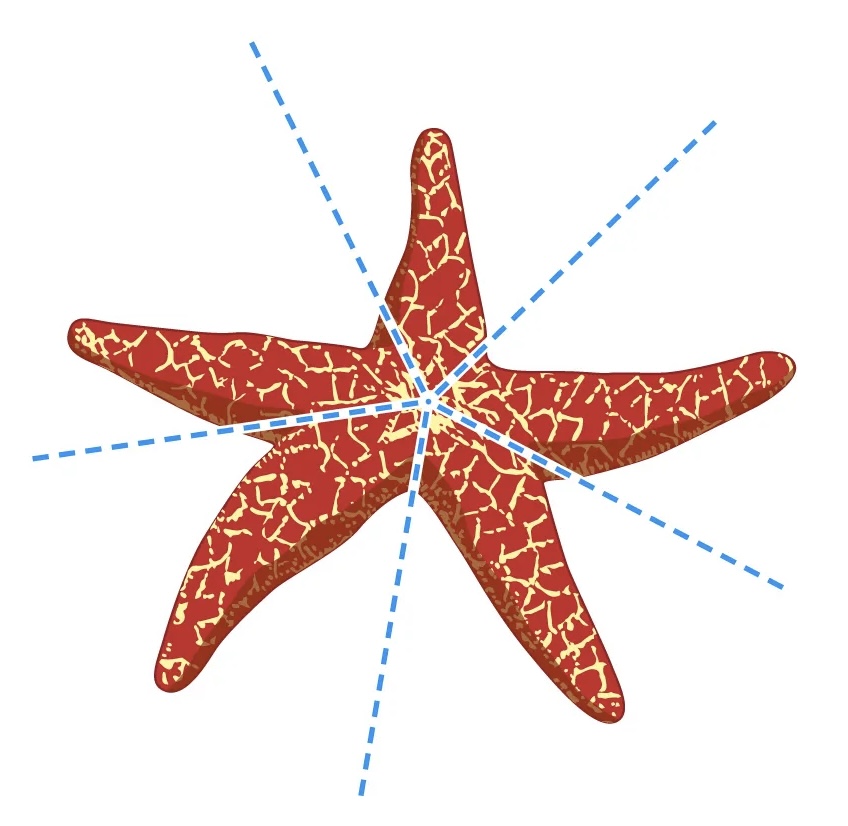
Radial symmetry
can be divided into two matching halves by many different lines, which all intersect one another at a single point in the center
Bilateral symmetry
can be divided into two mirror-image halves by a line down the middle
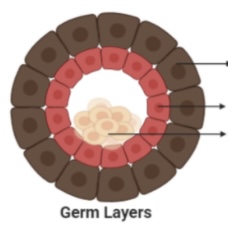
Outermost layer
Ectoderm
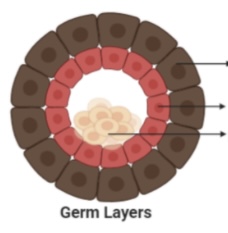
middle layer
Mesoderm
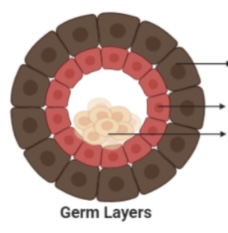
Innermost layer
Endoderm
Lobster phylum
Arthropoda
Which phylum does not have true tissue
Porifera
Which phylum have tissue
All but porifera
Which phylum have two tissue layers
Cnidaria
Which phylums have three tissue layers
arthropoda, annelida, chordata, echinoderms, mollusks, nematodes, platyhelminthes
Which phylums have radial symmetry
cnidaria, adult echinoderms
Which phyla are bilateral
Chordata, platyhelminthes, nematodes, larvae echinoderms, mollusks, annelida
Phyla with incomplete digestive systems (only one opening)
Porifera, platyhelminthes, cnidaria
Phyla with complete digestive systems (a mouth and an ass)
Nematoda, annelida, mollusca, arthropoda, chordata, echinoderms
Coelom
Fluid filled cavity in mesoderm, organs grow independently off body’s wall
Acoelomate (platyhelminthes)
Solid bodied animal that lacks cavity between gut and outer wall
Pseudocoelomate +example
Mesoderm lines outside of cavity (nematodes)
Hardy weinberg
allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences
porifera adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
asymmetrical, bilateral larval symmetry, neither, no true tissues, neither
Cnidaria adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
radial, bilateral larval, no proto/deutero, diploblastic, hydrostatic skeleton
hydrostatic skeleton
relies on the pressure of internal, fluid-filled cavities to provide support and shape. Muscles contract to change the pressure in these cavities, which then manipulates the fluid to allow for movement, such as bending, shortening, and lengthening the body. This system is common in soft-bodied invertebrates like earthworms, jellyfish, and sea anemones
platyhelminthes adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral, bilateral, protosome, triploblast, none
nematoda adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral, bilateral, protosome, triploblast, Hydrostatic (pseudocoelom as skeleton)
annelida adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral, bilateral, protosome, triploblast, Hydrostatic (true coelom)
molluska adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral (snails have secondary asymmetry), bilateral, protosome, triploblastic, exoskeleton
arthropoda adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral, bilateral, protostome, triploblast, exoskeleton (chitin)
echinodermata adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
radial, bilateral, deuterostome, triploblast, endoskeleton (calcium plates/ossicles)
chordata adult symmetry, larval symmetry, protostome/deuterostome/other, # of germ layers, and endo/exoskeleton
bilateral, bilateral, deuterosome, triploblast, endoskeleton (cartilage/bone)
which phylums are NOT triploblasts?
porifera, cnidaria
which phylums are protosomes
annelids, arthropoda, mollusks, nematoda, platyhelminthes,
which phylums are deuterostomes
echinoderms, chordata
which phylums have a true coelom
annelida, chordata, echinoderms, mollusca
which phylums have no coelom because they arent triploblasts
porifera, cnidaria
which phylums are acoelomates (no coelom despite having a triploblasts)
platyhelminthes (the space between the gut and body wall is filled with solid mesodermal tissue)
which phylums are pseudocoelomates
nematodas (body cavity not fully lined with mesoderm)
which phylums have a reduced coelom
arthropda (Most of the space in their body is a hemocoel/filled with blood, they do have a true coelom but its small)
correlations between endoskeleton and coelomates
all require coeloms (chordata, echinoderms)
correlations between exoskeleton and coelomates
no correlation, they can have a coelom but they do not require them.
which phyla have exoskeletons?
arthropoda (true exo, like bugs obvi), mollusks (technically but like a snail shell, external only), and nematoda (debatable- cuticle ts, not true exoskeleton and not hard)
What is allelic frequency?
The proportion of each allele in a population’s gene pool.
What is genotypic frequency?
The proportion of each genotype in a population.
What is phenotypic frequency?
The proportion of individuals with each phenotype in a population.
What are the assumptions of Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium?
No mutation, no migration, no genetic drift (infinite population), no natural selection, and random mating.
What causes deviation from H–W equilibrium?
Mutation, migration, selection, drift, nonrandom mating.
Define microevolution
Change in allele frequencies in a population over time.
What is a gene pool?
All alleles present in a population.
What is genetic drift?
Random change in allele frequencies, strongest in small populations.
What is the founder effect?
Drift resulting from a few individuals founding a new population.
What is phylogenetics
The study of evolutionary relationships among organisms.
What is cladistics?
A method of classification based on shared derived traits.
What is a phylogeny?
A hypothesis of evolutionary relationships, usually shown as a tree.
Define apomorphy
A derived trait.
What is a synapomorphy?
A shared derived trait used to define a clade.
What is a plesiomorphy
An ancestral character state.
What is a symplesiomorphy?
An ancestral trait shared by multiple groups (not useful for classification)
What is parsimony in phylogenetics?
The tree requiring the fewest evolutionary changes is preferred.
What is a polyphyletic group?
A group that excludes the common ancestor; united by homoplasy.
What is a homologous trait?
A trait shared due to common ancestry.
What is homoplasy?
A trait shared due to convergent evolution, not shared ancestry.
what is wood?
secondary xylem
what is a xylem
the plant tissue that transports water and dissolved nutrients from the roots up to the rest of the plant, also providing structural support
What is a fruit?
A mature ovary that protects seeds and aids dispersal.