Electronic Circuit Design 2 - asynchronous - week 5 - static limitations of op amps
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what does static refer to when talking about static limitations of op amps
static refers to when the op amp is operating at DC or very low freqeunecy
for an ideal op amp at the input stage what two assumptions are made
there is no current flowing into the input terminals of the op amp.
the open loop gain is infinite.
what is the bias current in an op amp
it is a small amount of current which can flow in either direction of the input terminals V+ and V- of an op amp
why must an average bias current be calculated instead of just the bias current.
what is the amp range that bias current is usually in .
write the equation for calculating the average bias current.
As the inputs to op amp can have slighlty different bias current flowing through them an average of the positive and negative terminals is used to calculate the average bias current.
bias current is usually in nA-fA range so very small

what is the difference between the two bias currents present at positive and negative input terminals of the op amp called.
the offset current.
what is the equation for calculating the offset current.
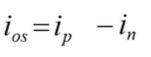
how much smaller is the offset current usually compared to the bias current?
offset current is usually 10 times smaller.
Do the derivation for calculating the effect of the bias and offshoot current on the voltage output of an inverting amplifier stating any steps along the way.
do from video
what is offset voltage?
it is when vp is not exactly equal to vn as it is in the ideal case.
do offest voltage derivation from video
what is the final equation for calculating the offset voltage?
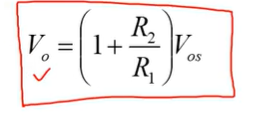
what is the final equation which shows the effect both the offset voltage and the offset current has on the output voltage.
what does this equation indicate about selecting circuit values to reduce offset voltage.
choose an op amp with a small offset to reduce offset error.
choose as small values for r1 and r2 as possible
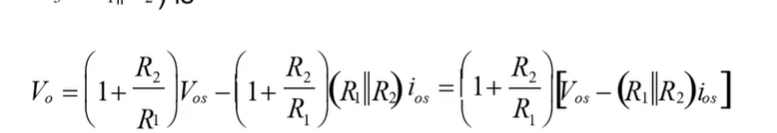
why will a pure integrator circuit not actually work in real life?
because the small offset voltage will constantly charge the capacitor and will make the circuit saturate.
Explain why there is a resistor connected to the non-inverting input of an op-amp for an inverting amplifier even if it does not affect the circuit gain?
To balance out the bias currents.
notice when you derivation how if you set r3 = to r1 and r2 in parrellel you can remove the term which is multiplied by the bias current hence removing it from final eqaution.