3. Protein Structure and F(x)
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Prions
Altered folded forms of normal proteins that can induce misfolding in other proteins, associated with diseases.
Molecular Chaperones
Proteins that facilitate folding and prevent inappropriate interactions between unfolded proteins
Condensation Reaction
A chemical reaction where two molecules combine, resulting in the loss of a small molecule (usually water), forming a larger molecule.
R Group (Side Chain)
The variable group attached to the central carbon of an amino acid that determines its specific characteristics and properties.
Ionization
The process by which an atom or molecule gains or loses an electron, forming charged ions, in this context involving amino and carboxyl groups in amino acids.
Denaturation
Denatured (unfolded) proteins don’t function normally
denatured = loss of 3D structure (unfolded) due to breakage of chemical bonds
Kuru
A prion disease that affects the brain, characterized by neurodegeneration, associated with the consumption of infected human tissue.
Attributes necessary for the origin of life
Molecules must be able to store genetic information,
They must catalyze chemical reactions
They should have the ability to self-replicate.
Structure of Amino Acids
Amino acids consist of a central carbon atom, an amino group (NH3+), a carboxyl group (COO-), a hydrogen atom, and a variable R group (side chain).
Solubility of Amino Acids
polar & charged R-groups are hydrophilic - dissolve
non-polar R-groups are hydrophobic - insolluble
Determine is an Amino Acid is Acidic, basic, or polar/nonpolar
Determined by R-group
Acidic - negative charge
Basic - positive charge
Polar - no charge, has Oxygen
Nonpolar - no charge, usually has C-H bond
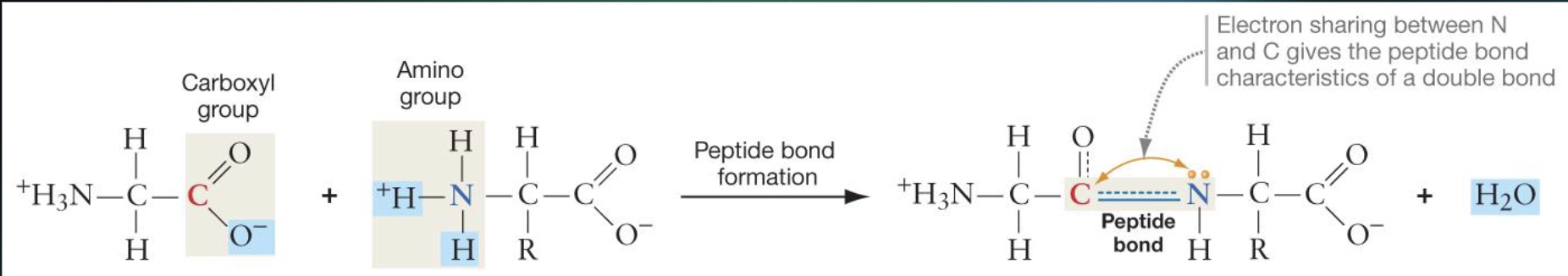
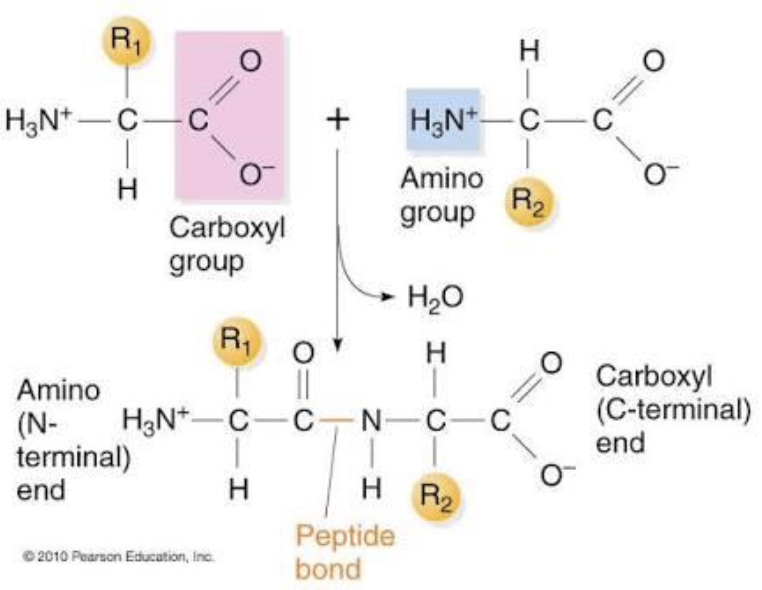
Explain how Peptide Bonds are formed
Through a condensation reaction where the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another, releasing water.
Primary Structure of Proteins
The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain, determining the protein's identity and function.
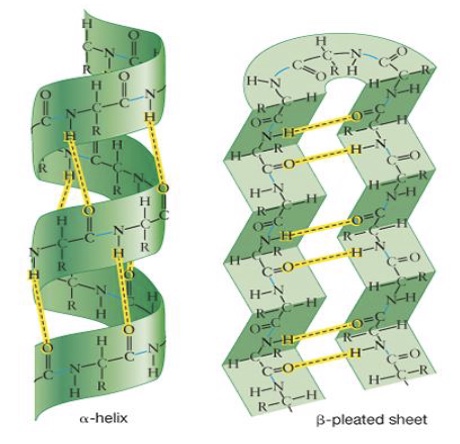
Secondary Structure of Proteins
The localized folding of the polypeptide chain into alpha helices or beta-pleated sheets bc of hydrogen bonds
Tertiary Structure of Proteins
The overall 3D shape of a SINGLE polypeptides.
cause chain of peptide bonds to bend & fold
caused by the 5 types of side chain interactions
Quaternary Structure of Proteins
The overall 3D shape formed from 2 or more polypeptide chains into a single functional protein.
Types of Interactions Affecting Protein Folding
Five types of interactions:
Hydrophobic interactions - force hydrophic side chains together
Hydrogen bonds,
Ionic bonds
Covalent -
Van der Waals forces - weak electrical interactions between hydrophobic side chains
Prion Diseases
Diseases caused by misfolded proteins that induce misfolding in normal proteins; Kuru is an example linked to consuming infected tissues.
Key Points About Peptide Bonds
R-group orientation
Directionality
on 1 end of backbone (chain of peptide bonds) there is a N-terminus (amino group) and on the other a C-terminus (carboxyl group)
Flexibility - the single bonds can rotate
Define poly- , oligo-, peptides and protein
peptide = amino acids linked by peptide bonds
oligopeptide = chain of <50 amino acids
polypeptide = chain of >50 amino acids
protein = may be composed of multiple polypeptides, complete & functional
Protein Folding & Function
normal protein folding is crucial & often spontaneous
folded proteins are more stable than unfolded ones, & energetically favorable