TOPIC 4: HUMAN CAPITAL
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What is human capital in the context of development economics?
It is society’s investment in the productive attributes of the population, similar to how a business owner invests capital in their business
What are the two most common forms of human capital investment?
Health and Education.
Why are health and education important for a country's productivity?
A healthy and educated workforce is generally more productive.
What are the two equations of motion with human capital in the solow swan model
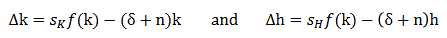
What has happened to health and education in developing countries over the past 70 years?
There have been major improvements in both health and education.
How have under-5 mortality rates changed since 1950?
They fell from 280 per 1,000 in 1950 to 69 in low-income and 49 in lower-middle-income countries.
Which diseases have been controlled or eliminated through vaccination?
Rubella and Polio have been largely controlled; Smallpox has been eliminated.
What is the current global literacy rate compared to 1970?
85% today, up from 63% in 1970.
What progress has been made in education regarding gender?
There have been continuing improvements in addressing gender discrimination in education.
How does greater health capital enhance the returns to education?
It improves school attendance, helps students learn more effectively, and increases the return to education through longer life expectancy.
How does greater education capital enhance the returns to health investments?
It supports public health programs, promotes hygiene and sanitation, and is essential for training health personnel.
What is an example of greater health capital and returns to investment in education
Miguel and Kremer (2004)
They conducted a randomized study on the effects of de-worming drugs in rural Kenyan primary schools.
Absenteeism dropped by at least 25% in treated schools, especially among younger children, and even neighboring schools saw increased participation.
What is an example of greater education capital leading to greater returns in investment in health
Glewwe (1999)
investigated the commonly observed
positive relationship between mother’s education and children’s health and nutrition
Literacy and numeracy skills learned in school enhance mothers' abilities to
treat child illnesses
The study concluded that the mother’s basic health knowledge was the most
important factor for improving child health
How does education contribute to economic growth in developing countries?
It enables the absorption of modern technology and production methods, boosting productivity.
Why might raising the average education level lead to productivity gains?
Because higher education is linked to higher earnings and productivity, especially in developing countries where marginal private returns to education are often very high.
What does Human Capital Theory say about education and productivity?
It argues that education and training improve worker skills, increasing future productivity.
What is a key challenge in linking education and economic growth at the macro level?
The direction of causality is unclear—high income may lead to high education or vice versa.
What did Jones (2001) find in a study of manufacturing firms in Ghana?
A clear link between education and productivity, though the study doesn’t fully rule out signalling (where education acts as a signal of productivity rather than causing it).
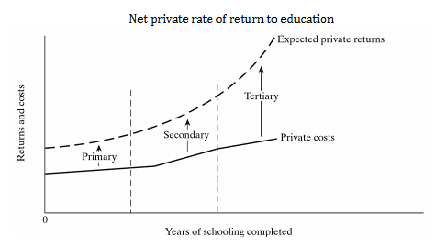
What is the net private rate of return to education?
It is the difference between the cost and benefit of each additional year of education for the individual.
What is the net social rate of return to education?
It includes returns to the individual while also accounting for societal costs, such as infrastructure and subsidies.
Why might the optimal education level differ for individuals and society?
Because private returns influence demand, while social returns determine supply, and unrecognized social benefits (e.g., better health outcomes) may not be fully captured.
can you illustrate this on a graph
How does health impact productivity at the individual level?
Good health is essential for productivity. Schultz and Tansel (1997) found that each ‘disabled day’ due to illness or injury significantly reduces worker productivity in Côte d'Ivoire and Ghana.
How does poor population health affect economic growth at the country level?
A high disease burden lowers productivity and limits economic growth
What did Gallup and Sachs (2000) find about the economic effects of malaria?
Countries with intensive malaria had 1.3% lower GDP per capita growth than those without, and malaria eradication led to substantially higher relative growth over the next 5 years.
How are health, productivity, and disease susceptibility linked to nutrition?
Good overall nutrition—especially in early life—is associated with better health, academic success, and higher productivity and earnings in adulthood.
What does low weight-for-age indicate in children?
It signals short-term exposure to disease and/or inadequate food; underweight is defined as 2 standard deviations below the average weight-for-age of a healthy reference group.
What does low height-for-age indicate in children?
It reflects long-term or repeated exposure to disease and inadequate nutrition; stunting is defined as height-for-age 2 standard deviations below the average of a healthy reference group.
Why is closing the educational gender gap important?
Women’s education has a higher social rate of return, as it increases productivity, lowers fertility, and leads to better child welfare, health, and future GDP growth
How does gender discrimination affect healthcare access for girls in developing countries?
In many developing countries, girls face discrimination in healthcare, with families more likely to seek medical care for sick boys than for sick girls.
What cultural and economic factors contribute to gender discrimination in healthcare?
Gender discrimination in healthcare is often influenced by cultural norms and economic constraints.
What did Bongaarts and Guilmoto (2015) find regarding missing women in Asia
They concluded that at least 126 million women are "missing" in Asia, mainly due to excess female mortality and, to a lesser degree, gender-selective abortion (especially in China and India).
Why may increases in family income not directly lead to improved human capital?
Even if increased income leads to more spending on food, it doesn’t guarantee improved health and nutrition, as income elasticity of nutrition is often less than 0.5.
What are the challenges in ensuring that increased income is spent on health and education?
There are many competing claims on a household's surplus income, meaning that boosting income doesn't guarantee it will be spent on health or education.
What type of policy addresses the problem of income not automatically improving health and education?
Conditional Cash Transfers (CCTs) directly target this issue by providing financial incentives tied to health or education outcomes.
What are Conditional Cash Transfers (CCTs) designed to address?
CCTs aim to reduce both immediate and intergenerational poverty by improving human capital, particularly among children.
How do Conditional Cash Transfers (CCTs) work?
CCTs provide cash transfers to poor households, contingent on fulfilling pre-specified conditions.
What typical conditions are required to receive Conditional Cash Transfers (CCTs)?
Conditions often include children attending regular health check-ups and being enrolled in school with good attendance.
What is an example of CCT’s
Mexico’s Progressa
Rigorous evaluation of the program has shown that the children of participant
households have:
▪ Lower levels of malnutrition
▪ Increased attendance at health facilities
▪ Higher school attendance and lower drop-out rates
▪ A lower probability of being employed as child labourers