unit1-5
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
revision
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What does the liver produce and what’s its digestive role?
: Produces bile (bile salts, pigments, cholesterol).
Function: emulsifies fats → ↑ surface area for lipase
What does the gallbladder do?
Stores & concentrates bile; contracts when CCK is released → sends bile via bile duct to duodenum.
What does the exocrine pancreas secrete?
Pancreatic juice with:
HCO₃⁻ (neutralises acid, pH 7–8).
Enzymes: amylase (CHO → maltose), lipase (triglycerides → FFA + monoglycerides), protease zymogens (trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidase), nucleases (DNA/RNA).
What does the sphincter of Oddi regulate?
Controls entry of bile + pancreatic juice into duodenum (hepatopancreatic ampulla).
What stimulates gastrin release and what does it do?
Stimuli: food in stomach, sight/smell of food, parasympathetic activity.
Action: stimulates gastric acid secretion.
What are the 3 macronutrients?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins (all yield energy).
What are micronutrients and examples?
Non-caloric, essential small molecules: vitamins (fat- & water-soluble), minerals (ions/trace metals).
Why must macromolecules be hydrolysed?
To cross lipid bilayers:
CHO → monosaccharides
Protein → amino acids, di-/tripeptides
Lipids → monoglycerides + FFA in micelles
What happens to excess CHO/protein?
Converted (via acetyl-CoA) to triglycerides → stored in adipose tissue.
Where are some micronutrients stored?
Depends on solubility:
Vit A in liver stellate cells
Others in liver, bone, or adipose.
Role of duodenum?
~25 cm, completes chemical digestion. It is the first section of the small intestine, where food is mixed with bile and pancreatic juices.
Role of jejunum?
~2.5 m, bulk nutrient absorption. It is the second section of the small intestine, primarily responsible for absorbing carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals into the bloodstream.
Role of ileum?
~3.5 m, absorbs bile salts + vitamin B12–IF complex.
When is CCK released and what does it do?
Released when chyme has fats/proteins.
Main Functions of CCK:
Stimulates the gallbladder → contracts to release bile (which emulsifies fats).
Stimulates the pancreas → releases digestive enzymes (lipase, amylase, proteases).
Slows gastric emptying → gives more time for fat digestion.
Acts on the brain → promotes the feeling of fullness (satiety) and reduces appetite.
What’s ghrelin’s source, trigger, and effect?
Source: stomach. Trigger: empty stomach (loss of stretch). Effect: stimulates hunger.
What triggers Gastric Inhibitory Peptide (GIP) and what are its effects?
Trigger: nutrient-rich chyme.
Effects: inhibits hunger, ↑ insulin release.
What triggers insulin and what is its effect on appetite?
Trigger: high blood glucose.
Effect: inhibits appetite (signals nutrient influx).
Where does leptin come from and what does it do?
Source: adipocytes (proportional to fat mass).
Effect: long-term appetite suppression.
What are the liver’s major roles beyond digestion?
Detoxification/biotransformation (alcohol, drugs).
Metabolic regulation: glycogenesis, lipogenesis.
Storage: fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), glycogen, limited fat.
RBC recycling (Kupffer cells → bilirubin → bile).
What are the effects of hepatic portal damage?
Loss of vitamin storage (A, D, E, K), impaired detox, metabolic dysregulation, jaundice.
What are the main functions of the large intestine?
Water reclamation.
Carbohydrate fermentation by microbiota.
Vitamin absorption.
Formation of feces (fiber, microbes, mucus, cells).
What are the two motility patterns in the large intestine?
Haustral churning (slow mixing, max absorption).
Mass peristalsis (propels stool to rectum).
What is a keto-acid and why important?
Carbon skeleton after deamination; can be converted into lipid or used for ATP.
How does inside vs outside of a resting neuron differ?
Inside: negative charge, fewer Na⁺. Outside: positive charge, more Na⁺.This difference in charge creates a resting membrane potential, essential for neuronal signaling.
What are the 4 types of CNS glial cells and their roles?
Astrocytes → blood–brain barrier, support.
Oligodendrocytes → myelin in CNS.
Microglia → immune defense (phagocytosis).
Ependymal cells → produce & circulate CSF.
Cranial nerve I
Olfactory Function: Sensory - smell 👃
Cranial nerve II
Optic Function: Sensory - vision 👀
Cranial nerve III
Oculomotor Function: Motor - eye movement (most eye muscles) 👁
Cranial nerve IV
Trochlear Function: Motor - eye movement (superior oblique muscle) 👁
Cranial nerve V
Trigeminal Function: Sensory & Motor - sensation in the face, motor for chewing muscles 😬
Cranial nerve VI
Abducens Function: Motor - eye movement (lateral rectus muscle) ↔
Cranial nerve VII
Facial Function: Sensory & Motor - taste (anterior 2/3 of tongue), motor for facial expressions 🙂
Cranial nerve IIX
Vestibulocochlear Function: Sensory - hearing and balance 👂
Cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal Function: Sensory & Motor - taste (posterior 1/3 of tongue), motor for swallowing 😋
Cranial nerve X
Vagus Function: Sensory & Motor - sensation from and motor to internal organs (e.g., heart, lungs, digestive tract)
Cranial nerve XI
Accessory (or Spinal Accessory) Function: Motor - neck and shoulder movement (sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles) 💪
Cranial nerve XII
Hypoglossal Function: Motor - tongue movement 👅
Acronyms for cranial nerves?
On occasion our trusty truck acts funny. very good vehicle any how. + some say marry money but my brother says big brains matter more.
Infant Reflex: Stroke cheek → what happens?
Rooting Reflex 4 months
Baby turns head + opens mouth (searching for nipple).
Neuro significance: Tests brainstem cranial nerves (V, VII, XI, XII).
Mnemonic:"Rooting = Ready cranial nerves."
Infant Reflex: Object placed in mouth → what happens?
Sucking Reflex (becomes voluntary at) 4 months
Baby sucks rhythmically when object is placed in mouth. Neuro significance: Brainstem/medulla intact, shows coordination of suck–swallow–breath. Mnemonic: "Suck = Survival medulla."
Infant Reflex: Object placed in palm → what happens?
Palmar Grasp Reflex 5-6 months.
Baby grips tightly when object is placed in palm. Neuro significance: Normal primitive reflex. Persistence = frontal lobe lesion (failure of inhibition). Mnemonic: "Grip won’t quit = Frontal hit."
Infant Reflex: Stroke sole of foot → what happens?
Plantar (Babinski) Reflex 12-24 months
Toes fan and big toe extends upward when sole of foot is stroked. Neuro significance: Normal in infants (immature corticospinal tract). In adults = UMN lesion. Mnemonic: "Babies Babinski = immature brain; Adults Babinski = damage again."
Infant Reflex: Sudden noise or loss of support → what happens?
Moro (Startle) Reflex 3-6 months
Arms extend then flex in, baby may cry in response to sudden noise or loss of support. Neuro significance: Brainstem + vestibular system function. Absence = CNS injury. Mnemonic: "No Moro = Neuro sorrow."
Infant Reflex: Head turned to one side → what happens?
Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR / Fencer Reflex) 4-6 months
Arm/leg on the side to which head is turned extends, while opposite side flexes. Neuro significance: Primitive postural reflex. Persistence = cerebral palsy. Mnemonic: "Fence that stays = motor delays."
Infant Reflex: Hold infant upright with feet touching surface → what happens?
Stepping Reflex 2 months
Baby makes stepping/walking motions when held upright with feet touching a surface. Neuro significance: Shows spinal cord central pattern generators intact. Absence = spinal/peripheral injury. Mnemonic: "No steps = Spinal missteps."
Alpha Receptor: α₁
Arteries (skin, GI tract), bladder sphincter, pupils. / Contraction of smooth muscle. Causes vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels) and pupil dilation.
Alpha Receptor: α₂
Presynaptic nerve endings, pancreatic islet cells. / Inhibition of norepinephrine release (negative feedback). Reduces sympathetic outflow, decreases insulin release.
Beta Receptor: β₁
Heart, kidneys. / Increases heart rate and force of contraction (cardiac output). Also stimulates renin release in kidneys.
Beta Receptor: β₂
Bronchioles of lungs, arteries of skeletal muscles, liver. / Relaxation of smooth muscle. Causes bronchodilation (widening of airways) and vasodilation in skeletal muscles.
Beta Receptor: β₃
Adipose (fat) tissue, bladder. / Lipolysis (fat breakdown for energy) and relaxation of the bladder wall (used in overactive bladder treatment).
Cervical region
muscles of the head/neck, diaphragmatic support via the diaphragm (see C3–C5), shoulder elevation, elbow flexion, wrist extension, hand/finger movements.
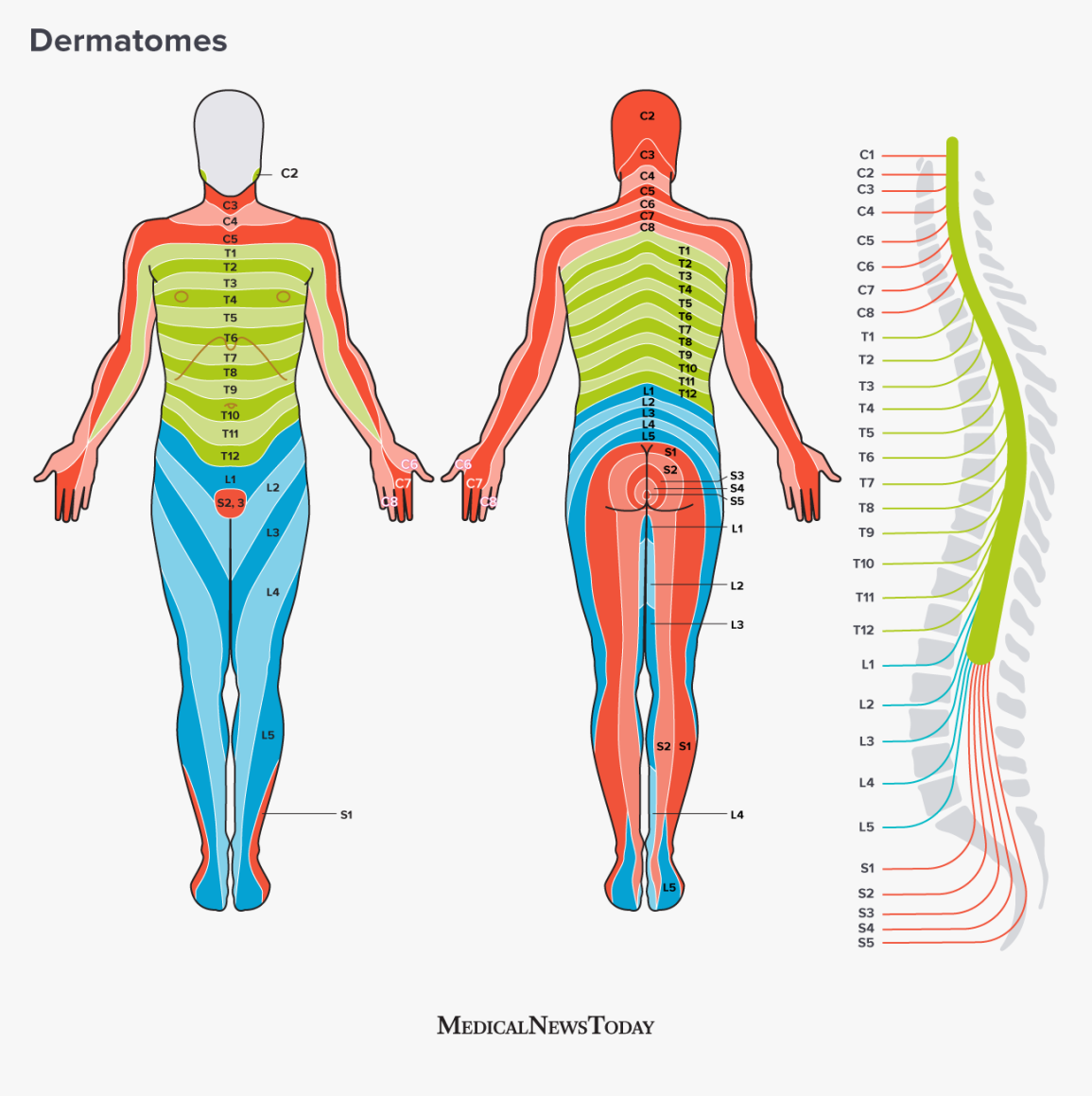
Thoracic region
internal thoracic/abdominal region muscles; some hand/finger involvement near the upper thorax; generally more trunk-related control.
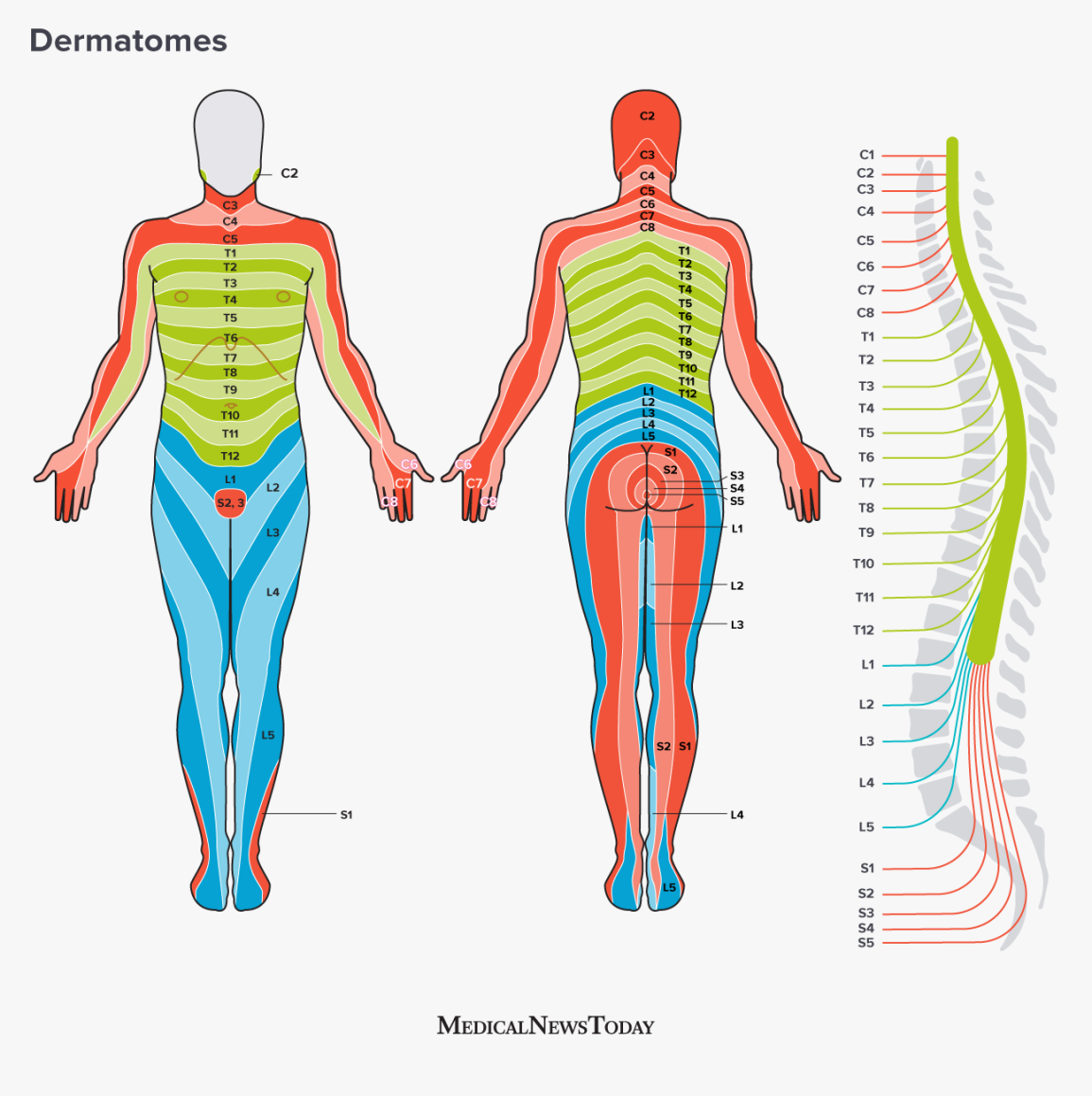
Lumbar region
hip, knee, and front of the leg movements; control of knee extension/flexion and ankle movements; sensation from front of legs; involvement in hip/knee actions.
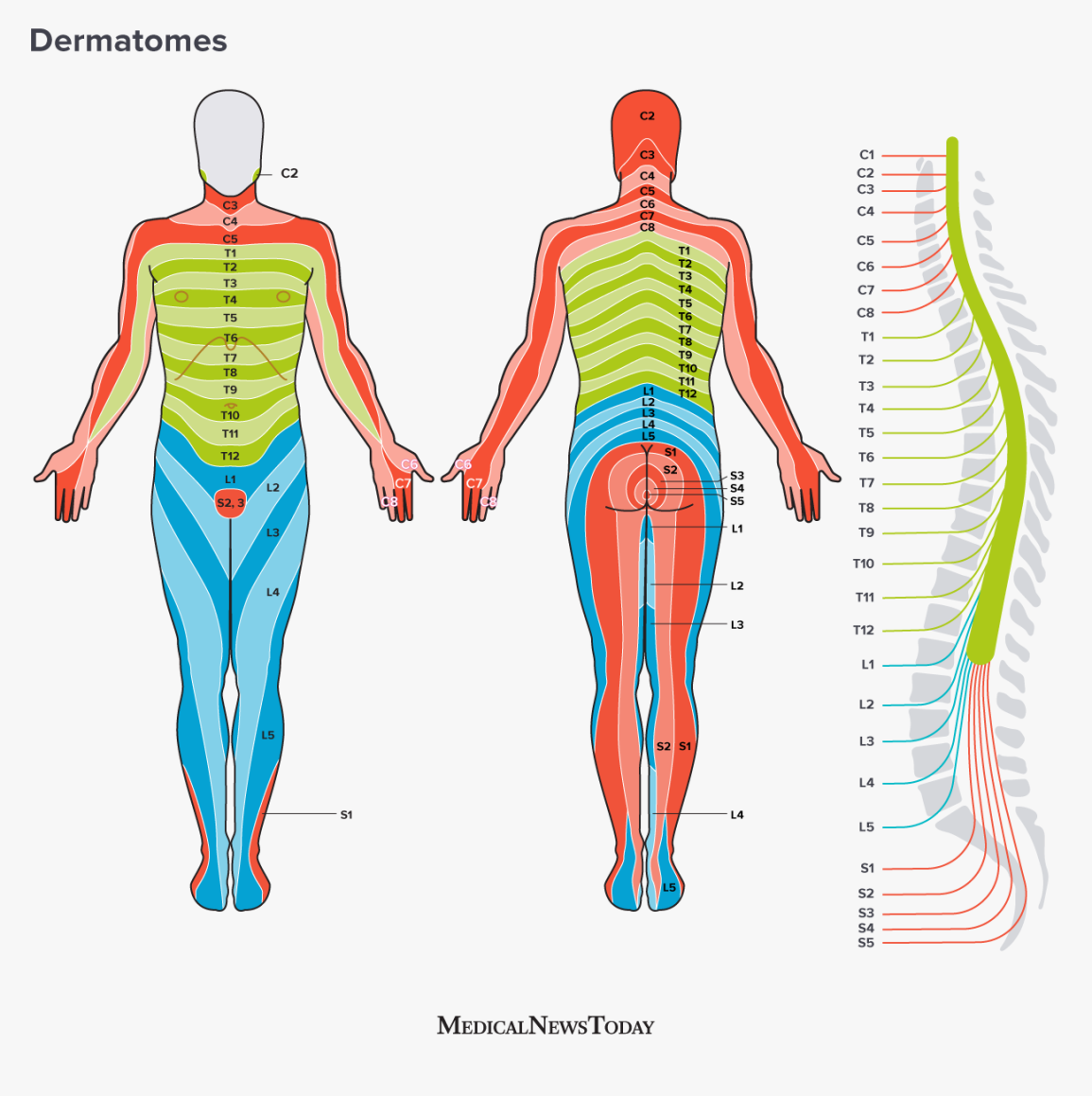
Sacral region
lower limbs (back of legs, feet) and pelvic region; also autonomic control related to bladder and anal sphincters via voluntary skeletal muscle control of pelvic floor and sphincters.
Count
The
Little
Segments

Function of RODS
highly sensitive to low-intensity light: crucial for night vision and for detecting movement and peripheral vision.
The light-sensitive pigment found in rods is called rhodopsin.
Function of CONES
responsible for color vision and for seeing fine detail. They are concentrated in the fovea, the central part of the retina.
A stroke that damages the corticospinal tract on the right side of the brain would result in the loss of:
muscle control on the left side of the body. The corticospinal tract begins in the motor cortex of the brain. The right motor cortex controls movement for the left side of the body.
Frontal Lobe function and parts
motor control.
Primary Motor Cortex: control voluntary muscle movements
Premotor Cortex: coordinates the motor programs
Broca's Area: This area is crucial for speech production.
Parietal Lobe function and location
processing sensation. behind frontal lobe
Temporal Lobe function, location and parts
hearing and language comprehension. on the side of the head, near the temples
Primary Auditory Cortex: This area processes auditory information, hear and interpret sounds
Wernicke's Area: language comprehension
Occipital Lobe function, location and parts
processing visual information.
very back
Primary Visual Cortex: receives raw visual data
Visual Association Cortex: integrates it with memories and other senses to allow us to make sense of what we are seeing. For example, it helps us recognize faces or objects.