MTEL Reading Section
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
distance between a subject and verb
mistakes in grammar that happen when subject and verb are separated in word groups or phrases
ex: the horses in the pasture next to the barn needs water (needs should be need)
collective nouns
nouns that refer to groups
British English uses a plural verb for collective nouns because these nouns are considered plural)
ex: crowd, jury, faculty, committee, etc in British English (take a plural verb)
singular nouns
nouns that refer to one person, place, or thing.
ex: crowd, jury, faculty, committee, etc in American English (take a singular verb)
collective noun confusion
occurs when a collective noun is treated as singular or plural, leading to subject-verb agreement errors.
American English: the search committee is ready to vote
British English: the search committee are ready to vote
indefinite pronouns
words that replace something non-specific
ex: anyone, anything, everyone, everybody, nobody, nothing, somebody, someone
should be treated as singular nouns
EXCEPTIONS: all, any, none, some are indefinite BUT can be singular OR plural
correlative conjunctions
pairs of conjunctions that connect equal elements in a sentence, such as neither/nor and either/or (used together to describe 2+ similar things)
regular verb
one that can change from present to past tense by adding -d or -ed
ex: loved, ended
if i were VS if i was
A grammatical distinction in English where "if I were" is used for hypothetical or contrary-to-fact situations (past subjunctive), while "if I was" is often seen in informal speech for real situations in the past.
sentence fragment
“incomplete sentence” that lacks a subject or verb and cannot stand alone.
independnt clause
clause with at lease one suject and one verb that can stand on its own as a sentence
subject
person, place, idea, or thing that is either doing something or being something in a sentence
run on sentence
aka a fused sentence
missing the right punctuation to flow properly
when two independent clauses are “fused” together without punctuation to form a complete sentence.
coordinating conjunctions
FANBOYS
comma splice
occurs any time a comma is inserted bwn two main clauses without a coordinating conjunction to connect them
technically a run on sentence
verb
expresses action or occurence
verb forms
are different variations of a verb that convey tense, mood, voice, or aspect, such as the base form, past tense, and past participle.
infinitive
is the base form of a verb preceded by "to," used to indicate actions in a non-finite way.
raw verb which hasn’t been conjugated, paired with a subject, or assigned a verb tense
ex: to run
infinitive phrases
an infinitive + any additional words that describe the action expressed by the infinitive
infinitive phrases hanging by themselves makes a sentence fragment
ex: to get up early tomorrow, to get a new job
can infinitives be a subject or main verb of sentence
subject
present participle
verb form ending in -ing
can be used as adjectives or verbs (but NOT main verb) in sentence
past participle
ends in -ed or -d
irregular verbs
verbs that do not follow the regular pattern of adding -ed for their past forms.
They often change completely or have different form of the past participle
ex: choose, fall
past participle of choose
chosen
past participle of fall
fallen
past particple of fly
flown
past participle of ring
rung
whre can past participles be used
adjectives
can be paired with helping verbs (to be, to have)
which verb tenses can past particples form when paired with helper verbs
Present perfect and past perfect
past perfect tense
a verb tense used to indicate that an action was completed before another took place, typically formed using "had" plus the past participle. It emphasizes the sequence of past actions.
present perfect tense
a verb tense used to express actions that have occurred at some indefinite time in the past or that began in the past and continue in the present, typically formed using "has" or "have" plus the past participle.
time reflected - past tense
an action that is completed
verb tense agreement - past
Most past tense verbs use the same form for singular and plural subjects.
time reflected - present tense
an action that is currently happening or occurs regularly.
verb tense agreement - present tense
Most present tense verbs have different forms for singular and plural subjects.
time reflected - future tense
an action that will occur
verb tense agreement - future tense
Most future tense verbs use the same form for singular and plural subjects.
time reflected - perfect tense
Actions that are indefinite or on-going
verb tense agreement - perfect tense
The form of 'have' or 'has' changes to reflect the singular or plural subject, but the main verb stays the same.
regular verb conjugations
same form in past and future tenses but its form varies in the present tense
If the subject is first person, second person, or third person plural, the present tense takes the infinitive form.
If the subject is third person singular, the present tense takes the infinitive form plus either '-s' or '-es.'
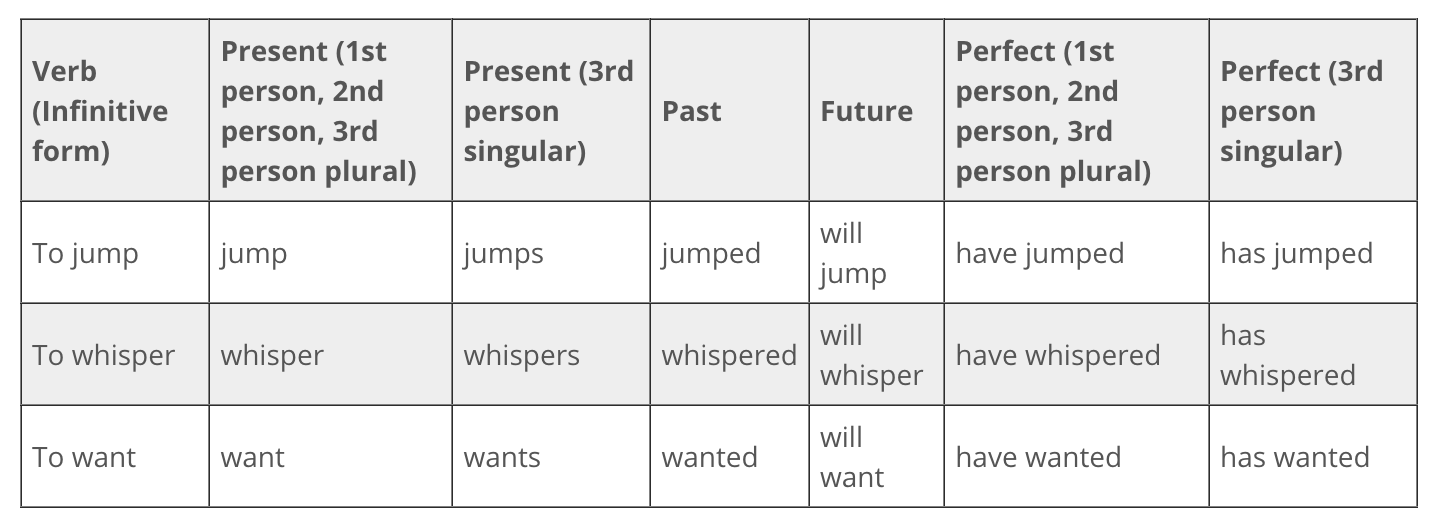
irregular verbs
do not follow basic conjugation patterns
tend to keep the same rules for present tense agreement but past tense and perfect tense are formed differently

indefinite pronooun
a pronoun that does not refer to a specific person or thing, often used for general or non-specific references.
If an indefinite pronoun is replacing a singular noun (one), the verb form should be singular. For example: A softball player should be prepared. Each needs to bring her own baseball glove.
If an indefinite pronoun is replacing a plural noun (more than one), the verb form should be plural. For example: Students without library cards cannot check out books. Many forget their library cards every day.
countable nouns
nouns that can be counted individually and have both singular and plural forms, such as "apple" and "apples." They can be preceded by numbers or quantifiers like "few" or "many."
uncountable nouns
nouns that cannot be counted individually and typically have no plural form, such as "water" or "information." They are often used with quantifiers like "some" or "much."
nouns that represent ideas which cannot by counted with numbers
compound subjects
two subjects joined by a conjunction
subject-verb inversion
the structure in a sentence where the verb precedes the subject, often used in questions or for emphasis.
relative pronouns
Words like "who," "whom," "whose," "which," and "that" used to connect clauses and refer to nouns.
connect the main clause of a sentence to a clause that adds detail or helpds describe the main clause, called a relative clause
who vs. whom
Terms used to denote the subject (who) and object (whom) in a sentence. They help clarify sentence structure and relationships.
which/whom - when a preposition precedes the word
interrogative pronouns
a pronoun that helps ask a question
ex: whose collectible action figures are these? to whom am i speaking
reflexive pronouns
reflect back on the subject of sentence or clause
ex: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themseves
antedecents
words or phrases that a pronoun refers to in a sentence, providing clarity in communication.
the word that a pronoun takes the place of or refers to
modifier
a word, phrase, or clause that describes or qualifies another word in a sentence, adding detail or context.
a word, phrase, or clause that modifies (or describes) another word
ex: adjective, adverb
misplaced modifiers
words or phrases that are incorrectly positioned in a sentence, leading to confusion or ambiguity about which word they modify.
dangling modifiers
words or phrases that modify a word not clearly stated in the sentence, often creating confusion. They typically appear at the beginning or end of a sentence.
preposition
a word that describes the relationship of one thing to something else
correlative
a word always paired with another word
conjunction that connects equal grammatical items.
What does it mean to edit for mechanics?
Edit for spelling, punctuation and capitalization errors
adverbs
words that modify verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, and sometimes whole sentences
What is the superlative form of the adverb skillfully? When is the superlative form of an adverb or adjective used?
more skillfully; it is used to tell us to what extent something occurs
We use the superlative form of an adjective or adverb to compare more than two people or things. For an adverb ending in '-ly', such as skillfully, you'll use 'most' to form the superlative.
superlative
the highest degree of comparison, used to describe the most extreme or remarkable instance of an adjective or adverb.
superlative form of adjective
used to show that someone or something has a quality to the greatest or least degree
superlative form of adverb
used to show that someone or something has performed an action to the greatest or least degree
superlative vs. comparative forms
comparative forms compare two things
superlative forms compare 3 or more things to say which one is of the greatest or least degree
regular superlatives
end with -est
ex: fastest
irregular superlatives
use most, best, or worst instead of -est.
The superlative form is used to _____
both describe one or more people, places or things within a larger group of people, places, or things, or state that an action is performed to the highest degree within a group of actions just like it
The words 'most' or 'least' are placed before _____.
adjectives with more than two syllables and adverbs ending in 'ly’
For adjectives with more than two syllables and adverbs ending in 'ly,' the superlative is formed by placing the words 'most' or 'least' before the word.
idiom
a phrase or expression with a figurative meaning different from its literal meaning.
first type of idiom
defined as an expression particular to one specific culture or language
a phrase that is not logical but has an understood meaning that differs from the literal meaning
will not translate into other languages
second type of idiom
a culturally accepted way of wording something
consist of a verb and a preposition
can translate between languages and still retain its meaning.
examples of the second type of idiom
include "give up" and "look after" and “apologize for”
homophone
words that sound the same but have different meanings or spellings.
homographs
words that are spelled the same but have different meanings or pronunciations.
homonyms
words that have the same spelling and pronunciation but different meanings.
refers to either a homophone or a homograph
Homophones _____(1), while homographs _____(2).
(1) have the same pronunciation but different meanings
(2) have the same spelling but different pronunciations and meanings.
Since there are several words that use similar sounds in the English language, what can help to distinguish them from one another?
Contextual clues and definitions.
We can distinguish words that use similar sounds because the spelling of these words can vary depending on the word and its meaning.
As a general rule, use the suffix -able when _____, and -ible when _____.
the word can stand alone without the suffix; it can't
One of the most common reasons for misspelling words is because of:
confusion with similar sounding words or homophones.
Why is capitalization important?
To show readers the importance of specific words and to indicate a change in meanings
Capitalization indicates the importance and meaning of certain words. It is not simply a formatting tool and has nothing to do with emotion.
What are the ways apostrophes are used?
Apostrophes are mainly used to create contractions and to indicate possession. Apostrophes are also used with non-possessive plurals to increase clarity
proofreading
The last step in the editing process
involves carefully reading over a document for the purpose of finding any errors in grammar, spelling, punctuation, or formatting that need to be corrected.
connotation
the emotional association or secondary meaning of a word
denotation
the direct meaning of a word
what you would find in the dictionary
synonyms
words that have the same or very similar meaning
analogy
comparison of two things that are similar in some way
word structure
describes how words are formed and can be broken down into component parts
prior knowledge vs context clues
Prior knowledge refers to the information and experiences a reader already has before engaging with text, while context clues are hints or details within the text that help readers infer meanings or understand content.
Structural Analysis
dividing words into parts to discover what an unknown word means
simile
uses the words 'like' or 'as' to draw a comparison between two things that are not particularly similar and to suggest a hidden likeness. A cat purring like a motorboat is an example of a simile
metaphor
a comparison between two dissimilar things, but it paints a verbal picture instead of using the words 'like' or 'as.' A comparison between a chimney and a black hole is a metaphor
personification
gives animals or inanimate objects human qualities or characteristics. Sparks are personified when they are portrayed as dancing and playing
onomatopoeia
words imitate sounds. For instance, the phrase 'the fire snapped and crackled' invites readers to remember the sound of a cozy fire
alliteration
repeats consonant or vowel sounds, usually at the beginnings of words. The fuzzy, furry, friendly, fat cat repeats the 'f' sound to tickle readers' ears and focuses their attention in a special way on the cat's characteristics
hyperbole
an overstatement or exaggeration. It is not meant to be taken literally, but is used for dramatic effect. A surprised child, for instance, might have eyes as wide as dinner plates, and a hungry man might feel like he could eat a whole herd of cows
litote
an understated expression or double negative that affirms a point by negating its opposite. For example, saying "not bad" to mean something is actually good.
pun
a play on words that exploits different meanings of a word or words that sound similar but have different meanings
paranomasia
a form of wordplay that exploits similar-sounding words for comedic or rhetorical effect, often involving puns.
aka punning
where words are used to have a specific sound effect to create a humorous or double meaning
double entendre
a figure of speech that has multiple meanings, often with one being risqué or suggestive. It relies on wordplay to convey ambiguity.
homophonic puns
puns made from words that have the same SOUND
ex: pun might be made from the word HAIR instead of HARE
homographic puns
puns from words that are SPELLED the same but have different meanings
ex: puns with TIES (ties shoes, ties hanging in the closet)
figurative language puns
a word or phrase used in a specific way to produce the desired effect or visual picture;
for instance, it's pointless to write with a broken pencil